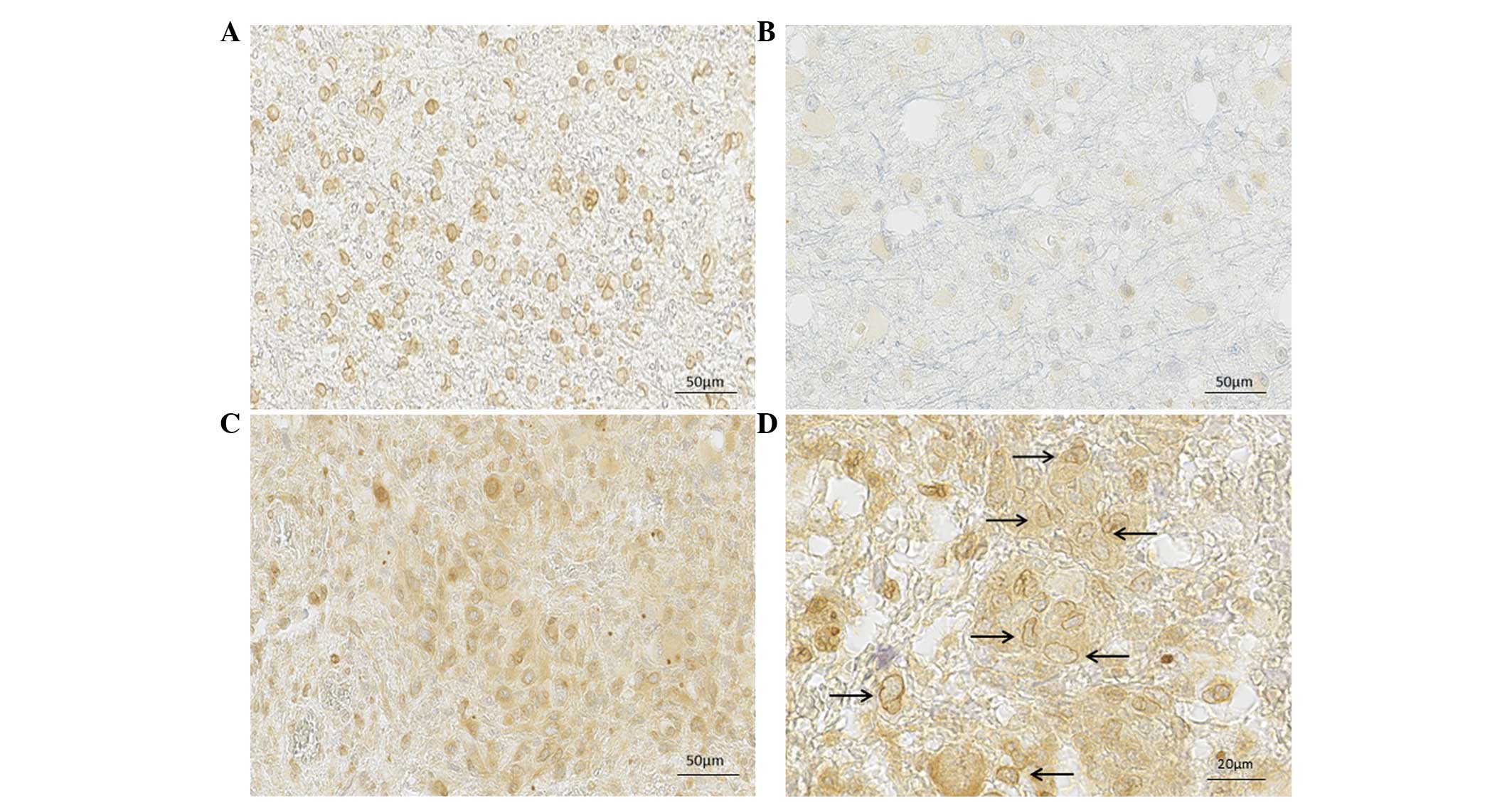
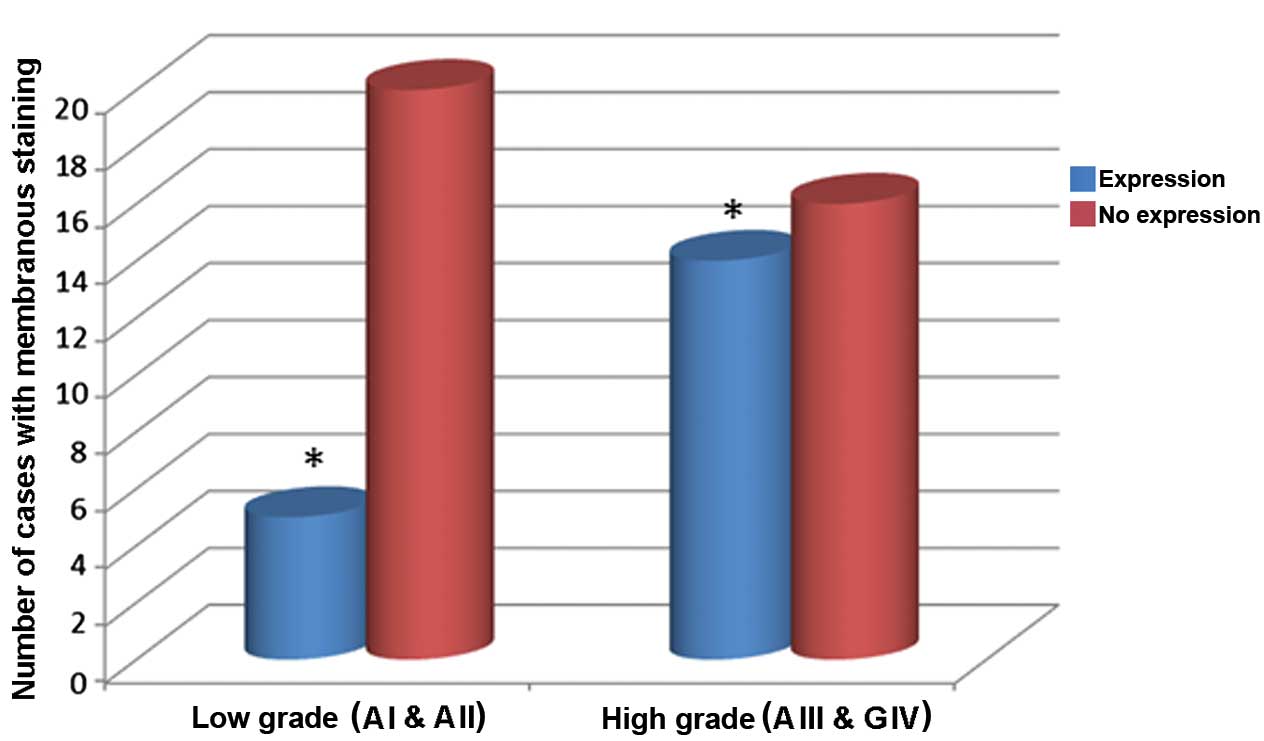
|
1
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rampazzo E, Persano L, Pistollato F, Moro
E, Frasson C, Porazzi P, Della Puppa A, Bresolin S, Battilana G,
Indraccolo S, et al: Wnt activation promotes neuronal
differentiation of glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5002013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rheinbay E, Suvè ML, Gillespie SM,
Wakimoto H, Patel AP, Shahid M, Oksuz O, Rabkin D, Martuza RL,
Rivera MN, et al: An aberrant transcription factor network
essential for Wnt signaling and stem cell maintenance in
glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 3:1567–1579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Delic S, Lottmann N, Stelzl A, Liesenberg
F, Wolter M, Götze S, Zapatka M, Shiio Y, Sabel MC, Felsberg J, et
al: MiR-328 promotes glioma cell invasion via SFRP1-dependent
Wnt-signaling activation. Neuro Oncol. 16:179–190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Nikuševa-Martić T, Beroš V, Pećina-Šlaus
N, Pećina HI and Bulić-Jakuš F: Genetic changes of CDH1, APC, and
CTNNB1 found in human brain tumors. Pathol Res Pract. 203:779–787.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pećina-Šlaus N, Martić TN, Kokotović T,
Kusec V, Tomas D and Hrasćan R: AXIN-1 protein expression and
localization in glioblastoma. Coll Antropol. 35(Suppl 1): 101–106.
2011.
|
|
7
|
Pećina-Šlaus N, Kafka A, Tomas D, Marković
L, Okštajner PK, Sukser V and Krušlin B: Wnt signaling
transcription factors TCF-1 and LEF-1 are upregulated in malignant
astrocytic brain tumors. Histol Histopathol. 29:1557–1564.
2014.
|
|
8
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling in cancer. Genes
Dev. 14:1837–1851. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fagotto F: Looking beyond the Wnt pathway
for the deep nature of β-catenin. EMBO Rep. 14:422–433. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kafka A, Bašić-Kinda S and Pećina-Šlaus N:
The cellular story of dishevelleds. Croat Med J. 55:459–467. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoang B, Moos M Jr, Vukicevic S and Luyten
FP: Primary structure and tissue distribution of FRZB, a novel
protein related to Drosophila frizzled, suggest a role in skeletal
morphogenesis. J Biol Chem. 271:26131–26137. 1997.
|
|
13
|
Shi Y, He B, You L and Jablons DM: Roles
of secreted frizzled-related proteins in cancer. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 28:1499–1504. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bovolenta P, Esteve P, Ruiz JM, Cisneros E
and Lopez-Rios J: Beyond Wnt inhibition: New functions of secreted
Frizzled-related proteins in development and disease. J Cell Sci.
121:737–746. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jones SE and Jomary C: Secreted
Frizzled-related proteins: Searching for relationships and
patterns. Bioessays. 24:811–820. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kawano Y and Kypta R: Secreted antagonists
of the Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Sci. 116:2627–2634. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Ueno K, Majid S, Saini
S and Dahiya R: Role of secreted frizzled-related protein 3 in
human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:1896–1905. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Surana R, Sikka S, Cai W, Shin EM, Warrier
SR, Tan HJ, Arfuso F, Fox SA, Dharmarajan AM and Kumar AP: Secreted
frizzled related proteins: Implications in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1845:53–65. 2014.
|
|
19
|
Mii Y and Taira M: Secreted Wnt
'inhibitors' are not just inhibitors: Regulation of extracellular
Wnt by secreted Frizzled-related proteins. Dev Growth Differ.
53:911–923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roth W, Wild-Bode C, Platten M, Grimmel C,
Melkonyan HS, Dichgans J and Weller M: Secreted Frizzled-related
proteins inhibit motility and promote growth of human malignant
glioma cells. Oncogene. 19:4210–4220. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harrison-Uy SJ and Pleasure SJ: Wnt
signaling and forebrain development. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 4:a0080942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao X, Huang H, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z,
Ma Q and Qiu M: Dynamic expression of secreted Frizzled-related
protein 3 (sFRP3) in the developing mouse spinal cord and dorsal
root ganglia. Neuroscience. 248:594–601. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun J, Bonaguidi MA, Jun H, Guo JU, Sun
GJ, Will B, Yang Z, Jang MH, Song H, Ming GL and Christian KM: A
septo-remporal molecular gradient of sfrp3 in the dentate gyrus
differentially regulates quiescent adult hippocampal neural stem
activation. Mol Brain. 8:522015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Pazanin L: Histopatholoy of glial tumors.
Medicina fluminensis. 47:157–166. 2011.In Croatian.
|
|
25
|
Lee JL, Chang CJ, Wu SY, Sargan DR and Lin
CT: Secreted frizzled-related protein 2 (SFRP2) is highly expressed
in canine mammary gland tumors but not in normal mammary glands.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 84:139–149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abu-Jawdeh G, Comella N, Tomita Y, Brown
LF, Tognazzi K, Sokol SY and Kocher O: Differential expression of
frpHE: A novel human stromal protein of the secreted frizzled gene
family, during the endometrial cycle and malignancy. Lab Investig.
79:439–447. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Drake J, Shearwood AM, White J, Friis R,
Zeps N, Charles A and Dharmarajan A: Expression of secreted
frizzled-related protein 4 (SFRP4) in primary serous ovarian
tumours. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 30:133–141. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang D, Yu B, Deng Y, Sheng W, Peng Z,
Qin W and Du X: SFRP4 was overexpressed in colorectal carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:395–401. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Paw I, Carpenter RC, Watabe K, Debinski W
and Lo HW: Mechanisms regulating glioma invasion. Cancer Lett.
362:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang H, Xu T, Jiang Y, Xu H, Yan Y, Fu D
and Chen J: The challenges and the promise of molecular targeted
therapy in malignant gliomas. Neoplasia. 17:239–255. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Uren A, Reichsman F, Anest V, Taylor WG,
Muraiso K, Bottaro DP, Cumberledge S and Rubin JS: Secreted
frizzled-related protein-1 binds directly to Wingless and is a
biphasic modulator of Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem. 275:4374–4382.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xaviera CP, Melikovaa M, Chumana Y, Üren
A, Baljinnyama B and Rubina JS: Secreted Frizzled-related protein
potentiation versus inhibition of Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling. Cell
Signal. 26:94–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lin K, Wang S, Julius MA, Kitajewski J,
Moos M Jr and Luyten FP: The cysteine-rich frizzled domain of
Frzb-1 is required and sufficient for modulation of Wnt signaling.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:11196–11200. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bafico A, Gazit A, Pramila T, Finch PW,
Yaniv A and Aaronson SA: Interaction of frizzled related protein
(FRP) with Wnt ligands and the frizzled receptor suggests
alternative mechanisms for FRP inhibition of Wnt signaling. J Biol
Chem. 274:16180–16187. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nikuševa Martić T, Pećina-Šlaus N, Kušec
V, Kokotović T, Mušinović H, Tomas D and Zeljko M: Changes of
AXIN-1 and beta-catenin in neuroepithelial brain tumors. Pathol
Oncol Res. 16:75–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT,
Colman H, Huang H, Xue J, Liu M, Wang Y, et al: FoxM1 promotes
β-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene
expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 20:427–442. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kahlert UD, Maciaczyk D, Doostkam S, Orr
BA, Simons B, Bogiel T, Reithmeier T, Prinz M, Schubert J,
Niedermann G, et al: Activation of canonical WNT/β-catenin
signaling enhances in vitro motility of glioblastoma cells by
activation of ZEB1 and other activators of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 325:42–53. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng YY, Yu J, Wong JP, Man EP, To KF,
Jin VX, Li J, Tao Q, Sung JJ, Chan JK and Leung WK: Frequent
epigenetic inactivation of secreted frizzled-related protein 2
(SFRP2) by promoter methylation in human gastric cancer. Br J
Cancer. 97:895–901. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schiefer L, Visweswaran M, Perumal V,
Arfuso F, Groth D, Newsholme P, Warrier S and Dharmarajan A:
Epigenetic regulation of the secreted frizzled-related protein
family in human glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Gene Ther.
21:297–303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan
AW, Weissman IL, Reya T, Yates JR III and Nusse R: Wnt proteins are
lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature.
423:448–452. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signaling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:834–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|