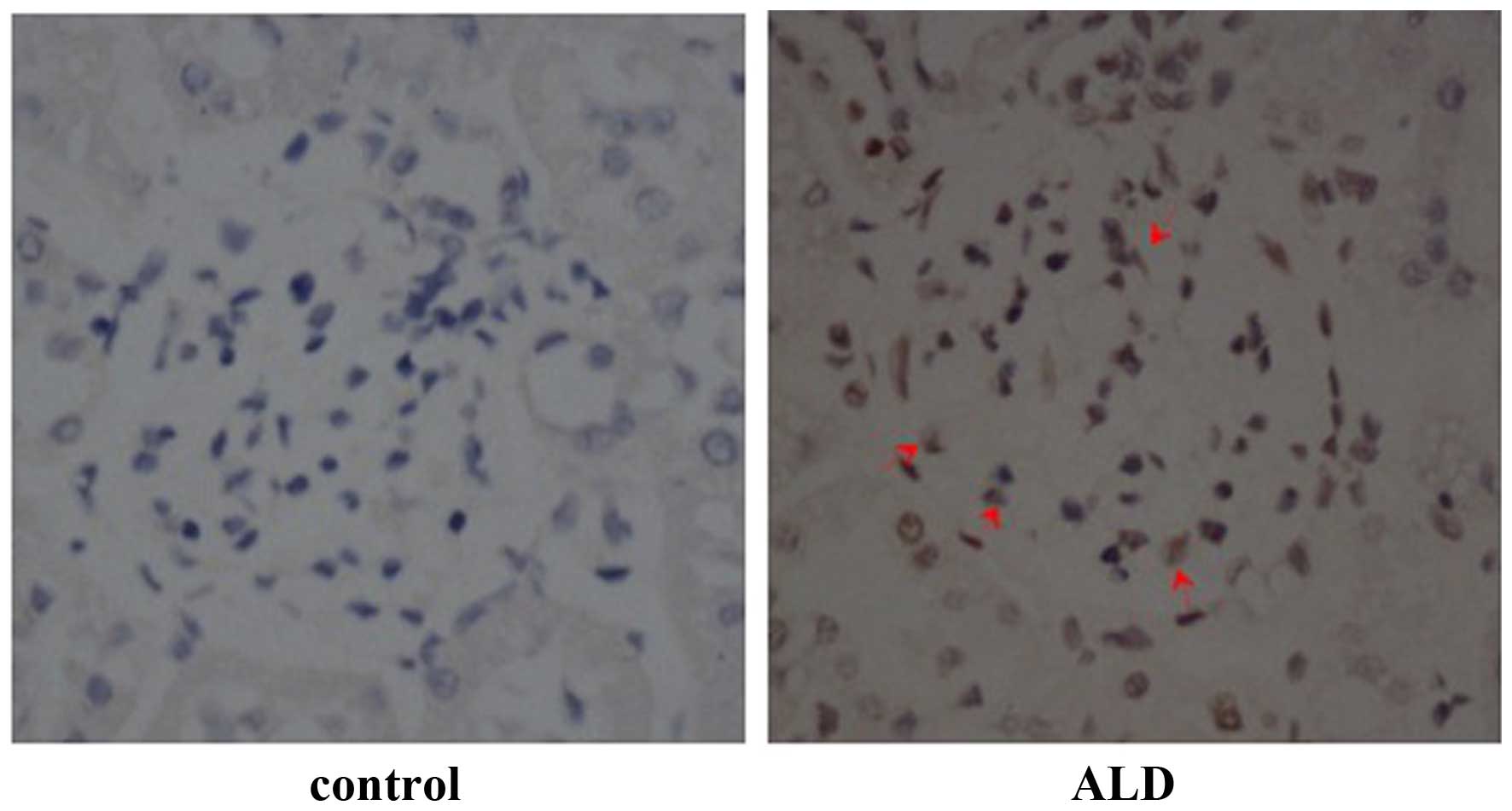
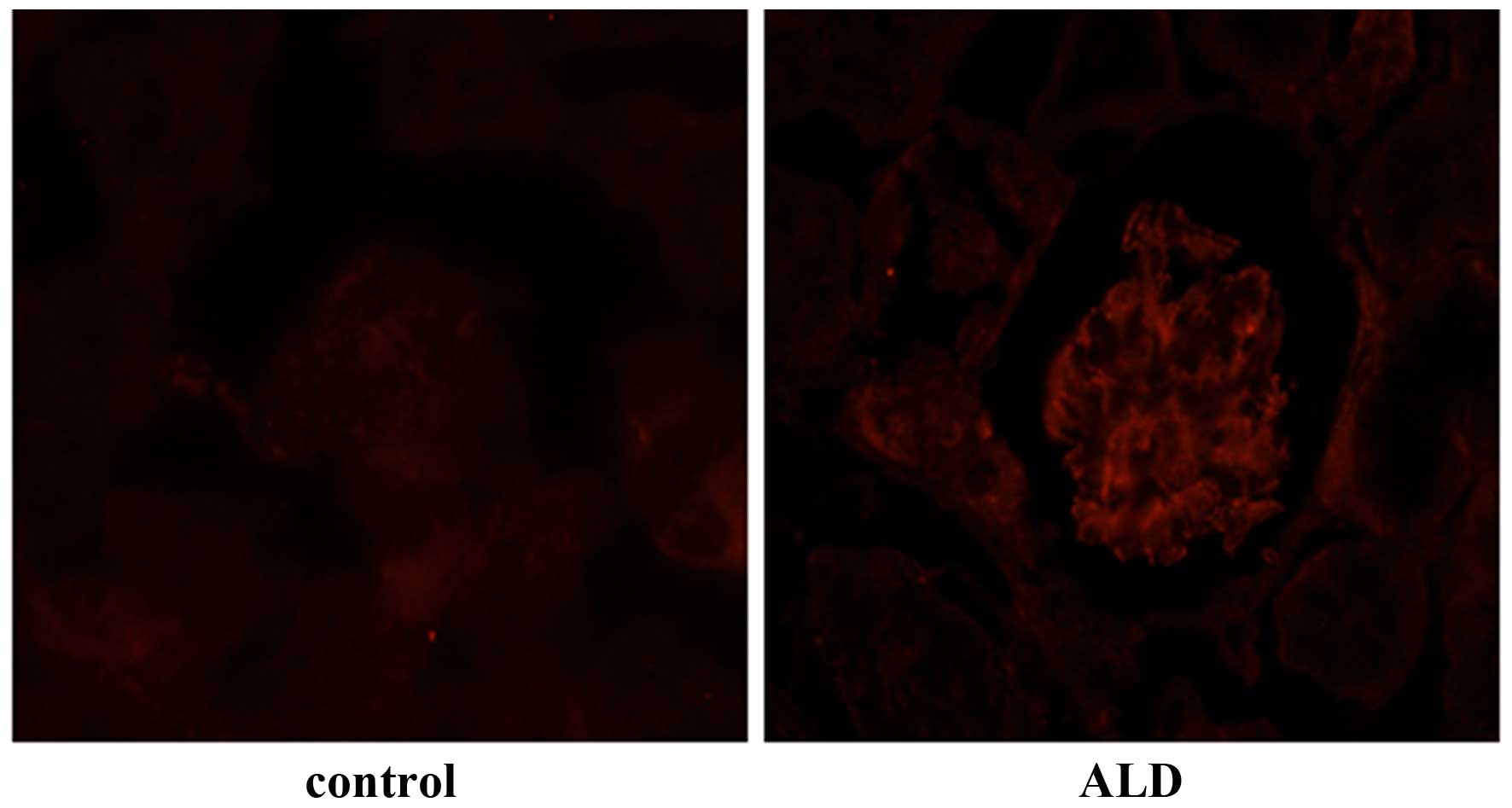
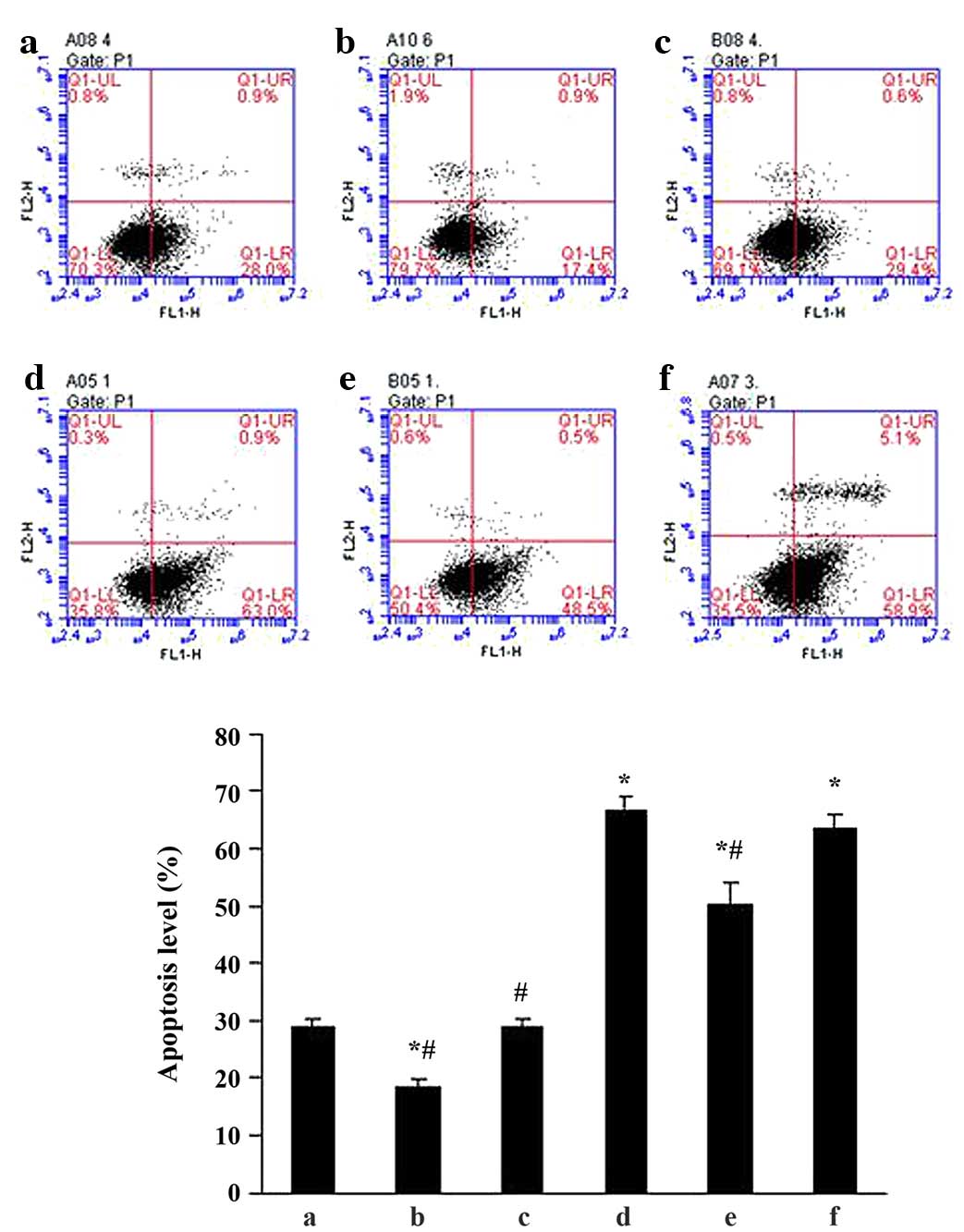
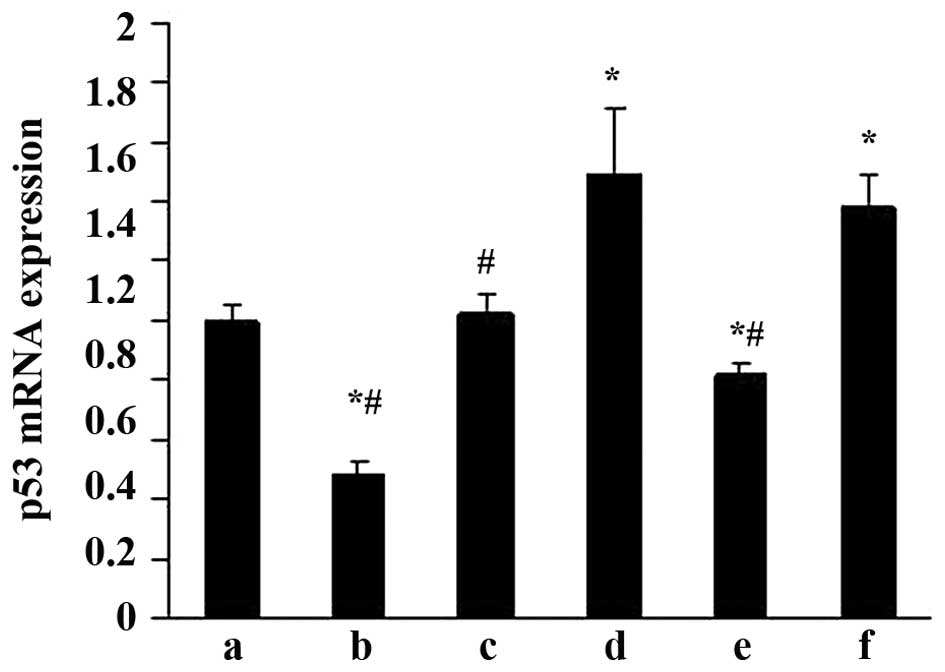
|
1
|
White SL, Cass A, Atkins RC and Chadban
SJ: Chronic kidney disease in the general population. Adv Chronic
Kidney Dis. 12:5–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bolignano D, Palmer SC, Navaneethan SD and
Strippoli GF: Aldosterone antagonists for preventing the
progression of chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
4:CD0070042014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Greene EL, Kren S and Hostetter TH: Role
of aldosterone in the remnant kidney model in the rat. J Clin
Invest. 98:1063–1068. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lai L, Chen J, Hao CM, Lin S and Gu Y:
Aldosterone promotes fibronectin production through a
Smad2-dependent TGF-beta1 pathway in mesangial cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 348:70–75. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang W, Chen C, Shi J, Ren Z, Hu F, van
Goor H, Singhal PC and Ding G: Disparate effects of eplerenone,
amlodipine and telmisartan on podocyte injury in
aldosterone-infused rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:789–799.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Del Vecchio L, Procaccio M, Vigano S and
Cusi D: Mechanisms of disease: The role of aldosterone in kidney
damage and clinical benefits of its blockade. Nat Clin Pract
Nephrol. 3:42–49. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nishiyama A, Yao L, Nagai Y, Miyata K,
Yoshizumi M, Kagami S, Kondo S, Kiyomoto H, Shokoji T, Kimura S, et
al: Possible contributions of reactive oxygen species and
mitogen-activated protein kinase to renal injury in
aldosterone/salt-induced hypertensive rats. Hypertension.
43:841–848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fan YY, Baba R, Nagai Y, Miyatake A,
Hosomi N, Kimura S, Sun GP, Kohno M, Fujita M, Abe Y and Nishiyama
A: Augmentation of intrarenal angiotensin II levels in
uninephrectomized aldosterone/salt-treated hypertensive rats;
renoprotective effects of an ultrahigh dose of olmesartan.
Hypertens Res. 29:169–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kiyomoto H, Rafiq K, Mostofa M and
Nishiyama A: Possible underlying mechanisms responsible for
aldosterone and mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent renal injury.
J Pharmacol Sci. 108:399–405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawachi H
and Fujita T: Podocyte as the target for aldosterone: Roles of
oxidative stress and Sgk1. Hypertension. 49:355–364. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nagase M and Fujita T: Endocrinological
aspects of proteinuria and podocytopathy in diabetes: Role of the
aldosterone/mineralocorticoid receptor system. Curr Diabetes Rev.
7:8–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Epstein M: Aldosterone blockade: An
emerging strategy for abrogating progressive renal disease. Am J
Med. 119:912–919. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu D, Yu H, He H, Ding J, Tang J, Cao D
and Hao L: Spironolactone inhibits apoptosis in rat mesangial cells
under hyperglycaemic conditions via the Wnt signalling pathway. Mol
Cell Biochem. 380:185–193. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nagase M and Fujita T: Aldosterone and
glomerular podocyte injury. Clin Exp Nephrol. 12:233–242. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Merkel CE, Karner CM and Carroll TJ:
Molecular regulation of kidney development: Is the answer blowing
in the Wnt? Pediatr Nephrol. 22:1825–1838. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen C, Liang W, Jia J, van Goor H,
Singhal PC and Ding G: Aldosterone induces apoptosis in rat
podocytes: Role of PI3-K/Akt and p38MAPK signaling pathways.
Nephron Exp Nephrol. 113:e26–e34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abboud HE: Mesangial cell biology. Exp
Cell Res. 318:979–985. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brunskill EW and Potter SS: Changes in the
gene expression programs of renal mesangial cells during diabetic
nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 13:702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dalla Vestra M, Saller A, Mauer M and
Fioretto P: Role of mesangial expansion in the pathogenesis of
diabetic nephropathy. J Nephrol. 14(Suppl 4): S51–S57. 2001.
|
|
21
|
Kitamura H, Shimizu A, Masuda Y, Ishizaki
M, Sugisaki Y and Yamanaka N: Apoptosis in glomerular endothelial
cells during the development of glomerulosclerosis in the
remnant-kidney model. Exp Nephrol. 6:328–336. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shimizu A, Masuda Y, Kitamura H, Ishizaki
M, Sugisaki Y and Yamanaka N: Apoptosis in progressive crescentic
glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 74:941–951. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mishra R, Emancipator SN, Kern T and
Simonson MS: High glucose evokes an intrinsic proapoptotic
signaling pathway in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 67:82–93. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sugiyama H, Kashihara N, Makino H,
Yamasaki Y and Ota A: Apoptosis in glomerular sclerosis. Kidney
Int. 49:103–111. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ford HL, Sclafani RA and DeGregori J: Cell
cycle and growth control: Biomolecular regulation and cancer. Stein
GSaP AB: Cell cycle regulatory cascades Hoboken, New Jersey:
Wiley-Liss; pp. 95–128. 2004
|
|
26
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chrysostomou A and Becker G:
Spironolactone in addition to ACE inhibition to reduce proteinuria
in patients with chronic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 345:925–926.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rocha R, Chander PN, Zuckerman A and Stier
CT Jr: Role of aldosterone in renal vascular injury in stroke-prone
hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 33:232–237. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blasi ER, Rocha R, Rudolph AE, Blomme EA,
Polly ML and McMahon EG: Aldosterone/salt induces renal
inflammation and fibrosis in hypertensive rats. Kidney Int.
63:1791–1800. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miric G, Dallemagne C, Endre Z, Margolin
S, Taylor SM and Brown L: Reversal of cardiac and renal fibrosis by
pirfenidone and spironolactone in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Br
J Pharmacol. 133:687–694. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Aldigier JC, Kanjanbuch T, Ma LJ, Brown NJ
and Fogo AB: Regression of existing glomerulosclerosis by
inhibition of aldosterone. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:3306–3314. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han SY, Chang EJ, Choi HJ, Kwak CS, Park
SB, Kim HC and Mun KC: Apoptosis by cyclosporine in mesangial
cells. Transplant Proc. 38:2244–2246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oltvani ZN and Korsmeyer SJ: Checkpoints
of dueling dimers foli death wishes. Cell. 79:189–192. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: p53 function
and dysfunction. Cell. 70:523–526. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miyashita T and Reed JC: Tumor suppressor
p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene.
Cell. 80:293–299. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pierzchalski P, Reiss K, Cheng W, Cirielli
C, Kajstura J, Nitahara JA, Rizk M, Capogrossi MC and Anversa P:
p53 induces myocyte apoptosis via the activation of the
renin-angiotensin system. Exp Cell Res. 234:57–65. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Leri A, Fiordaliso F, Setoguchi M, Limana
F, Bishopric NH, Kajstura J, Webster K and Anversa P: Inhibition of
p53 function prevents renin-angiotensin system activation and
stretch-mediated myocyte apoptosis. Am J Pathol. 157:843–857. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
el-Deiry WS: Regulation of p53 downstream
genes. Semin Cancer Biol. 8:345–357. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chang NS: A potential role of p53 and WOX1
in mitochondrial apoptosis (review). Int J Mol Med. 9:19–24.
2002.
|