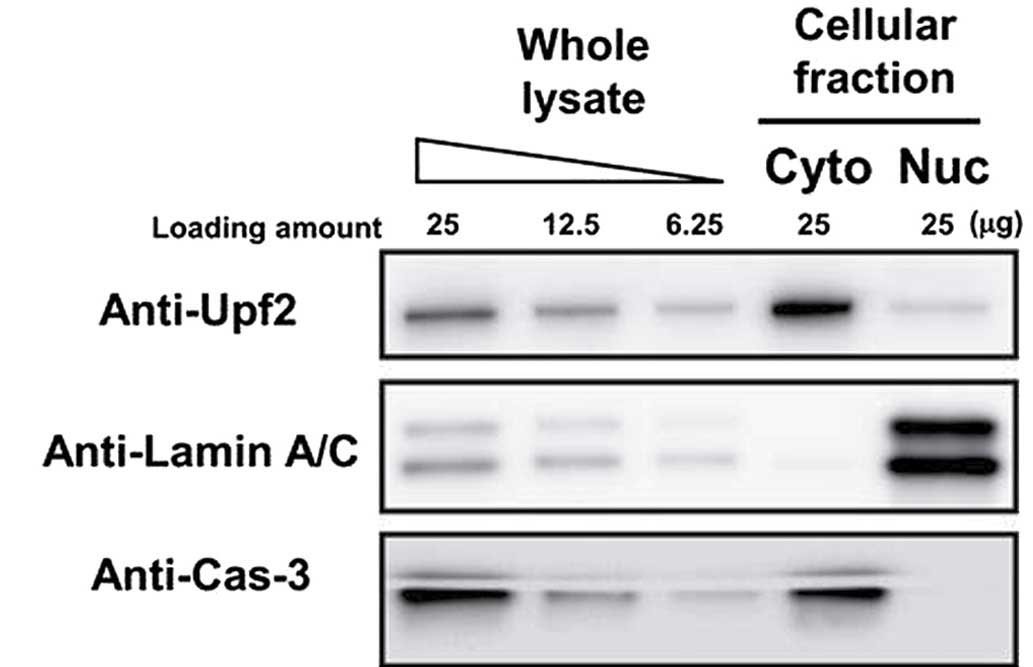
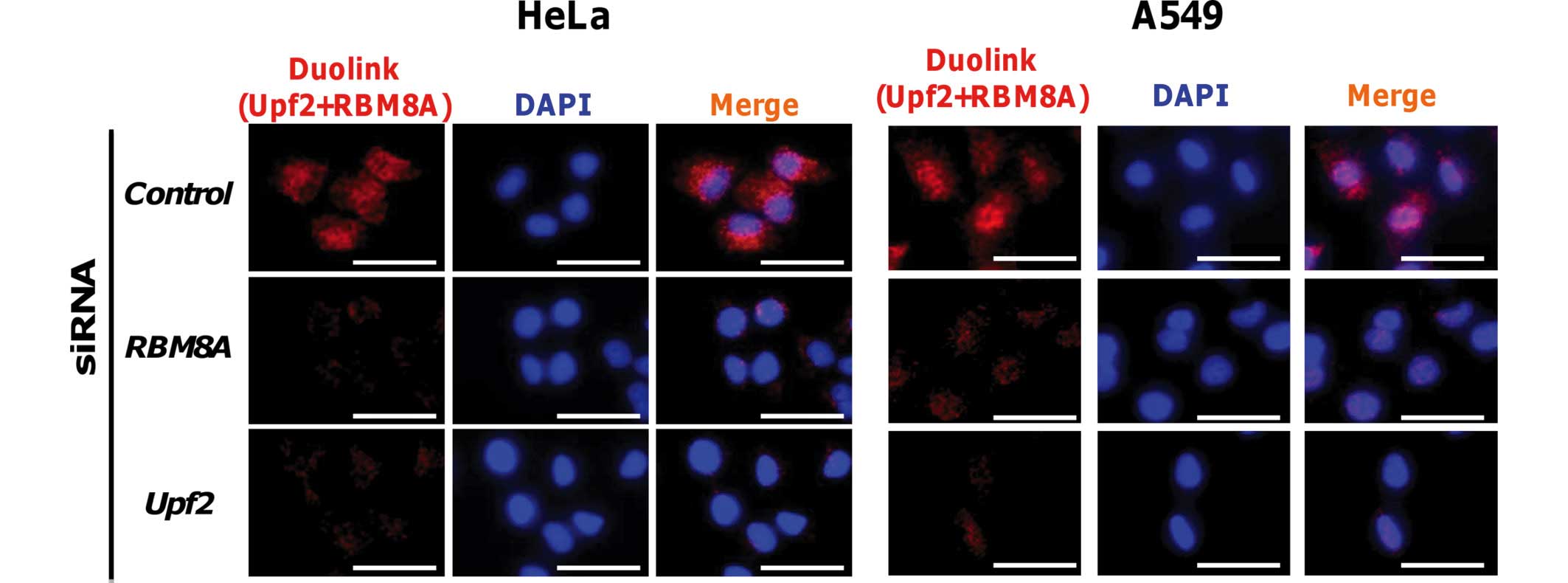
|
1
|
Nguyen LS, Kim HG, Rosenfeld JA, Shen Y,
Gusella JF, Lacassie Y, Layman LC, Shaffer LG and Gécz J:
Contribution of copy number variants involving nonsense-medated
mRNA decay pathway genes to neuro-developmental disorders. Hum Mol
Genet. 22:1816–1825. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tarpey PS, Raymond FL, Nguyen LS,
Rodriguez J, Hackett A, Vandeleur L, Smith R, Shoubridge C, Edkins
S, Stevens C, et al: Mutations in UPF3B, a member of the
nonsense-mediated mRNA decay complex, cause syndromic and
nonsyndromic mental retardation. Nat Genet. 39:1127–1133. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bühler M, Wilkinson MF and Mühlemann O:
Intranuclear degradation of nonsense codon-containing mRNA. EMBO
Rep. 3:646–651. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chamieh H, Ballut L, Bonneau F and Le Hir
H: NMD factors UPF2 and UPF3 bridge UPF1 to the exon junction
complex and stimulate its RNA helicase activity. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 15:85–93. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mühlemann O, Eberle AB, Stalder L and
Zamudio Orozco R: Recognition and elimination of nonsense mRNA.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1779:538–549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maquat LE, Tarn WY and Isken O: The
pioneer round of translation: Features and functions. Cell.
142:368–374. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gehring NH, Neu-Yilik G, Schell T, Hentze
MW and Kulozik AE: Y14 and hUpf3b form an NMD-activating complex.
Mol Cell. 11:939–949. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gehring NH, Lamprinaki S, Hentze MW and
Kulozik AE: The hierarchy of exon-junction complex assembly by the
spliceosome explains key features of mammalian nonsense-mediated
mRNA decay. PLoS Biol. 7:e10001202009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kataoka N, Yong J, Kim VN, Velazquez F,
Perkinson RA, Wang F and Dreyfuss G: Pre-mRNA splicing imprints
mRNA in the nucleus with a novel RNA-binding protein that persists
in the cytoplasm. Mol Cell. 6:673–682. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim VN, Kataoka N and Dreyfuss G: Role of
the nonsense-mediated decay factor hUpf3 in the splicing-dependent
exon-exon junction complex. Science. 293:1832–1836. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Serin G, Gersappe A, Black JD, Aronoff R
and Maquat LE: Identification and characterization of human
orthologues to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Upf2 protein and Upf3
protein (Caenorhabditis elegans SMG-4). Mol Cell Biol. 21:209–223.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kashima I, Yamashita A, Izumi N, Kataoka
N, Morishita R, Hoshino S, Ohno M, Dreyfuss G and Ohno S: Binding
of a novel SMG-1-Upf1-eRF1-eRF3 complex (SURF) to the exon junction
complex triggers Upf1 phosphorylation and nonsense-mediated mRNA
decay. Genes Dev. 20:355–367. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lykke-Andersen J, Shu MD and Steitz JA:
Human Upf proteins target an mRNA for nonsense-mediated decay when
bound downstream of a termination codon. Cell. 103:1121–1131. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim VN, Yong J, Kataoka N, Abel L, Diem MD
and Dreyfuss G: The Y14 protein communicates to the cytoplasm the
position of exon-exon junctions. EMBO J. 20:2062–2068. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Le Hir H, Gatfield D, Izaurralde E and
Moore MJ: The exon-exon junction complex provides a binding
platform for factors involved in mRNA export and nonsense-mediated
mRNA decay. EMBO J. 20:4987–4997. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schell T, Kulozik AE and Hentze MW:
Integration of splicing, transport and translation to achieve mRNA
quality control by the nonsense-mediated decay pathway. Genome
Biol. 3:REVIEWS10062002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ishigaki Y, Li X, Serin G and Maquat LE:
Evidence for a pioneer round of mRNA translation: mRNAs subject to
nonsense-mediated decay in mammalian cells are bound by CBP80 and
CBP20. Cell. 106:607–617. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang YF, Imam JS and Wilkinson MF: The
nonsense-mediated decay RNA surveillance pathway. Annu Rev Biochem.
76:51–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maquat LE: Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay:
Splicing, translation and mRNP dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:89–99. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh G, Jakob S, Kleedehn MG and
Lykke-Andersen J: Communication with the exon-junction complex and
activation of nonsense-mediated decay by human Upf proteins occur
in the cytoplasm. Mol Cell. 27:780–792. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao X, Nogawa A, Matsunaga T, Takegami T,
Nakagawa H and Ishigaki Y: Proteasome inhibitors and knockdown of
SMG1 cause accumulation of Upf1 and Upf2 in human cells. Int J
Oncol. 44:222–228. 2014.
|
|
22
|
Ishigaki Y, Nakamura Y, Tatsuno T,
Hashimoto M, Shimasaki T, Iwabuchi K and Tomosugi N: Depletion of
RNA-binding protein RBM8A (Y14) causes cell cycle deficiency and
apoptosis in human cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 238:889–897.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ishigaki Y, Nakamura Y, Tatsuno T,
Hashimoto M, Iwabuchi K and Tomosugi N: RNA binding protein RBM8A
(Y14) and MAGOH localize to centrosome in human A549 cells.
Histochem Cell Biol. 141:101–109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Söderberg O, Gullberg M, Jarvius M,
Ridderstråle K, Leuchowius KJ, Jarvius J, Wester K, Hydbring P,
Bahram F, Larsson LG and Landegren U: Direct observation of
individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity
ligation. Nat Methods. 3:995–1000. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hervouet E, Lalier L, Debien E, Cheray M,
Geairon A, Rogniaux H, Loussouarn D, Martin SA, Vallette FM and
Cartron PF: Disruption of Dnmt1/PCNA/UHRF1 interactions promotes
tumorigenesis from human and mice glial cells. PLoS One.
5:e113332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spector DL, Fu XD and Maniatis T:
Associations between distinct pre-mRNA splicing components and the
cell nucleus. EMBO J. 10:3467–3481. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
den Engelsman J, Bennink EJ, Doerwald L,
Onnekink C, Wunderink L, Andley UP, Kato K, de Jong WW and Boelens
WC: Mimicking phosphorylation of the small heat-shock protein
alphaB-crystallin recruits the F-box protein FBX4 to nuclear SC35
speckles. Eur J Biochem. 271:4195–4203. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zirwes RF, Eilbracht J, Kneissel S and
Schmidt-Zachmann MS: A novel helicase-type protein in the
nucleplus: Protein NOH61. Mol Cell Biol. 11:1153–1167. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Schmidt U, Richter K, Berger AB and
Lichter P: In vivo BiFC analysis of Y14 and NXF1 mRNA export
complexes: Preferential localization within and around SC35
domains. J Cell Biol. 172:373–381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wittmann J, Hol EM and Jäck HM: hUPF2
silencing identifies physiologic substrates of mammalian
nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Mol Cell Biol. 26:1272–1287. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|