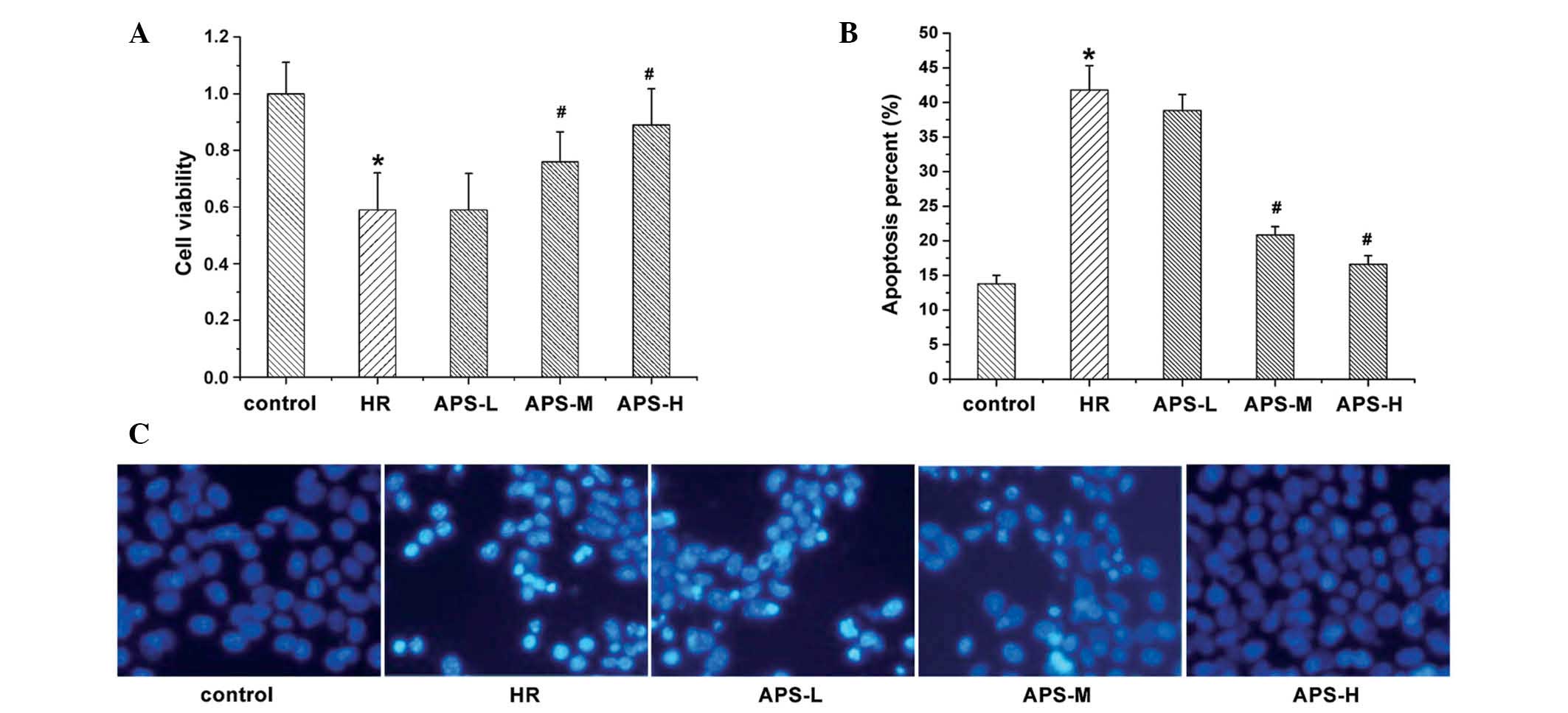
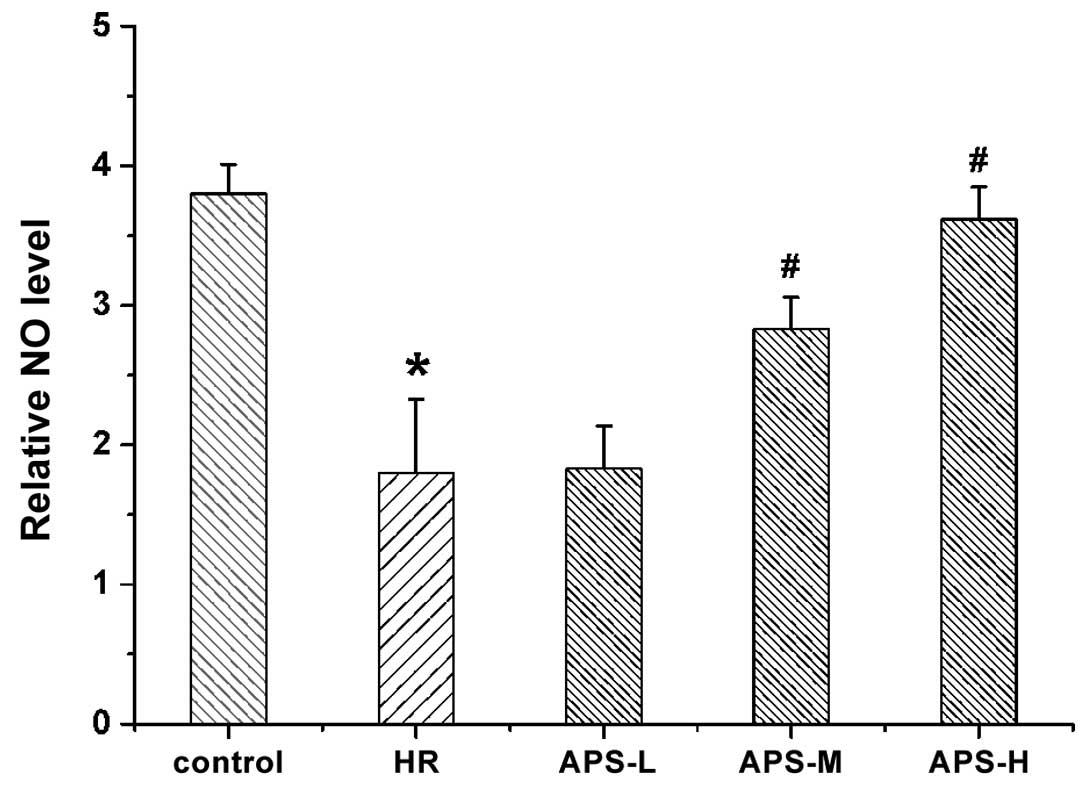
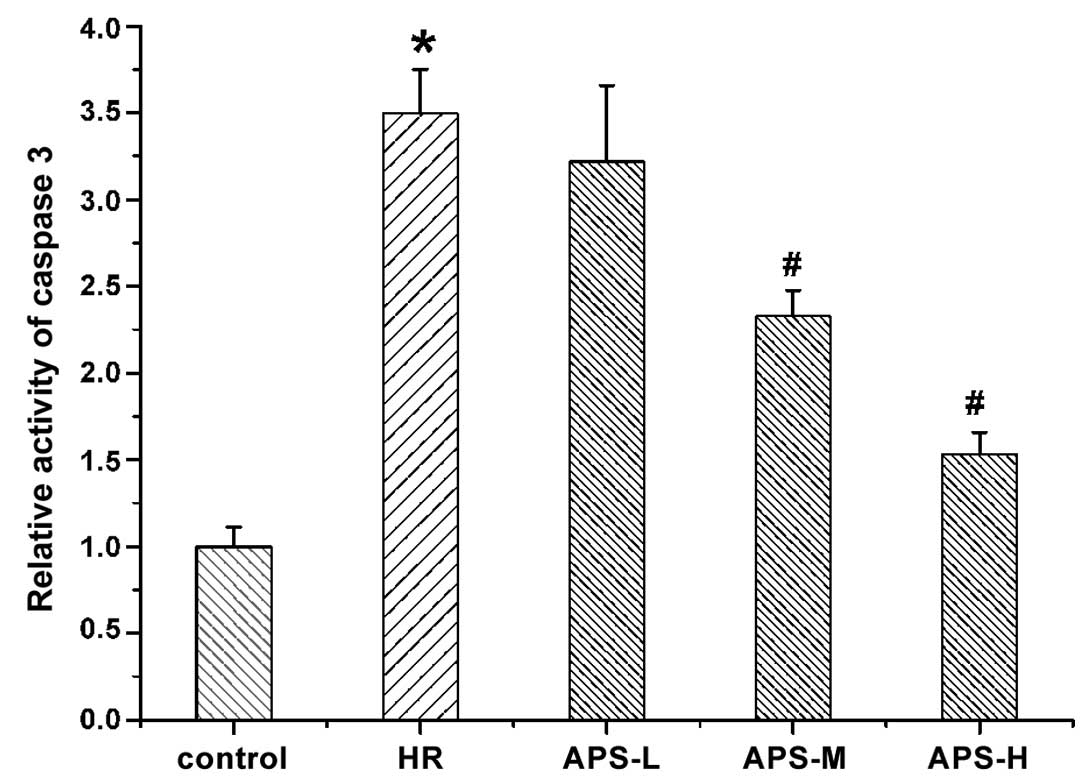
|
1
|
Mangge H, Becker K, Fuchs D and Gostner
JM: Antioxidants, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. World J
Cardiol. 6:462–477. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao G, Cai H, Cai B and Tu S: Effect of
5-hydroxymethylfurfural derived from processed Cornus officinalis
on the prevention of high glucose-induced oxidative stress in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells and its mechanism. Food Chem.
140:273–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang J, Wang Z, Zuo G, Li B, Zhang J,
Tian N and Chen S: Low shear stress induces human vascular
endothelial cell apoptosis by activating Akt signal and increasing
reactive oxygen species. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 33:313–317.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu L, Sun Y and Hu J: Catalpol inhibits
apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-induced endothelium by activating
the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and modulating expression of Bcl-2
and Bax. Eur J Pharmacol. 628:155–163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ginter E, Simko V and Panakova V:
Antioxidants in health and disease. Bratisl Lek Listy. 115:603–606.
2014.
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Xu X and Wang N: Progress of
studies on protective mechanism of Radix Astragali in vascular
endothelial cells. Chinese Pharm J. 48:1526–1530. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Hai-Yan Z, Yong-Hong G, Zhi-Yao W, Bing X,
Ai-Ming W, Yan-Wei X, Bei L, Li-Xia L and Li-Xin C: Astragalus
polysaccharide suppresses the expression of adhesion molecules
through the regulation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in human
cardiac microvascular endothelial cells after ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:2804932013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu B, Zhu H, Gao Y, Liu B, Zhu L and Chen
L: Influences of Astragalus polysaccharides on genetic
transcription of P-selectin and E-selectin in human cardiac
microvascular endothelial cells after ischemia-reperfusion injury.
J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med. 34:177–180. 2011.
|
|
9
|
Yin Y, Li P, Lu G, Liang J and Zhao F:
Protective effects of APS-A3 on blood vessel endothelium function
induced by paraoxon. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res. 22:583–585.
2011.
|
|
10
|
Li T, Chen L, Li Q, Zhou Y, Tang H and
Cheng S: The protective effects of tetramethylpyrazine (TMP)
combined with Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on vascular
endothelial cells (VECs). China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm.
26:2672–2675. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Zhong Y, Cheng C, Huang H, Li A, Liu B and
Liu S: Astragalus polysaccharides protects advanced glycation
end-products induced endothelial cells apoptosis. Clin Med Eng.
21:18–20. 2014.
|
|
12
|
Xu H, Wu Q, Xie X and Kong D: Effect of
Astragalus polysaccharides on peripheral endothelial progenitor
cells via PI3K/Akt/eNOS signal pathway in patients with type 2
diabetes. J Clin Rehabilitative Tissue Eng Res. 15:4272–4276.
2011.
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Feng Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Xu D and
Ruan K: The effect of polysaccharide from Radix Astragali on cells
survival against oxygen glucose deprivation and phosphorylation of
Akt. Pharm Biotechnol. 18:288–290. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Zhu H, Chen L and Zhu L: Effect of
astragalus polysaccharides on expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in
human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells after hypoxia and
reoxygenation. Liaoning J Tradit Chinese Med. 35:293–295. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Suriyo T, Watcharasit P, Thiantanawat A
and Satayavivad J: Arsenite promotes apoptosis and dysfunction in
microvascular endothelial cells via an alteration of intracellular
calcium homeostasis. Toxicol In Vitro. 26:386–395. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mukai Y, Shimokawa H, Matoba T, Hiroki J,
Kunihiro I, Fujiki T and Takeshita A: Acute vasodilator effects of
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: Involvement of PI3-kinase/Akt pathway
and Kv channels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 42:118–124. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu YP, Shen T, Lin YJ, Chen BD, Ruan Y,
Cao Y, Qiao Y, Man Y, Wang S and Li J: Astragalus polysaccharides
suppress ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in TNF-α-treated human
vascular endothelial cells by blocking NF-ĸB activation. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 34:1036–1042. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu M, Qin J, Hao Y, Liu M, Luo J, Luo T
and Wei L: Astragalus polysaccharide suppresses skeletal muscle
myostatin expression in diabetes: Involvement of ROS-ERK and NF-ĸB
pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:7824972013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang WM, Liang YQ, Tang LJ, Ding Y and
Wang XH: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Astragalus
polysaccharide on EA.hy926 cells. Exp Ther Med. 6:199–203.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zuo H, Liao D, Lin L, Zhang R and Li X:
Resveratrol attenuates hypoxia-reperfusion injury induced rat
myocardium microvascular endothelial cell dysfunction through
upregulating PI3K/Akt/SVV pathways. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za
Zhi. 42:670–674. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Su C, Xia T, Ren S, Qing S, Jing D, Lian
H, Bin Q, Yuan Z and Xiang Z: Effect of diazoxide preconditioning
on cultured rat myocardium microvascular endothelial cells against
apoptosis and relation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Balkan Med J. 31:83–87.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cao Y, Ruan Y, Shen T, Huang X, Li M, Yu
W, Zhu Y, Man Y, Wang S and Li J: Astragalus polysaccharide
suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating the
PI3k/Akt and p38MAPK pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2014:6742192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ye MN, Chen HF, Zhou RJ and Liao MJ:
Effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on proliferation and Akt
phosphorylation of the basal-like breast cancer cell line. Zhong Xi
Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 9:1339–1346. 2011.In Chinese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim BH, Oh I, Kim JH, Jeon JE, Jeon B,
Shin J and Kim TY: Anti-inflammatory activity of compounds isolated
from Astragalus sinicus L. in cytokine-induced keratinocytes and
skin. Exp Mol Med. 46:e872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jia Y, Zuo D, Li Z, Liu H, Dai Z, Cai J,
Pang L and Wu Y: Astragaloside IV inhibits doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis mediated by mitochondrial apoptotic pathway
via activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
62:45–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ge GH, Dou HJ, Yang SS, Ma JW, Cheng WB,
Qiao ZY, Hou YM and Fang WY: Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects
against cardiac microvascular endothelial cells injured by high
glucose. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:73–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Velotta JB, Kimura N, Chang SH, Chung J,
Itoh S, Rothbard J, Yang PC, Steinman L, Robbins RC and Fischbein
MP: αB-crystallin improves murine cardiac function and attenuates
apoptosis in human endothelial cells exposed to
ischemia-reperfusion. Ann Thorac Surg. 91:1907–1913. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao B, Xu Y, He H, Jiang QL, Li SY, Shu
HY, Liang EY, Yi ZS, Ye JY, Huang LF, et al: Anti-apoptotic effect
of Astragalus polysaccharide on myeloid cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 21:1243–1247. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|