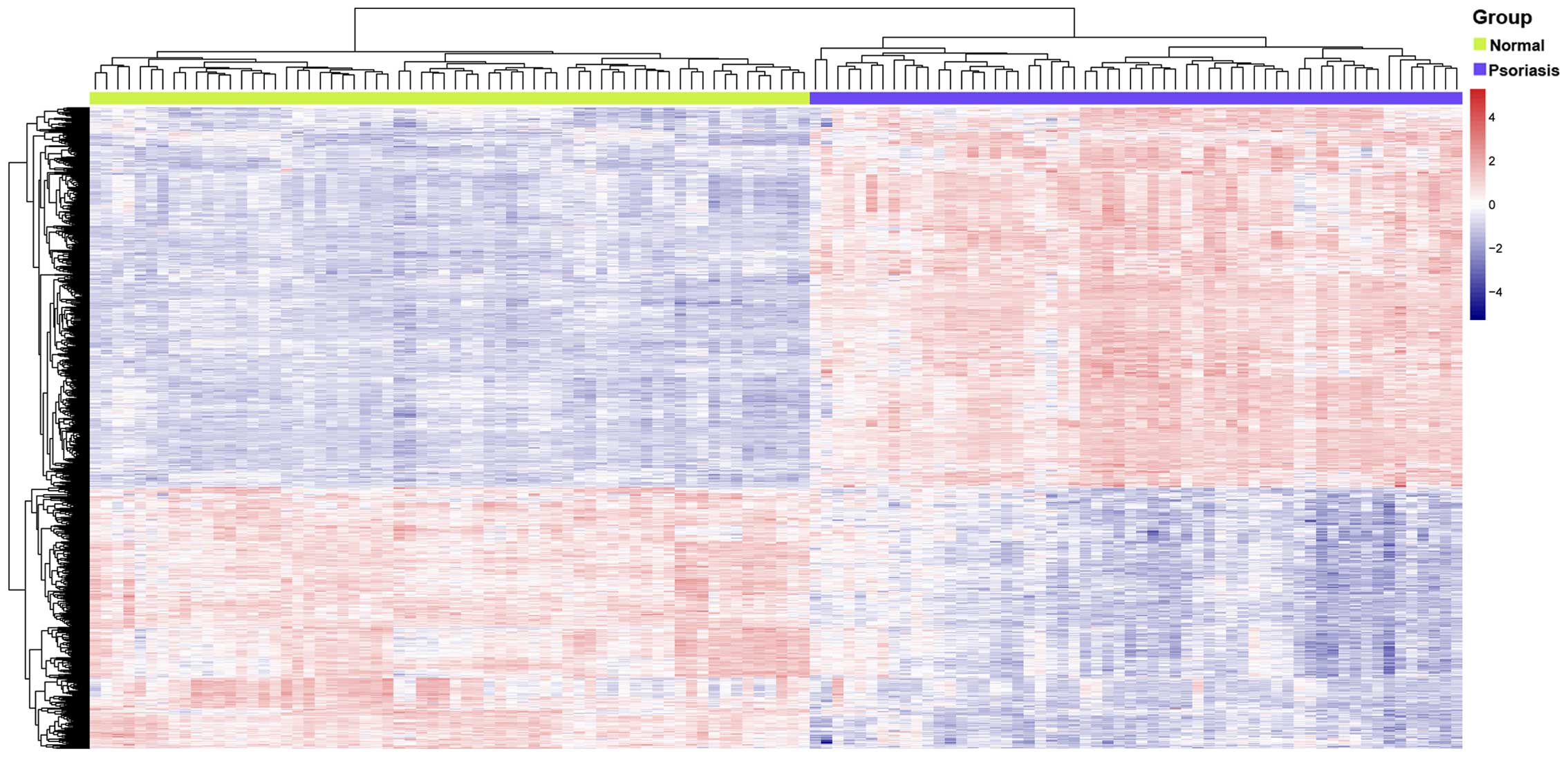
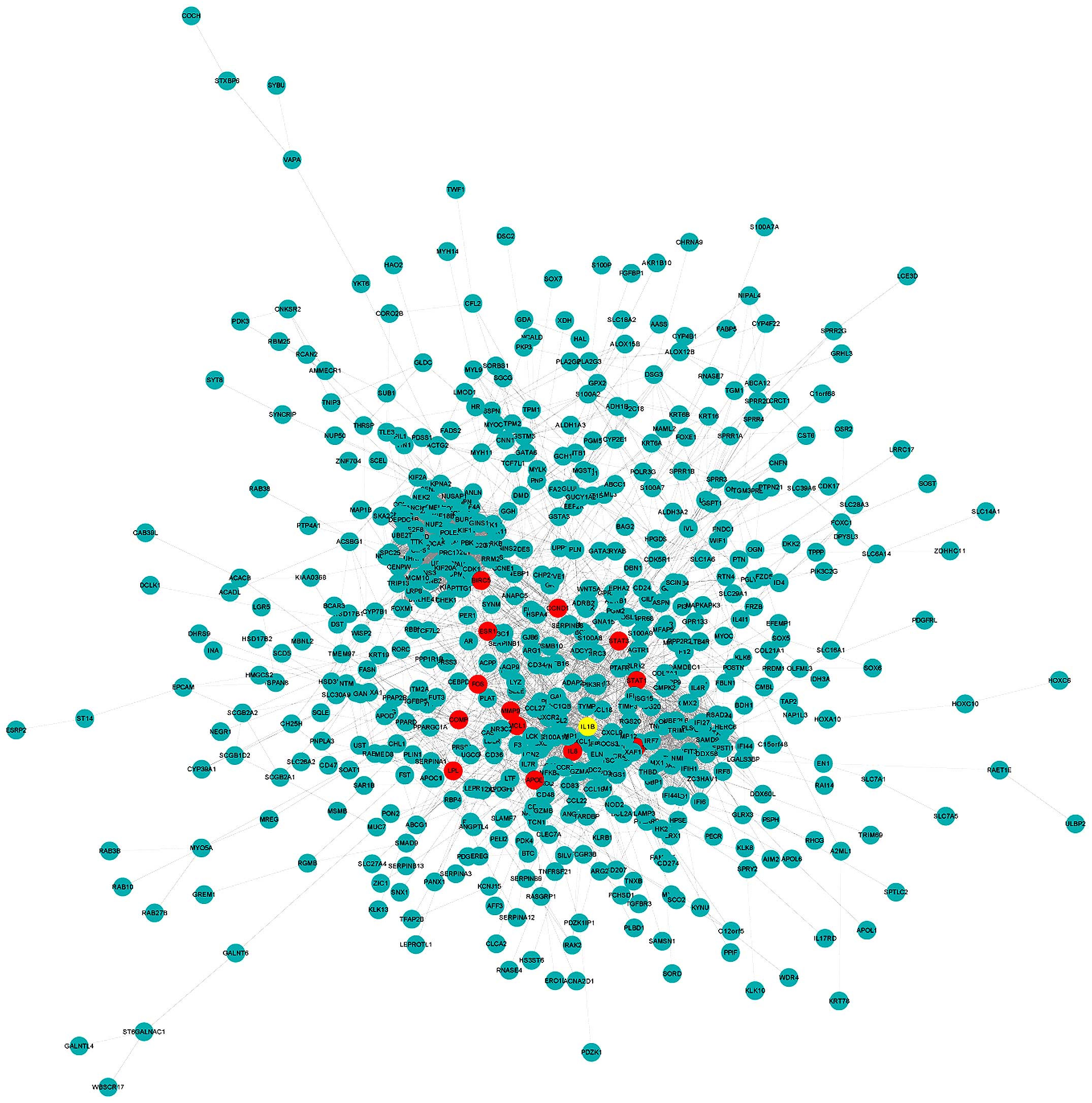
|
1
|
Christophers E: Psoriasis-epidemiology and
clinical spectrum. Clin Exp Dermatol. 26:314–320. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nestle FO, Kaplan DH and Barker J:
Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 361:496–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Laporte M, Galand P, Fokan D, de Graef C
and Heenen M: Apoptosis in established and healing psoriasis.
Dermatology. 200:314–316. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Madonna S, Scarponi C, Pallotta S, Cavani
A and Albanesi C: Anti-apoptotic effects of suppressor of cytokine
signaling 3 and 1 in psoriasis. Cell Death Dis. 3:e3342012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Portt L, Norman G, Clapp C, Greenwood M
and Greenwood MT: Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: A review.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:238–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sanchez MI, Shearwood AM, Chia T, Davies
SM, Rackham O and Filipovska A: Estrogen-mediated regulation of
mitochondrial gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 29:14–27. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Miller LS: Toll-like receptors in skin.
Adv Dermatol. 24:71–87. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nair RP, Duffin KC, Helms C, Ding J,
Stuart PE, Goldgar D, Gudjonsson JE, Li Y, Tejasvi T, Feng BJ, et
al: Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23
and NF-kappaB pathways. Nat Genet. 41:199–204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Swindell WR, Johnston A, Carbajal S, Han
G, Wohn C, Lu J, Xing X, Nair RP, Voorhees JJ, Elder JT, et al:
Genome-wide expression profiling of five mouse models identifies
similarities and differences with human psoriasis. PloS One.
6:e182662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kerr MK: Linear models for microarray data
analysis: Hidden similarities and differences. J Computat Biol.
10:891–901. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Song EK, Collins NR,
Uversky VN, Dunker AK, O'Malley BW, Geistlinger TR, Carroll JS,
Brown M and Nakshatri H: Interplay between estrogen receptor and
AKT in estradiol-induced alternative splicing. BMC Med Genomics.
6:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database Issue): D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Snel B, Lehmann G, Bork P and Huynen MA:
STRING: A web-server to retrieve and display the repeatedly
occurring neighbourhood of a gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:3442–3444.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Page L, Brin S, Motwani R and Winograd T:
The Page Rank citation ranking: Bringing order to the web. Stanford
Info Lab. 1999.
|
|
15
|
Dellavalle RP, Schilling LM, Rodriguez MA,
Van de Sompel H and Bollen J: Refining dermatology journal impact
factors using Page Rank. J Am Acad Dermatol. 57:116–119. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Griffiths TL, Steyvers M and Firl A:
Google and the mind: Predicting fluency with Page Rank. Psychol
Sci. 18:1069–1076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bánky D, Iván G and Grolmusz V: Equal
opportunity for low-degree network nodes: A Page Rank-based method
for protein target identification in metabolic graphs. PloS One.
8:e542042013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Albert R and Barabási AL: Statistical
mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys. 74:47–97. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Park YK and Jang BC: UVB-induced
anti-survival and pro-apoptotic effects on HaCaT human
keratinocytes via caspase- and PKC-dependent downregulation of PKB,
HIAP-1, Mcl-1, XIAP and ER stress. Int J Mol Med. 33:695–702.
2014.
|
|
22
|
Rasmussen MK, Iversen L, Johansen C,
Finnemann J, Olsen LS, Kragballe K and Gesser B: IL-8 and p53 are
inversely regulated through JNK, p38 and NF-kappaB p65 in HepG2
cells during an inflammatory response. Inflamm Res. 57:329–339.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chaturvedi V, Sitailo LA, Qin JZ, Bodner
B, Denning MF, Curry J, Zhang W, Brash D and Nickoloff BJ:
Knockdown of p53 levels in human keratinocytes accelerates Mcl-1
and Bcl-x(L) reduction thereby enhancing UV-light induced
apoptosis. Oncogene. 24:5299–5312. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zang YC, Halder JB, Hong J, Rivera VM and
Zhang JZ: Regulatory effects of estriol on T cell migration and
cytokine profile: Inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappa B. J
Neuroimmunol. 124:106–114. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang KC, Wang Y, Oh IG, Jenkins S,
Freedman LP, Thompson CC, Chung JH and Nagpal S: Estrogen receptor
beta is a novel therapeutic target for photoaging. Mol Pharmacol.
77:744–750. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paolillo N, Piccirilli S, Giardina E,
Rispoli V, Colica C and Nisticò S: Effects of paraquat and
capsaicin on the expression of genes related to inflammatory,
immune responses and cell death in immortalized human HaCat
keratinocytes. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 24:861–868. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Petersson S, Bylander A, Yhr M and
Enerback C: S100A7 (Psoriasin), highly expressed in ductal
carcinoma in situ (DCIS), is regulated by IFN-gamma in mammary
epithelial cells. BMC Cancer. 7:2052007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sneh A, Deol YS, Ganju A, Shilo K, Rosol
TJ, Nasser MW and Ganju RK: Differential role of psoriasin (S100A7)
in estrogen receptor alpha positive and negative breast cancer
cells occur through actin remodeling. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
138:727–739. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsu HH, Kuo WW, Ju DT, Yeh YL, Tu CC, Tsai
YL, Shen CY, Chang SH, Chung LC and Huang CY: Estradiol agonists
inhibit human LoVo colorectal-cancer cell proliferation and
migration through p53. World J Gastroenterol. 20:16665–16673. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koçak M, Bozdogan O, Erkek E, Atasoy P and
Birol A: Examination of Bcl-2, Bcl-X and bax protein expression in
psoriasis. Int J Dermatol. 42:789–793. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gabr SA, Berika MY and Alghadir AH:
Apoptosis and clinical severity in patients with psoriasis and HCV
infection. Indian J Dermatol. 59:230–236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gündüz K, Demireli P, Vatansever S and
Inanir I: Examination of bcl-2 and p53 expressions and apoptotic
index by TUNEL method in psoriasis. J Cutan Pathol. 33:788–792.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Yin H, Zhao M and Lu Q: TLR2 and
TLR4 in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Clin Rev
Allergy Immunol. 47:136–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dallaglio K, Marconi A and Pincelli C:
Survivin: A dual player in healthy and diseased skin. J Invest
Dermatol. 132:18–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hsu I, Yeh CR, Slavin S, Miyamoto H, Netto
GJ, Tsai YC, Muyan M, Wu XR, Messing EM, Guancial EA and Yeh S:
Estrogen receptor alpha prevents bladder cancer via INPP4B
inhibited akt pathway in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget.
5:7917–7935. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|