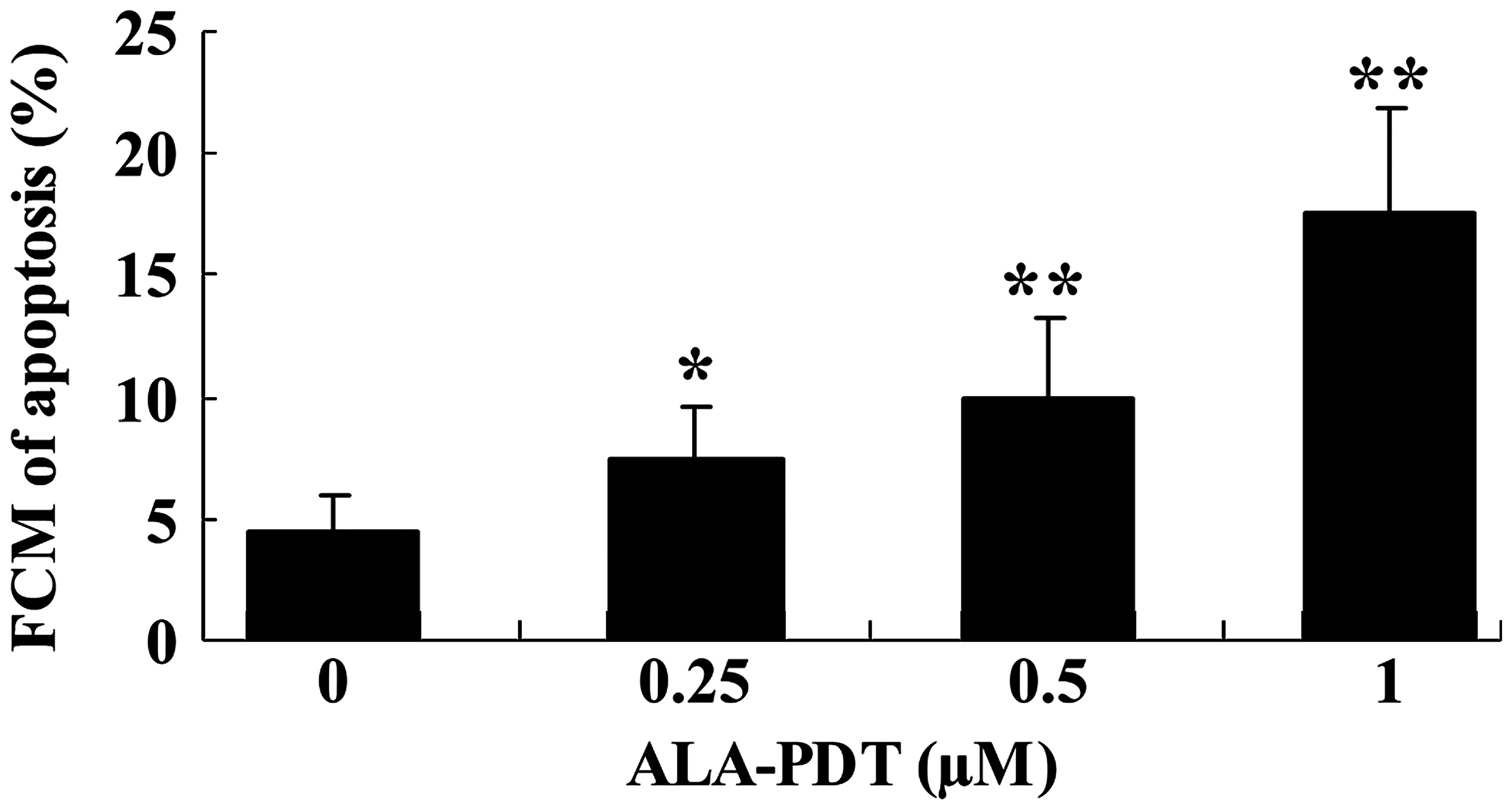
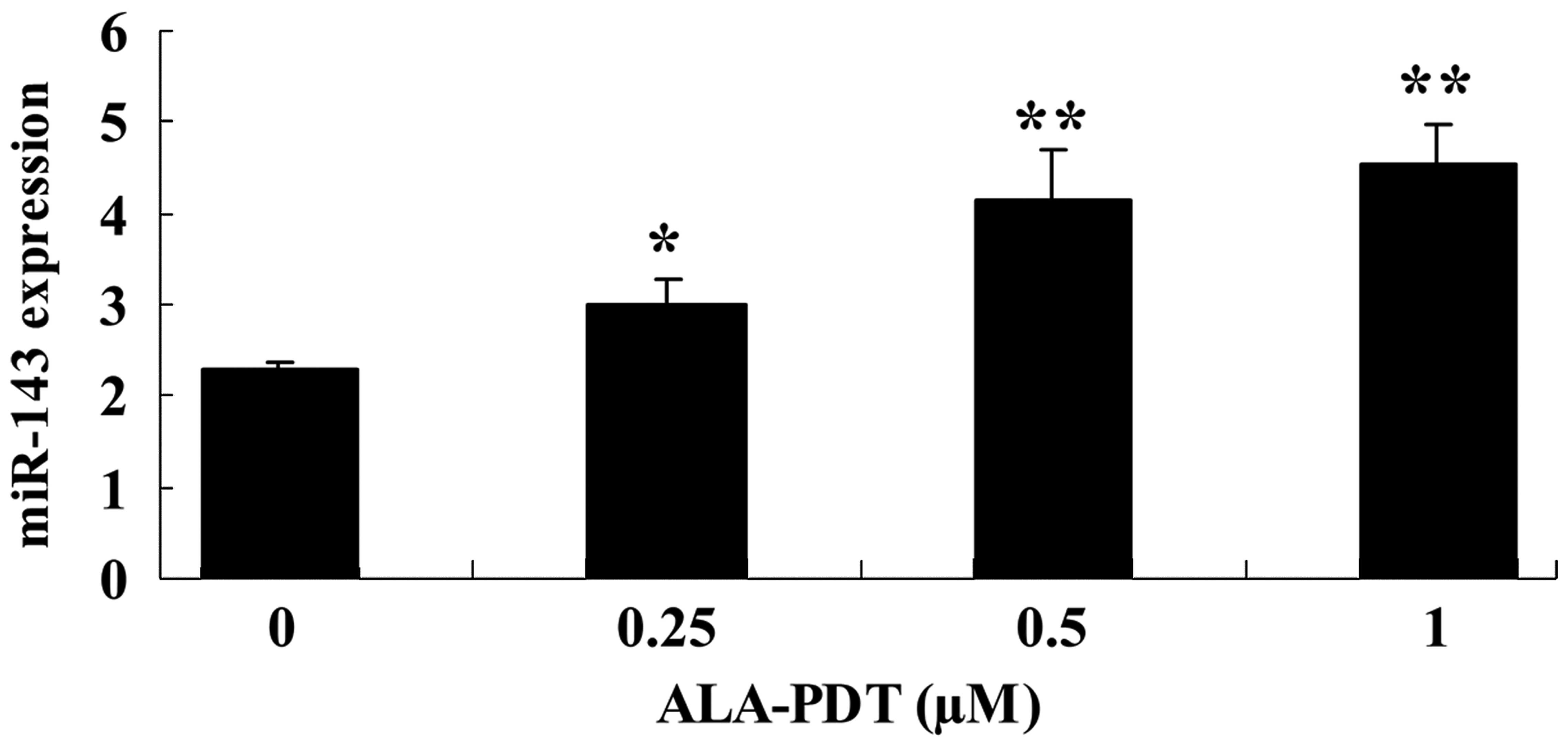
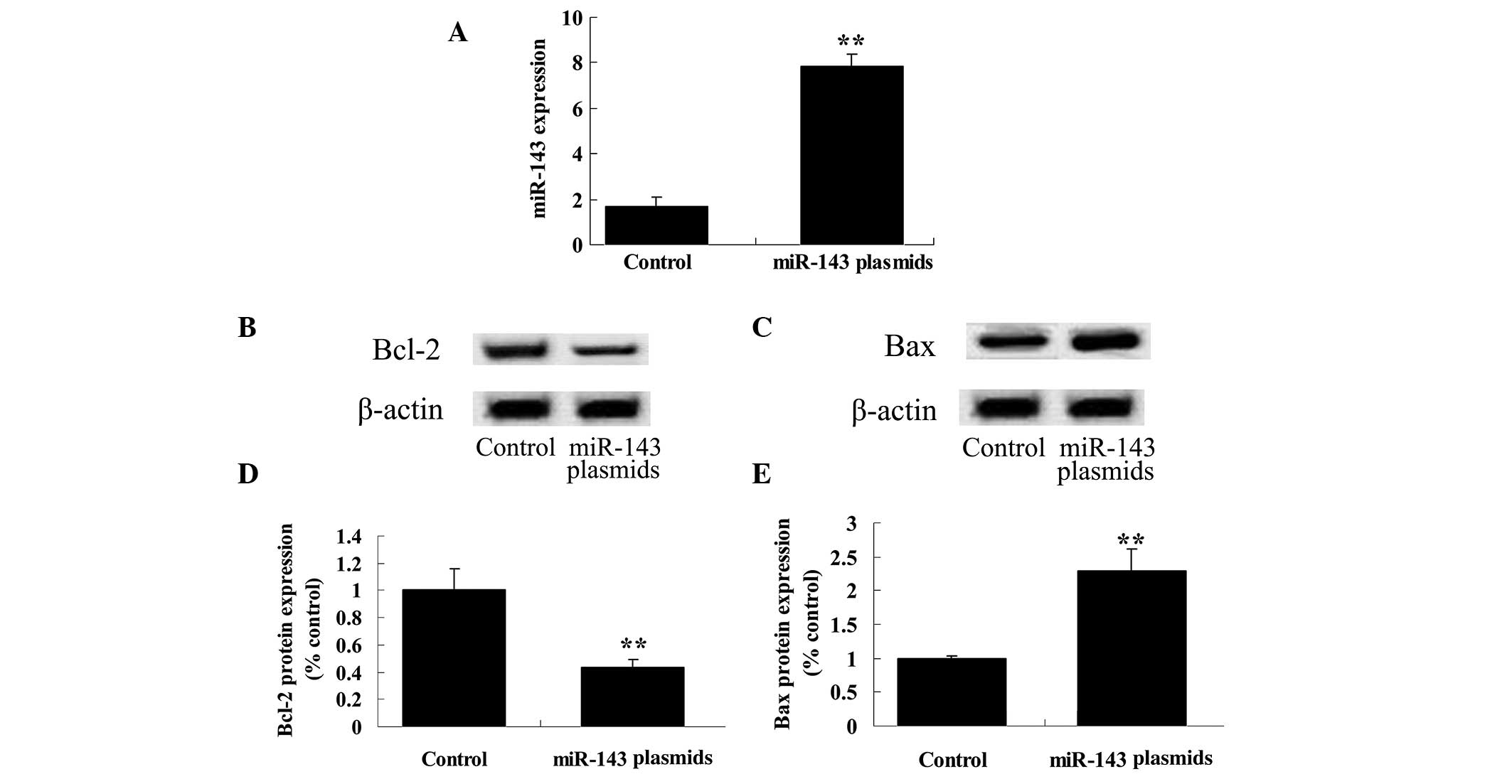
|
1
|
Zeng T and Li G: MicroRNA-10a enhances the
metastatic potential of cervical cancer cells by targeting
phosphatase and tensin homologue. Mol Med Rep. 10:1377–1382.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shi YA, Zhao Q, Zhang LH, Du W, Wang XY,
He X, Wu S and Li YL: Knockdown of hTERT by siRNA inhibits cervical
cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 45:1216–1224.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
World Health Organization (WHO): WHO
guidelines for screening and treatment of precancerous lesions for
cervical cancer prevention world health organization. WHO; Geneva,
Switzerland: 2013
|
|
4
|
Wang N, Xu Z, Wang K, Zhu M and Li Y:
Construction and analysis of regulatory genetic networks in
cervical cancer based on involved microRNAs, target genes,
transcription factors and host genes. Oncol Lett. 7:1279–1283.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
González-Quintana V, Palma-Berré L,
Campos-Parra AD, López-Urrutia E, Peralta-Zaragoza O, Vazquez-Romo
R and Pérez-Plasencia C: MicroRNAs are involved in cervical cancer
development, progression, clinical outcome and improvement
treatment response (Review). Oncol Rep. Oct 30–2015.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jiang H, Zhao PJ, Su D, Feng J and Ma SL:
Paris saponin I induces apoptosis via increasing the Bax/Bcl-2
ratio and caspase-3 expression in gefitinib-resistant non-small
cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 9:2265–2272.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tarantino G, Scopacasa F, Colao A, Capone
D, Tarantino M, Grimaldi E and Savastano S: Serum Bcl-2
concentrations in overweight-obese subjects with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 17:5280–5288. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Qu L, Zhong H, Xu K, Qiu X and Wang
E: Low expression of Mig-6 is associated with poor survival outcome
in NSCLC and inhibits cell apoptosis via ERK-mediated upregulation
of Bcl-2. Oncol Rep. 31:1707–1714. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Divaris DX, Kennedy JC and Pottier RH:
Phototoxic damage to sebaceous glands and hair follicles of mice
after systemic administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid correlates
with localized protoporphyrin IX fluorescence. Am J Pathol.
136:891–897. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ji J, Fan Z, Zhou F and Wang X, Shi L,
Zhang H, Wang P, Yang D, Zhang L, Chen WR and Wang X: Improvement
of DC vaccine with ALA-PDT induced immunogenic apoptotic cells for
skin squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:17135–17146. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang HW, Zhang LL, Miao F, Lv T, Wang XL
and Huang Z: Treatment of HPV infection-associated cervical
condylomata acuminata with 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated
photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol. 88:565–569. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kennedy JC, Pottier RH and Pross DC:
Photodynamic therapy with endogenous protoporphyrin IX: Basic
principles and present clinical experience. J Photochem Photobiol
B. 6:143–148. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shin HT, Kim JH, Shim J, Lee JH, Lee DY,
Lee JH and Yang JM: Photodynamic therapy using a new formulation of
5-aminolev-ulinic acid for wrinkles in Asian skin: A randomized
controlled split face study. J Dermatolog Treat. 26:246–51. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wei XQ, Ma HQ, Liu AH and Zhang YZ:
Synergistic anticancer activity of 5-aminolevulinic acid
photodynamic therapy in combination with low-dose cisplatin on HeLa
cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:3023–3028. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang P, Shen K, Wang X, Song H, Yue Y and
Liu T: TPX2 regulates tumor growth in human cervical carcinoma
cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:2347–2351. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu Y, Zhang Y and Zhang S: MicroRNA-92
regulates cervical tumorigenesis and its expression is upregulated
by human papillo-mavirus-16 E6 in cervical cancer cells. Oncol
Lett. 6:468–474. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hadizadeh M and Fateh M: Synergistic
Cytotoxic Effect of Gold Nanoparticles and 5-Aminolevulinic
Acid-Mediated Photo-dynamic Therapy against Skin Cancer Cells. Iran
J Med Sci. 39:452–458. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Ji J, Zhang H, Fan Z, Zhang L, Shi
L, Zhou F, Chen WR, Wang H and Wang X: Stimulation of dendritic
cells by DAMPs in ALA-PDT treated SCC tumor cells. Oncotarget. Nov
26–2015.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
19
|
Gui T, Wang Y, Mao Y, Liu J, Sun S, Cao D,
Yang J and Shen K: Comparisons of 5-aminolevulinic acid
photodynamic therapy and after-loading radiotherapy in vivo in
cervical cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 15:434–442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Koczorowska MM, Kwasniewska A and
Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A: IGF1 mRNA isoform expression in the cervix of
HPV-positive women with pre-cancerous and cancer lesions. Exp Ther
Med. 2:149–156. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masliah-Planchon J, Garinet S and Pasmant
E: RAS-MAPK pathway epigenetic activation in cancer: miRNAs in
action. Oncotarget. Dec 5–2015.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ju H, Yang Y, Sheng A and Jiang X: Role of
microRNAs in skeletal muscle development and rhabdomyosarcoma
(review). Mol Med Rep. 11:4019–4024. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jamali Z, Asl Aminabadi N, Attaran R,
Pournagiazar F, Ghertasi Oskouei S and Ahmadpour F: MicroRNAs as
prognostic molecular signatures in human head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol.
51:321–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nair VS, Maeda LS and Ioannidis JP:
Clinical outcome prediction by microRNAs in human cancer: A
systematic review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:528–540. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang X and Jia Z: Construction of
HCC-targeting artificial miRNAs using natural miRNA precursors. Exp
Ther Med. 6:209–215. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu L, Yu X, Guo X, Tian Z, Su M, Long Y,
Huang C, Zhou F, Liu M, Wu X and Wang X: miR-143 is downregulated
in cervical cancer and promotes apoptosis and inhibits tumor
formation by targeting Bcl-2. Mol Med Rep. 5:753–760. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Qiao WL, Wang GM, Shi Y, Wu JX, Qi YJ,
Zhang JF, Sun H and Yan CD: Differential expression of Bcl-2 and
Bax during gastric ischemia-reperfusion of rats. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:1718–1724. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu LH, Zhou YJ, Ding L, Zhang SZ, Sun J
and Cao JG: Induction of apoptosis by VB1 in breast cancer cells:
The role of reactive oxygen species and Bcl-2 family proteins. Int
J Mol Med. 33:423–430. 2014.
|
|
29
|
Deng B, Zhang XF, Zhu XC, Huang H, Jia HL,
Ye QH, Dong QZ and Qin LX: Correlation and prognostic value of
osteopontin and Bcl-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after
curative resection. Oncol Rep. 30:2795–2803. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He GF, Bian ML, Zhao YW, Xiang Q, Li HY
and Xiao C: A study on the mechanism of 5-aminolevulinic acid
photodynamic therapy in vitro and in vivo in cervical cancer. Oncol
Rep. 21:861–868. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|