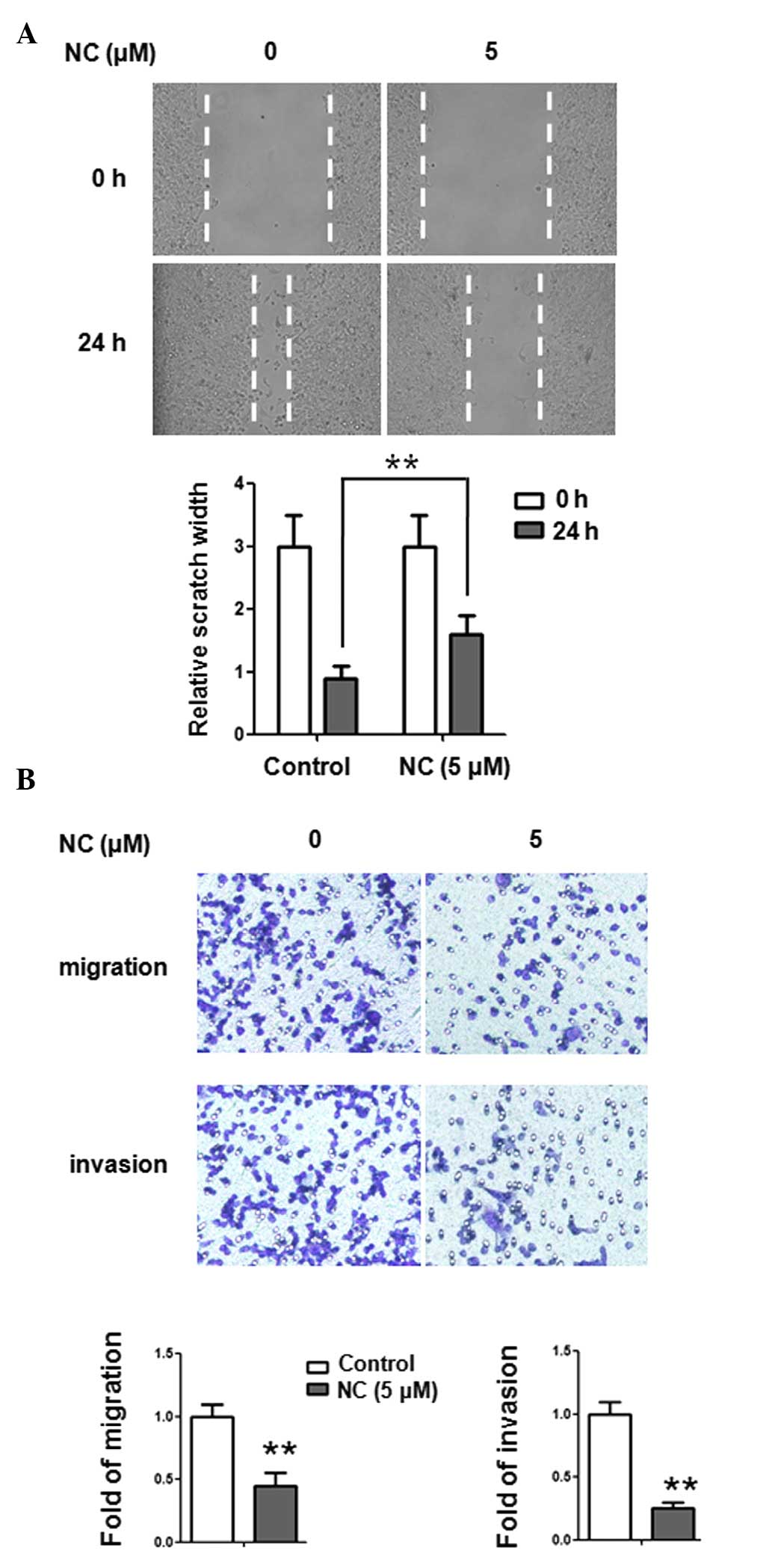
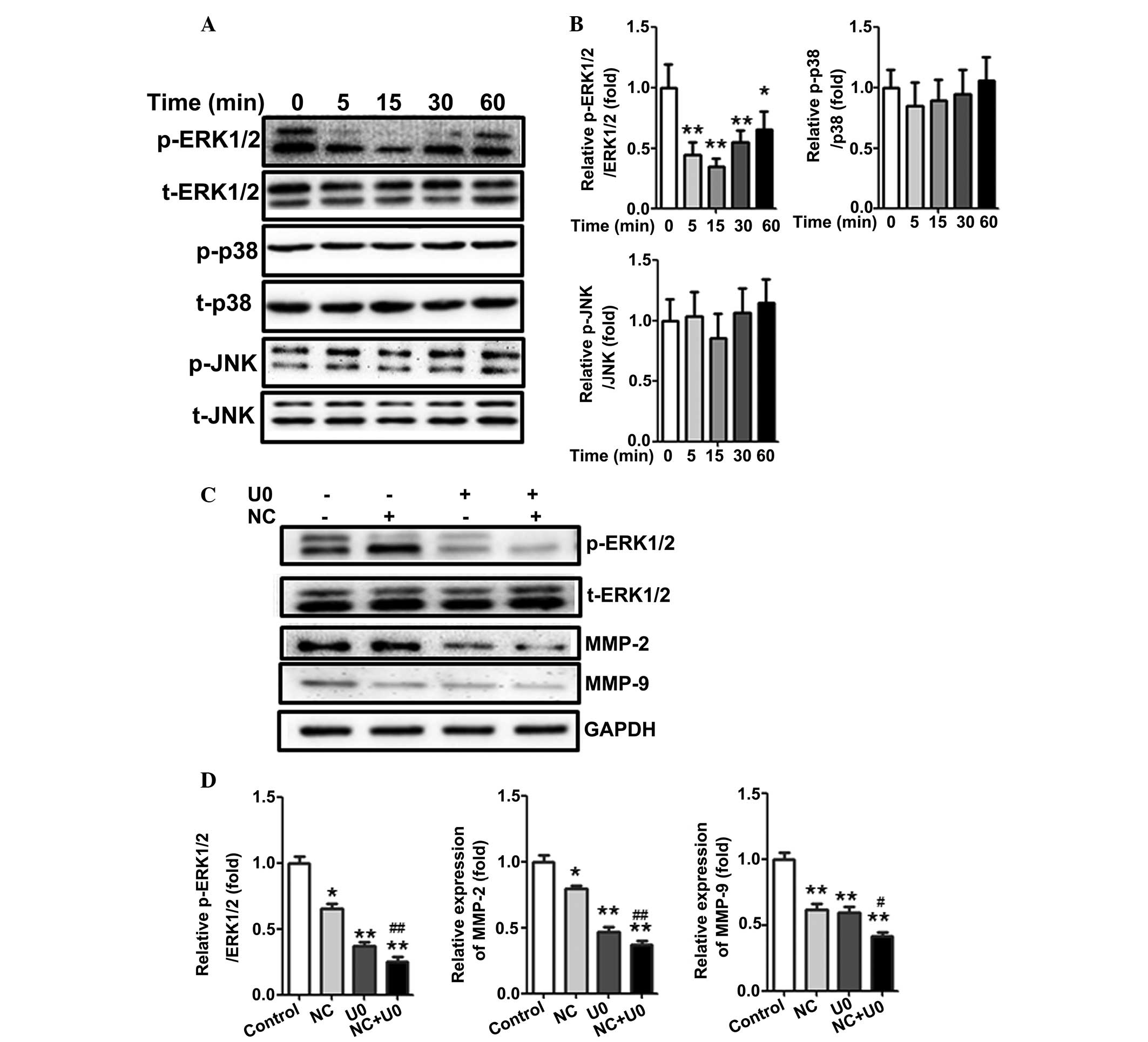
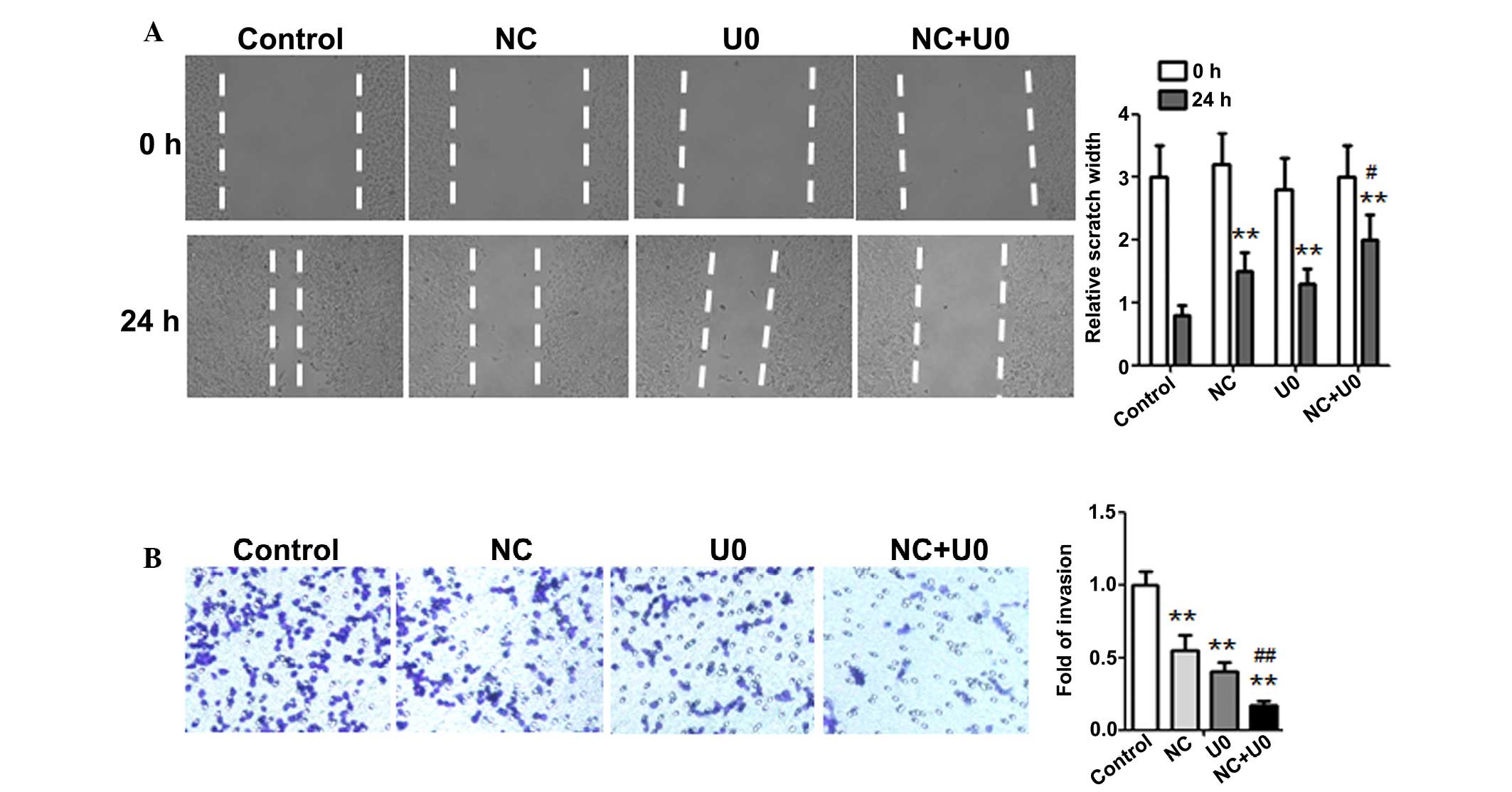
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun ZL, Tang YJ, Wu WG, Xing J, He YF, Xin
DM, Yu YL, Yang Y and Han P: AZD1480 can inhibit the biological
behavior of ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells in vitro. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:4823–4827. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holschneider CH and Berek JS: Ovarian
cancer: Epidemiology, biology, and prognostic factors. Semin Surg
Oncol. 19:3–10. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vaughan S, Coward JI, Bast RC Jr, Berchuck
A, Berek JS, Brenton JD, Coukos G, Crum CC, Drapkin R,
Etemadmoghadam D, et al: Rethinking ovarian cancer: Recommendations
for improving outcomes. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:719–725. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stallings-Mann M and Radisky D: Matrix
metalloproteinase-induced malignancy in mammary epithelial cells.
Cells Tissues Organs. 185:104–110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liotta LA and Stetler-Stevenson WG:
Metalloproteinases and cancer invasion. Semin Cancer Biol.
1:99–106. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Himelstein BP, Canete-Soler R, Bernhard
EJ, Dilks DW and Muschel RJ: Metalloproteinases in tumor
progression: The contribution of MMP-9. Invasion Metastasis.
14:246–258. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim BS, Park JY, Kang HJ, Kim HJ and Lee
J: Fucoidan/FGF-2 induces angiogenesis through JNK- and
p38-mediated activation of AKT/MMP-2 signalling. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 450:1333–1338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin YJ, Park I, Hong IK, Byun HJ, Choi J,
Kim YM and Lee H: Fibronectin and vitronectin induce AP-1-mediated
matrix metal-loproteinase-9 expression through integrin alpha
α(5)β(1)/α(v) β(3)-dependent Akt, ERK and JNK signaling pathways in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cell Signal. 23:125–134.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Jiang W, Zhang Z, Qian M and Du B:
Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines
production via MAPK and NF-kappab pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 144:145–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Del Poeta M, Chen SF, Von Hoff D, Dykstra
CC, Wani MC, Manikumar G, Heitman J, Wall ME and Perfect JR:
Comparison of in vitro activities of camptothecin and nitidine
derivatives against fungal and cancer cells. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 43:2862–2868. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fang Z, Tang Y, Jiao W, Xing Z, Guo Z,
Wang W, Xu Z and Liu Z: Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis and
inhibits tumor cell proliferation via suppressing ERK signaling
pathway in renal cancer. Food Chem Toxicol. 66:210–216. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fang Z, Tang Y, Jiao W, Xing Z, Guo Z,
Wang W, Shi B, Xu Z and Liu Z: Nitidine chloride inhibits renal
cancer cell metastasis via suppressing AKT signaling pathway. Food
Chem Toxicol. 60:246–251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liao J, Xu T, Zheng JX, Lin JM, Cai QY, Yu
DB and Peng J: Nitidine chloride inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma
cell growth in vivo through the suppression of the JAK1/STAT3
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 32:79–84. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen J, Wang J, Lin L, He L, Wu Y, Zhang
L, Yi Z, Chen Y, Pang X and Liu M: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling
pathway by nitidine chloride suppressed the angiogenesis and growth
of human gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:277–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pan X, Han H, Wang L, Yang L, Li R, Li Z,
Liu J, Zhao Q, Qian M, Liu M and Du B: Nitidine Chloride inhibits
breast cancer cells migration and invasion by suppressing c-Src/FAK
associated signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 313:181–191. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun M, Zhang N, Wang X, Cai C, Cun J, Li
Y, Lv S and Yang Q: Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis, cell cycle
arrest, and synergistic cytotoxicity with doxorubicin in breast
cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 35:10201–10212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Li R, Meng Y, Li S, Donelan W,
Zhao Y, Qi L, Zhang M, Wang X, Cui T, Yang LJ, et al: Irisin
stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated
protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling.
Diabetes. 63:514–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kallakury BV, Karikehalli S, Haholu A,
Sheehan CE, Azumi N and Ross JS: Increased expression of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases 1 and 2 correlate with poor prognostic variables
in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 7:3113–3119.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rajoria S, Suriano R, Wilson YL, Schantz
SP, Moscatello A, Geliebter J and Tiwari RK: 3,3′-diindolylmethane
inhibits migration and invasion of human cancer cells through
combined suppression of ERK and AKT pathways. Oncol Rep.
25:491–497. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Surh YJ: Cancer chemoprevention with
dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:768–780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thomasset SC, Berry DP, Garcea G, Marczylo
T, Steward WP and Gescher AJ: Dietary polyphenolic
phytochemicals-promising cancer chemopreventive agents in humans? A
review of their clinical properties. Int J Cancer. 120:451–458.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li LN, Zhou X, Gu Y and Yan J: Prognostic
value of MMP-9 in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:4107–4113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fu Z, Xu S, Xu Y, Ma J, Li J and Xu P: The
expression of tumor-derived and stromal-derived matrix
metalloproteinase 2 predicted prognosis of ovarian cancer. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 25:356–362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thompson N and Lyons J: Recent progress in
targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway with inhibitors in cancer drug
discovery. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 5:350–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gendron S, Couture J and Aoudjit F:
Integrin alpha2beta1 inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis in T
lymphocytes by protein phosphatase 2A-dependent activation of the
MAPK/ERK pathway. J Biol Chem. 278:48633–48643. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shelton JG, Steelman LS, White ER and
McCubrey JA: Synergy between PI3K/Akt and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in
IGF-1R mediated cell cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis
in hematopoietic cells. Cell Cycle. 3:372–379. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ono H, Basson MD and Ito H: PTK6 promotes
cancer migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells dependent
on ERK signaling. PloS One. 9:e960602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|