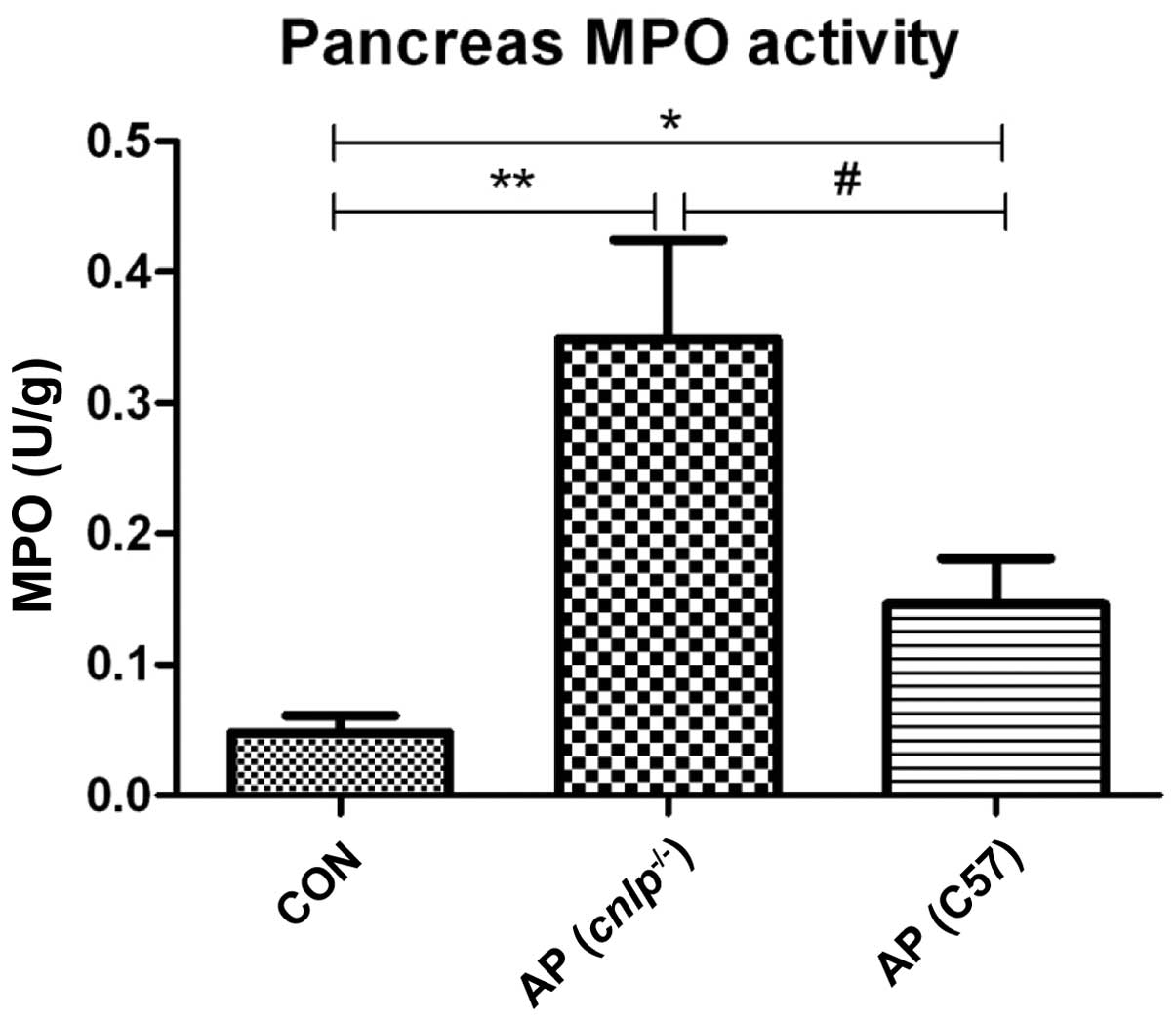
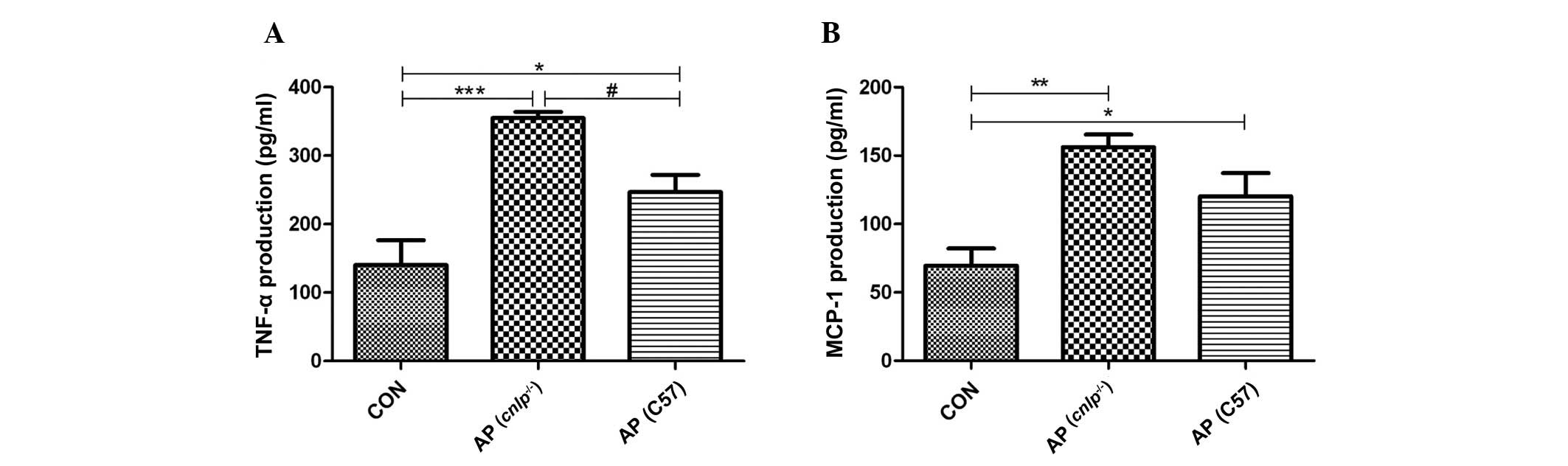
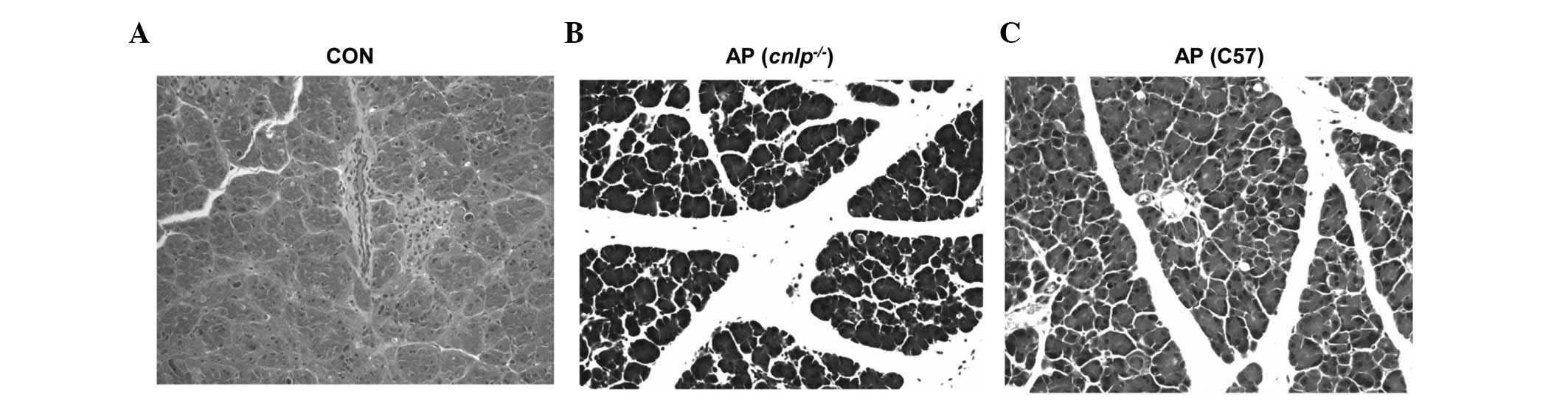
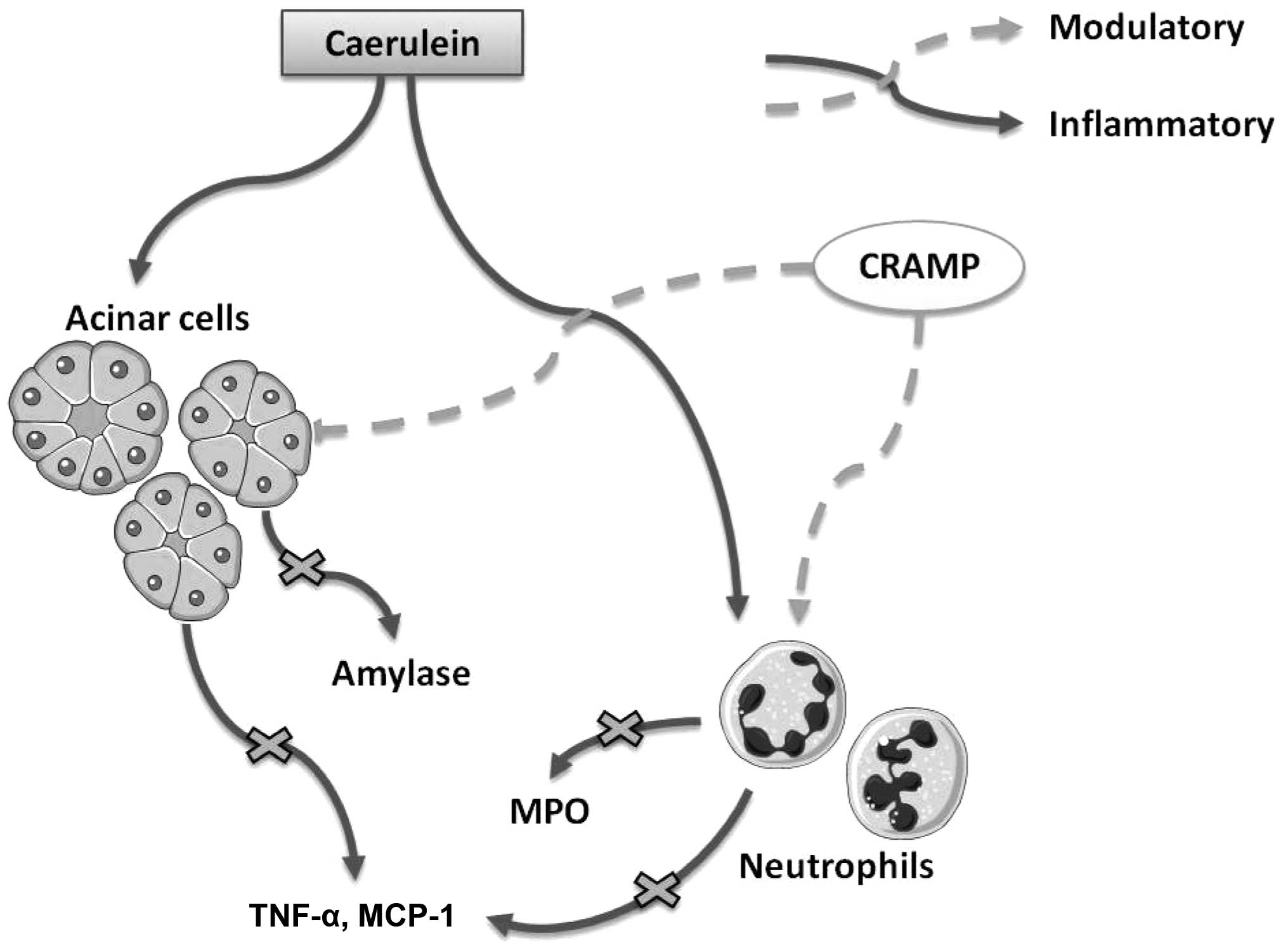
|
1
|
Bell D, Keane MG and Pereira SP: Acute
pancreatitis. Medicine. 43:174–181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Petrov M: Nutrition, inflammation, and
acute pancreatitis. ISRN Inflamm. 2013:3414102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kylänpää L, Rakonczay Z Jr and O'Reilly
DA: The clinical course of acute pancreatitis and the inflammatory
mediators that drive it. Int J Inflam. 2012:3606852012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Johnson CD and Abu-Hilal M: Persistent
organ failure during the first week as a marker of fatal outcome in
acute pancreatitis. Gut. 53:1340–1344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
DiMagno MJ and DiMagno EP: New advances in
acute pancreatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 23:494–501.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Abdulla A, Awla D, Thorlacius H and Regnér
S: Role of neutrophils in the activation of trypsinogen in severe
acute pancreatitis. J Leukoc Biol. 90:975–982. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Akinosoglou K and Gogos C:
Immune-modulating therapy in acute pancreatitis: Fact or fiction.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:15200–15215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bhatia M, Neoptolemos JP and Slavin J:
Inflammatory mediators as therapeutic targets in acute
pancreatitis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2:496–501. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cunha DM, Koike MK, Barbeiro DF, Barbeiro
HV, Hamasaki MY, Coelho Neto GT, Machado MC and da Silva FP:
Increased intestinal production of α-defensins in aged rats with
acute pancreatic injury. Exp Gerontol. 60:215–219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gallo RL and Hooper LV: Epithelial
antimicrobial defence of the skin and intestine. Nat Rev Immunol.
12:503–516. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hiemstra PS: Defensins and cathelicidins
in inflammatory lung disease: Beyond antimicrobial activity.
Biochem Soc Trans. 34:276–278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hilchie AL, Wuerth K and Hancock RE:
Immune modulation by multifaceted cationic host defense
(antimicrobial) peptides. Nat Chem Biol. 9:761–768. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sørensen OE, Follin P, Johnsen AH, Calafat
J, Tjabringa GS, Hiemstra PS and Borregaard N: Human cathelicidin,
hCAP-18, is processed to the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by
extracellular cleavage with proteinase 3. Blood. 97:3951–3959.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zanetti M, Gennaro R and Romeo D:
Cathelicidins: A novel protein family with a common proregion and a
variable C-terminal antimicrobial domain. FEBS Lett. 374:1–5. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zanetti M: The role of cathelicidins in
the innate host defenses of mammals. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
7:179–196. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shaykhiev R, Beisswenger C, Kändler K,
Senske J, Püchner A, Damm T, Behr J and Bals R: Human endogenous
antibiotic LL-37 stimulates airway epithelial cell proliferation
and wound closure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
289:L842–L848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nagaoka I, Tamura H and Hirata M: An
antimicrobial cathelicidin peptide, human CAP18/LL-37, suppresses
neutrophil apoptosis via the activation of formyl-peptide
receptor-like 1 and P2X7. J Immunol. 176:3044–3052. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wehkamp J, Harder J, Weichenthal M,
Mueller O, Herrlinger KR, Fellermann K, Schroeder JM and Stange EF:
Inducible and constitutive beta-defensins are differentially
expressed in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel
Dis. 9:215–223. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dawra R, Sah RP, Dudeja V, Rishi L,
Talukdar R, Garg P and Saluja AK: Intra-acinar trypsinogen
activation mediates early stages of pancreatic injury but not
inflammation in mice with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology.
141:2210–2217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bhatia M: Apoptosis versus necrosis in
acute pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
286:G189–G196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sah RP and Saluja A: Molecular mechanisms
of pancreatic injury. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 27:444–451. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sah RP, Dawra RK and Saluja AK: New
insights into the pathogenesis of pancreatitis. Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 29:523–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Criddle DN, McLaughlin E, Murphy JA,
Petersen OH and Sutton R: The pancreas misled: Signals to
pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 7:436–446. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meguro S, Tomita M, Katsuki T, Kato K, Oh
H, Ainai A, Ito R, Kawai T, Itoh H and Hasegawa H: Plasma
antimicrobial peptide LL-37 level is inversely associated with HDL
cholesterol level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J
Endocrinol. 2014:7036962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xue J, Sharma V and Habtezion A: Immune
cells and immune-based therapy in pancreatitis. Immunol Res.
58:378–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mayerle J, Dummer A, Sendler M, Malla SR,
van den Brandt C, Teller S, Aghdassi A, Nitsche C and Lerch MM:
Differential roles of inflammatory cells in pancreatitis. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27(Suppl 2): 47–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bhatia M, Brady M, Shokuhi S, Christmas S,
Neoptolemos JP and Slavin J: Inflammatory mediators in acute
pancreatitis. JPathol. 190:117–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Norman JG, Fink GW and Franz MG: Acute
pancreatitis induces intrapancreatic tumor necrosis factor gene
expression. Arch Surg. 130:966–970. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun J and Bhatia M: Blockade of
neurokinin-1 receptor attenuates CC and CXC chemokine production in
experimental acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 292:G143–G153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|