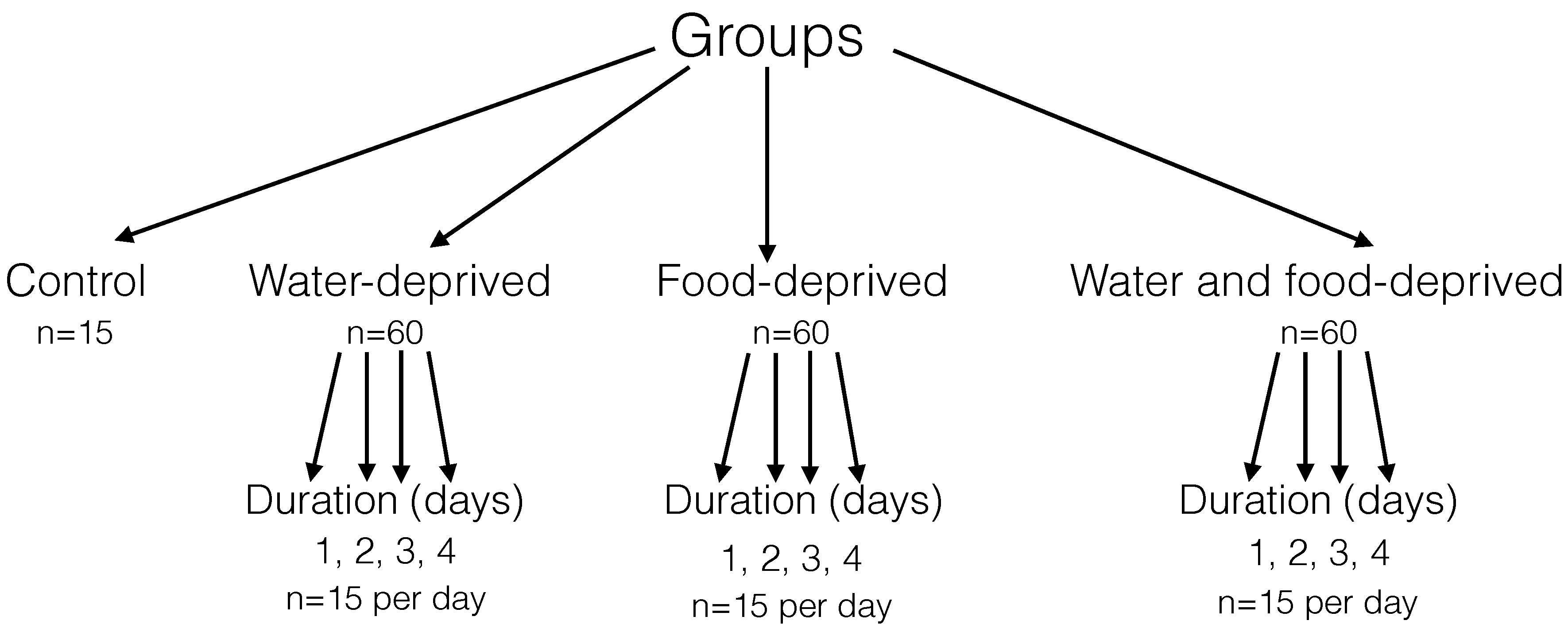
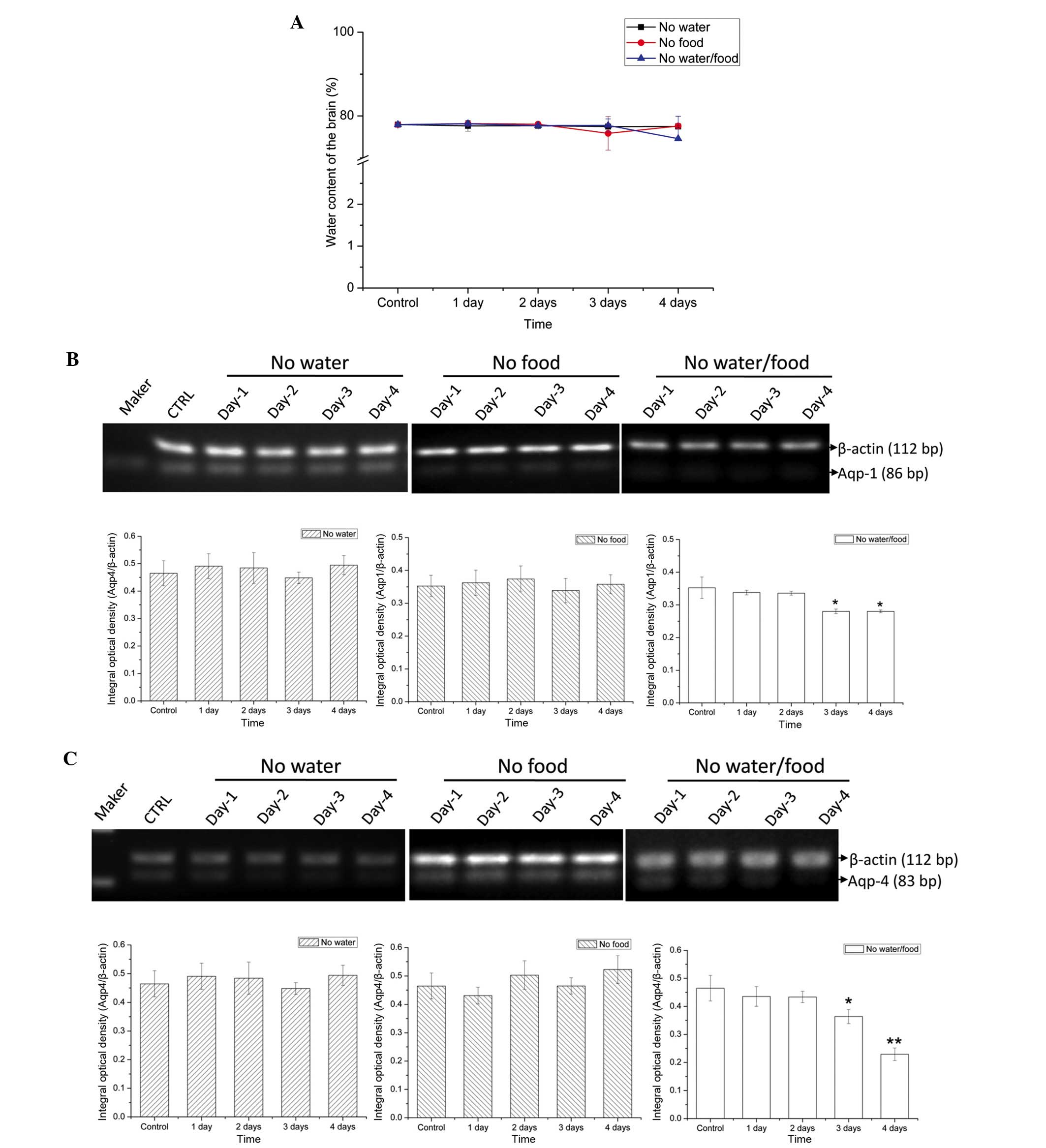
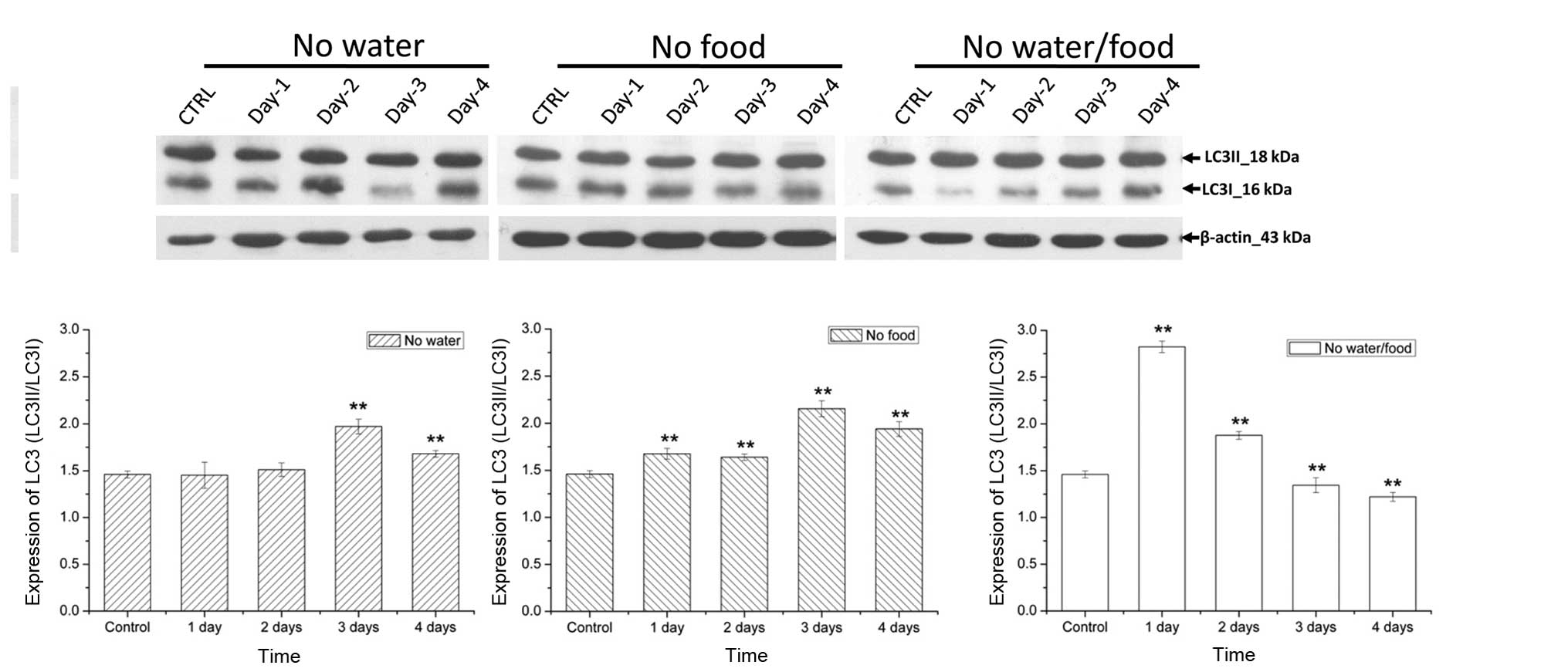
|
1
|
Peters A, Pellerin L, Dallman M, Oltmanns
KM, Schweiger U, Born J and Fehm HL: Causes of obesity: Looking
beyond the hypothalamus. Prog Neurobiol. 81:61–88. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shulman RG, Rothman DL, Behar KL and Hyder
F: Energetic basis of brain activity: Implications for
neuroimaging. Trends Neurosci. 27:489–495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bélanger M, Allaman I and Magistretti PJ:
Brain energy metabolism: Focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic
cooperation. Cell Metab. 14:724–738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown AM and Ransom BR: Astrocyte glycogen
and brain energy metabolism. Glia. 55:1263–1271. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rosenblatt F: The perceptron: A
probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the
brain. Psychol Rev. 65:386–408. 1958. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Erecinska M, Cherian S and Silver IA:
Energy metabolism in mammalian brain during development. Prog
Neurobiol. 73:397–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ebert D, Haller RG and Walton ME: Energy
contribution of octanoate to intact rat brain metabolism measured
by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Neurosci.
23:5928–5935. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peters A, Schweiger U, Pellerin L, Hubold
C, Oltmanns KM, Conrad M, Schultes B, Born J and Fehm HL: The
selfish brain: Competition for energy resources. Neurosci Biobehav
Rev. 28:143–180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peters A, Schweiger U, Fruhwald-Schultes
B, Born J and Fehm HL: The neuroendocrine control of glucose
allocation. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 110:199–211. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hitze B, Hubold C, Van Dyken R,
Schlichting K, Lehnert H, Entringer S and Peters A: How the selfish
brain organizes its supply and demand. Fron Neuroenergetics.
2(7)2010.
|
|
11
|
Kennedy GC: The role of depot fat in the
hypothalamic control of food intake in the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B
Biol Sci. 140:578–596. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D,
Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E and Flier JS: Role of leptin in the
neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature. 382:250–252. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ,
Bloom SR and Lechler RI: Leptin modulates the T-cell immune
response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature.
394:897–901. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ahima RS, Saper CB, Flier JS and Elmquist
JK: Leptin regulation of neuroendocrine systems. Front
Neuroendocrinol. 21:263–307. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mayer J: Regulation of energy intake and
the body weight: The glucostatic theory and the lipostatic
hypothesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 63:15–43. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kubera B, Hubold C, Zug S, Wischnath H,
Wilhelm I, Hallschmid M, Entringer S, Langemann D and Peters A: The
brain's supply and demand in obesity. Front Neuroenergetics.
4(4)2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Badaut J, Fukuda AM, Jullienne A and Petry
KG: Aquaporin and brain diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1840.1554–1565. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Badaut J, Lasbennes F, Magistretti PJ and
Regli L: Aquaporins in brain: Distribution, physiology and
pathophysiology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:367–378. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Papadopoulos MC and Verkman AS:
Aquaporin-4 and brain edema. Pediatr Nephrol. 22:778–784. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suzuki R, Okuda M, Asai J, Nagashima G,
Itokawa H, Matsunaga A, Fujimoto T and Suzuki T: Astrocytes
co-express aquaporin-1,-4 and vascular endothelial growth factor in
brain edema tissue associated with brain contusion. Acta Neurochir
Suppl. 96:398–401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Henell F, Berkenstam A, Ahlberg J and
Glaumann H: Degradation of short-and long-lived proteins in
perfused liver and in isolated autophagic vacuoles-lysosomes. Exp
Mol Pathol. 46:1–14. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanida I, Minematsu-Ikeguchi N, Ueno T and
Kominami E: Lysosomal turnover, but not a cellular level, of
endogenous LC3 is a marker for autophagy. Autophagy. 1:84–91. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shen Z, Qu W, Wang W, Lu Y, Wu Y, Li Z,
Hang X, Wang X, Zhao D and Zhang C: MPprimer: A program for
reliable multiplex PCR primer design. BMC Bioinformatics.
11(143)2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fehm HL, Kern W and Peters A: The selfish
brain: Competition for energy resources. Prog Brain Res.
153:129–140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tait MJ, Saadoun S, Bell BA and
Papadopoulos MC: Water movements in the brain: Role of aquaporins.
Trends Neurosci. 31:37–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Griesdale DE and Honey CR: Aquaporins and
brain edema. Surg Neurol. 61:418–421. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuma A, Matsui M and Mizushima N: LC3, an
autophagosome marker, can be incorporated into protein aggregates
independent of autophagy: Caution in the interpretation of LC3
localization. Autophagy. 3:323–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mizushima N and Klionsky DJ: Protein
turnover via autophagy: Implications for metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr.
27:19–40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: A double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Y, McMillan-Ward E, Kong J, Israels S
and Gibson S: Oxidative stress induces autophagic cell death
independent of apoptosis in transformed and cancer cells. Cell
Death Differ. 15:171–182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|