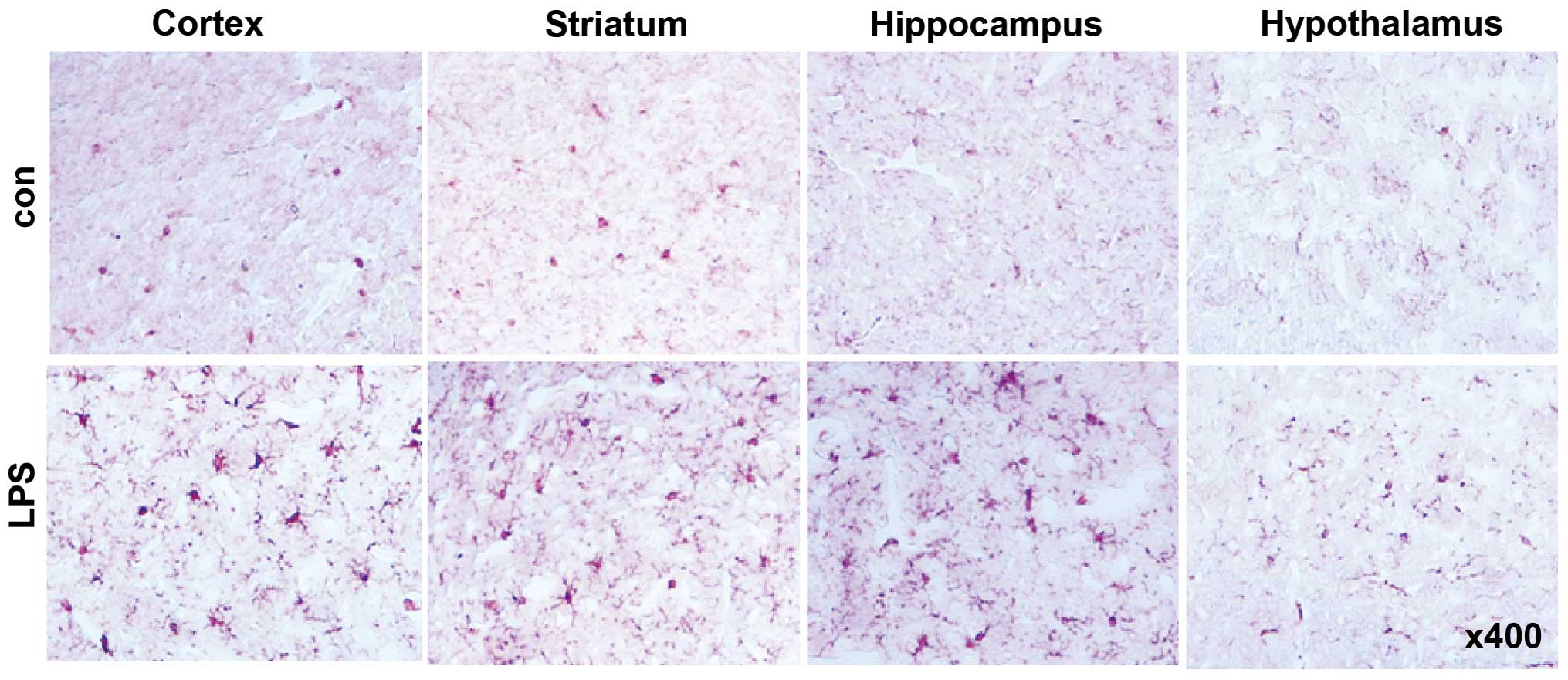
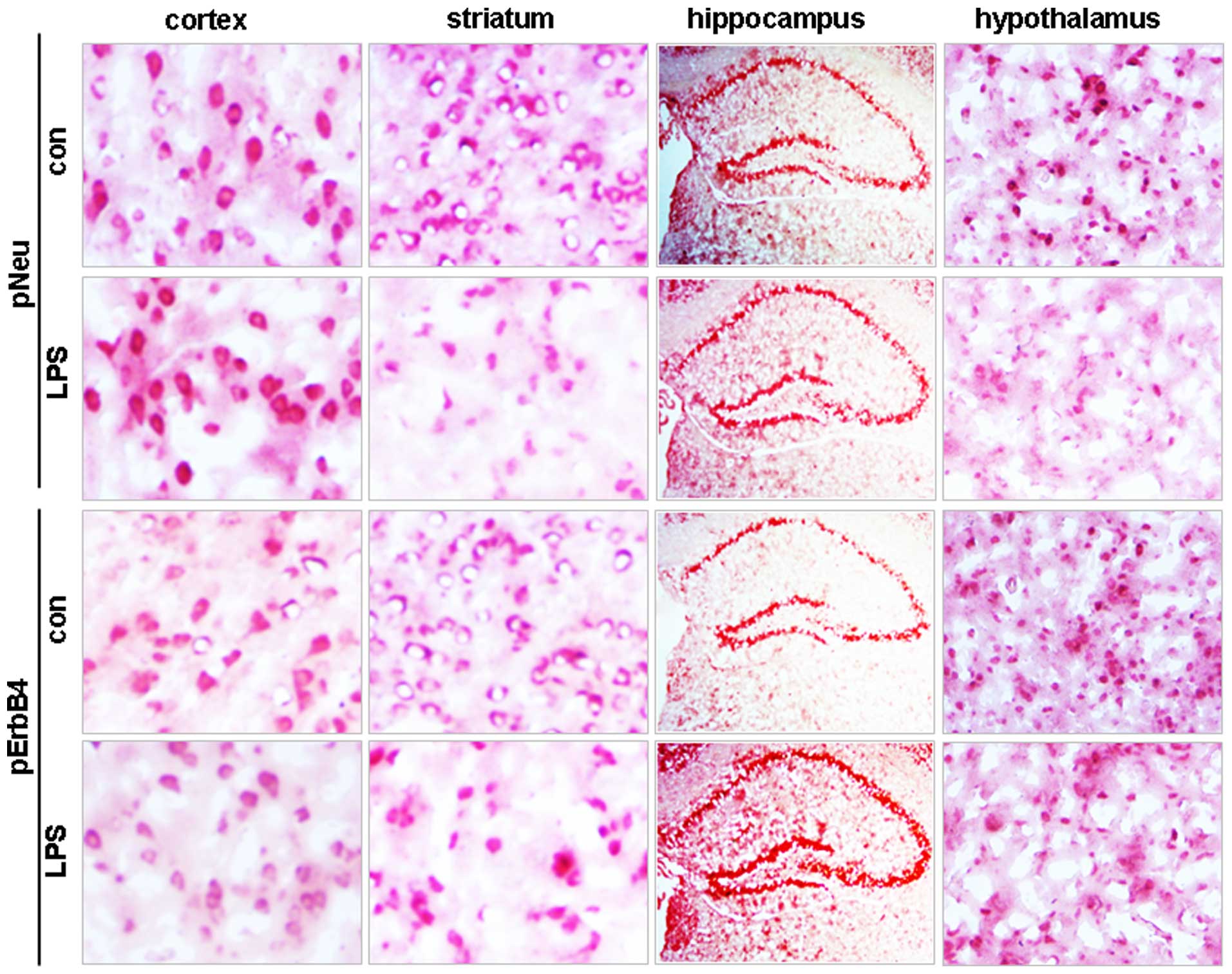
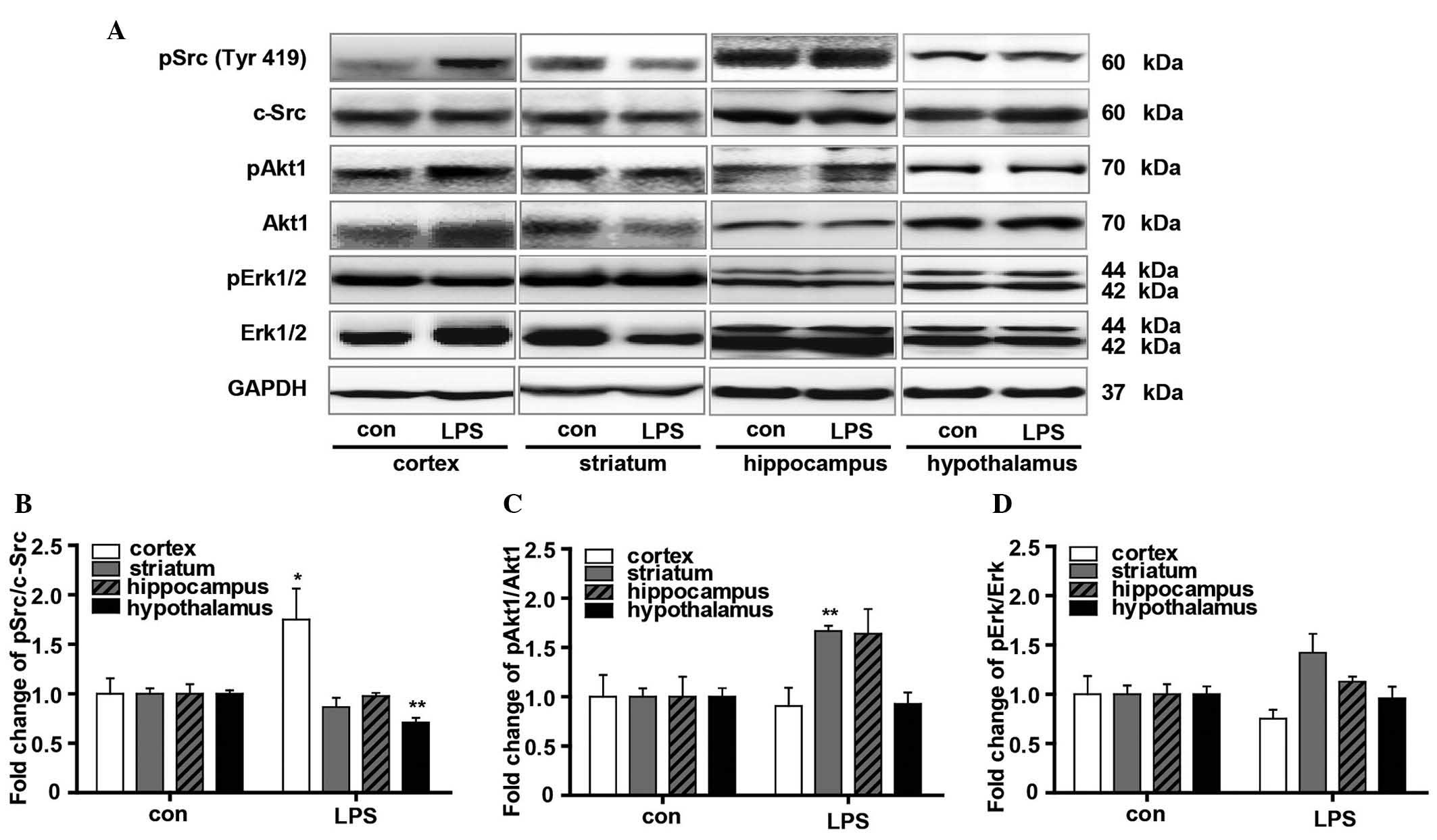
|
1
|
Woo RS, Li XM, Tao Y, Carpenter-Hyland E,
Huang YZ, Weber J, Neiswender H, Dong XP, Wu J, Gassmann M, et al:
Neuregulin-1 enhances depolarization-induced GABA release. Neuron.
54:599–610. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hancock ML, Canetta SE, Role LW and
Talmage DA: Presynaptic type III neuregulin1-ErbB signaling targets
alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to axons. J Gen Physiol.
131:i42008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu J and Kern JA: Neuregulin-1 activates
the JAK-STAT pathway and regulates lung epithelial cell
proliferation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 27:306–313. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shamir A and Buonanno A: Molecular and
cellular characterization of Neuregulin-1 type IV isoforms. J
Neurochem. 113:1163–1176. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, Yang HI,
Thajeb P and Li H: Neuregulin-1 reduces ischemia-induced brain
damage in rats. Neurobiol Aging. 25:935–944. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao W and Ren SG: Neuregulin-1 (Nrg1) is
mainly expressed in rat pituitary gonadotroph cells and possibly
regulates prolactin (PRL) secretion in a juxtacrine manner. J
Neuroendocrinol. 23:1252–1262. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao W, Shen Y and Ren S: Endogenous
expression of Neuregulin-1 (Nrg1) as a potential modulator of
prolactin (PRL) secretion in GH3 cells. Cell Tissue Res.
344:313–320. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao WJ and Ren SG: Endogenous
neuregulin-1 expression in the anterior pituitary of female
Wistar-Furth rats during the estrous cycle. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue
Xue Bao. 31:921–927. 2011.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peles E, Ben-Levy R, Tzahar E, Liu N, Wen
D and Yarden Y: Cell-type specific interaction of Neu
differentiation factor (NDF/heregulin) with Neu/HER-2 suggests
complex ligand-receptor relationships. EMBO J. 12:961–971.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Puricelli L, Proietti CJ, Labriola L,
Salatino M, Balañá ME, Aguirre Ghiso J, Lupu R, Pignataro OP,
Charreau EH, Bal de Kier Joffé E and Elizalde PV: Heregulin
inhibits proliferation via ERKs and phosphatidyl-inositol 3-kinase
activation but regulates urokinase plasminogen activator
independently of these pathways in metastatic mammary tumor cells.
Int J Cancer. 100:642–653. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rebola N, Simões AP, Canas PM, Tomó AR,
Andrade GM, Barry CE, Agostinho PM, Lynch MA and Cunha RA:
Adenosine A2A receptors control neuroinflammation and consequent
hippocampal neuronal dysfunction. J Neurochem. 117:100–111. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chaudhury AR, Gerecke KM, Wyss JM, Morgan
DG, Gordon MN and Carroll SL: Neuregulin-1 and erbB4
immunoreactivity is associated with neuritic plaques in Alzheimer
disease brain and in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 62:42–54. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Viehover A, Miller RH, Park SK, Fischbach
G and Vartanian T: Neuregulin: An oligodendrocyte growth factor
absent in active multiple sclerosis lesions. Dev Neurosci.
23:377–386. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Corfas G, Roy K and Buxbaum JD: Neuregulin
1-erbB signaling and the molecular/cellular basis of schizophrenia.
Nat Neurosci. 7:575–580. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ritch PA, Carroll SL and Sontheimer H:
Neuregulin-1 enhances motility and migration of human astrocytic
glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 278:20971–20978. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirsch EC and Hunot S: Neuroinflammation
in Parkinson's disease: A target for neuroprotection? Lancet
Neurol. 8:382–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gaillard PJ, de Boer AB and Breimer DD:
Pharmacological investigations on lipopolysaccharide-induced
permeability changes in the blood-brain barrier in vitro. Microvasc
Res. 65:24–31. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Glezer I, Simard AR and Rivest S:
Neuroprotective role of the innate immune system by microglia.
Neuroscience. 147:867–883. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nawa H and Takei N: Recent progress in
animal modeling of immune inflammatory processes in schizophrenia:
Implication of specific cytokines. Neurosci Res. 56:2–13. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoffmann I, Bueter W, Zscheppang K,
Brinkhaus MJ, Liese A, Riemke S, Dörk T, Dammann O and Dammann CE:
Neuregulin-1, the fetal endothelium, and brain damage in preterm
newborns. Brain Behav Immun. 24:784–791. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Cao M, Zheng H, Tan X, Xu W, Rui Y, Li L,
Liu X, Xu G, Cui G, Xu J, et al: Upregulation of CBLL1 in rat brain
cortex after lipopolysaccharide treated. J Mol Histol. 44:135–145.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chiu K, Lau WM, Lau HT, So KF and Chang
RC: Micro-dissection of rat brain for RNA or protein extraction
from specific brain region. J Vis Exp. 269:2007.
|
|
23
|
Dreymueller D, Martin C, Schumacher J,
Groth E, Boehm JK, Reiss LK, Uhlig S and Ludwig A: Smooth muscle
cells relay acute pulmonary inflammation via distinct ADAM17/ErbB
axes. J Immunol. 192:722–731. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhu L, Bi W and Lu D, Zhang C, Shu X, Wang
H, Qi R, Shi Q and Lu D: Regulation of ubiquitin-specific
processing protease 8 suppresses neuroinflammation. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 64:74–83. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu Z, Jiang J, Ford G and Ford BD:
Neuregulin-1 is neuro-protective and attenuates inflammatory
responses induced by ischemic stroke. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
322:440–446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bermingham-McDonogh O, McCabe KL and Reh
TA: Effects of GGF/neuregulins on neuronal survival and neurite
outgrowth correlate with erbB2/neu expression in developing rat
retina. Development. 122:1427–1438. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Verdi JM, Groves AK, Farinas I, Jones K,
Marchionni MA, Reichardt LF and Anderson DJ: A reciprocal cell-cell
interaction mediated by NT-3 and neuregulins controls the early
survival and development of sympathetic neuroblasts. Neuron.
16:515–527. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vaskovsky A, Lupowitz Z, Erlich S and
Pinkas-Kramarski R: ErbB-4 activation promotes neurite outgrowth in
PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 74:979–987. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Erlich S, Goldshmit Y, Lupowitz Z and
Pinkas-Kramarski R: ErbB-4 activation inhibits apoptosis in PC12
cells. Neuroscience. 107:353–362. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goldshmit Y, Erlich S and Pinkas-Kramarski
R: Neuregulin rescues PC12-ErbB4 cells from cell death induced by
H2O2. Regulation of reactive oxygen species
levels by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem.
276:46379–46385. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marchionni MA, Goodearl AD, Chen MS,
Bermingham-McDonogh O, Kirk C, Hendricks M, Danehy F, Misumi D,
Sudhalter J, Kobayashi K, et al: Glial growth factors are
alternatively spliced erbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous
system. Nature. 362:312–318. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pinkas-Kramarski R, Eilam R, Spiegler O,
Lavi S, Liu N, Chang D, Wen D, Schwartz M and Yarden Y: Brain
neurons and glial cells express Neu differentiation
factor/heregulin: A survival factor for astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 91:9387–9391. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pinkas-Kramarski R, Eilam R, Alroy I,
Levkowitz G, Lonai P and Yarden Y: Differential expression of
NDF/neuregulin receptors ErbB-3 and ErbB-4 and involvement in
inhibition of neuronal differentiation. Oncogene. 15:2803–2815.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Eilam R, Pinkas-Kramarski R, Ratzkin BJ,
Segal M and Yarden Y: Activity-dependent regulation of Neu
differentiation factor/neuregulin expression in rat brain. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:1888–1893. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Erlich S, Shohami E and Pinkas-Kramarski
R: Closed head injury induces up-regulation of ErbB-4 receptor at
the site of injury. Mol Cell Neurosci. 16:597–608. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Esper RM, Pankonin MS and Loeb JA:
Neuregulins: Versatile growth and differentiation factors in
nervous system development and human disease. Brain Res Rev.
51:161–175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ghosh S, May MJ and Kopp EB: NF-kappa B
and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:225–260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Buonanno A and Fischbach GD: Neuregulin
and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr
Opin Neurobiol. 11:287–296. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li BS, Ma W, Jaffe H, Zheng Y, Takahashi
S, Zhang L, Kulkarni AB and Pant HC: Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 is
involved in neuregulin-dependent activation of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase and Akt activity mediating neuronal survival. J Biol Chem.
278:35702–35709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|