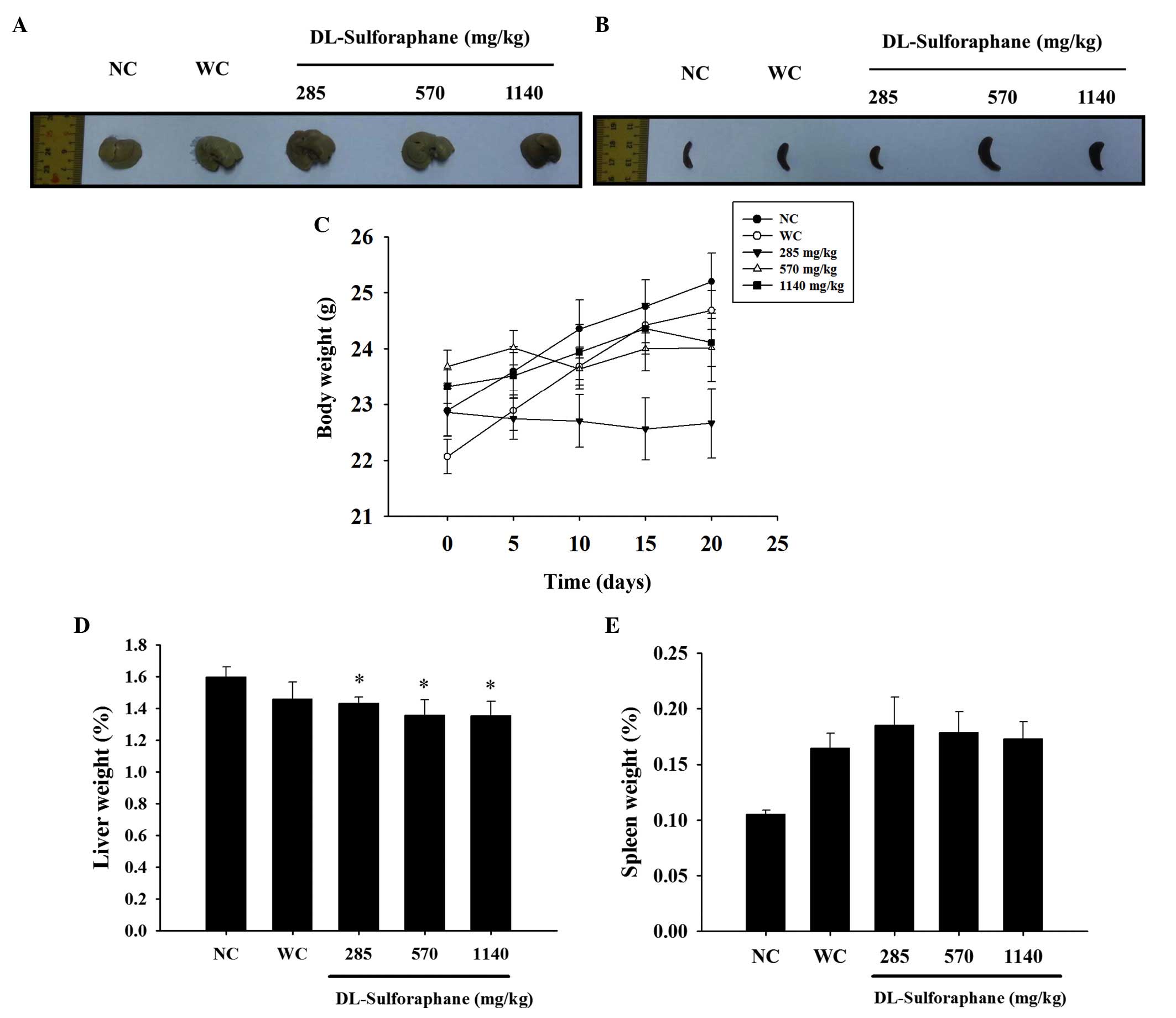
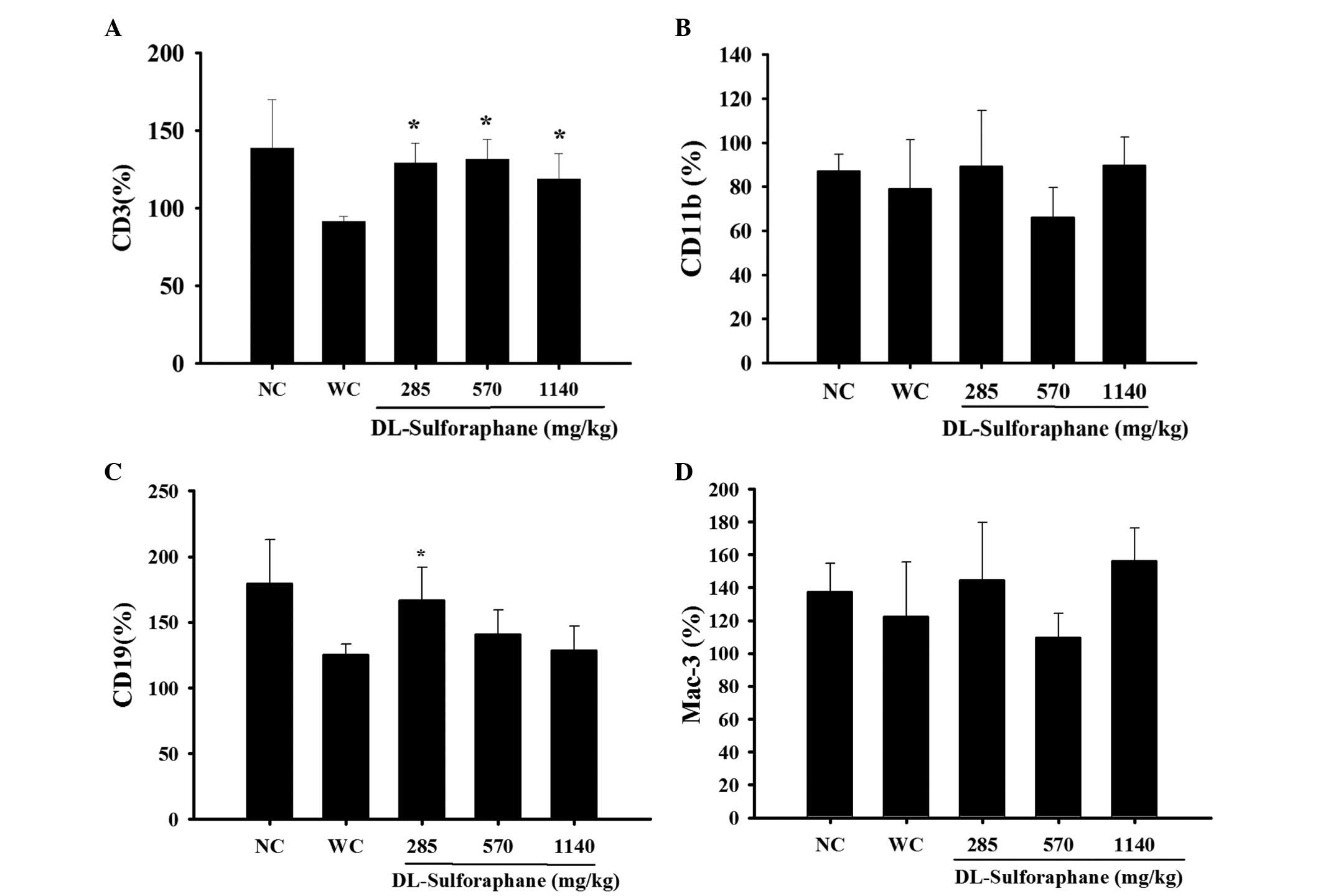
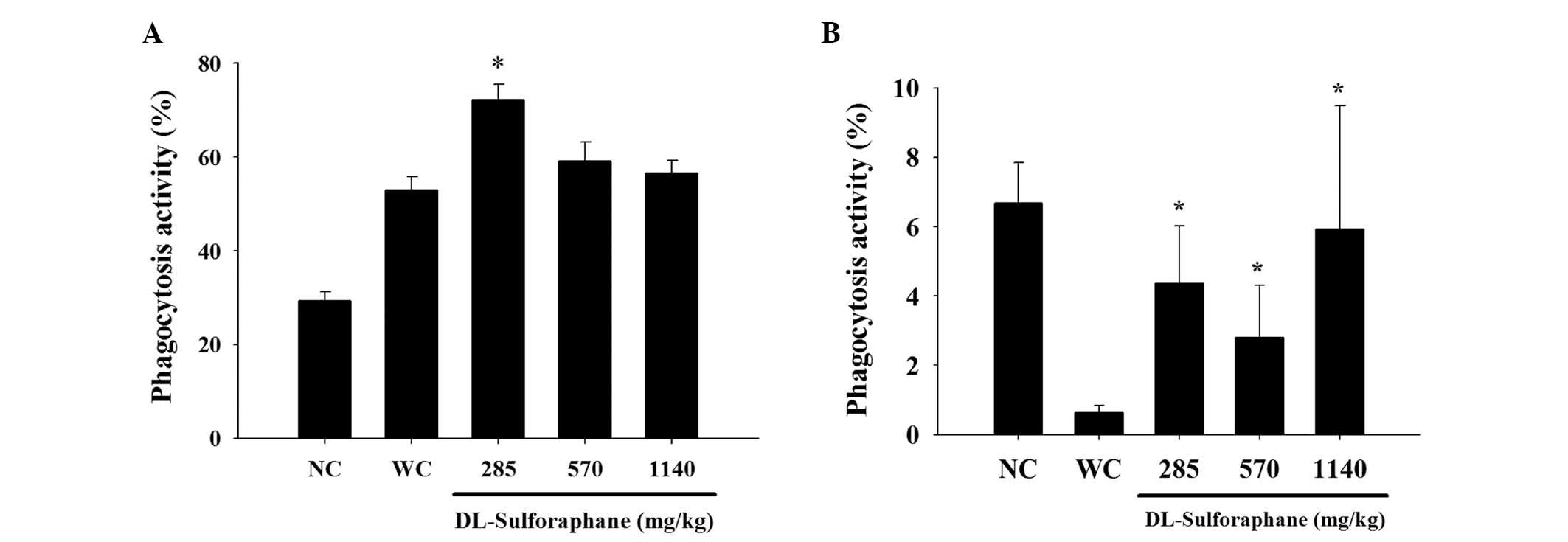
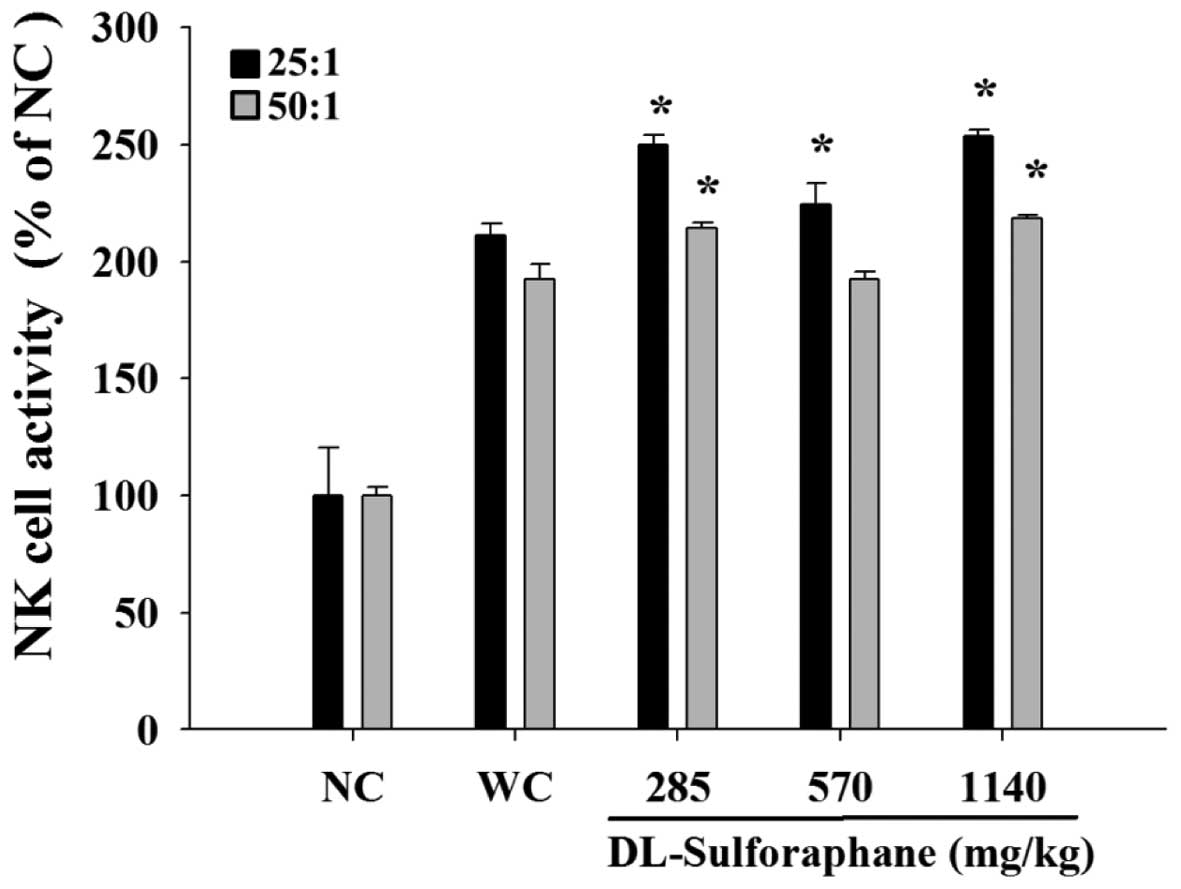
|
1
|
Alabsi AM, Ali R, Ideris A, Omar AR, Bejo
MH, Yusoff K and Ali AM: Anti-leukemic activity of Newcastle
disease virus strains AF2240 and V4-UPM in murine myelomonocytic
leukemia in vivo. Leuk Res. 36:634–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dameshek W: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia -
an accumulative disease of immunolgically incompetent lymphocytes.
Blood. 29(Suppl): 566–584. 1967.
|
|
3
|
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning
RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM,
Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A, et al: The 2008 revision of the
World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms
and acute leukemia: Rationale and important changes. Blood.
114:937–951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marshall GM, Dalla Pozza L, Sutton R, Ng
A, de Groot-Kruseman HA, van der Velden VH, Venn NC, van den Berg
H, de Bont ES, Maarten Egeler R, et al: High-risk childhood acute
lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission treated with novel
intensive chemotherapy and allogeneic transplantation. Leukemia.
27:1497–1503. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conaway CC, Wang CX, Pittman B, Yang YM,
Schwartz JE, Tian D, McIntee EJ, Hecht SS and Chung FL: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate and sulforaphane and their N-acetylcysteine
conjugates inhibit malignant progression of lung adenomas induced
by tobacco carcinogens in A/J mice. Cancer Res. 65:8548–8557. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fimognari C, Nüsse M, Berti F, Iori R,
Cantelli-Forti G and Hrelia P: Isothiocyanates as novel cytotoxic
and cytostatic agents: Molecular pathway on human transformed and
non-transformed cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:1133–1138. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trachootham D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Demizu Y,
Chen Z, Pelicano H, Chiao PJ, Achanta G, Arlinghaus RB, Liu J, et
al: Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells through a
ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate. Cancer
Cell. 10:241–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu C, Shen G, Yuan X, Kim JH,
Gopalkrishnan A, Keum YS, Nair S and Kong AN: ERK and JNK signaling
pathways are involved in the regulation of activator protein 1 and
cell death elicited by three isothiocyanates in human prostate
cancer PC-3 cells. Carcinogenesis. 27:437–445. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fahey JW, Haristoy X, Dolan PM, Kensler
TW, Scholtus I, Stephenson KK, Talalay P and Lozniewski A:
Sulforaphane inhibits extracellular, intracellular, and
antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori and prevents
benzo[a]pyrene-induced stomach tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:7610–7615. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Kensler TW, Cho CG, Posner GH and
Talalay P: Anticarcinogenic activities of sulforaphane and
structurally related synthetic norbornyl isothiocyanates. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:3147–3150. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Keck AS and Finley JW: Cruciferous
vegetables: Cancer protective mechanisms of glucosinolate
hydrolysis products and selenium. Integr Cancer Ther. 3:5–12. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fimognari C, Lenzi M, Sciuscio D,
Cantelli-Forti G and Hrelia P: Cell-cycle specificity of
sulforaphane-mediated apoptosis in Jurkat T-leukemia cells. In
Vivo. 21:377–380. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi WY, Choi BT, Lee WH and Choi YH:
Sulforaphane generates reactive oxygen species leading to
mitochondrial perturbation for apoptosis in human leukemia U937
cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 62:637–644. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fimognari C, Lenzi M, Cantelli-Forti G and
Hrelia P: Induction of differentiation in human promyelocytic cells
by the isothiocyanate sulforaphane. In Vivo. 22:317–320.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moon DO, Kim MO, Kang SH, Choi YH and Kim
GY: Sulforaphane suppresses TNF-alpha-mediated activation of
NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis through activation of reactive
oxygen species-dependent caspase-3. Cancer Lett. 274:132–142. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Suppipat K, Park CS, Shen Y, Zhu X and
Lacorazza HD: Sulforaphane induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. PLoS One. 7:e512512012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fimognari C, Turrini E, Sestili P,
Calcabrini C, Carulli G, Fontanelli G, Rousseau M, Cantelli-Forti G
and Hrelia P: Antileukemic activity of sulforaphane in primary
blasts from patients affected by myelo- and lympho-proliferative
disorders and in hypoxic conditions. PLoS One. 9:e1019912014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu HF, Tung WL, Yang JS, Huang FM, Lee CS,
Huang YP, Liao WY, Chen YL and Chung JG: In vitro suppression of
growth of murine WEHI-3 leukemia cells and in vivo promotion of
phagocytosis in a leukemia mice model by indole-3-carbinol. J Agric
Food Chem. 60:7634–7643. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu FS, Yang JS, Yu CS, Chiang JH, Lu CC,
Chung HK, Yu CC, Wu CC, Ho HC and Chung JG: Safrole suppresses
murine myelomonocytic leukemia WEHI-3 cells in vivo, and stimulates
macrophage phagocytosis and natural killer cell cytotoxicity in
leukemic mice. Environ Toxicol. 28:601–608. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin JJ, Lu KW, Ma YS, Tang NY, Wu PP, Wu
CC, Lu HF, Lin JG and Chung JG: Alpha-phellandrene, a natural
active monoterpene, influences a murine WEHI-3 leukemia model in
vivo by enhancing macrophague phagocytosis and natural killer cell
activity. In Vivo. 28:583–588. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hattori Y, Satouchi M, Shimada T, Urata Y,
Yoneda T, Mori M, Nishimura T, Sunadome H, Kumagai T, Imamura F, et
al: A phase 2 study of bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin
and paclitaxel in patients with non-squamous non-small-cell lung
cancer harboring mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR) after failing first-line EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(HANSHIN Oncology Group 0109). Lung Cancer. 87:136–140. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee J, Kim J, Chang E, Choi W, Lee K, Yoon
H, Jung S, Park M, Yoon J and Kim S: A Phase II Trial of
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with Genexol (Paclitaxel) and Epirubicin
for Locally Advanced Breast Cancer. J Breast Cancer. 17:344–349.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Otake A, Yoshino K, Ueda Y, Sawada K,
Mabuchi S, Kimura T, Kobayashi E, Isobe A, Egawa-Takata T,
Matsuzaki S, et al: Usefulness of duloxetine for Paclitaxel-induced
peripheral neuropathy treatment in gynecological cancer patients.
Anticancer Res. 35:359–363. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmid D, Jarvis GE, Fay F, Small DM,
Greene MK, Majkut J, Spence S, McLaughlin KM, McCloskey KD,
Johnston PG, et al: Nanoencapsulation of ABT-737 and camptothecin
enhances their clinical potential through synergistic antitumor
effects and reduction of systemic toxicity. Cell Death Dis.
5:e14542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie S, Chen M, Yan B, He X, Chen X and Li
D: Identification of a role for the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
in innate immune cells. PLoS One. 9:e944962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guleria I and Pollard JW: The trophoblast
is a component of the innate immune system during pregnancy. Nat
Med. 6:589–593. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Z, Sinzger C, Reichel JJ, Just M and
Mertens T: Natural killer cells can inhibit the transmission of
human cytomegalovirus in cell culture using mechanisms from innate
and adaptive immune response. J Virol. 89:2906–2917. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|