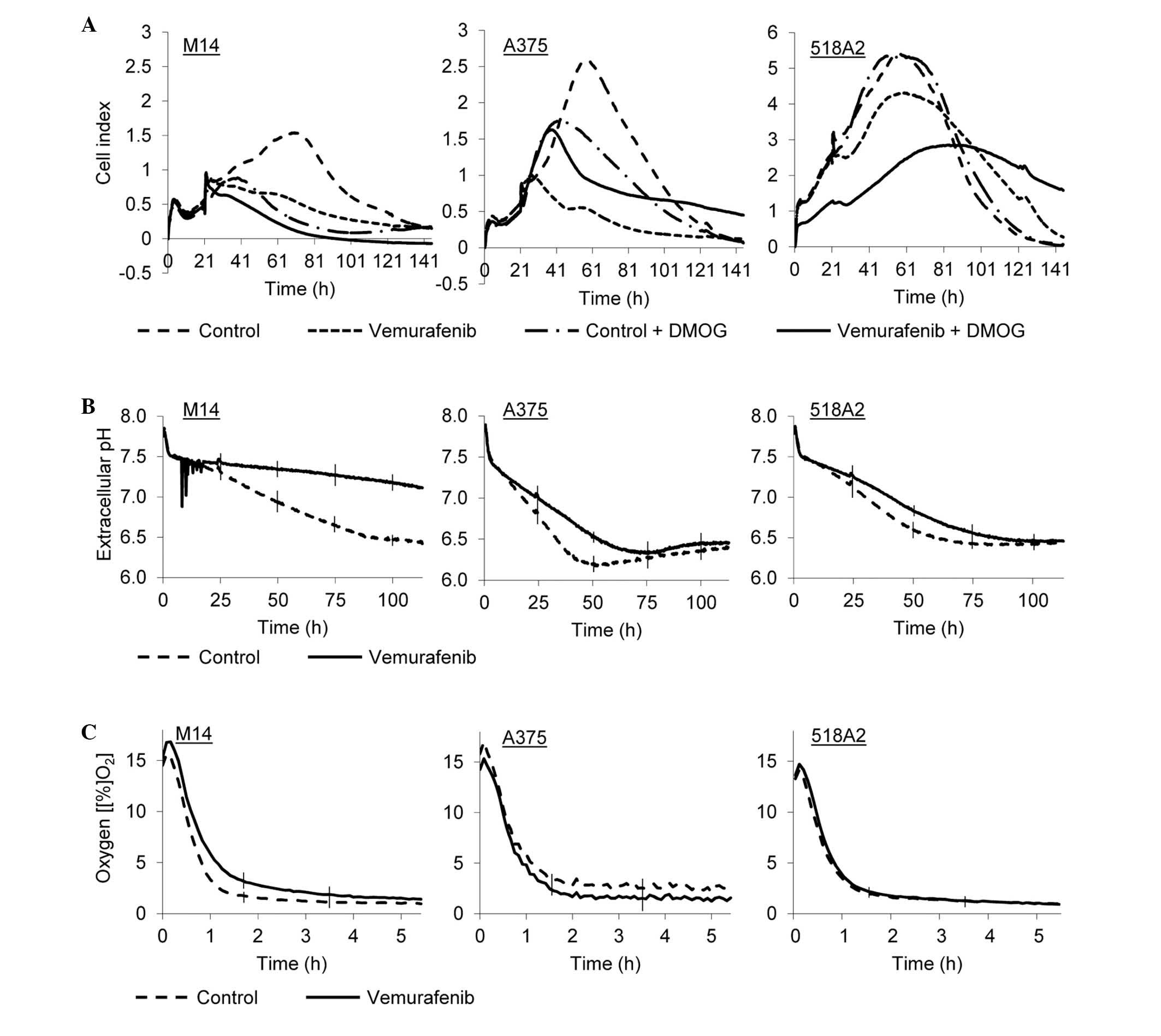
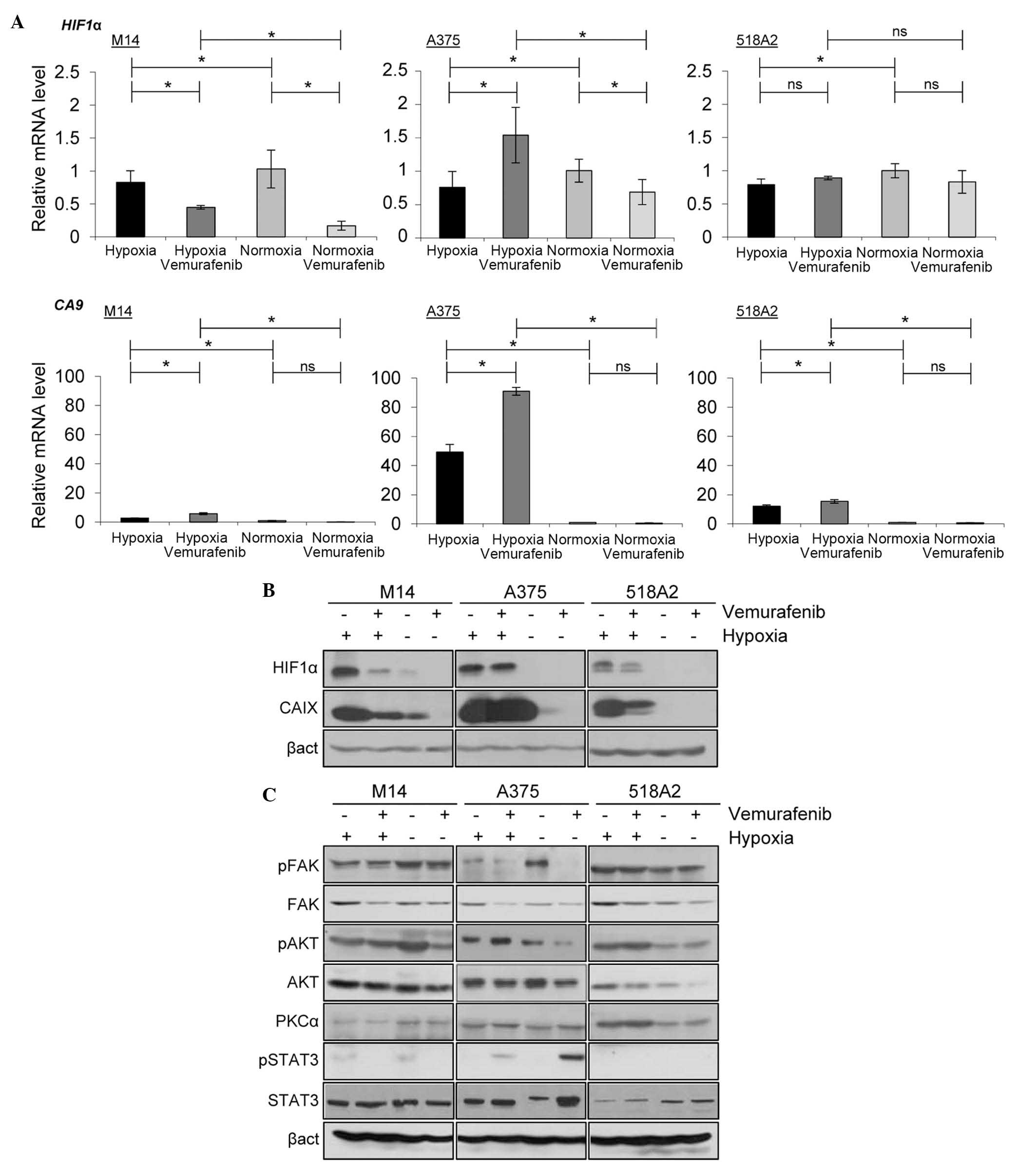
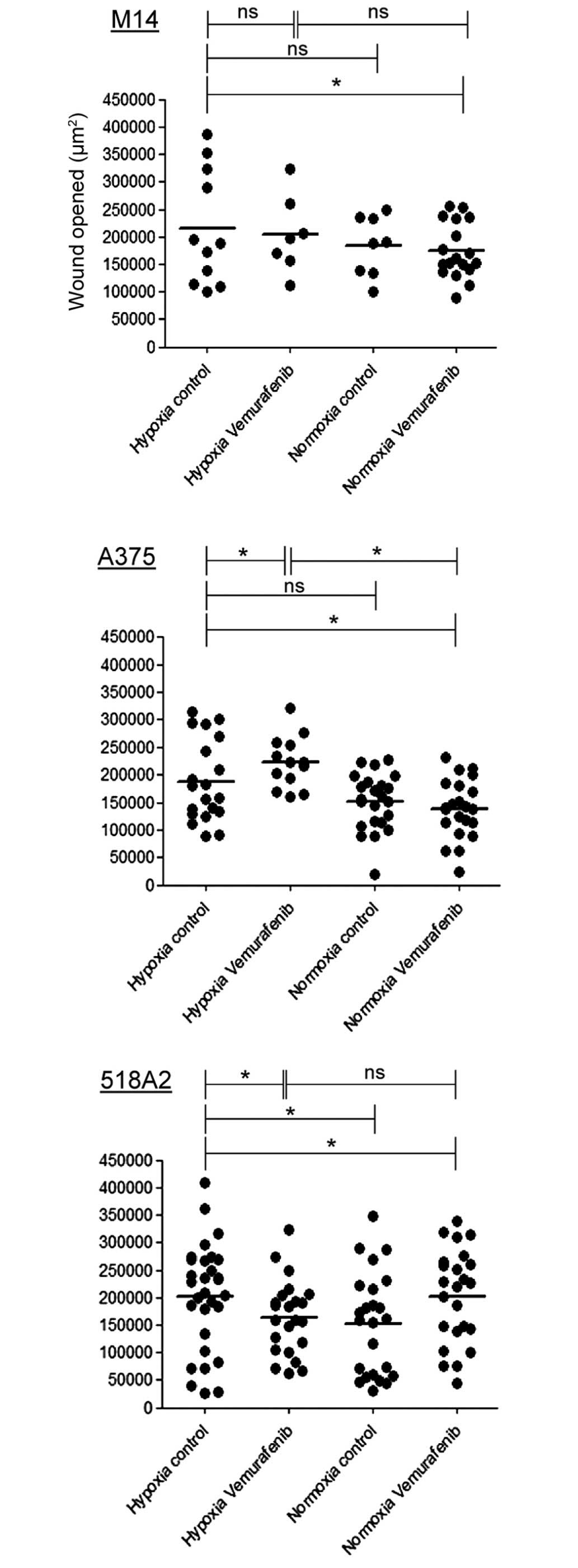
|
1
|
Rohwer N and Cramer T: Hypoxia-mediated
drug resistance: Novel insights on the functional interaction of
HIFs and cell death pathways. Drug Resist Update. 14:191–201. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pastorek J and Pastorekova S:
Hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX as a target for cancer
therapy: From biology to clinical use. Semin Cancer Biol. 31:52–64.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hanna SC, Krishnan B, Bailey ST, Moschos
SJ, Kuan PF, Shimamura T, Osborne LD, Siegel MB, Duncan LM, O'Brien
ET III, et al: HIF1 alpha and HIF2α independently activate SRC to
promote melanoma metastases. J Clin Invest. 123:2078–2093. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors:
Mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 33:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ivanov S, Liao SY, Ivanova A,
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Tarasova N, Weirich G, Merrill MJ,
Proescholdt MA, Oldfield EH, Lee J, et al: Expression of
hypoxia-inducible cell-surface transmembrane carbonic anhydrases in
human cancer. Am J Pathol. 158:905–919. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chrastina A, Závada J, Parkkila S, Kaluz
T, Kaluzová M, Rajcáni J, Patorek J and Pastoreková S:
Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of I-125I-labeled monoclonal
antibody M75 specific for carbonic anhydrase IX, an intrinsic
marker of hypoxia, in nude mice xenografted with human colorectal
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 105:873–881. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Syrjänen L, Luukkaala T, Leppilampi M,
Kallioinen M, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J, Waheed A, Sly WS, Parkkila
S and Karttunen T: Expression of cancer-related carbonic anhydrases
IX and XII in normal skin and skin neoplasms. APMIS. 122:880–889.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kumar SM, Yu H, Edwards R, Chen L,
Kazianis S, Brafford P, Acs G, Herlyn M and Xu XW: Mutant V600E
BRAF increases hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha expression in
melanoma. Cancer Res. 67:3177–3184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Halaban R, Zhang W, Bacchiocchi A, Cheng
E, Parisi F, Ariyan S, Krauthammer M, McCusker JP, Kluger Y and
Sznol M: PLX4032, a selective BRAF (V600E) kinase inhibitor,
activates the ERK pathway and enhances cell migration and
proliferation of BRAF (WT) melanoma cells. Pigm Cell Melanoma Res.
23:190–200. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Botton T, Yeh I, Nelson T, Vemula SS,
Sparatta A, Garrido MC, Allegra M, Rocchi S, Bahadoran P, McCalmont
TH, et al: Recurrent BRAF kinase fusions in melanocytic tumors
offer an opportunity for targeted therapy. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 26:845–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Azijli K, Stelloo E, Peters GJ and VAN DEN
Eertwegh AJ: New developments in the treatment of metastatic
melanoma: Immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies.
Anticancer Res. 34:1493–1505. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JT, Li L, Brafford PA, van den Eijnden
M, Halloran MB, Sproesser K, Haass NK, Smalley KS, Tsai J, Bollag G
and Herlyn M: PLX4032, a potent inhibitor of the B-Raf V600E
oncogene, selectively inhibits V600E-positive melanomas. Pigment
Cell Melanoma Res. 23:820–827. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen
JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et
al: Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E
mutation. N Engl J Med. 364:2507–2516. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wagenaar TR, Ma LY, Roscoe B, Park SM,
Bolon DN and Green MR: Resistance to vemurafenib resulting from a
novel mutation in the BRAFV600E kinase domain. Pigm Cell Melanoma
Res. 27:124–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
O'Connell MP, Marchbank K, Webster MR,
Valiga AA, Kaur A, Vultur A, Li L, Herlyn M, Villanueva J, Liu Q,
et al: Hypoxia induces phenotypic plasticity and therapy resistance
in melanoma via the tyrosine kinase receptors ROR1 and ROR2. Cancer
Discov. 3:1378–1393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wagner S, Hafner C, Allwardt D, Jasinska
J, Ferrone S, Zielinski CC, Scheiner O, Wiedermann U, Pehamberger H
and Breiteneder H: Vaccination with a human high molecular weight
melanoma-associated antigen mimotope induces a humoral response
inhibiting melanoma cell growth in vitro. J Immunol. 174:976–982.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pastoreková S, Závadová Z, Kostál M,
Babusíková O and Závada J: A novel quasi-viral agent, Ma Tu, is a
2-component system. Virology. 187:620–626. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Svastova E, Witarski W, Csaderova L, Kosik
I, Skvarkova L, Hulikova A, Zatovicova M, Barathova M, Kopacek J,
Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX interacts with
bicarbonate transporters in lamellipodia and increases cell
migration via its catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 287:3392–3402.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–5. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Widmer DS, Hoek KS, Cheng PF, Eichhoff OM,
Biedermann T, Raaijmakers MI, Hemmi S, Dunnmer R and Levesque MP:
Hypoxia contributes to melanoma heterogeneity by triggering
HIF1α-dependent phenotype switching. J Invest Dermatol.
133:2436–2443. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|