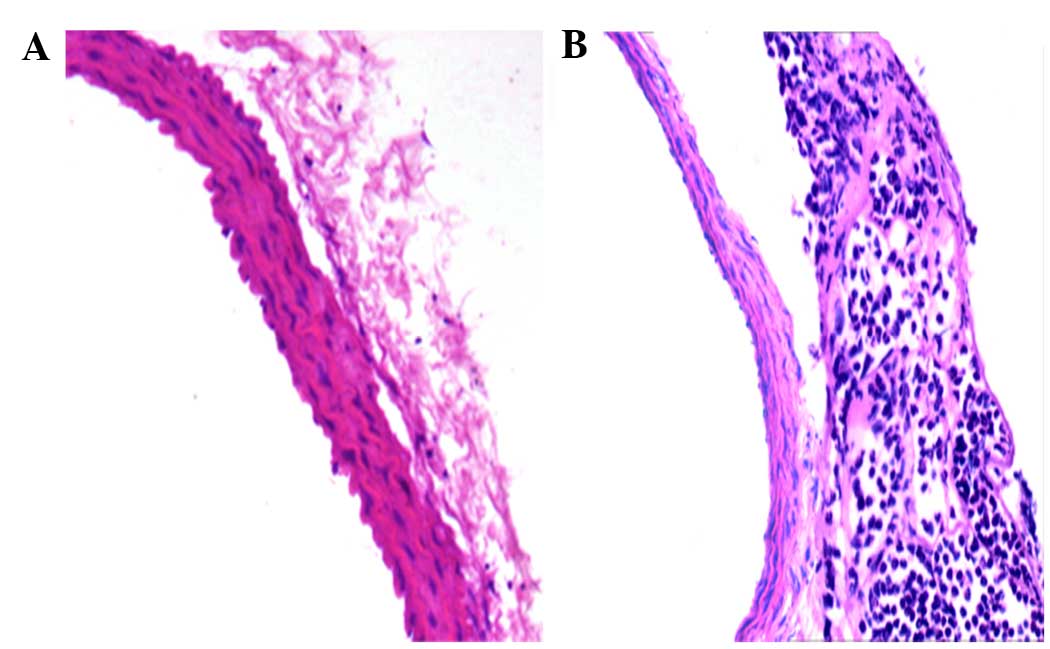
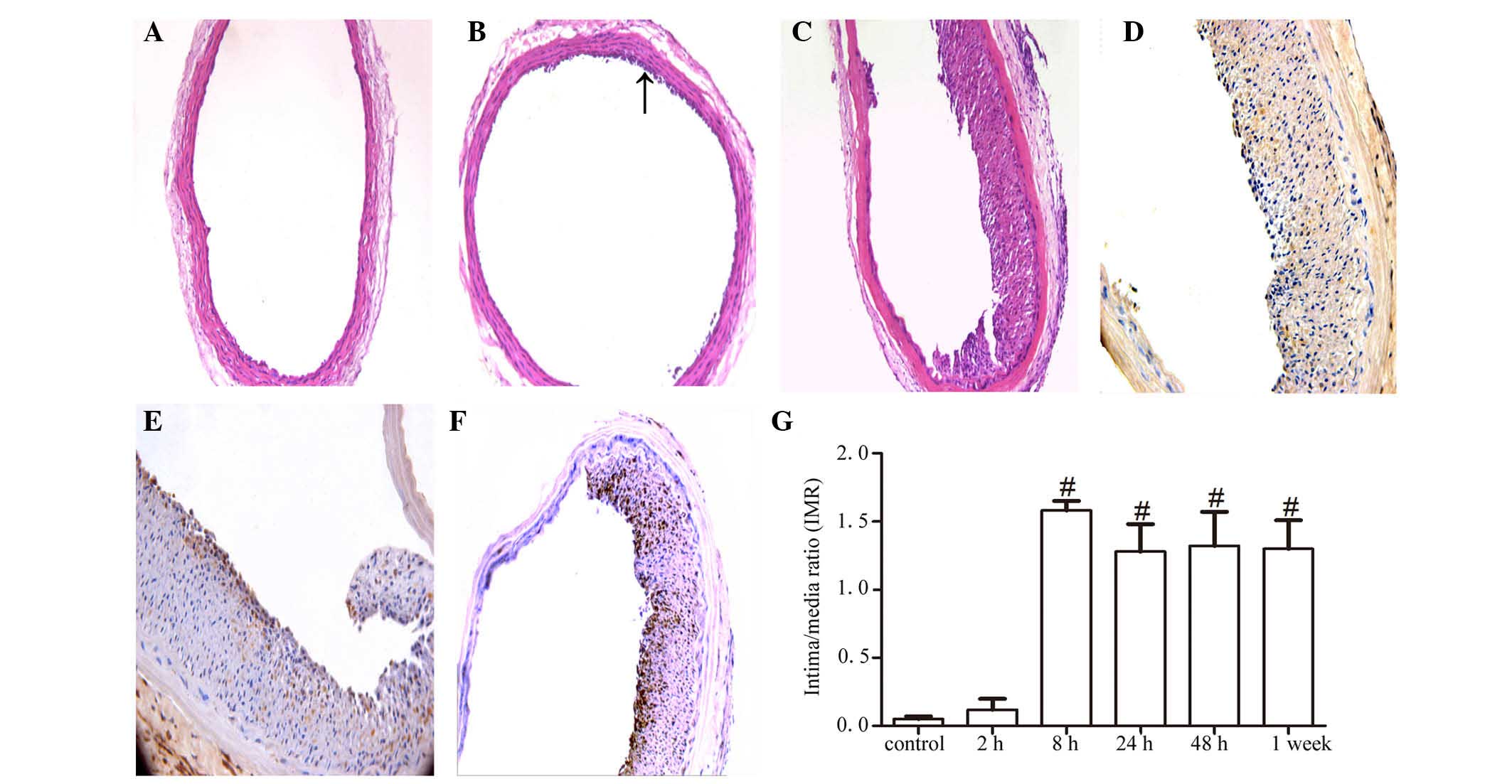
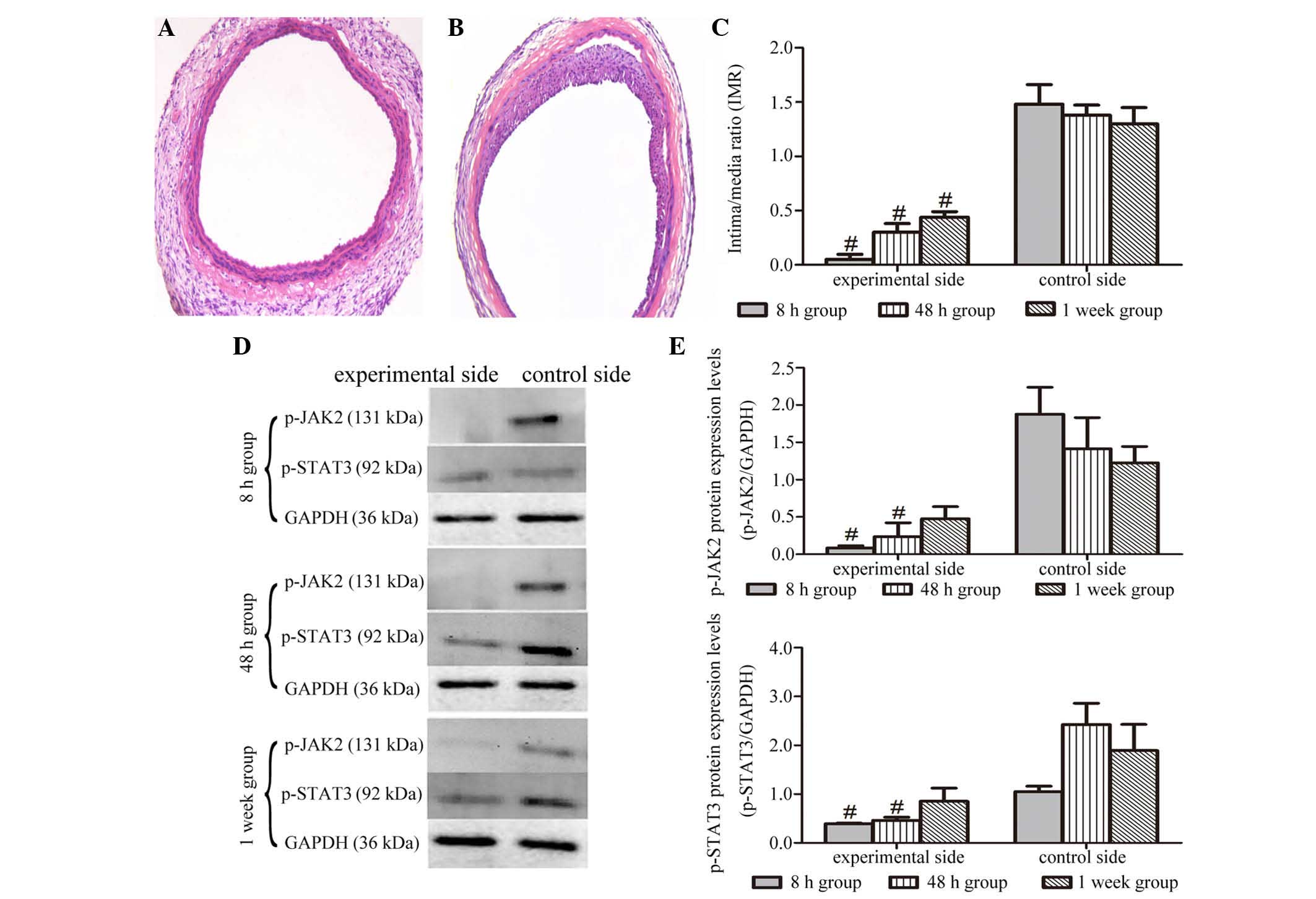
|
1
|
Clarke MC, Talib S, Figg NL and Bennett
MR: Vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis induces
interleukin-1-directed inflammation: Effects of
hyperlipidemia-mediated inhibition of phagocytosis. Circ Res.
106:363–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kleemann R, Zadelaar S and Kooistra T:
Cytokines and atherosclerosis: A comprehensive review of studies in
mice. Cardiovasc Res. 79:360–376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sprague AH and Khalil RA: Inflammatory
cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem
Pharmacol. 78:539–552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Soehnlein O and Weber C: Myeloid cells in
atherosclerosis: Initiators and decision shapers. Semin
Immunopathol. 31:35–47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Subbotin VM: Neovascularization of
coronary tunica intima (DIT) is the cause of coronary
atherosclerosis. Lipoproteins invade coronary intima via
neovascularization from adventitial vasa vasorum, but not from the
arterial lumen: A hypothesis. Theor Biol Med Model. 9:112012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Maseri A:
Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:1135–1143. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lim S and Park S: Role of vascular smooth
muscle cell in the inflammation of atherosclerosis. BMB Rep.
47:1–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vogt F, Zernecke A, Beckner M, Krott N,
Bosserhoff AK, Hoffmann R, Zandvoort MA, Jahnke T, Kelm M, Weber C
and Blindt R: Blockade of angio-associated migratory cell protein
inhibits smooth muscle cell migration and neointima formation in
accelerated atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 52:302–311. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schwartz CJ and Mitchell JR: Cellular
infiltration of the human arterial adventitia associated with
atheromatous plaques. Circulation. 26:73–78. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Watanabe M, Sangawa A, Sasaki Y, Yamashita
M, Tanaka-Shintani M, Shintaku M and Ishikawa Y: Distribution of
inflammatory cells in adventitia changed with advancing
atherosclerosis of human coronary artery. J Atheroscler Thromb.
14:325–331. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Parums D and Mitchinson MJ: Demonstration
of immunoglobulin in the neighbourhood of advanced atherosclerotic
plaques. Atherosclerosis. 38:211–216. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao L, Moos MP, Gräbner R, Pédrono F, Fan
J, Kaiser B, John N, Schmidt S, Spanbroek R, Lötzer K, et al: The
5-lipoxygenase pathway promotes pathogenesis of
hyperlipidemia-dependent aortic aneurysm. Nat Med. 10:966–973.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moos MP, John N, Gräbner R, Nossmann S,
Günther B, Vollandt R, Funk CD, Kaiser B and Habenicht AJ: The
lamina adventitia is the major site of immune cell accumulation in
standard chow-fed apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:2386–2391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Galkina E, Kadl A, Sanders J, Varughese D,
Sarembock IJ and Ley K: Lymphocyte recruitment into the aortic wall
before and during development of atherosclerosis is partially
L-selectin dependent. J Exp Med. 203:1273–1282. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rayner K, Van Eersel S, Groot PH and Reape
TJ: Localisation of mRNA for JE/MCP-1 and its receptor CCR2 in
atherosclerotic lesions of the ApoE knockout mouse. J Vasc Res.
37:93–102. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kortelainen ML and Porvari K: Adventitial
macrophage and lymphocyte accumulation accompanying early stages of
human coronary atherogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 23:193–197. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shimokawa H, Ito A, Fukumoto Y, Kadokami
T, Nakaike R, Sakata M, Takayanagi T, Egashira K and Takeshita A:
Chronic treatment with interleukin-1 beta induces coronary intimal
lesions and vasospastic responses in pigs in vivo. The role of
platelet-derived growth factor. J Clin Invest. 97:769–776. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fukumoto Y, Shimokawa H, Ito A, Kadokami
T, Yonemitsu Y, Aikawa M, Owada MK, Egashira K, Sueishi K, Nagai R,
et al: Inflammatory cytokines cause coronary arteriosclerosis-like
changes and alterations in the smooth-muscle phenotypes in pigs. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 29:222–231. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tedgui A and Mallat Z: Cytokines in
atherosclerosis: Pathogenic and regulatory pathways. Physiol Rev.
86:515–581. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liao M, Xu J, Clair AJ, Ehrman B, Graham
LM and Eagleton MJ: Local and systemic alterations in signal
transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) associated with
human abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Surg Res. 176:321–328. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mo ZC, Xiao J, Liu XH, Hu YW, Li XX, Yi
GH, Wang Z, Tang YL, Liao DF and Tang CK: AOPPs inhibits
cholesterol efflux by down-regulating ABCA1 expression in a
JAK/STAT signaling pathway-dependent manner. J Atheroscler Thromb.
18:796–807. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beyazit Y, Sayilir A, Suvak B and Torun S:
The missing link between obesity and hepatocellular carcinoma:
IL-6-mediated STAT-3 activation as a key player in
hepatocarcinogenesis. Digestion. 84:185–186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Manea A, Tanase LI, Raicu M and Simionescu
M: Jak/STAT signaling pathway regulates nox1 and nox4-based NADPH
oxidase in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 30:105–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ortiz-Munoz G, Martin-Ventura JL,
Hernandez-Vargas P, Mallavia B, Lopez-Parra V, Lopez-Franco O,
Muñoz-Garcia B, Fernandez-Vizarra P, Ortega L, Egido J and
Gomez-Guerrero C: Suppressors of cytokine signaling modulate
JAK/STAT-mediated cell responses during atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:525–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song B, Jin H, Yu X, Zhang Z, Yu H, Ye J,
Xu Y, Zhou T, Oudit GY, Ye JY, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme
2 attenuates oxidative stress and VSMC proliferation via the
JAK2/STAT3/SOCS3 and profiling-1/MAPK signaling pathways. Regul
Pept. 185:44–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jinno T, Iwai M, Li Z, Li JM, Liu HW, Cui
TX, Rakugi H, Ogihara T and Horiuchi M: Calcium channel blocker
azelnidipine enhances vascular protective effects of AT1 receptor
blocker olmesartan. Hypertension. 43:263–269. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Banes AK, Shaw SM, Tawfik A, Patel BP,
Ogbi S, Fulton D and Marrero MB: Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway
in vascular smooth muscle by serotonin. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
288:C805–C812. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun J, Zheng J, Ling KH, Zhao K, Xie Z, Li
B, Wang T, Zhu Z, Patel AN, Min W, et al: Preventing intimal
thickening of vein grafts in vein artery bypass using STAT-3 siRNA.
J Transl Med. 10:22012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dronadula N, Liu Z, Wang C, Cao H and Rao
GN: STAT-3-dependent cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression is
required for thrombin-induced vascular smooth muscle cell motility.
J Biol Chem. 280:3112–3120. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Watanabe S, Mu W, Kahn A, Jing N, Li JH,
Lan HY, Nakagawa T, Ohashi R and Johnson RJ: Role of JAK/STAT
pathway in IL-6-induced activation of vascular smooth muscle cells.
Am J Nephrol. 24:387–392. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shimokawa H, Morishige K, Miyata K,
Kandabashi T, Eto Y, Ikegaki I, Asano T, Kaibuchi K and Takeshita
A: Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase induces a regression of
arteriosclerotic coronary lesions in a porcine model in vivo.
Cardiovasc Res. 51:169–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeller I, Knoflach M, Seubert A,
Kreutmayer SB, Stelzmüller ME, Wallnoefer E, Blunder S, Frotschnig
S, Messner B, Willeit J, et al: Lead contributes to arterial
intimal hyperplasia through nuclear factor erythroid 2-related
factor-mediated endothelial interleukin 8 synthesis and subsequent
invasion of smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:1733–1740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Sukhova GK, Sun JS, Xu WH, Libby P
and Shi GP: Lysosomal cysteine proteases in atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:1359–1366. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pauletto P, Sartore S and Pessina AC:
Smooth-muscle-cell proliferation and differentiation in neointima
formation and vascular restenosis. Clin Sci (Lond). 87:467–479.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Raible DJ, Frey LC and Brooks-Kayal AR:
Effects of JAK2-STAT3 signaling after cerebral insults. JAKSTAT.
3:e295102014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Levy DE and Darnell JE Jr: Stats:
Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 3:651–662. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sansone P and Bromberg J: Targeting the
interleukin-6/Jak/stat pathway in human malignancies. J Clin Oncol.
30:1005–1014. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seki Y, Kai H, Shibata R, Nagata T,
Yasukawa H, Yoshimura A and Imaizumi T: Role of the JAK/STAT
pathway in rat carotid artery remodeling after vascular injury.
Circ Res. 87:12–18. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Recinos A III, LeJeune WS, Sun H, Lee CY,
Tieu BC, Lu M, Hou T, Boldogh I, Tilton RG and Brasier AR:
Angiotensin II induces IL-6 expression and the Jak-STAT3 pathway in
aortic adventitia of LDL receptor-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis.
194:125–133. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shibata R, Kai H, Seki Y, Kato S, Wada Y,
Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, Yoshimura A and Imaizumi T: Inhibition of
STAT3 prevents neointima formation by inhibiting proliferation and
promoting apoptosis of neointimal smooth muscle cells. Hum Gene
Ther. 14:601–610. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Neria F, Caramelo C, Peinado H,
González-Pacheco FR, Deudero JJ, de Solis AJ, Fernández-Sánchez R,
Peñate S, Cano A and Castilla MA: Mechanisms of endothelial cell
protection by blockade of the JAK2 pathway. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 292:C1123–C1131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Neeli I, Liu Z, Dronadula N, Ma ZA and Rao
GN: An essential role of the Jak-2/STAT-3/cytosolic phospholipase
A(2) axis in platelet-derived growth factor BB-induced vascular
smooth muscle cell motility. J Biol Chem. 279:46122–46128. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sasaguri T, Teruya H, Ishida A, Abumiya T
and Ogata J: Linkage between alpha(1) adrenergic receptor and the
Jak/STAT signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 268:25–30. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Newby AC: Matrix metalloproteinases
regulate migration, proliferation and death of vascular smooth
muscle cells by degrading matrix and non-matrix substrates.
Cardiovasc Res. 69:614–624. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang L, Li Y, Liu Y, Wang X, Chen M, Xing
Y and Zhu D: STAT3-mediated MMP-2 expression is required for
15-HETE-induced vascular adventitial fibroblast migration. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 149C:106–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jo DH and Kim JH, Cho CS, Cho YL, Jun HO,
Yu YS, Min JK and Kim JH: STAT3 inhibition suppresses proliferation
of retinoblastoma through down-regulation of positive feedback loop
of STAT3/miR-17-92 clusters. Oncotarget. 5:11513–11525. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mesa RA, Verstovsek S, Gupta V,
Mascarenhas JO, Atallah E, Burn T, Sun W, Sandor V and Gotlib J:
Effects of ruxolitinib treatment on metabolic and nutritional
parameters in patients with myelofibrosis from COMFORT-I. Clin
Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 15:214.e1–221.e1. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|