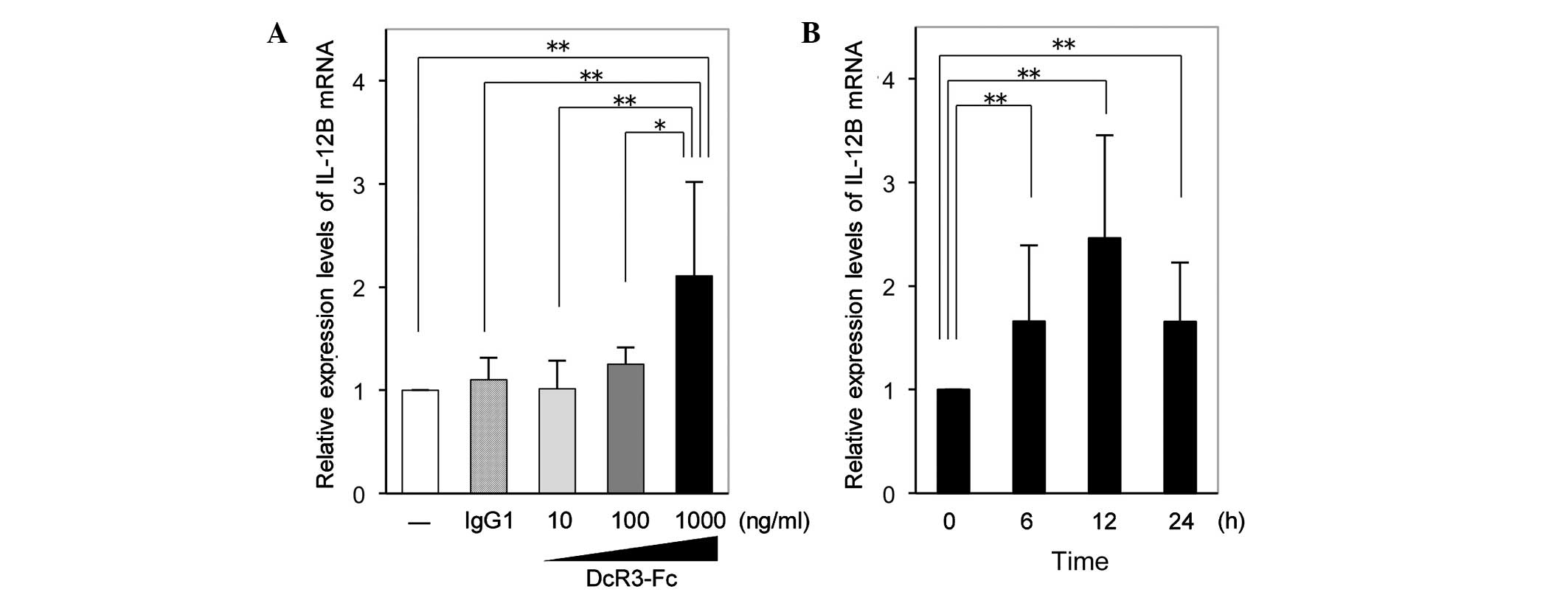
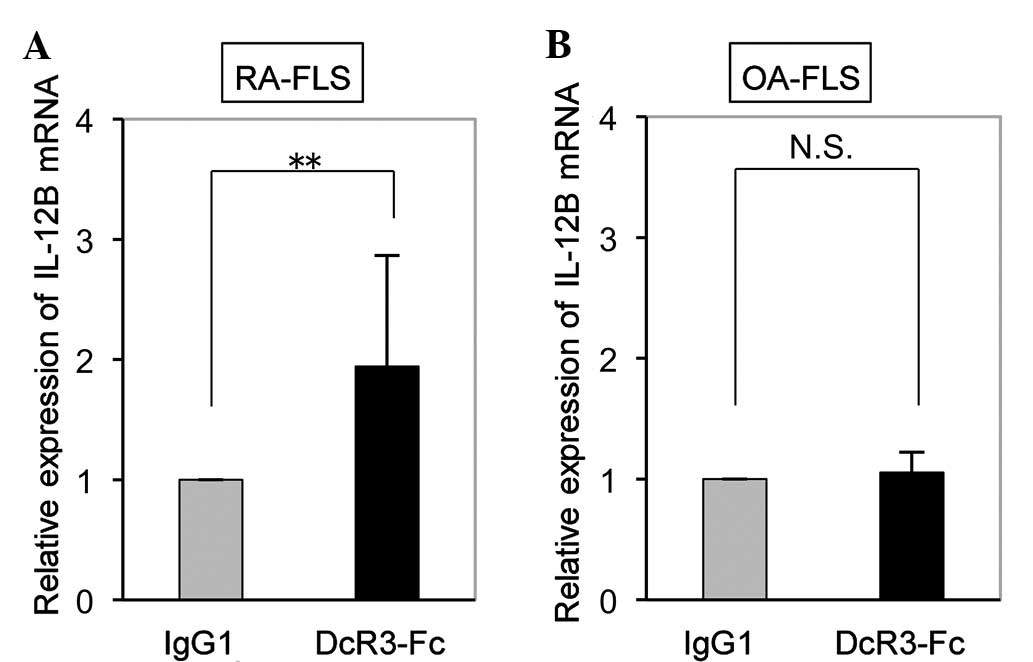
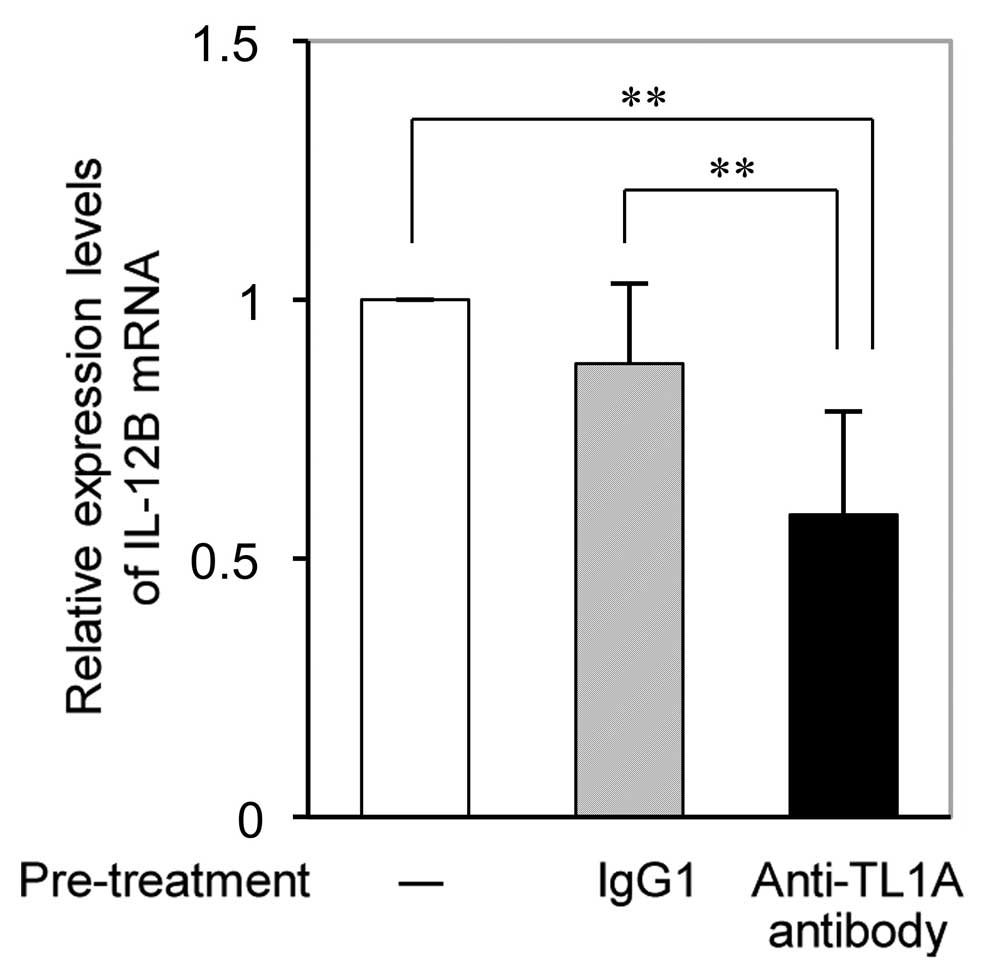
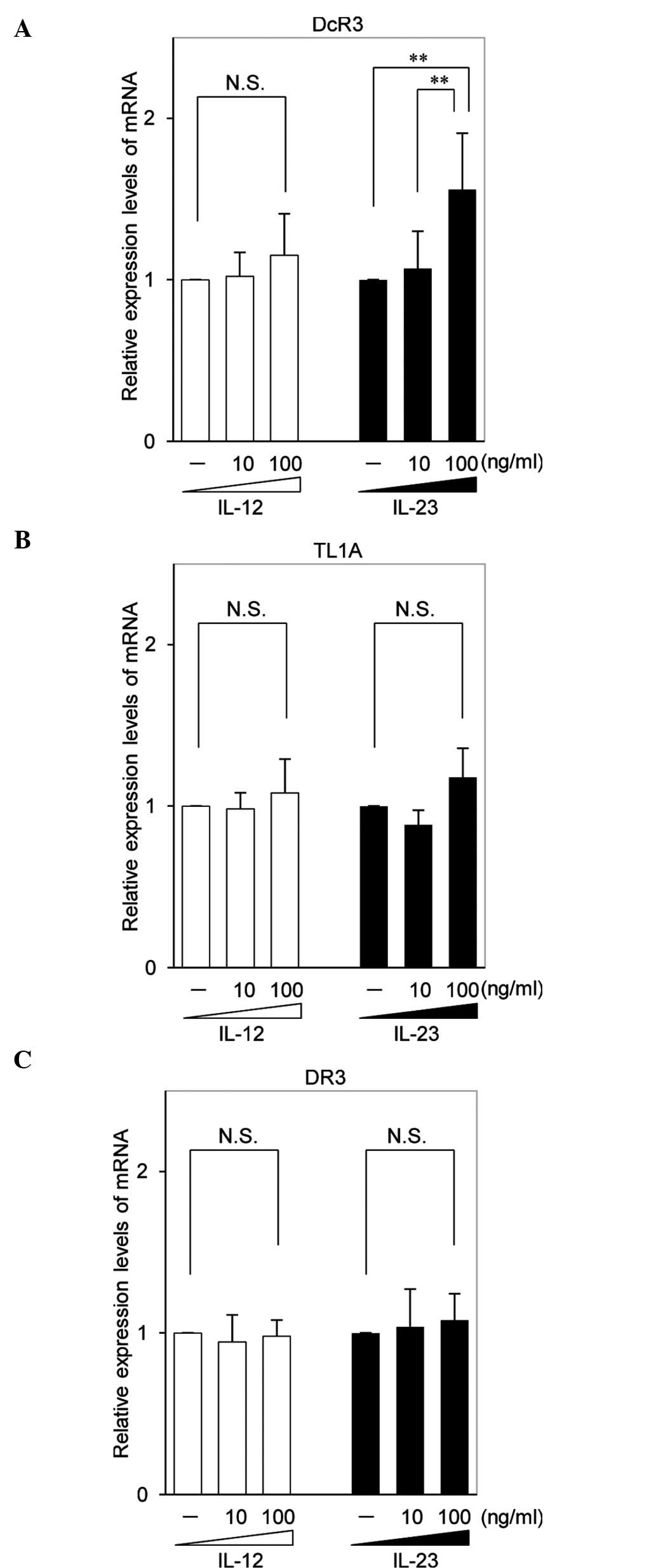
|
1
|
Goldring SR: Pathogenesis of bone and
cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 42(Suppl 2): ii11–ii16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
McInnes IB and Schett G: Cytokines in the
pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:429–442.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Lawrence DA, Roy M,
Kischkel FC, Dowd P, Huang A, Donahue CJ, Sherwood SW, Baldwin DT,
et al: Genomic amplification of a decoy receptor for Fas ligand in
lung and colon cancer. Nature. 396:699–703. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shi G, Wu Y, Zhang J and Wu J: Death decoy
receptor TR6/DcR3 inhibits T cell chemotaxis in vitro and in vivo.
J Immunol. 171:3407–3414. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Migone TS, Zhang J, Luo X, Zhuang L, Chen
C, Hu B, Hong JS, Perry JW, Chen SF, Zhou JX, et al: TL1A is a
TNF-like ligand for DR3 and TR6/DcR3 and functions as a T cell
costimulator. Immunity. 16:479–492. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bai C, Connolly B, Metzker ML, Hilliard
CA, Liu X, Sandig V, Soderman A, Galloway SM, Liu Q, Austin CP and
Caskey CT: Overexpression of M68/DcR3 in human gastrointestinal
tract tumors independent of gene amplification and its location in
a four-gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:1230–1235. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen J, Zhang L and Kim S: Quantification
and detection of DcR3, a decoy receptor in TNFR family. J Immunol
Methods. 285:63–70. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohshima K, Haraoka S, Sugihara M, Suzumiya
J, Kawasaki C, Kanda M and Kikuchi M: Amplification and expression
of a decoy receptor for fas ligand (DcR3) in virus (EBV or HTLV-I)
associated lymphomas. Cancer Lett. 160:89–97. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsuji S, Hosotani R, Yonehara S, et al:
Endogenous decoy receptor 3 blocks the growth inhibition signals
mediated by Fas ligand in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 106:17–25. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu KY, Kwon B, Ni J, Zhai Y, Ebner R and
Kwon BS: A newly identified member of tumor necrosis factor
receptor superfamily (TR6) suppresses LIGHT-mediated apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 274:13733–13736. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hayashi S, Miura Y, Nishiyama T, Mitani M,
Tateishi K, Sakai Y, Hashiramoto A, Kurosaka M, Shiozawa S and
Doita M: Decoy receptor 3 expressed in rheumatoid synovial
fibroblasts protects the cells against Fas-induced apoptosis.
Arthritis Rheum. 56:1067–1075. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang CR, Wang JH, Hsieh SL, Wang SM, Hsu
TL and Lin WW: Decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) induces osteoclast formation
from monocyte/macrophage lineage precursor cells. Cell Death
Differ. 11(Suppl 1): S97–S107. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hsu MJ, Lin WW, Tsao WC, Chang YC, Hsu TL,
Chiu AW, Chio CC and Hsieh SL: Enhanced adhesion of monocytes via
reverse signaling triggered by decoy receptor 3. Exp Cell Res.
292:241–251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tateishi K, Miura Y, Hayashi S, Takahashi
M and Kurosaka M: DcR3 protects THP-1 macrophages from apoptosis by
increasing integrin alpha4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
389:593–598. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takahashi M, Miura Y, Hayashi S, Tateishi
K, Fukuda K and Kurosaka M: DcR3-TL1A signalling inhibits
cytokine-induced proliferation of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts.
Int J Mol Med. 28:423–427. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fukuda K, Miura Y, Maeda T, Takahashi M,
Hayashi S and Kurosaka M: Decoy receptor 3 regulates the expression
of various genes in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Int
J Mol Med. 32:910–916. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lupardus PJ and Garcia KC: The structure
of interleukin-23 reveals the molecular basis of p40 subunit
sharing with interleukin-12. J Mol Biol. 382:931–941. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Haskó G and Szabó C: IL-12 as a
therapeutic target for pharmacological modulation in
immune-mediated and inflammatory diseases: Regulation of T helper
1/T helper 2 responses. Br J Pharmacol. 127:1295–1304. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Paradowska-Gorycka A, Grzybowska-Kowalczyk
A, Wojtecka-Lukasik E and Maslinski S: IL-23 in the pathogenesis of
rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 71:134–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Swaak AJ, van den Brink HG and Aarden LA:
Cytokine production in whole blood cell cultures of patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 56:693–695. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu FL, Chen CH, Chu SJ, Chen JH, Lai JH,
Sytwu HK and Chang DM: Interleukin (IL)-23 p19 expression induced
by IL-1beta in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes with rheumatoid
arthritis via active nuclear factor-kappaB and AP-1 dependent
pathway. Rheumatology (Oxford). 46:1266–1273. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim HR, Cho ML, Kim KW, Juhn JY, Hwang SY,
Yoon CH, Park SH, Lee SH and Kim HY: Up-regulation of IL-23p19
expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by IL-17
through PI3-kinase-, NF-kappaB- and p38 MAPK-dependent signalling
pathways. Rheumatology (Oxford). 46:57–64. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane
DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH and Luthra
HS: The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for
the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
31:315–324. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thiel CT, Kraus C, Rauch A, Ekici AB,
Rautenstrauss B and Reis A: A new quantitative PCR multiplex assay
for rapid analysis of chromosome 17p11.2-12 duplications and
deletions leading to HMSN/HNPP. Eur J Hum Genet. 11:170–178. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR,
Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM and Weaver CT: Interleukin
17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct
from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 6:1123–1132.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Iwakura Y and Ishigame H: The IL-23/IL-17
axis in inflammation. J Clin Invest. 116:1218–1222. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Manetti R, Parronchi P, Giudizi MG,
Piccinni MP, Maggi E, Trinchieri G and Romagnani S: Natural killer
cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12 [IL-12]) induces T helper
type 1 (Th1)-specific immune responses and inhibits the development
of IL-4-producing Th cells. J Exp Med. 177:1199–1204. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gottlieb A and Narang K: Ustekinumab in
the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: Latest findings and clinical
potential. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 5:277–285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mannon PJ, Fuss IJ, Mayer L, Elson CO,
Sandborn WJ, Present D, Dolin B, Goodman N, Groden C, Hornung RL,
et al: Anti-interleukin-12 antibody for active Crohn's disease. N
Engl J Med. 351:2069–2079. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sakkas LI, Johanson NA, Scanzello CR and
Platsoucas CD: Interleukin-12 is expressed by infiltrating
macrophages and synovial lining cells in rheumatoid arthritis and
osteoarthritis. Cell Immunol. 188:105–110. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kitagawa M, Mitsui H, Nakamura H, Yoshino
S, Miyakawa S, Ochiai N, Onobori M, Suzuki H and Sumida T:
Differential regulation of rheumatoid synovial cell interleukin-12
production by tumor necrosis factor alpha and CD40 signals.
Arthritis Rheum. 42:1917–1926. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|