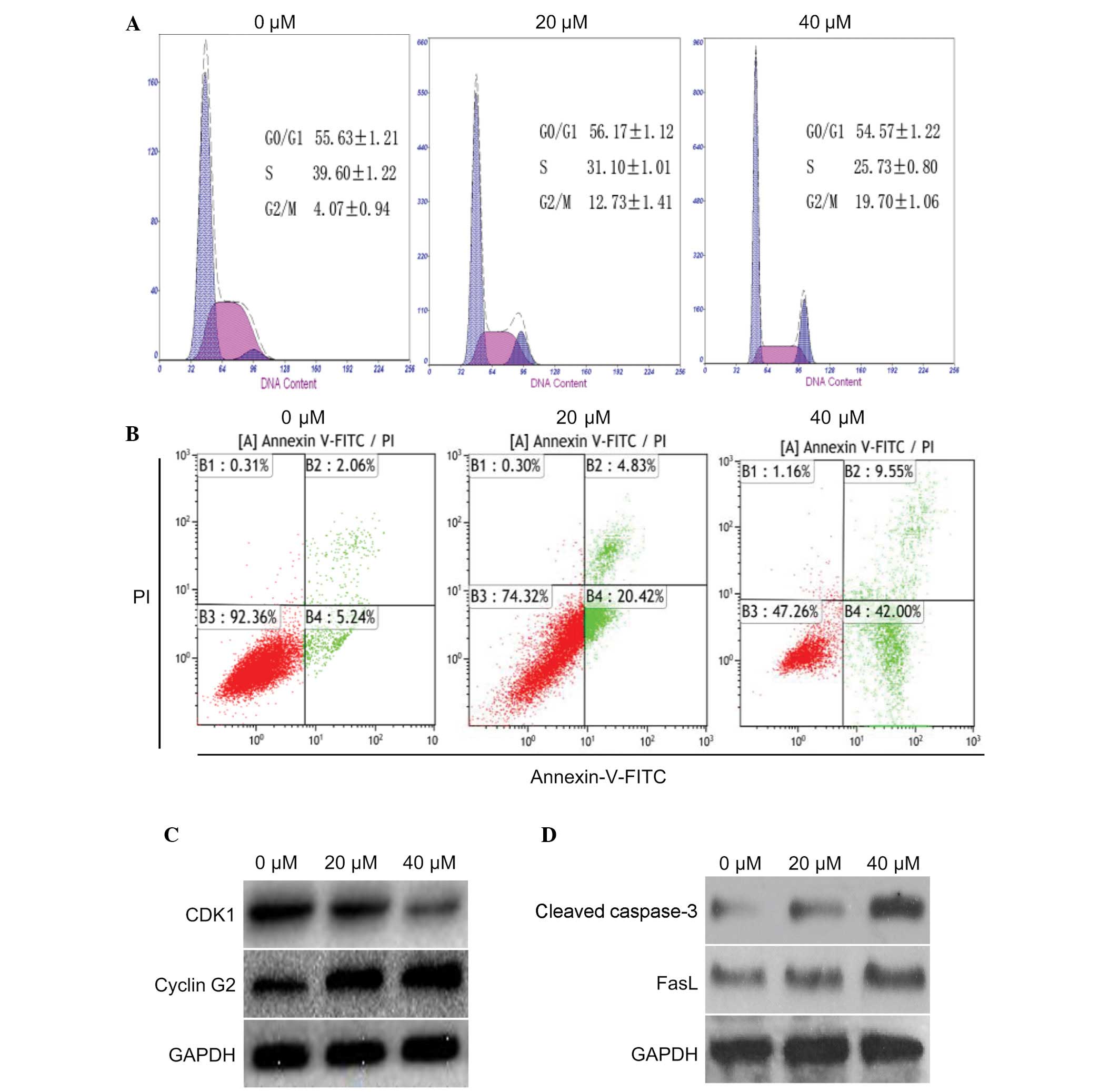
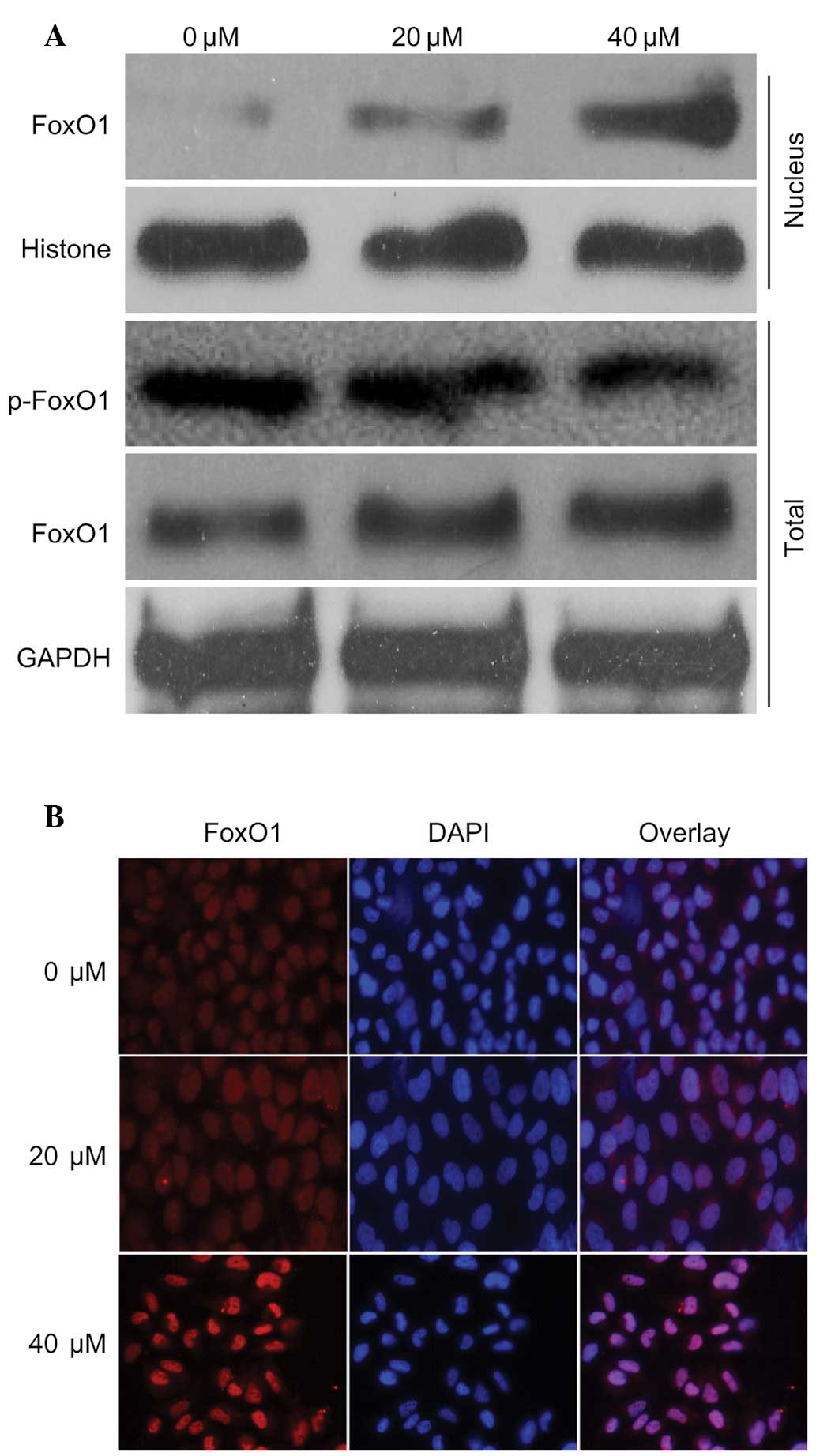
|
1
|
Grossman SA, Ye X, Piantadosi S, Desideri
S, Nabors LB, Rosenfeld M and Fisher J; NABTT CNS Consortium:
Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with
radiation and temozolomide in research studies in the United
States. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2443–2449. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Garodia P, Ichikawa H, Malani N, Sethi G
and Aggarwal BB: From ancient medicine to modern medicine:
Ayurvedic concepts of health and their role in inflammation and
cancer. J Soc Integr Oncol. 5:25–37. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cole GM, Teter B and Frautschy SA:
Neuroprotective effects of curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 595:197–212.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chuang SE, Kuo ML, Hsu CH, Chen CR, Lin
JK, Lai GM, Hsieh CY and Cheng AL: Curcumin-containing diet
inhibits diethylnitrosamine-induced murine hepatocarcinogenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 21:331–335. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lim GP, Chu T, Yang F, Beech W, Frautschy
SA and Cole GM: The curry spice curcumin reduces oxidative damage
and amyloid pathology in an Alzheimer transgenic mouse. J Neurosci.
21:8370–8377. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiyagarajan M and Sharma SS:
Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery
occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci.
74:969–985. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
LoTempio MM, Veena MS, Steele HL,
Ramamurthy B, Ramalingam TS, Cohen AN, Chakrabarti R, Srivatsan ES
and Wang MB: Curcumin suppresses growth of head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6994–7002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang D, Veena MS, Stevenson K, Tang C, Ho
B, Suh JD, Duarte VM, Faull KF, Mehta K, Srivatsan ES and Wang MB:
Liposome-encapsulated curcumin suppresses growth of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in xenografts through the
inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB by an AKT-independent pathway.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:6228–6236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin YG, Kunnumakkara AB, Nair A, Merritt
WM, Han LY, Armaiz-Pena GN, Kamat AA, Spannuth WA, Gershenson DM,
Lutgendorf SK, et al: Curcumin inhibits tumor growth and
angiogenesis in ovarian carcinoma by targeting the nuclear
factor-kappaB pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3423–3430. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhuang W, Long L, Zheng B, Ji W, Yang N,
Zhang Q and Liang Z: Curcumin promotes differentiation of
glioma-initiating cells by inducing autophagy. Cancer Sci.
103:684–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kumar A, Ahuja A, Ali J and Baboota S:
Curcumin-loaded lipid nanocarrier for improving bioavailability,
stability and cytotoxicity against malignant glioma cells. Drug
Deliv. 23:214–229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Greer EL and Brunet A: FOXO transcription
factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression.
Oncogene. 24:7410–7425. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu MC, Lee DF, Xia W, Golfman LS, Ou-Yang
F, Yang JY, Zou Y, Bao S, Hanada N, Saso H, et al: IkappaB kinase
promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell.
117:225–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Taylor S, Lam M, Pararasa C, Brown JE,
Carmichael AR and Griffiths HR: Evaluating the evidence for
targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Cell
Int. 15:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang H, Zhao R, Yang HY and Lee MH:
Constitutively active FOXO4 inhibits Akt activity, regulates p27
Kip1 stability, and suppresses HER2-mediated tumorigenicity.
Oncogene. 24:1924–1935. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ramaswamy S, Nakamura N, Sansal I,
Bergeron L and Sellers WR: A novel mechanism of gene regulation and
tumor suppression by the transcription factor FKHR. Cancer Cell.
2:81–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prakobwong S, Gupta SC, Kim JH, Sung B,
Pinlaor P, Hiraku Y, Wongkham S, Sripa B, Pinlaor S and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in
human biliary cancer cells through modulation of multiple cell
signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis. 32:1372–1380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moragoda L, Jaszewski R and Majumdar AP:
Curcumin induced modulation of cell cycle and apoptosis in gastric
and colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 21:873–878. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shao J, Zheng D, Jiang Z, Xu H, Hu Y, Li X
and Lu X: Curcumin delivery by methoxy polyethylene glycol-poly
(caprolactone) nanoparticles inhibits the growth of C6 glioma
cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:267–274. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Vallianou NG, Evangelopoulos A, Schizas N
and Kazazis C: Potential anticancer properties and mechanisms of
action of curcumin. Anticancer Res. 35:645–651. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weir NM, Selvendiran K, Kutala VK, Tong L,
Vishwanath S, Rajaram M, Tridandapani S, Anant S and Kuppusamy P:
Curcumin induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant
human ovarian cancer cells by modulating Akt and p38 MAPK. Cancer
Biol Ther. 6:178–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luthra PM, Kumar R and Prakash A:
Demethoxycurcumin induces Bcl-2 mediated G2/M arrest and apoptosis
in human glioma U87 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 384:420–425.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo H, Xu YM, Ye ZQ, Yu JH and Hu XY:
Curcumin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of prostate cancer
cells by regulating the expression of IkappaBalpha, c-Jun and
androgen receptor. Pharmazie. 68:431–434. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang H and Tindall DJ: Dynamic FoxO
transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 120:2479–2487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo
P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J and Greenberg ME: Akt
promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead
transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Biggs WH III, Cavenee WK and Arden KC:
Identification and characterization of members of the FKHR (FOX O)
subclass of winged-helix transcription factors in the mouse. Mamm
Genome. 12:416–425. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Furuyama T, Nakazawa T, Nakano I and Mori
N: Identification of the differential distribution patterns of
mRNAs and consensus binding sequences for mouse DAF-16 homologues.
Biochem J. 349:629–634. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin K, Dorman JB, Rodan A and Kenyon C:
daf-16: An HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double
the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 278:1319–1322.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ogg S, Paradis S, Gottlieb S, Patterson
GI, Lee L, Tissenbaum HA and Ruvkun G: The fork head transcription
factor DAF-16 transduces insulin-like metabolic and longevity
signals in C. elegans. Nature. 389:994–999. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang H, Regan KM, Lou Z, Chen J and
Tindall DJ: CDK2-dependent phosphorylation of FOXO1 as an apoptotic
response to DNA damage. Science. 314:294–297. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Modur V, Nagarajan R, Evers BM and
Milbrandt J: FOXO proteins regulate tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis inducing ligand expression. Implications for PTEN
mutation in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 277:47928–47937. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dijkers PF, Medema RH, Lammers JW,
Koenderman L and Coffer PJ: Expression of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2
family member Bim is regulated by the forkhead transcription factor
FKHR-L1. Curr Biol. 10:1201–1204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJ, Lens SM,
Coffer PJ, Burgering BM and Medema RH: The forkhead transcription
factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim in response
to IL-2. J Immunol. 168:5024–5031. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|