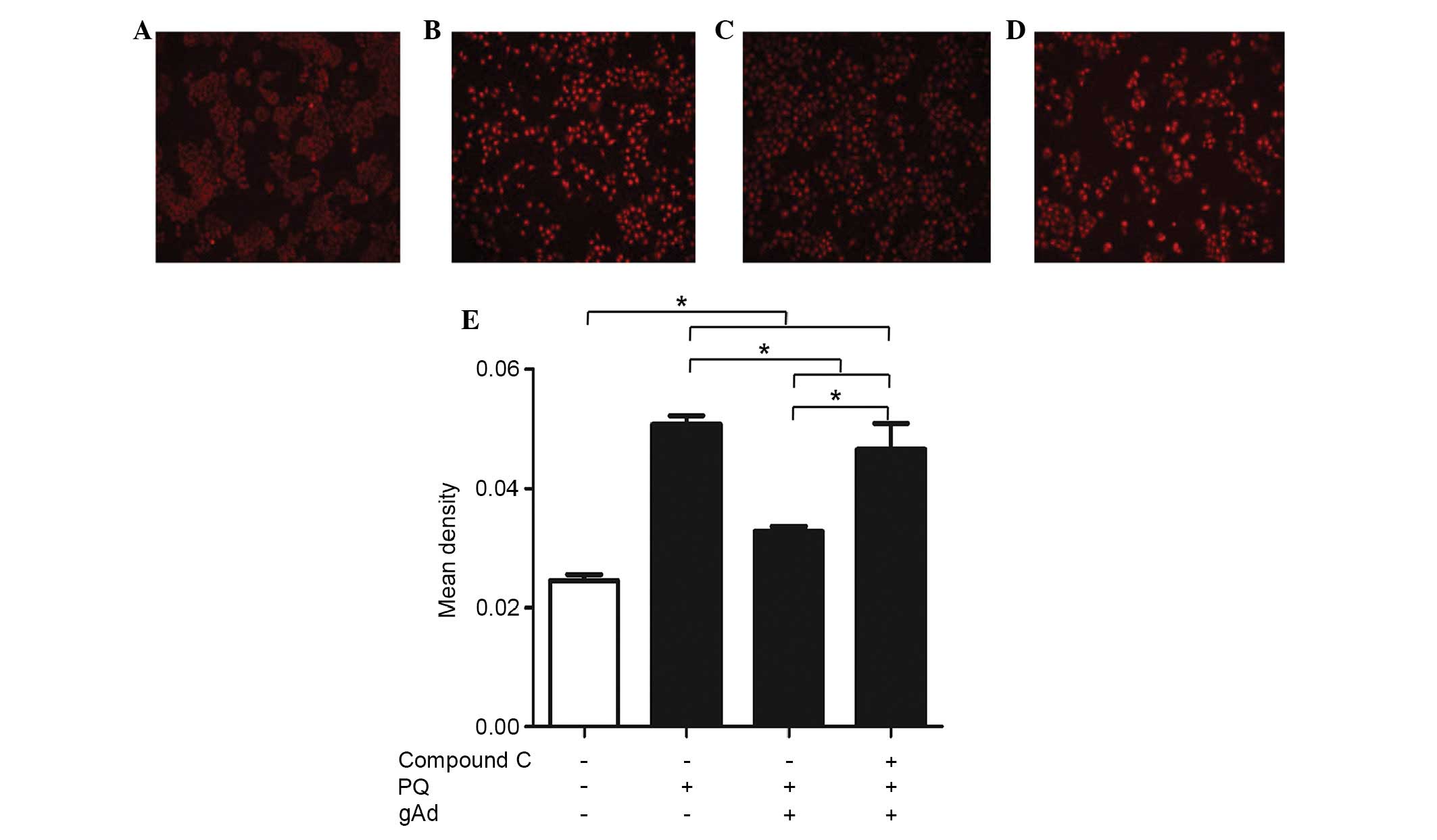
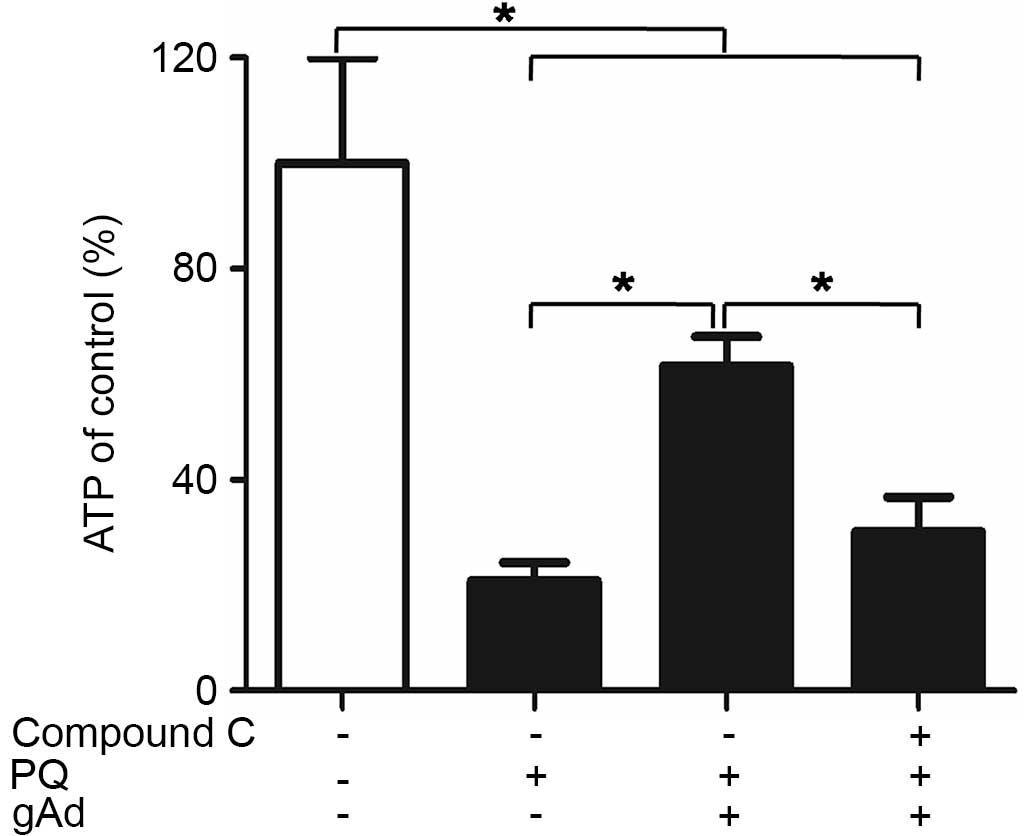
|
1
|
Vieira DN and de Azevedo-Bernarda R:
Paraquat poisoning. Pulmonary lesions. J Toxicol Clin Exp.
9:177–186. 1989.In French. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cai Q, Lu Z, Hong G, Jiang X, Wu Z, Zheng
J, Song Q and Chang Z: Recombinant adenovirus Ad-RUNrf2 reduces
paraquat-induced A549 injury. Hum Exp Toxicol. 31:1102–1112. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Golbidi S, Botta A, Gottfred S, Nusrat A,
Laher I and Ghosh S: Glutathione administration reduces
mitochondrial damage and shifts cell death from necrosis to
apoptosis in ageing diabetic mice hearts during exercise. Br J
Pharmacol. 171:5345–5360. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haagsman HP, Schuurmans EA, Batenburg JJ
and Van Golde LM: Phospholipid synthesis in isolated alveolar type
II cells exposed in vitro to paraquat and hyperoxia. Biochem J.
245:119–126. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kurokawa H, Sugiyama S, Nozaki T, Sugamura
K, Toyama K, Matsubara J, Fujisue K, Ohba K, Maeda H, Konishi M, et
al: Telmisartan enhances mitochondrial activity and alters cellular
functions in human coronary artery endothelial cells via
AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Atherosclerosis. 239:375–385.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barreto-Torres G, Hernandez JS, Jang S,
Rodríguez-Muñoz AR, Torres-Ramos CA, Basnakian AG and Javadov S:
The beneficial effects of AMP kinase activation against oxidative
stress are associated with prevention of PPARα-cyclophilin D
interaction in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
308:H749–H758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berg AH, Combs TP and Scherer PE:
ACRP30/adiponectin: An adipokine regulating glucose and lipid
metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 13:84–89. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okamoto Y, Kihara S, Funahashi T,
Matsuzawa Y and Libby P: Adiponectin: A key adipocytokine in
metabolic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond). 110:267–278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Robinson K, Prins J and Venkatesh B:
Clinical review: Adiponectin biology and its role in inflammation
and critical illness. Crit Care. 15:2212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T and Kubota N: The
physiological and pathophysiological role of adiponectin and
adiponectin receptors in the peripheral tissues and CNS. FEBS Lett.
582:74–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fang X and Sweeney G: Mechanisms
regulating energy metabolism by adiponectin in obesity and
diabetes. Biochem Soc Trans. 34:798–801. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tao L, Gao E, Jiao X, Yuan Y, Li S,
Christopher TA, Lopez BL, Koch W, Chan L, Goldstein BJ and Ma XL:
Adiponectin cardioprotection after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
involves the reduction of oxidative/nitrative stress. Circulation.
115:1408–1416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim JE, Song SE, Kim YW, Kim JY, Park SC,
Park YK, Baek SH, Lee IK and Park SY: Adiponectin inhibits
palmitate-induced apoptosis through suppression of reactive oxygen
species in endothelial cells: Involvement of cAMP/protein kinase A
and AMP-activated protein kinase. J Endocrinol. 207:35–44. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei CD, Li Y, Zheng HY, Sun KS, Tong YQ,
Dai W, et al: Globular adiponectin protects H9c2 cells from
palmitate-induced apoptosis via Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.
Lipids Health Dis. 11:1352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yan W, Zhang H, Liu P, Wang H, Liu J, Gao
C, Liu Y, Lian K, Yang L, Sun L, et al: Impaired mitochondrial
biogenesis due to dysfunctional adiponectin-AMPK-PGC-1α signaling
contributing to increased vulnerability in diabetic heart. Basic
Res Cardiol. 108:3292013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim JE, Ahn MW, Baek SH, Lee IK, Ki YW,
Kim JY, Dan JM and Park SY: AMPK activator, AICAR, inhibits
palmitate-induced apoptosis in osteoblast. Bone. 43:394–404. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Krysko DV, Vanden Berghe T, D'Herde K and
Vandenabeele P: Apoptosis and necrosis: Detection, discrimination
and phagocytosis. Methods. 44:205–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Radad K, Rausch WD and Gille G: Rotenone
induces cell death in primary dopaminergic culture by increasing
ROS production and inhibiting mitochondrial respiration. Neurochem
Int. 49:379–386. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper
PL, Wishnok JS and Tannenbaum SR: Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and
15 N.nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 126:131–138. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akao M, Ohler A, O'Rourke B and Marbán E:
Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels inhibit apoptosis
induced by oxidative stress in cardiac cells. Circ Res.
88:1267–1275. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yeh ST, Guo HR, Su YS, Lin HJ, Hou CC,
Chen HM, Chang MC and Wang YJ: Protective effects of
N-acetylcysteine treatment post acute paraquat intoxication in rats
and in human lung epithelial cells. Toxicology. 223:181–190. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Onyon LJ and Volans GN: The epidemiology
and prevention of paraquat poisoning. Hum Toxicol. 6:19–29. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gaudreault P, Karl PI and Friedman PA:
Paraquat and putrescine uptake by lung slices of fetal and newborn
rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 12:550–552. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang GY, Hirai K and Shimada H:
Mitochondrial breakage induced by the herbicide paraquat in
cultured human lung cell. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 3:181–184.
1992.
|
|
25
|
Chen YW, Yang YT, Hung DZ, Su CC and Chen
KL: Paraquat induces lung alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis via
Nrf-2-regulated mitochondrialdysfunction and ER stress. Arch
Toxicol. 86:1547–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shokrzadeh M, Shaki F, Mohammadi E,
Rezagholizadeh N and Ebrahimi F: Edaravone decreases paraquat
toxicity in a549 cells and lung isolated mitochondria. Iran J Pharm
Res. 13:675–681. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang X, Lu W, Dou T, Wang X, Lou D, Sun
X, et al: Paraquat inhibits cell viability via enhanced oxidative
stress and apoptosis in human neural progenitor cells. Chem Biol
Interact. 206:248–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang CL, Lee YC, Yang YC, Kuo TY and
Huang NK: Minocycline prevents paraquat-induced cell death through
attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial
dysfunction. Toxicol Lett. 209:203–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Helewski KJ, Kowalczyk-Ziomek GI and
Konecki J: Apoptosis and necrosis-two different ways leading to the
same target. Wiad Lek. 59:679–684. 2006.In Polish.
|
|
30
|
Kasahara A and Scorrano L: Mitochondria:
From cell death executioners to regulators of cell differentiation.
Trends Cell Biol. 24:761–770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Wang J, Xie R, Liu R and Lu Y:
Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species play an important role
in Doxorubicin-induced platelet apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci.
16:11087–11100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park M, Youn B, Zheng XL, Wu D, Xu A and
Sweeney G: Globular adiponectin, acting via AdipoR1/APPL1, protects
H9c2 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis. PLoS One.
6:e191432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin Z, Wu F, Lin S, Pan X, Jin L, Lu T,
Shi L, Wang Y, Xu A and Li X: Adiponectin protects against
acetaminophen-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and acute liver
injury by promoting autophagy in mice. J Hepatol. 61:825–831. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zheng A, Li H, Xu J, Cao K, Li H, Pu W,
Yang Z, Peng Y, Long J, Liu J and Feng Z: Hydroxytyrosol improves
mitochondrial function and reduces oxidative stress in the brain of
db/db mice: Role of AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Br J
Nutr. 113:1667–1676. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen H, Wang JP, Santen RJ and Yue W:
Adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK), a mediator
of estradiol-induced apoptosis in long-term estrogen deprived
breast cancer cells. Apoptosis. 20:821–830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen LJ, Na R, Gu M and Ran QT: Reduction
in mitochondria H2O2 protects against insulin resistance through a
mechanism of Akt and AMPK activation. Free Radic Biol Med.
47:S852009.
|
|
37
|
Pan JS, Huang L, Belousova T, Lu L, Yang
Y, Reddel R, Chang A, Ju H, DiMattia G, Tong Q, et al:
Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via an
AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol.
26:364–378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Wu SB, Wu YT, Wu TP and Wei YH: Role of
AMPK-mediated adaptive responses in human cells with mitochondrial
dysfunction to oxidative stress. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1840.1331–1344. 2014.
|
|
39
|
Qiao LP, Kinney B, Yoo HS, Lee B, Schaack
J and Shao JH: Adiponectin increases skeletal muscle mitochondrial
biogenesis by suppressing mitogen-activated protein kinase
phosphatase-1. Diabetes. 61:1463–1470. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou M, Xu A, Tam PK, Lam KS, Chan L, Hoo
RL, Liu J, Chow KH and Wang Y: Mitochondrial dysfunction
contributes to the increased vulnerabilities of adiponectin
knockout mice to liver injury. Hepatology. 48:1087–1096. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yamauchi T, Iwabu M, Okada-Iwabu M and
Kadowaki T: Adiponectin receptors: A review of their structure,
function and how they work. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab.
28:15–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|