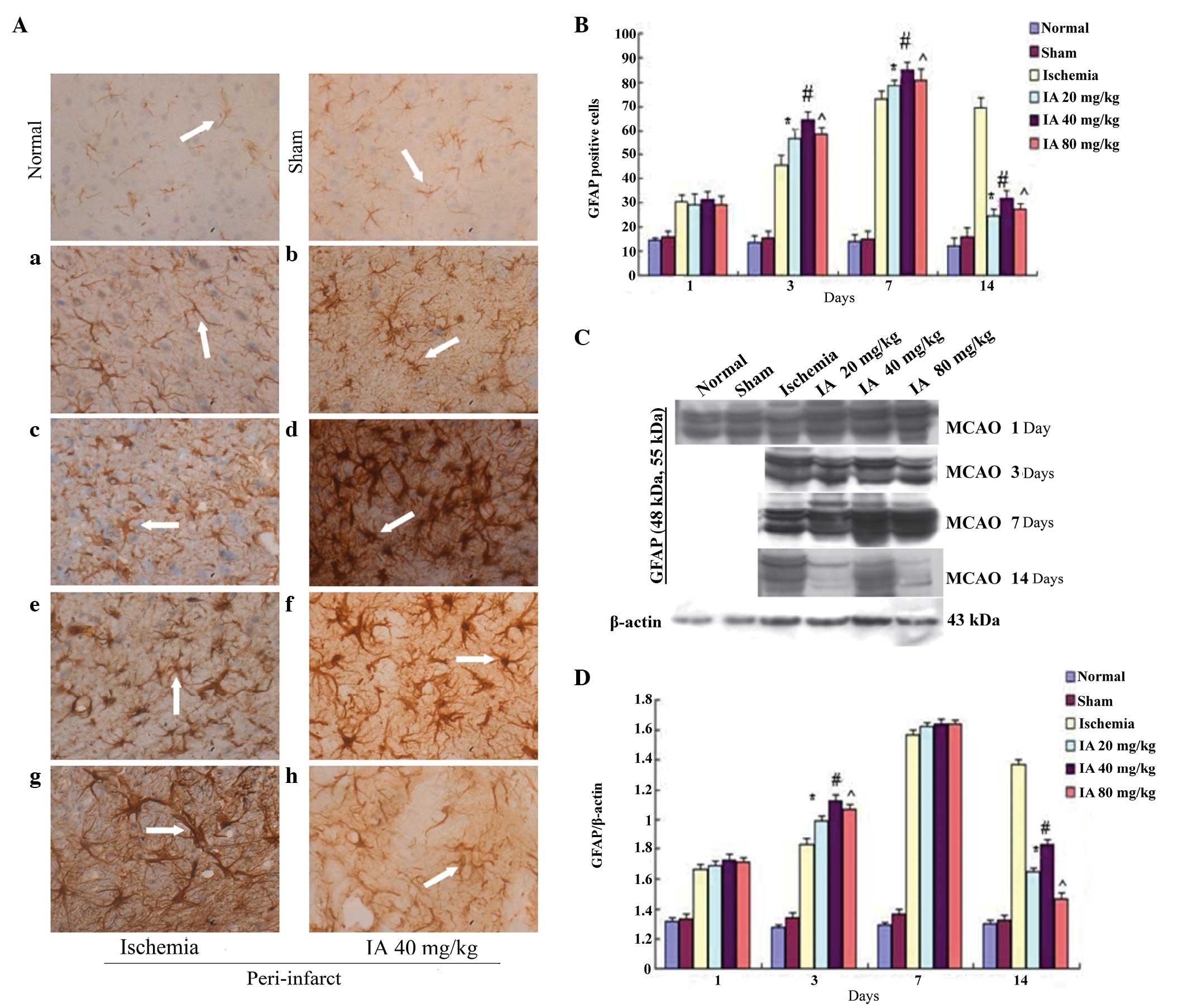
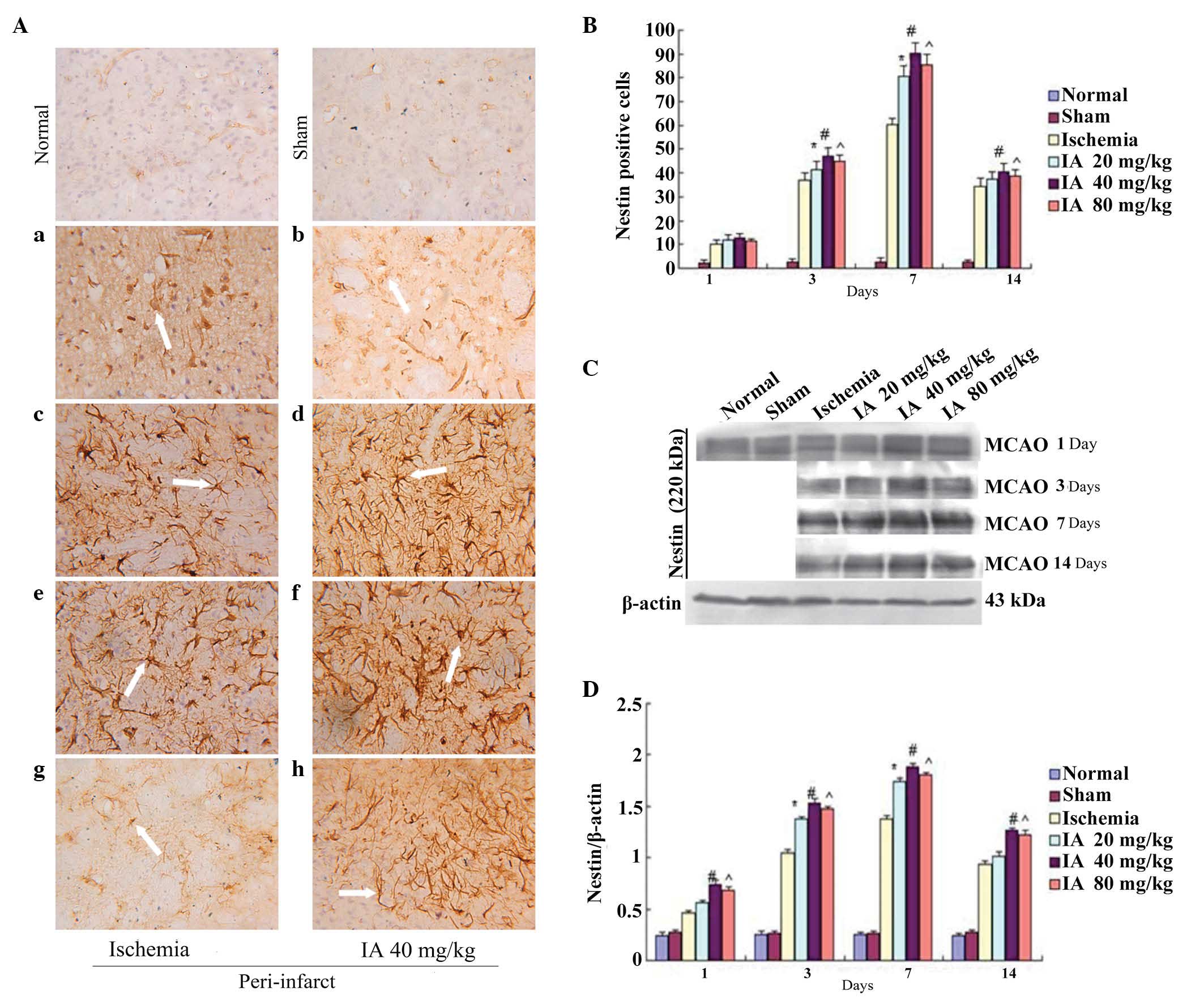
|
1
|
Fu XC, Xu Z and Chen JJ: Effects of MDQR4
on cardiac function and hemodynamics in anesthetized dogs. Zhong Xi
Yi Jie He Xin Nao Xue Guan Bing. 9:1471–1473. 2011.In Chinese.
|
|
2
|
Li XR: Overview of research progresses on
pharmacological effects Ilex phescens. Glob Trad Chin Med.
9:238–240. 2011.
|
|
3
|
Huang XW, You ZD, Chen J and Xian SX:
Effect of Radix Ilecis Pubescentis on heart function and the
miR133a expression in chronic heart failure rats. Zhong Yao Xin Yao
Yu Lin Chuang Yao Li. 25:48–92. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
4
|
Hua HY and Li YY: The pharmacological
effects of Ilexonin A. Chin J Med. 8:137–138. 2006.
|
|
5
|
Sheng HL, Dong XL and Jiang YF: Protective
effects of Radix Ilicis Pubescentis extract on focal cerebral
ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Zhongguo Xin Yao Za Zh.
18:1020–1022. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
6
|
Zheng GY and Shi WQ: Influence of Ilexonin
A on the expression of bFGF, GAP-43 and neurogenesis after cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 46:1065–1071.
2011.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim DH, Kim S, Jung WY, Park SJ, Park DH,
Kim JM, Cheong JH and Ryu JH: The neuroprotective effects of the
seeds of Cassia obtusifolia on transient cerebral global ischemia
in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:1473–1479. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee CH, Yoo KY, Hwang IK, Choi JH, Park
OK, Li H, Kang IJ, Kwon YG, Kim YM and Won MH: Hypothyroid state
does not protect but delays neuronal death in the hippocampal CA1
region following transient cerebral ischemia: Focus on oxidative
stress and gliosis. J Neurosci Res. 88:2661–2668. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Villapol S, Gelot A, Renolleau S and
Charriaut-Marlangue C: Astrocyte responses after neonatal ischemia:
The yin and the yang. Neuroscientist. 14:339–344. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Badoer E: Microglia: Activation in acute
and chronic inflammatory states and in response to cardiovascular
dysfunction. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1580–1585. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang N, Zhang Y, Wu L, Wang Y, Cao Y, He
L, Li X and Zhao J: Puerarin protected the brain from cerebral
ischemia injury via astrocyte apoptosis inhibition.
Neuropharmacology. 79:282–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shen Y, Sun A, Wang Y, Cha D, Wang H, Wang
F, Feng L, Fang S and Shen Y: Upregulation of mesencephalic
astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor in glial cells is associated
with ischemia-induced glial activation. J Neuroinflammation.
9:2542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yenari MA, Xu L, Tang XN, Qiao Y and
Giffard RG: Microglia potentiate damage to blood-brain barrier
constituents: improvement by minocycline in vivo and in vitro.
Stroke. 37:1087–1093. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Z, Zhong L, Zhong S, Xian R and Yuan
B: Hypoxia induces microglia autophagy and neural inflammation
injury in focal cerebral ischemia model. Exp Mol Pathol.
98:219–224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shin HY, Kim JH, Phi JH, Park CK, Kim JE,
Kim J-H, Paek SH, Wang KC and Kim DG: Endogenous neurogenesis and
neovascularization in the neocortex of the rat after focal cerebral
ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 86:356–367. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Navaratna D, Guo S, Arai K and Lo EH:
Mechanisms and targets for angiogenic therapy after stroke. Cell
Adh Migr. 3:216–223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mac Gabhann F, Qutub AA, Annex BH and
Popel AS: Systems biology of pro-angiogenic therapies targeting the
VEGF system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2:694–707. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Zhang J and Liang SD: Function and
mechanism of VEGF in the nervous system. Shenjing Jiepouxue Zazhi.
26:561–563. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
19
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
cranicetomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abedin V, Toctam S and Mahdi Z: Evaluation
the protective effect of aminoguanidine on cortex and striatum
damage in acute phase of focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Physiol
Pharmacol. 11:38–43. 2007.
|
|
21
|
Chu X, Fu X, Zou L, Qi C, Li Z, Rao Y and
Ma K: Oncosis, the possible cell death pathway in astrocytes after
focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1149:157–164. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Buffo A, Rite I, Tripathi P, Lepier A,
Colak D, Horn AP, Mori T and Götz M: Origin and progeny of reactive
gliosis: A source of multipotent cells in the injured brain. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3581–3586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sirko S, Behrendt G, Johansson PA,
Tripathi P, Costa M, Bek S, Heinrich C, Tiedt S, Colak D, Dichgans
M, et al: Reactive glia in the injured brain acquire stem cell
properties in response to sonic hedgehog. Cell Stem Cell.
12:426–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hayakawa K, Nakano T, Irie K, Higuchi S,
Fujioka M, Orito K, Iwasaki K, Jin G, Lo EH, Mishima K and Fujiwara
M: Inhibition of reactive astrocytes with fluorocitrate retards
neurovascular remodeling and recovery after focal cerebral ischemia
in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:871–882. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jing L, Mai L, Zhang JZ, Wang JG, Chang Y,
Dong JD, Guo FY and Li PA: Diabetes inhibits cerebral
ischemia-induced astrocyte activation - an observation in the
cingulate cortex. Int J Biol Sci. 9:980–988. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin CH, Cheng FC, Lu YZ, Chu LF, Wang CH
and Hsueh CM: Protection of ischemic brain cells is dependent on
astrocyte-derived growth factors and their receptors. Exp Neurol.
201:225–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tonchev AB, Boneva NB, Kaplamadzhiev DB,
Kikuchi M, Mori Y, Sahara S and Yamashima T: Expression of
neurotrophin receptors by proliferating glia in postischemic
hippocampal CA1 sector of adult monkeys. J Neuroimmunol. 205:20–24.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ding J, Yu JZ, Li QY, Wang X, Lu CZ and
Xiao BG: Rho kinase inhibitor Fasudil induces neuroprotection and
neurogenesis partially through astrocyte-derived G-CSF. Brain Behav
Immun. 23:1083–1088. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang QG, Wang R, Tang H, Dong Y, Chan A,
Sareddy GR, Vadlamudi RK and Brann DW: Brain-derived estrogen
exerts anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions in the rat
hippo-campus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 389:84–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li L, Lundkvist A, Andersson D,
Wilhelmsson U, Nagai N, Pardo AC, Nodin C, Ståhlberg A, Aprico K,
Larsson K, et al: Protective role of reactive astrocytes in brain
ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:468–481. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jeong HK, Jou I and Joe EH: Absence of
delayed neuronal death in ATP-injected brain: Possible roles of
astrogliosis. Exp Neurobiol. 22:308–314. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Takano T, Oberheim N, Cotrina ML and
Nedergaard M: Astrocytes and Ischemic Injury. Stroke. 40:8–12.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Davies SJ, Goucher DR, Doller C and Silver
J: Robust regeneration of adult sensory axons in degenerating white
matter of the adult rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 19:5810–5822.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Garcia JA, Cardona SM and Cardona AE:
Analyses of microglia effector function using CX3CR1-GFP knock-in
mice. Methods Mol Biol. 1041:307–317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schilling M, Besselmann M, Leonhard C,
Mueller M, Ringelstein EB and Kiefer R: Microglial activation
precedes and predominates over macrophage infiltration in transient
focal cerebral ischemia: A study in green fluorescent protein
transgenic bone marrow chimeric mice. Exp Neurol. 183:25–33. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lalancette-Hébert M, Gowing G, Simard A,
Weng YC and Kriz J: Selective ablation of proliferating microglial
cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain. J Neurosci.
27:2596–2605. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Breckwoldt MO, Chen JW, Stangenberg L,
Aikawa E, Rodriguez E, Qiu S, Moskowitz MA and Weissleder R:
Tracking the inflammatory response in stroke in vivo by sensing the
enzyme myeloperoxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18584–18589.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nakajima K and KoItsaka S: Microglia:
Neuroprotective and neurotrophic cells in the central nervous
system. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 4:65–84.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim SU and de Vellis J: Microglia in
health and disease. J Neurosci Res. 81:302–313. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li L, Lua J, Taya SS, Moochhalab SM and
Hea BP: The function of microglia, either neuroprotection or
neurotoxicity, is determined by the equilibrium among factors
released from activated microglia in vitro. Brain Res. 1159:8–17.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ekdahl CT, Kokaia Z and Lindvall O: Brain
inflammation and adult neurogenesis: The dual role of microglia.
Neuroscience. 158:1021–1029. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang JP, Yang ZT, Liu C, Zhao YZ and Chen
YB: Activated microglia provide a neuroprotective role by balancing
glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor and tumor necrosis
factor-α secretion after subacute cerebral ischemia. Int J Mol Med.
31:172–178. 2013.
|
|
43
|
Hu X, Li P, Guo Y, Wang H, Leak RK, Chen
S, Gao Y and Chen J: Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics
reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral
ischemia. Stroke. 43:3063–3070. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Arroba AI, Alvarez-Lindo N, van Rooijen N
and de la Rosa EJ: Microglia-mediated IGF-I neuroprotection in the
rd10 mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 52:9124–9130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Montero M, González B and Zimmer J:
Immunotoxic depletion of microglia in mouse hippocampal slice
cultures enhances ischemia-like neurodegeneration. Brain Res.
1291:140–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu W, Song DL, Zhang GH, Chen JW, Xie RH,
Lin HJ, et al: Nestin expression in different area of brain after
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Zu Zhong Yu Shen Jing Ji
Bing. 16:34–36. 2009.
|
|
47
|
Song H, Stevens CF and Gage FH: Astroglia
induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells. Nature.
417:39–44. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shin YJ, Kim HL, Park JM, Cho JM, Kim SY
and Lee MY: Characterization of nestin expression and vessel
association in the ischemic core following focal cerebral ischemia
in rats. Cell Tissue Res. 351:383–395. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kronenberg G, Gertz K, Cheung G, Buffo A,
Kettenmann H, Gotz M and Endres M: Modulation of fate determinants
Olig2 and Pax6 in resident glia evokes spiking neuroblasts in a
model of mild brain ischemia. Stroke. 41:2944–2949. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim HJ, Leeds P and Chuang DM: The HDAC
inhibitor, sodium butyrate, stimulates neurogenesis in the ischemic
brain. J Neurochem. 110:1226–1240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yao RQ, Zhang L, Wang W and Li L: Cornel
iridoid glycoside promote neurogenesis and angiogenesis and
improves neurological function after focal cerebral ischemia in
rats. Brain Res Bull. 79:69–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhong J, Tang MK, Zhang Y, Xu QP and Zhang
JT: Effect of salvianolic acid B on neural cells damage and
neurogenesis after brain ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Yao Xue Xue
Bao. 42:716–721. 2007.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang YQ, Cui HR, Yang SZ, Sun HP, Qiu MH,
Feng XY and Sun FY: VEGF enhance cortical newborn neurons and their
neurite development in adult rat brain after cerebral ischemia.
Neurochem Int. 55:629–636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang JP, Liu HJ and Liu XF: VEGF promotes
angiogenesis and functional recovery in stroke rats. J Invest Surg.
23:149–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Herz J, Reitmeir R, Hagen SI, Reinboth BS,
Guo Z, Zechariah A, ElAli A, Doeppner TR, Bacigaluppi M, Pluchino
S, et al: Intracerebroventricularly delivered VEGF promotes
contralesional corticorubral plasticity after focal cerebral
ischemia via mechanisms involving anti-inflammatory actions.
Neurobiol Dis. 45:1077–1085. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Li P, Huang JJ, Ni JJ and Sun FY:
WITHDRAWN: VEGF evokes reactive astroglia to convert into neuronal
cells by affecting the biological function of MeCP2 in adult rat
brain after cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. 2012.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wang Y, Kilic E, Kilic U, Weber B,
Bassetti CL, Marti HH and Hermann DM: VEGF overexpression induces
post-ischaemic neuroprotection, but facilitates haemodynamic steal
phenomena. Brain. 128:52–63. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Chibay Y, Sasayama T, Miyake TS, Koyama J,
Kondoh T, Hosoda K and Kohmura E: Anti-VEGF receptor antagonist
(VGA1155) reduces infarction in rat permanent focal brain ischemia.
Kobe J Med Sci. 54:E136–E146. 2008.
|
|
59
|
Li Z, Wang R, Li S, Wei J, Zhang Z, Li G,
Dou W, Wei Y and Feng M: Intraventricular pre-treatment with
rAAV-VEGF induces intracranial hypertension and aggravates ischemic
injury at the early stage of transient focal cerebral ischemia in
rats. Neurol Res. 30:868–875. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Manoonkitiwongsa PS, Schultz RL, McCreery
DB, Whitter EF and Lyden PD: Neuroprotection of ischemic brain by
vascular endothelial growth factor is critically dependent on
proper dosage and may be compromised by angiogenesis. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 24:693–702. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Katsumata A, Sugiu K, Tokunaga K, Kusaka
N, Watanabe K, Nishida A, Namba K, Hamada H, Nakashima H and Date
I: Optimal dose of plasmid vascular endothelial growth factor for
enhancement of angiogenesis in the rat brain ischemia model. Neurol
Med Chir (Tokyo). 50:449–455. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Yang JP, Guo L, Liu RC and Liu HJ:
Neuroprotective effects of VEGF administration after focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion: Dose response and time window. Neurochem Int.
60:592–596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hermann DM and Zechariah A: Implications
of vascular endothelial growth factor for postischemic
neurovascular remodeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:1620–1643.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO,
Logvinova A and Greenberg DA: VEGF-induced neuroprotection,
neurogenesis and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin
Invest. 111:1843–1851. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Choi JS, Kim HY, Cha JH, Choi JY, Chun MH
and Lee MY: Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor
receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1 in rat hippocampus after transient
forebrain ischemia. J Neurotrauma. 24:521–531. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Vogel C, Bauer A, Wiesnet M, Preissner K,
Schaper W, Marti HH and Fischer S: Flt-1, but not Flk-1 mediates
hyperpermeability through activation of the PI3-K/Akt pathway. J
Cell Physiol. 212:236–243. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|