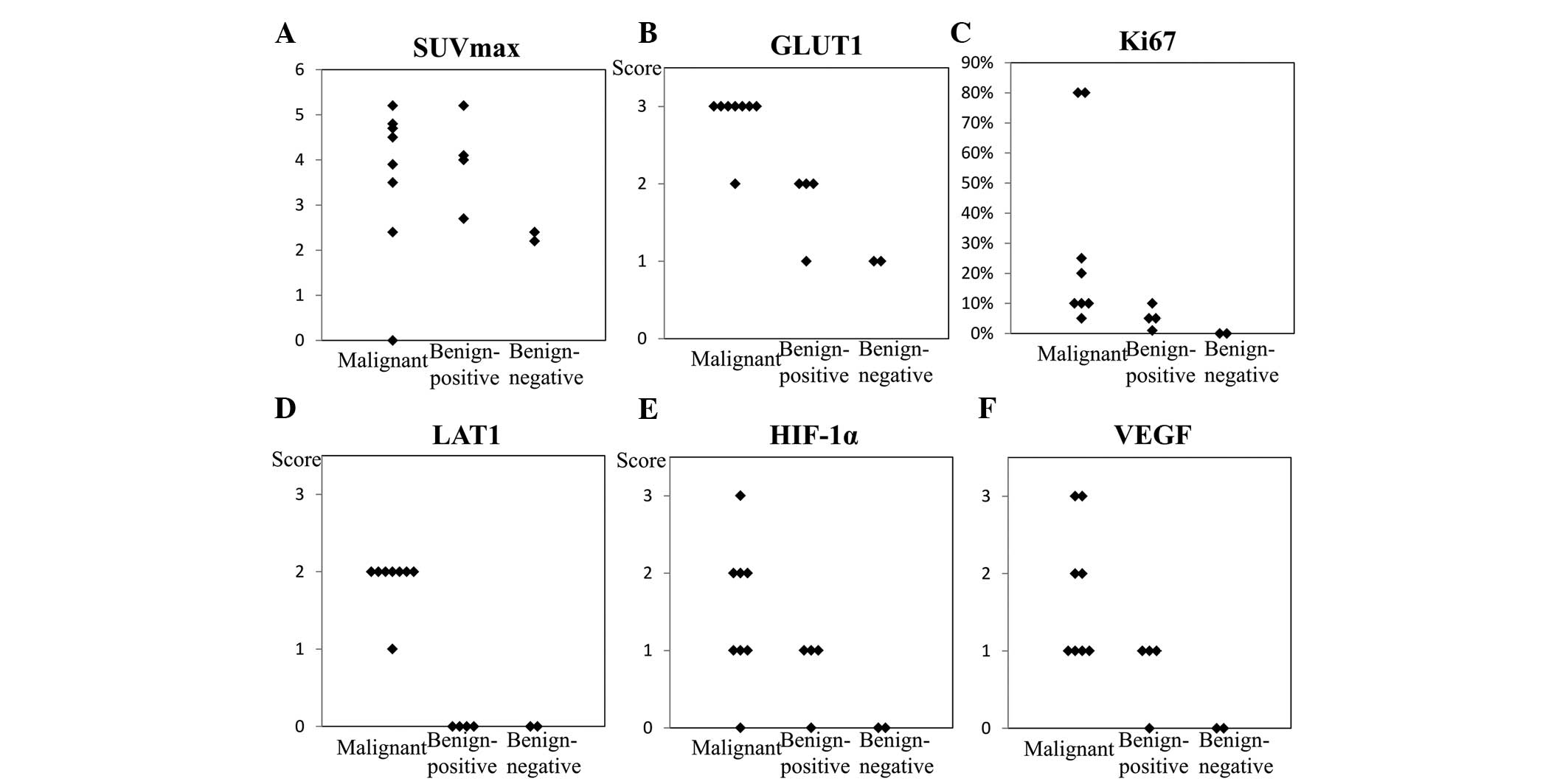
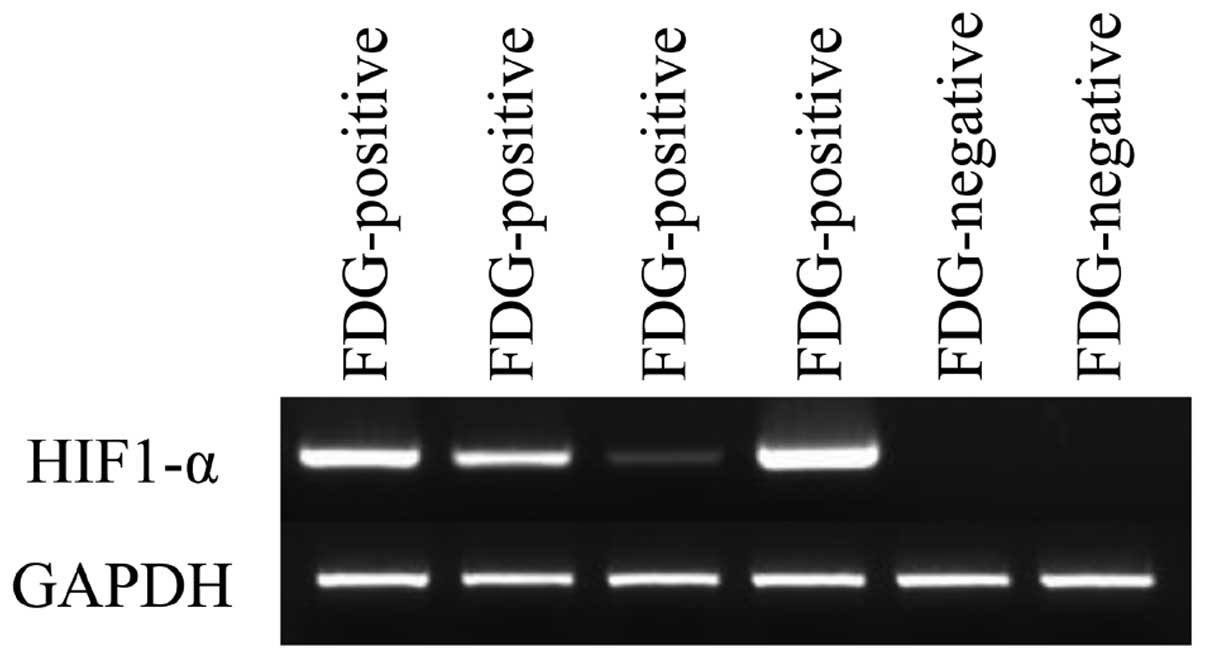
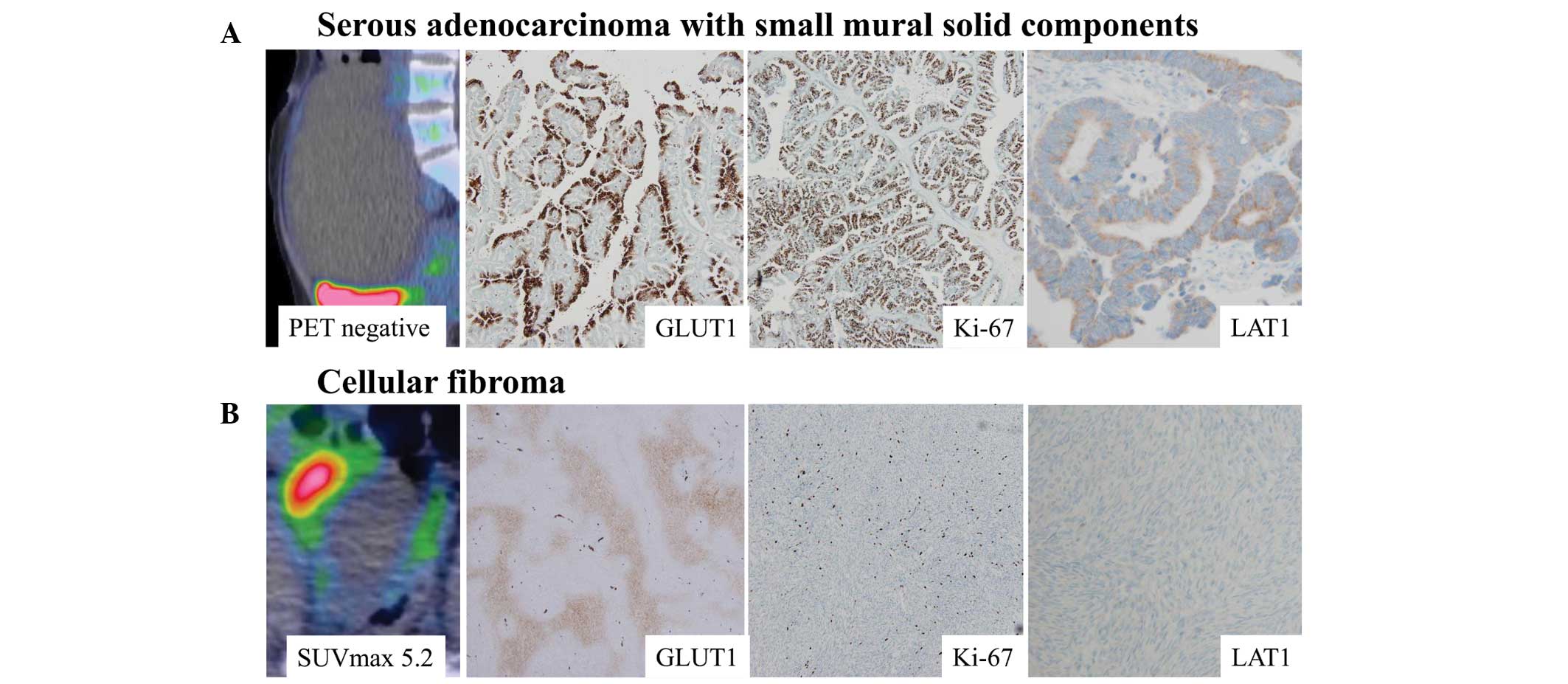
|
1
|
Salemis NS, Panagiotopoulos N, Papamichail
V, Kiriakopoulos K and Niakas E: Bilateral ovarian fibrothecoma. An
uncommon cause of a large pelvic mass. Int J Surg Case Rep.
2:29–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fenchel S, Kotzerke J, Stöhr I, Grab D,
Nüssle K, Rieber A, Kreienberg R, Brambs HJ and Reske SN:
Preoperative assessment of asymptomatic adnexal tumors by positron
emission tomography and F 18 fluorodeoxyglucose. Nuklearmedizin.
38:101–107. 1999.In German.
|
|
3
|
Fenchel S, Grab D, Nuessle K, Kotzerke J,
Rieber A, Kreienberg R, Brambs HJ and Reske SN: Asymptomatic
adnexal masses: Correlation of FDG PET and histopathologic
findings. Radiology. 223:780–788. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schwartz RK, Levine D, Hatabu H and
Edelman RR: Ovarian fibroma: Findings by contrast-enhanced MRI.
Abdom Imaging. 22:535–537. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adad SJ, Laterza VL, Dos Santos CD, Ladeia
AA, Saldanha JC, da Silva CS, E Souza LR and Murta EF: Cellular
fibroma of the ovary with multiloculated macroscopic
characteristics: Case report. Case Rep Med.
2012(283948)2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW,
Laughner E, Wenger RH, Gassmann M, Gearhart JD, Lawler AM, Yu AY
and Semenza GL: Cellular and developmental control of O2
homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev.
12:149–162. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang GL and Semenza GL: Purification and
characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem.
270:1230–1237. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA and Semenza GL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS
heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 92:5510–5514. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wenger RH and Gassmann M: Oxygen(es) and
the hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Biol Chem. 378:609–616.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Semenza GL and Wang GL: A nuclear factor
induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human
erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional
activation. Mol Cell Biol. 12:5447–5454. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Levy AP, Levy NS, Wegner S and Goldberg
MA: Transcriptional regulation of the rat vascular endothelial
growth factor gene by hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 270:13333–13340. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Cox SR, Morita T and Kourembanas S:
Hypoxia regulates vascular endothelial growth factor gene
expression in endothelial cells. Identification of a 5′ enhancer.
Circ Res. 77:638–643. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ebert BL, Firth JD and Ratcliffe PJ:
Hypoxia and mitochondrial inhibitors regulate expression of glucose
transporter-1 via distinct Cis-acting sequences. J Biol Chem.
270:29083–29089. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Firth JD, Ebert BL, Pugh CW and Ratcliffe
PJ: Oxygen-regulated control elements in the phosphoglycerate
kinase 1 and lactate dehydrogenase A genes: Similarities with the
erythropoietin 3′ enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:6496–6500.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang HM and Wang GL:
Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by
hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 269:23757–23763.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Firth JD, Ebert BL and Ratcliffe PJ:
Hypoxic regulation of lactate dehydrogenase A. Interaction between
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and cAMP response elements. J Biol Chem.
270:21021–21027. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marti HJ, Bernaudin M, Bellail A, Schoch
H, Euler M, Petit E and Risau W: Hypoxia-induced vascular
endothelial growth factor expression precedes neovascularization
after cerebral ischemia. Am J Pathol. 156:965–976. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin KL, Mao XO, Nagayama T, Goldsmith PC
and Greenberg DA: Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor
and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by global ischemia in rat
brain. Neuroscience. 99:577–585. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH,
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ and Harris AL: The expression and
distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and
HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers and tumor-associated
macrophages. Am J Pathol. 157:411–421. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: Upstream and downstream
of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 20:51–56. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
McCluggage WG, Staats PN, Kiyokawa T and
Young RH: Sex cord-stromal tumours - pure stromal tumours. WHO
Classification of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs. 4th
edition. Kurman RJ, Carcangiu MS, Herrington CS and Young RH:
International Agency for Research of Cancer; Lyon: 2014
|
|
22
|
Kanai Y, Segawa H, Miyamoto Ki, Uchino H,
Takeda E and Endou H: Expression cloning and characterization of a
transporter for large neutral amino acids activated by the heavy
chain of 4F2 antigen (CD98). J Biol Chem. 273:23629–23632. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee MS, Cho HC, Lee YH and Hong SR:
Ovarian sclerosing stromal tumors: Gray scale and color Doppler
sonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med. 20:413–417. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|