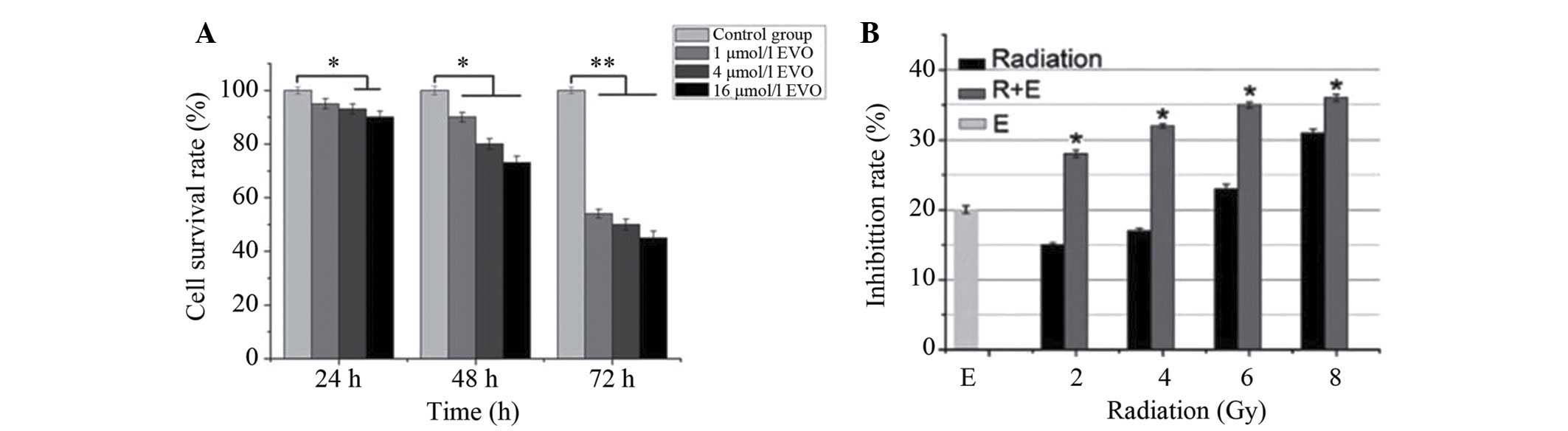
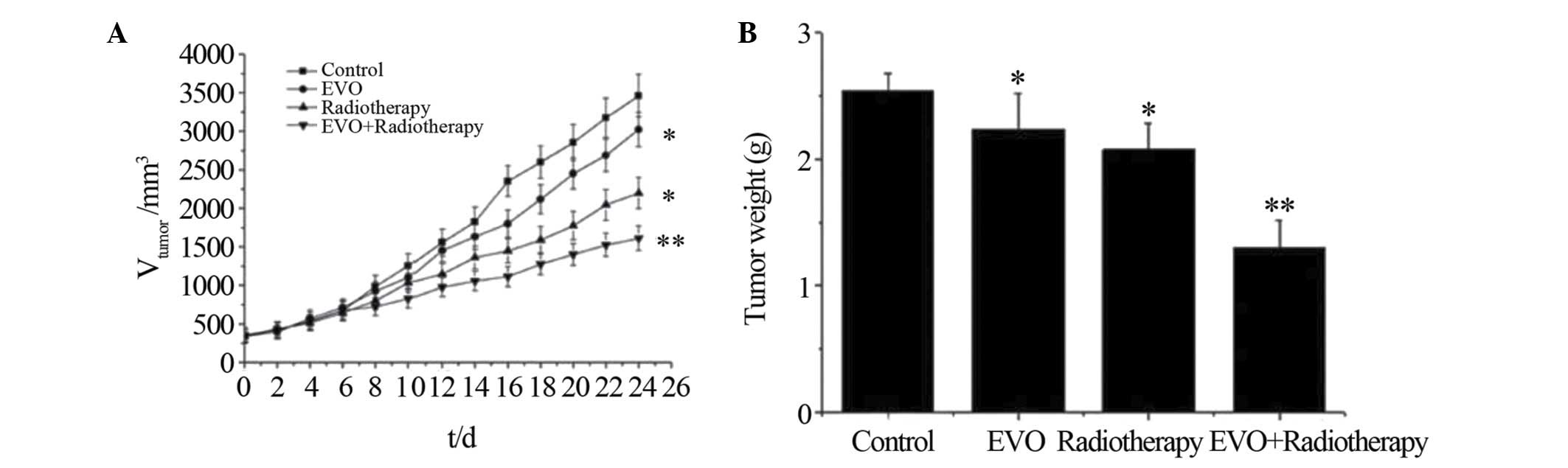
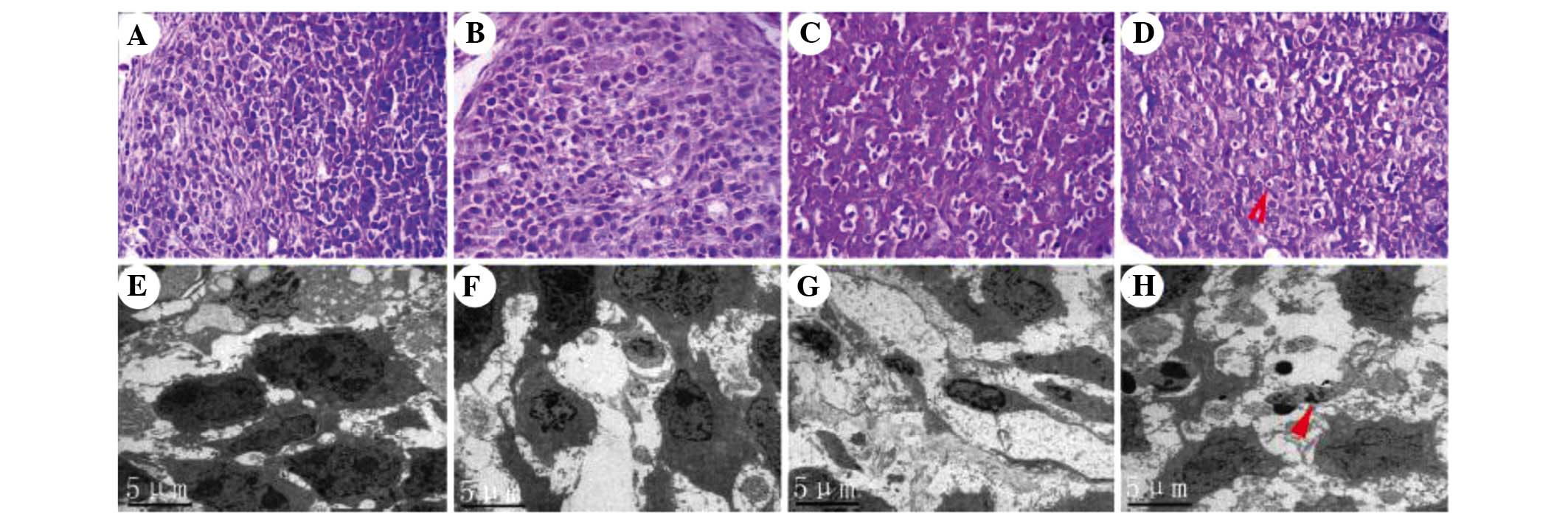
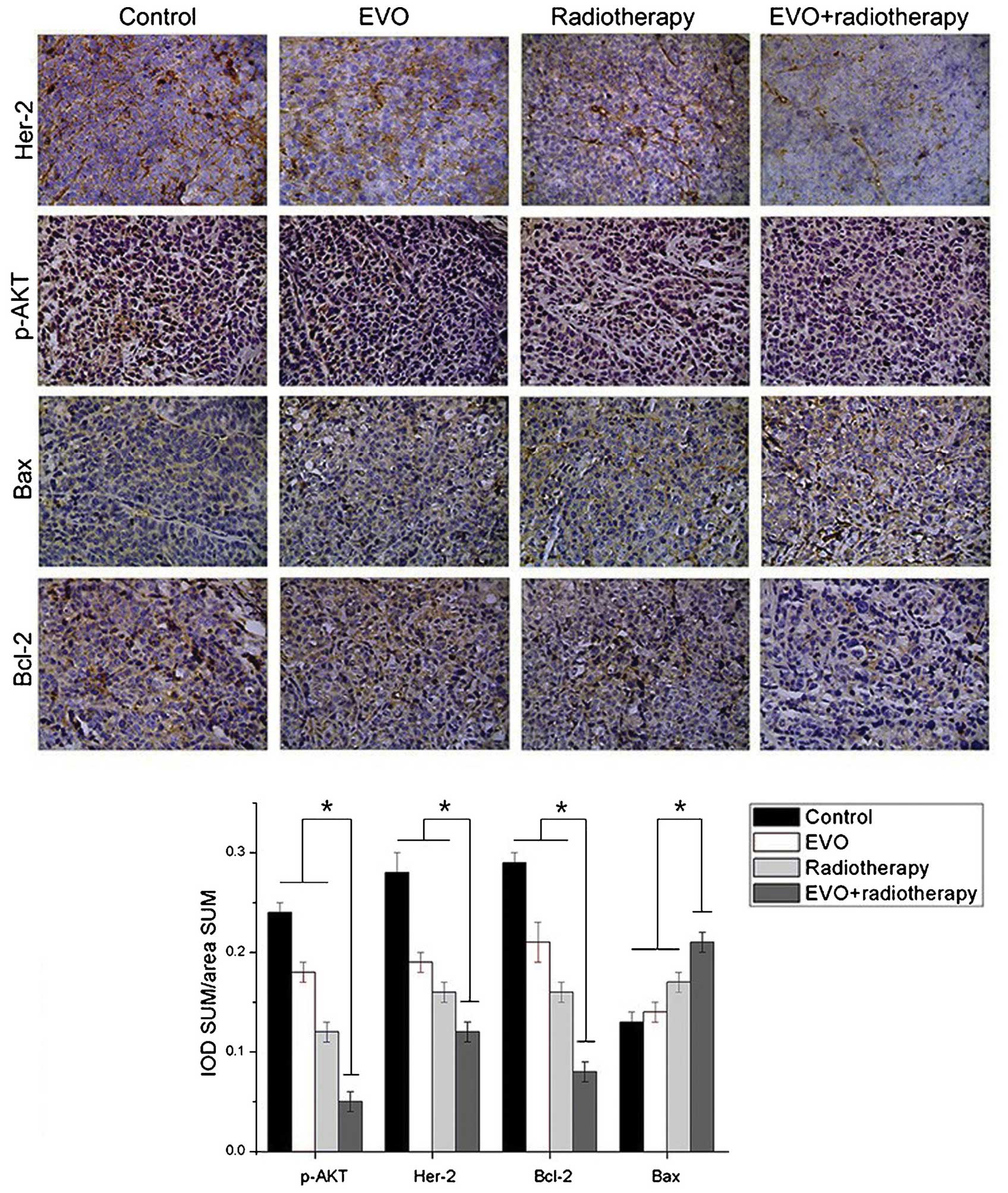
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. Ca-Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohtsu A, Shah MA, Van Cutsem E, Rha SY,
Sawaki A, Park SR, Lim HY, Yamada Y, Wu J, Langer B, et al:
Bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy as first-line therapy
in advanced gastric cancer: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 29:3968–3976.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maier-Hauff K, Ulrich F, Nestler D,
Niehoff H, Wust P, Thiesen B, Orawa H, Budach V and Jordan A:
Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic
iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy
on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol.
103:317–324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Begg AC, Stewart FA and Vens C: Strategies
to improve radiotherapy with targeted drugs. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:239–253. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li-Weber M: Targeting apoptosis pathways
in cancer by Chinese medicine. Cancer Lett. 332:304–312. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shu L, Cheung KL, Khor TO, Chen C and Kong
AN: Phytochemicals: Cancer chemoprevention and suppression of tumor
onset and metastasis. Cancer Metast Rev. 29:483–502. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yuan SM, Gao K, Wang DM, Quan XZ, Liu JN,
Ma CM, Qin C and Zhang LF: Evodiamine improves congnitive abilities
in SAMP8 and APP(swe)/PS1(ΔE9) transgenic mouse models of
Alzheimer's disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:295–302. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu H, Jin H, Gong W, Wang Z and Liang H:
Pharmacological actions of multi-target-directed evodiamine.
Molecules. 18:1826–1843. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xia YY, Xu HY, Cai YY, Si DY and Liu CX:
Simultaneous determination of evodiamine and evodine in Beagle dog
plasma using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J
Asian Nat Prod Res. 15:235–243. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schwarz NA, Spillane M, La Bounty P,
Grandjean PW, Leutholtz B and Willoughby DS: Capsaicin and
evodiamine ingestion does not augment energy expenditure and fat
oxidation at rest or after moderately-intense exercise. Nutr Res.
33:1034–1042. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liao JF, Chiou WF, Shen YC, Wang GJ and
Chen CF: Anti-inflammatory and anti-infectious effects of Evodia
rutaecarpa (Wuzhuyu) and its major bioactive components. Chin Med.
6:62011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han YY: The Radio Sensitizing Effects of
EVO on Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Lanzhou University; 2014, In
Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Li J, Zhang KL, Hu CQ, et al: Inhibitory
effect of evodiamine combined with radiotherapy on the growth of
xenografts of human tongue squamous-cell carcinoma Tca-8113 cells
in nude mice. Tumor. 2:108–112. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
14
|
Ueno S, Yamazaki R, Ikeda T, Yaegashi T
and Matsuzaki T: Antitumor effect of a novel phenanthroindolizidine
alkaloid derivative through inhibition of protein synthesis.
Anticancer Res. 34:3391–3397. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun H, Hou H, Lu P, et al: Isocorydine
inhibits cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. PloS one.
7:e368082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lawrence YR, Vikram B, Dignam JJ,
Chakravarti A, Machtay M, Freidlin B, Takebe N, Curran WJ Jr,
Bentzen SM, Okunieff P, et al: NCI-RTOG translational program
strategic guidelines for the early-stage development of
radiosensitizers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 105:11–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ma S, Jiao B and Liu X, Yi H, Kong D, Gao
L, Zhao G, Yang Y and Liu X: Approach to radiation therapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:157–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Morris ZS and Harari PM: Interaction of
radiation therapy with molecular targeted agents. J Clin Onocl.
32:2886–2893. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Waseem M and Parvez S: Mitochondrial
dysfunction mediated cisplatin induced toxicity: Modulatory role of
curcumin. Food Chem Toxicol. 53:334–342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang J, Cai X, Lu W, Hu C, Xu X, Yu Q and
Cao P: Evodiamine inhibits STAT3 signaling by inducing phosphatase
shatterproof 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
328:243–251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang KL, Hsia SM, Yeh JY, Cheng SC, Wang
PS and Wang SW: Anti-proliferative effects of evodiamine on human
breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e672972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kan SF, Huang WJ, Lin LC and Wang PS:
Inhibitory effects of evodiamine on the growth of human prostate
cancer cell line LNCaP. Int J Cancer. 110:641–651. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sukawa Y, Yamamoto H, Nosho K, et al: HER2
expression and PI3K-Akt pathway alterations in gastric cancer.
Digestion. 89:12–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi L, Chen J, Yang J, Pan T, Zhang S and
Wang Z: MiR-21 protected human glioblastoma U87MG cells from
chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide induced apoptosis by decreasing
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity. Brain Res. 1352:255–264.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schwartzberg LS, Franco SX, Florance A,
O'Rourke L, Maltzman J and Johnston S: Lapatinib plus letrozole as
first-line therapy for HER-2+ hormone receptor-positive metastatic
breast cancer. Oncologist. 15:122–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gravalos C and Jimeno A: HER2 in gastric
cancer: a new prognostic factor and a novel therapeutic target. Ann
Oncol. 19:1523–1529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dave B, Migliaccio I, Gutierrez MC, Wu MF,
Chamness GC, Wong H, Narasanna A, Chakrabarty A, Hilsenbeck SG,
Huang J, et al: Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog or
phosphoinositol-3 kinase activation and response to trastuzumab or
lapatinib in human epidermal growth factor receptor
2-overexpressing locally advanced breast cancers. J Clin Oncol.
29:166–173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bacus SS, Altomare DA, Lyass L, Spohn B,
Bartholomeusz G, Yan DH and Hung MC: AKT2 is frequently upregulated
in HER-2/neu-positive breast cancers and may contribute to tumor
aggressiveness by enhancing cell survival. Oncogene. 21:3532–3540.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wong KK, Engelman JA and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K signaling pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 20:87–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Chen KC, Hsieh CL, Peng CC and Peng RY:
Exercise rescued chronic kidney disease by attenuating cardiac
hypertrophy through the cardiotrophin-1 - LIFR/gp 130 - JAK/STAT3
pathway. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 21:507–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ridnour LA, Barasch KM, Windhausen AN,
Dorsey TH, Lizardo MM, Yfantis HG, Lee DH, Switzer CH, Cheng RY,
Heinecke JL, et al: Nitric oxide synthase and breast cancer: Role
of TIMP-1 in NO-mediated Akt activation. PLoS One. 7:e440812012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng KW, Wang XM, Ko H, Kwon HC, Cha JW
and Yang HO: Hyperoside protects primary rat cortical neurons from
neurotoxicity induced by amyloid β-protein via the
PI3K/Akt/Bad/Bcl(XL)-regulated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Eur
J Pharmacol. 672:45–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sakamaki J, Daitoku H, Ueno K, Hagiwara A,
Yamagata K and Fukamizu A: Arginine methylation of BCL-2 antagonist
of cell death (BAD) counteracts its phosphorylation and
inactivation by Akt. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:6085–6090. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao A, Zeng Q, Xie X, Zhou J, Yue W, Li Y
and Pei X: MicroRNA-125b induces cancer cell apoptosis through
suppression of Bcl-2 expression. J Genet Genomics. 39:29–35. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|