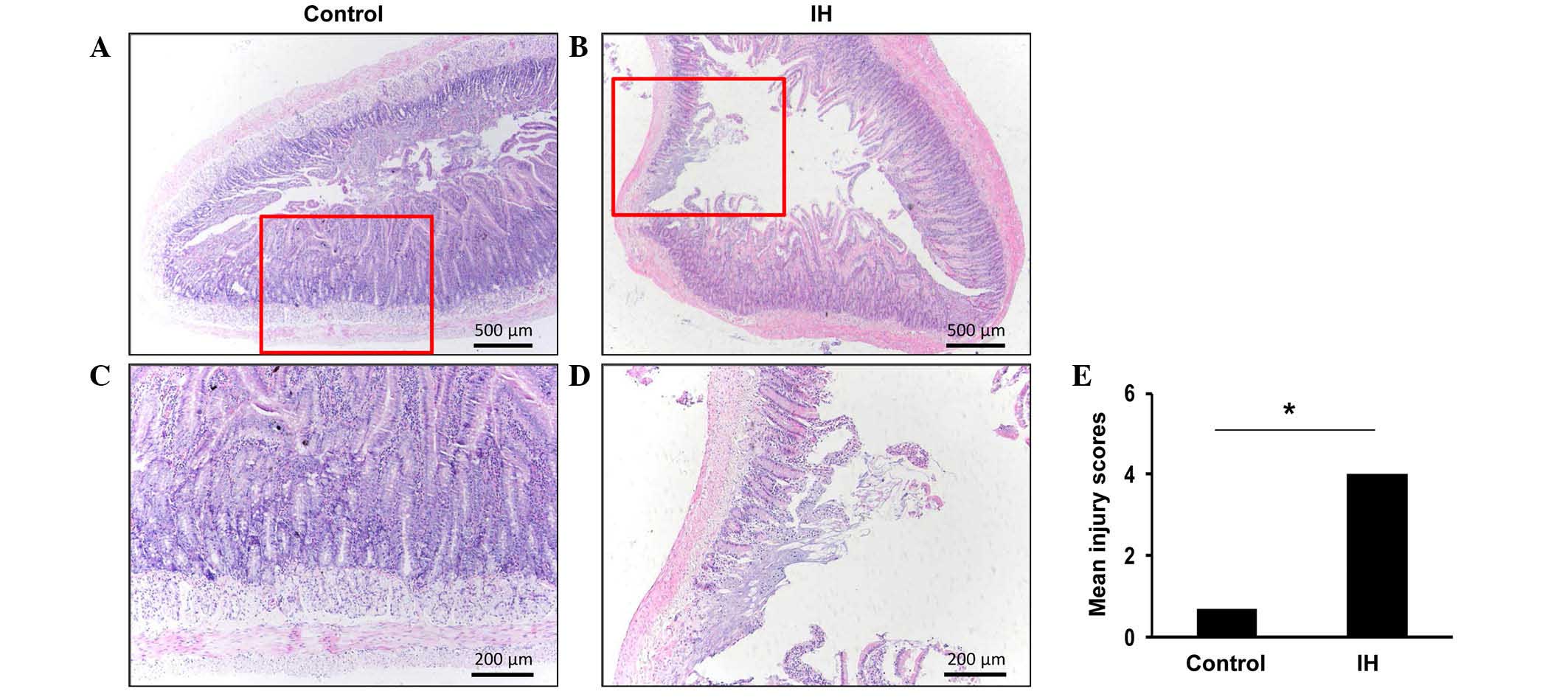
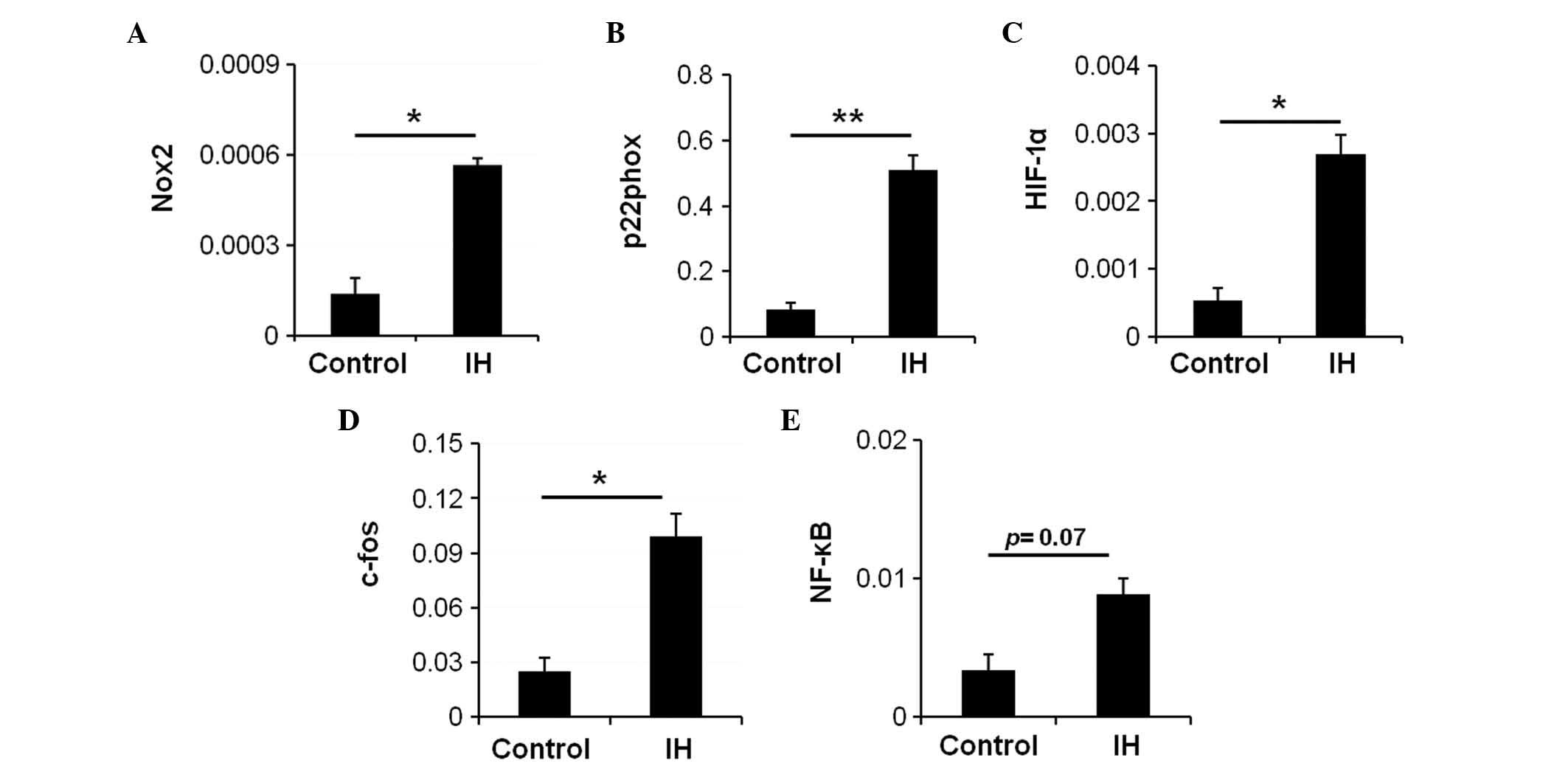
|
1
|
Lurie A: Obstructive sleep apnea in
adults: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and treatment options.
Adv Cardiol. 46:1–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dempsey JA, Veasey SC, Morgan BJ and
O'Donnell CP: Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol Rev.
90:47–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Punjabi NM: The epidemiology of adult
obstructive sleep apnea. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 5:136–143. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kendzerska T, Mollayeva T, Gershon AS,
Leung RS, Hawker G and Tomlinson G: Untreated obstructive sleep
apnea and the risk for serious long-term adverse outcomes: A
systematic review. Sleep Med Rev. 18:49–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shiao TH, Liu CJ, Luo JC, Su KC, Chen YM,
Chen TJ, Chou KT, Shiao GM and Lee YC: Sleep apnea and risk of
peptic ulcer bleeding: A nationwide population-based study. Am J
Med. 126:249–255.e1. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsukita S, Furuse M and Itoh M:
Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:285–293. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zahraoui A, Louvard D and Galli T: Tight
junction, a platform for trafficking and signaling protein
complexes. J Cell Biol. 151:F31–F36. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mitic LL, Van Itallie CM and Anderson JM:
Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions I.
Tight junction structure and function: Lessons from mutant animals
and proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
279:G250–G254. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lurie A: Inflammation, oxidative stress,
and procoagulant and thrombotic activity in adults with obstructive
sleep apnea. Adv Cardiol. 46:43–66. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Prabhakar NR: Oxygen sensing during
intermittent hypoxia: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 90:1986–1994. 2001.
|
|
11
|
Bonsignore MR and Eckel J: ERS Meeting
Report. Metabolic aspects of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur
Respir Rev. 18:113–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
González-Mariscal L, Tapia R and Chamorro
D: Crosstalk of tight junction components with signaling pathways.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1778:729–756. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Feng J, Wang QS, Chiang A and Chen BY: The
effects of sleep hypoxia on coagulant factors and hepatic
inflammation in emphysematous rats. PLoS One. 5:e132012010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ and
Gurd FN: Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. I A
morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg.
101:478–483. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lavie L: Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome
- an oxidative stress disorder. Sleep Med Rev. 7:35–51. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng X, Mao Y, Cai J, Li Y, Liu W, Sun P,
Zhang JH, Sun X and Yuan H: Hydrogen-rich saline protects against
intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Free Radic Res.
43:478–484. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang R, Gallo DJ, Baust JJ, Watkins SK,
Delude RL and Fink MP: Effect of hemorrhagic shock on gut barrier
function and expression of stress-related genes in normal and
gnotobiotic mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
283:R1263–R1274. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ban K, Peng Z and Kozar RA: Inhibition of
ERK1/2 worsens intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One.
8:e767902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou W, Li S, Wan N, Zhang Z, Guo R and
Chen B: Effects of various degrees of oxidative stress induced by
intermittent hypoxia in rat myocardial tissues. Respirology.
17:821–829. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yuan G, Khan SA, Luo W, Nanduri J, Semenza
GL and Prabhakar NR: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 mediates increased
expression of NADPH oxidase-2 in response to intermittent hypoxia.
J Cell Physiol. 226:2925–2933. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nanduri J, Vaddi DR, Khan SA, Wang N,
Makarenko V, Semenza GL and Prabhakar NR: HIF-1α activation by
intermittent hypoxia requires NADPH oxidase stimulation by xanthine
oxidase. PLoS One. 10:e01197622015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yuan G, Nanduri J, Khan S, Semenza GL and
Prabhakar NR: Induction of HIF-1alpha expression by intermittent
hypoxia: Involvement of NADPH oxidase, Ca2+ signaling,
prolyl hydroxylases, and mTOR. J Cell Physiol. 217:674–685. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nanduri J, Yuan G, Kumar GK, Semenza GL
and Prabhakar NR: Transcriptional responses to intermittent
hypoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 164:277–281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng YJ, Yuan G, Ramakrishnan D, Sharma
SD, Bosch-Marce M, Kumar GK, Semenza GL and Prabhakar NR:
Heterozygous HIF-1alpha deficiency impairs carotid body-mediated
systemic responses and reactive oxygen species generation in mice
exposed to intermittent hypoxia. J Physiol. 577:705–716. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ryan S, Taylor CT and McNicholas WT:
Systemic inflammation: A key factor in the pathogenesis of
cardiovascular complications in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome?
Thorax. 64:631–636. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ryan S, McNicholas WT and Taylor CT: A
critical role for p38 map kinase in NF-kappaB signaling during
intermittent hypoxia/reoxygenation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
355:728–733. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Greenberg HE, Sica AL, Scharf SM and
Ruggiero DA: Expression of c-fos in the rat brainstem after chronic
intermittent hypoxia. Brain Res. 816:638–645. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Peterson LW and Artis D: Intestinal
epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune
homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:141–153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hering NA, Fromm M and Schulzke JD:
Determinants of colonic barrier function in inflammatory bowel
disease and potential therapeutics. J Physiol. 590:1035–1044. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saeedi B, Kendrick A, Schwisow K, Bayless
A, Colgan S and Glover L: A role for hypoxia inducible factor in
the junctional integrity and barrier function of intestinal
epithelial cells (60.1). FASEB J. 28:S60.12014.
|
|
32
|
Furuta GT, Turner JR, Taylor CT, Hershberg
RM, Comerford K, Narravula S, Podolsky DK and Colgan SP:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent induction of intestinal
trefoil factor protects barrier function during hypoxia. J Exp Med.
193:1027–1034. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guma M, Stepniak D, Shaked H, Spehlmann
ME, Shenouda S, Cheroutre H, Vicente-Suarez I, Eckmann L, Kagnoff
MF and Karin M: Constitutive intestinal NF-κB does not trigger
destructive inflammation unless accompanied by MAPK activation. J
Exp Med. 208:1889–1900. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fischer A, Gluth M, Pape UF, Wiedenmann B,
Theuring F and Baumgart DC: Adalimumab prevents barrier dysfunction
and antagonizes distinct effects of TNF-α on tight junction
proteins and signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 304:G970–G979. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ye D, Ma I and Ma TY: Molecular mechanism
of tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulation of intestinal epithelial
tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
290:G496–G504. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang Y, Clayburgh DR, Mittal N, Goretsky
T, Dirisina R, Zhang Z, Kron M, Ivancic D, Katzman RB, Grimm G, et
al: Epithelial NF-kappaB enhances transmucosal fluid movement by
altering tight junction protein composition after T cell
activation. Am J Pathol. 176:158–167. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Chen ML, Ge Z, Fox JG and Schauer DB:
Disruption of tight junctions and induction of proinflammatory
cytokine responses in colonic epithelial cells by Campylobacter
jejuni. Infect Immun. 74:6581–6589. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Al-Sadi R, Ye D, Boivin M, Guo S, Hashimi
M, Ereifej L and Ma TY: Interleukin-6 modulation of intestinal
epithelial tight junction permeability is mediated by JNK pathway
activation of claudin-2 gene. PLoS One. 9:e853452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Taylor CT and Colgan SP: Hypoxia and
gastrointestinal disease. J Mol Med Berl. 85:1295–1300. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Colgan SP and Taylor CT: Hypoxia: An alarm
signal during intestinal inflammation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 7:281–287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Eltzschig HK and Carmeliet P and Carmeliet
P: Hypoxia and inflammation. N Engl J Med. 364:656–665. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sitkovsky M and Lukashev D: Regulation of
immune cells by local-tissue oxygen tension: HIF1 α and adenosine
receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:712–721. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|