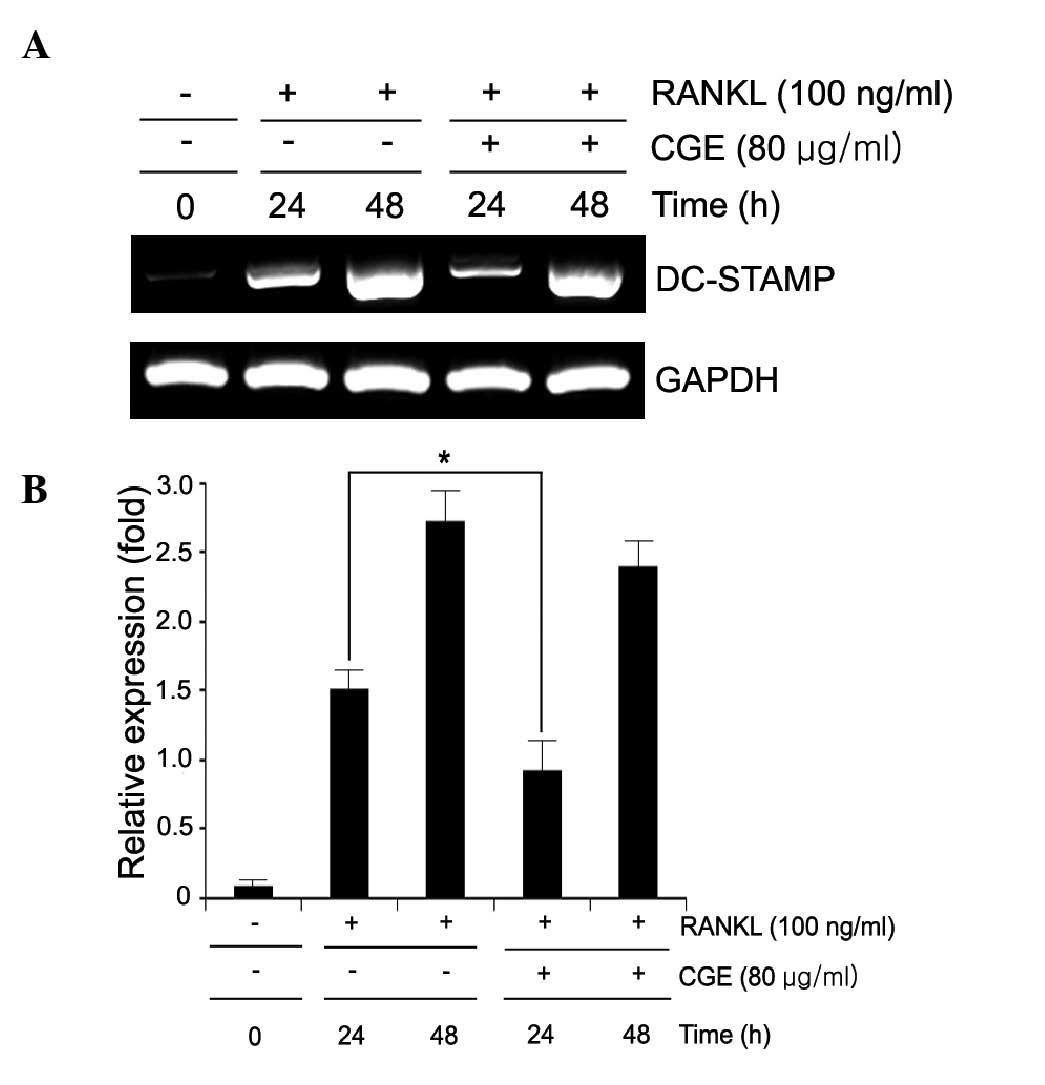
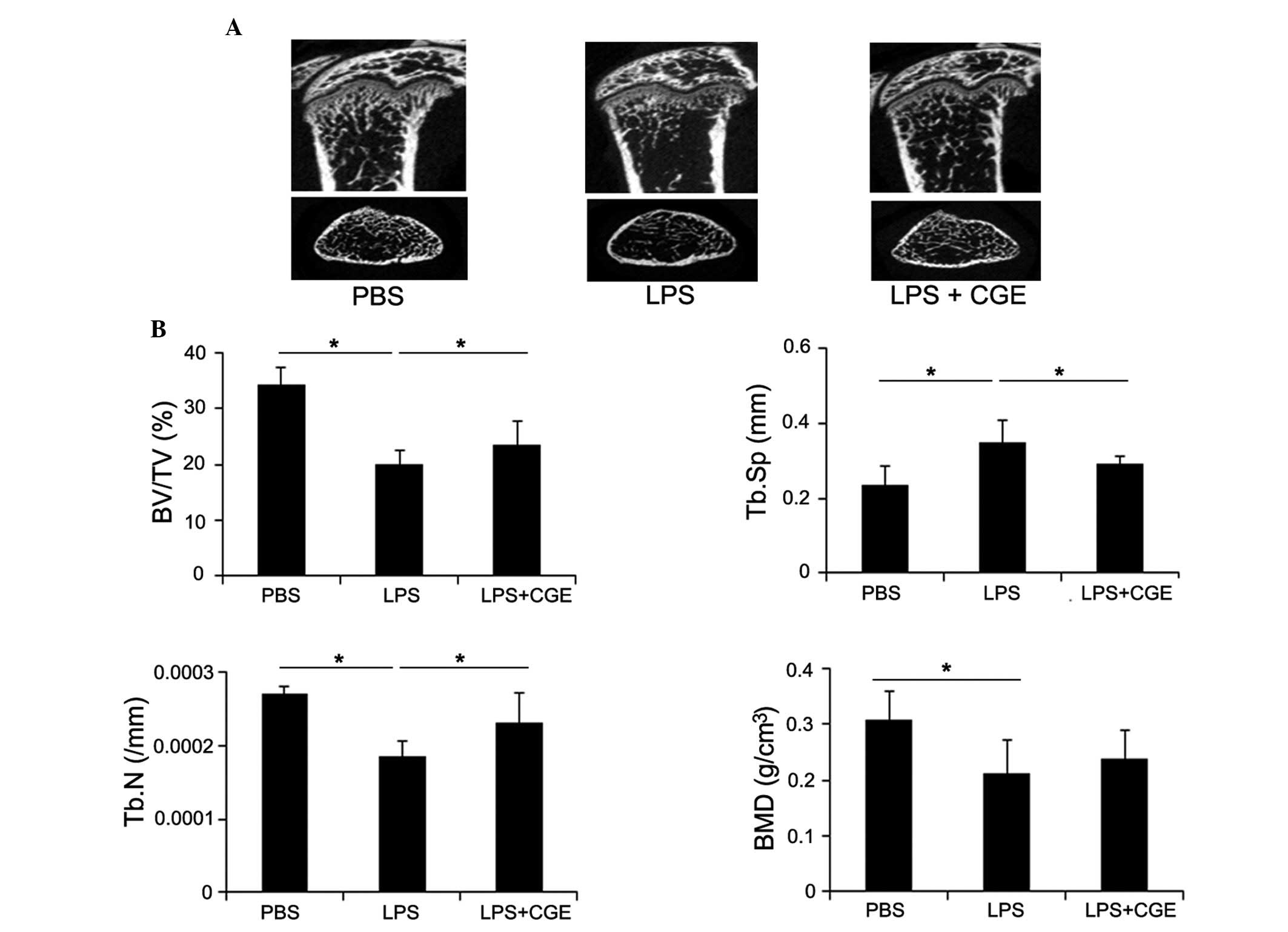
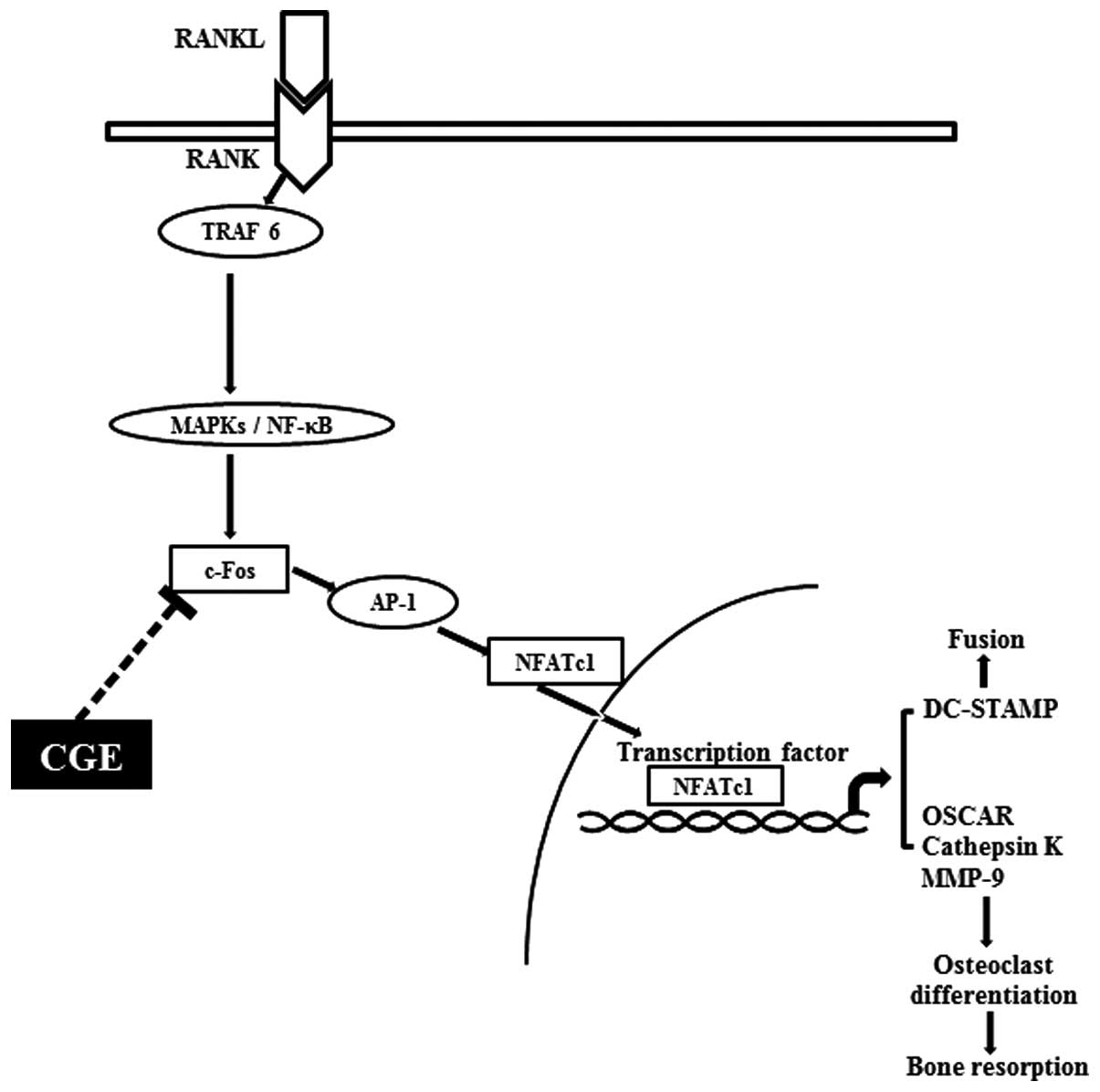
|
1
|
Kwak HB, Lee BK, Oh J, Yeon JT, Choi SW,
Cho HJ, Lee MS, Kim JJ, Bae JM, Kim SH and Kim HS: Inhibition of
osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by rotenone, through
down-regulation of RANKL-induced c-Fos and NFATc1 expression. Bone.
46:724–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kim HJ, Yoon KA, Lee MK, Kim SH, Lee IK
and Kim SY: A novel small molecule, NecroX-7, inhibits osteoclast
differentiation by suppressing NF-κB activity and c-Fos expression.
Life Sci. 91:928–934. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choi J, Choi SY, Lee SY, Lee JY, Kim HS,
Lee SY and Lee NK: Caffeine enhances osteoclast differentiation and
maturation through p38 MAP kinase/Mitf and DC-STAMP/CtsK and TRAP
pathway. Cell Signal. 25:1222–1227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ghayor C, Correro RM, Lange K,
Karfeld-Sulzwe LS, Grätz KW and Weber FE: Inhibition of osteoclast
differentiation and bone resorption by N-Methylpyrrolidone. J Biol
Chem. 286:24458–24466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim HH, Kim JH, Kwak HB, Huang H, Han SH,
Ha H, Lee SW, Woo ER and Lee ZH: Inhibition of osteoclast
differentiation and bone resorption by tanshinone IIA isolated from
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Biochem Pharmacol. 67:1647–1656. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim BG, Kwak HB, Choi EY, Kim HS, Kim MH,
Kim SH, Choi MK, Chun CH, Oh J and Kim JJ: Amorphigenin inhibits
osteoclast differentiation by suppressing c-Fos and nuclear factor
of activated T cells. Anat Cell Biol. 43:310–316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fumimoto R, Sakai E, Yamaguchi Y, Sakamoto
H, Fukuma Y, Nishishita K, Okamoto K and Tsukuba T: The coffee
diterpene kahweol prevents osteoclastogenesis via impairment of
NFATc1 Expression and blocking of Erk phosphorylation. J Pharmacol
Sci. 118:479–486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park YR, Eun JS, Choi HJ, Nepal M, Kim DK,
Seo SY, Li R, Moon WS, Cho NP, Cho SD, et al: Hexane-Soluble
fraction of the common fig, Ficus carica, inhibits osteoclast
differentiation in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages and RAW
264.7 Cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 13:417–424. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wada T, Nakashima T, Hiroshi N and
Penninger JM: RANKL-RANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis and bone
disease. Trends Mol Med. 12:17–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mochizuki A, Takami M, Miyamoto Y,
Nakamaki T, Tomoyasu S, Kadono Y, Tanaka S, Inoue T and Kamijo R:
Cell adhesion signaling regulates RANK expression in osteoclast
precursors. PLoS One. 7:e487952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Q, Wang X, Liu Y, He A and Jia R:
NFATc1: Functions in osteoclasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
42:576–579. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Badaboina S, Bai HW, Park CH, Jang DM,
Choi BY and Chung BY: Molecular mechanism of apoptosis induction in
skin cancer cells by the centipedegrass extract. BMC complement
Altern Med. 13:3502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barampuram S, Chung BY, Lee SS, An BC, Lee
EM and Cho JY: Development of an embryogenic callus induction
method for centipede grass (Eremochloa ophiuroides Munro) and
subsequent plant regeneration. In Vitro Cell Dev Bio Plant.
45:155–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wiseman BR, Gueldner RC, Lynch RE and
Severson RF: Biochemical activity of centipedegrass against fall
armyworm larvae. J Chem Ecol. 16:2677–2690. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park HJ, Chung BY, Lee MK, Song Y, Lee SS,
Chu GM, Kang SN, Song YM, Kim GS and Cho JH: Centipede grass exerts
anti-adipogenic activity through inhibition of C/EBPβ, C/EBPα, and
PPARγ expression and the AKT signaling pathway in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:2302012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Choi HJ, Park YR, Nepal M, Choi BY, Cho
NP, Choi SH, Heo SR, Kim HS, Yang MS and Soh Y: Inhibition of
osteoclastogenic differentiation by Ikarisoside A in RAW 264.7
cells via JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol.
636:28–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC, USA;
2011
|
|
18
|
Han KY, Yang D, Chang EJ, Lee Y, Huang H,
Sung SH, Lee ZH, Kim YC and Kim HH: Inhibition of osteoclast
differentiation and bone resorption by sauchinone. Biochem
Pharmacol. 74:911–923. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nepal M, Choi HJ, Choi BY, Yang MS, Chae
JI, Li L and Soh Y: Hispidulin attenuates bone resorption and
osteoclastogenesis via the RANKL-induced NF-κB and NFATc1 pathways.
Eur J Pharmacol. 715:96–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kwak HB, Yang D, Ha H, Lee JH, Kim HN, Woo
ER, Lee S, Kim HH and Lee ZH: Tanshinone IIA inhibits osteoclast
differentiation through down-regulation of c-Fos and NFATc1. Exp
Mol Med. 38:256–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Sawatani Y, Iwamoto K,
Hosogane N, Fujita N, Morita K, Ninomiya K, Suzuki T, Miyamoto K,
et al: DC-STAMP is essential for cell-cell fusion in osteoclasts
and foreign body giant cells. J Exp Med. 202:345–351. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Toyama Y and Suda T:
Role of DC-STAMP in cellular fusion of osteoclasts and macrophage
giant cells. J Bone Miner Metab. 24:355–358. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|