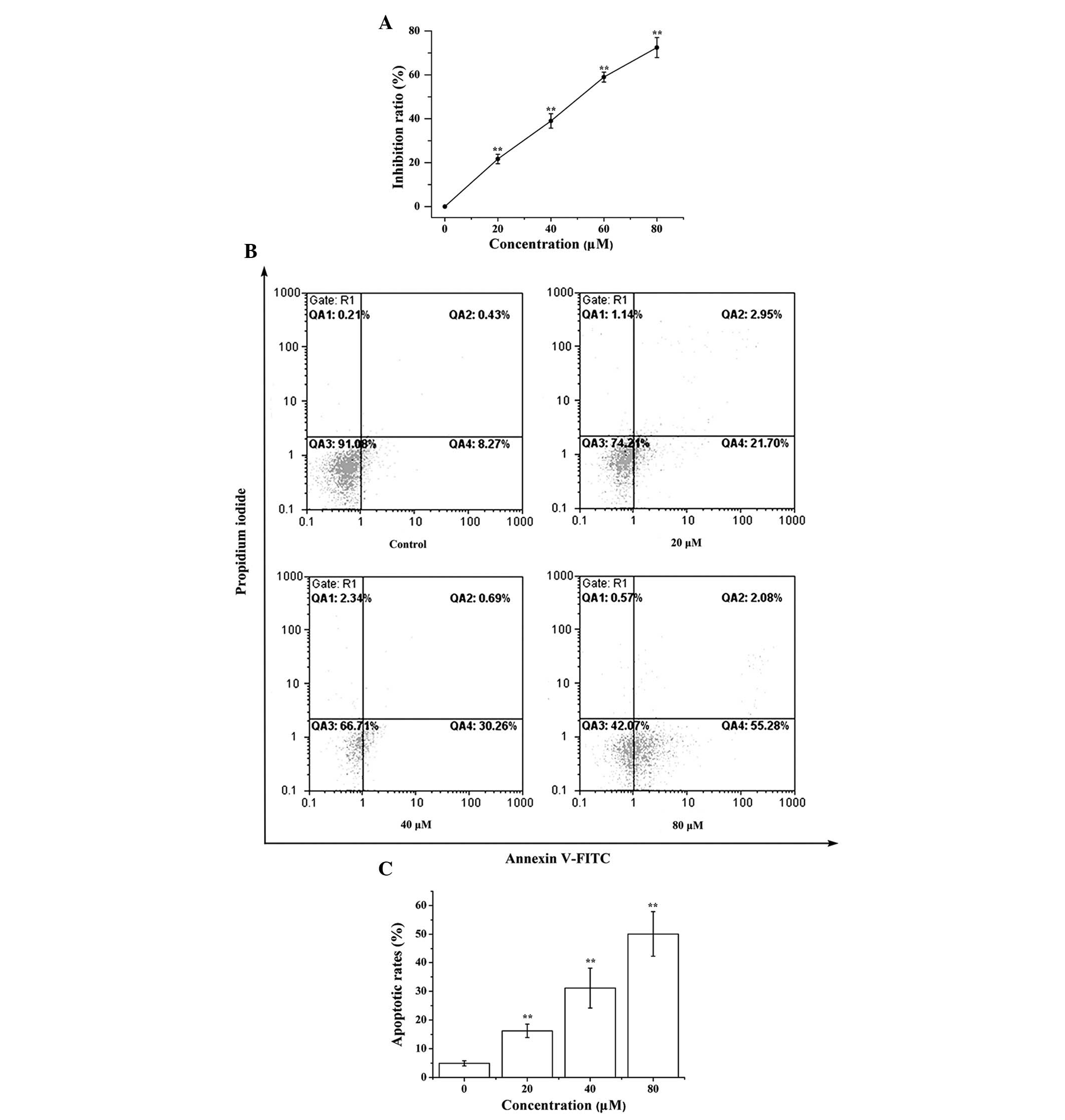
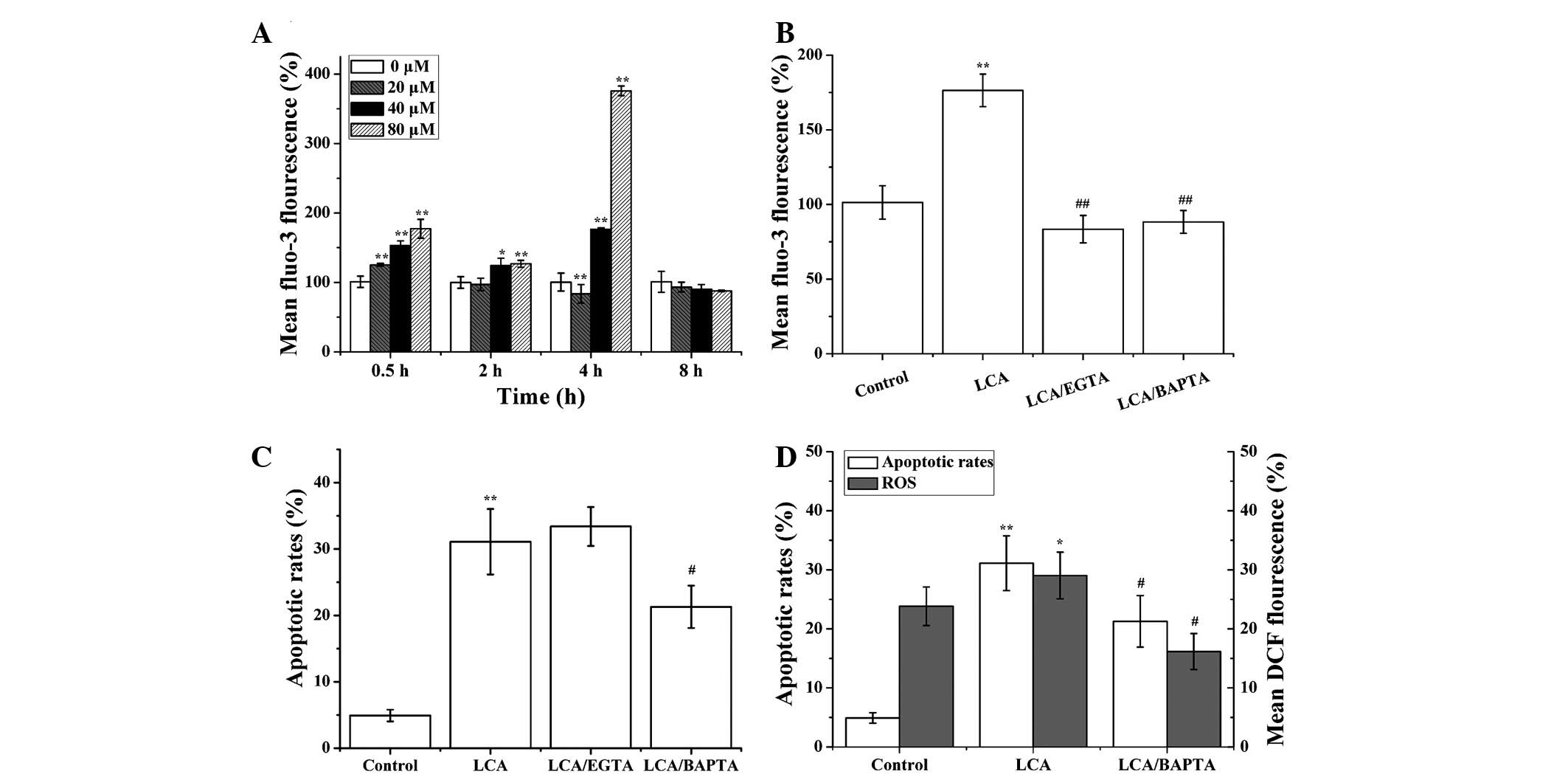
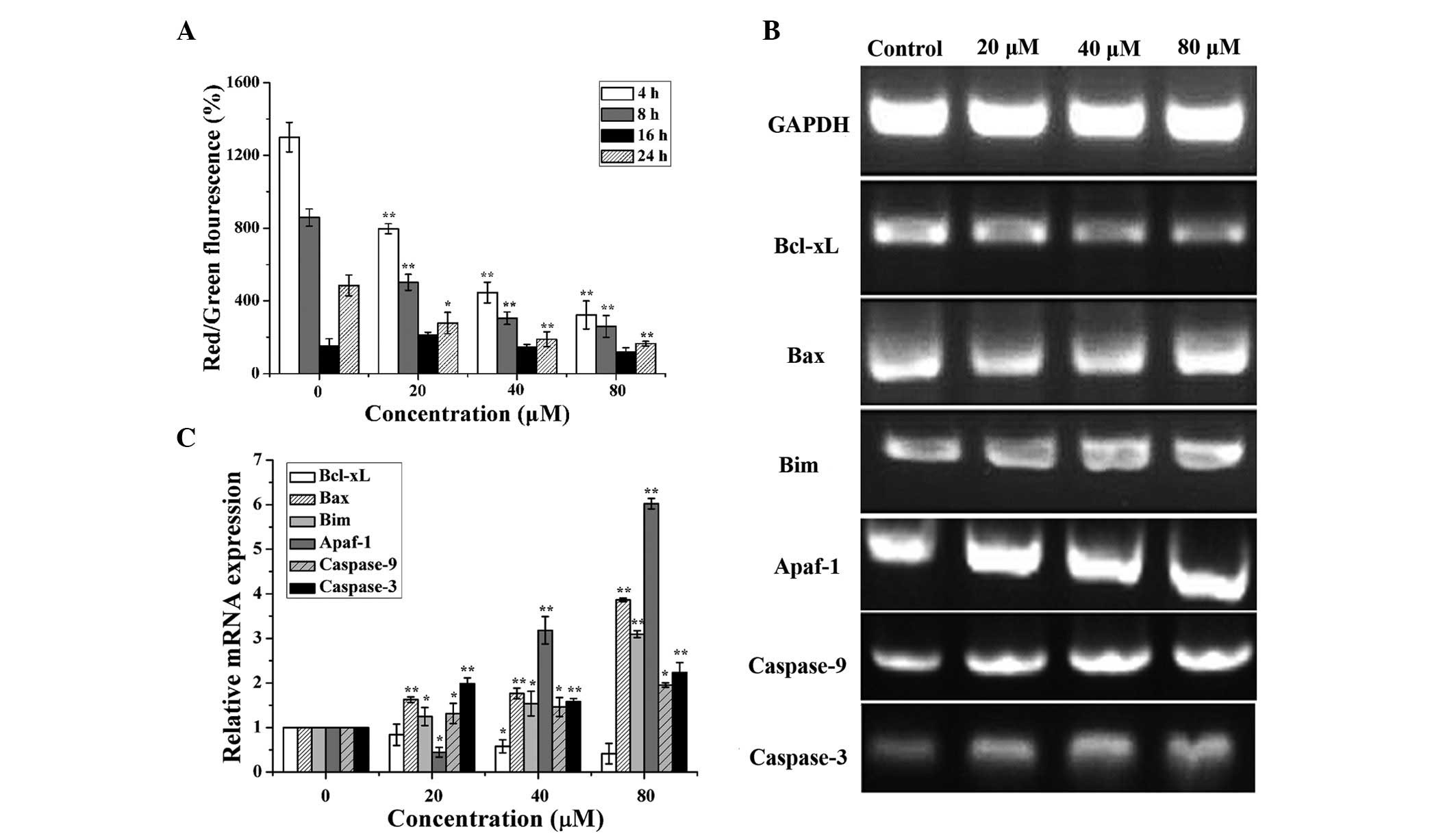
|
1
|
Wang X, Feng Y, Wang N, Cheung F, Tan HY,
Zhong S, Li C and Kobayashi S: Chinese medicines induce cell death:
The molecular and cellular mechanisms for cancer therapy. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:5303422014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lu C and Mei X: Study on anti-tumor
activity of extracts from cultured cells of Taxus chinensis. Zhong
Yao Cai. 26:335–337. 2003.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Q, Du H, Geng G, Zhou H, Xu M, Cao H,
Zhang B, Song G and Hu T: Matrine inhibits proliferation and
induces apoptosis via BID-mediated mitochondrial pathway in
esophageal cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 41:3009–3020. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao H, Jiang JT and Zheng QS: Advance in
studies on pharmacological effects of licochalcone A. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 38:3814–3818. 2013.In Chinese.
|
|
5
|
Fukai T, Marumo A, Kaitou K, Kanda T,
Terada S and Nomura T: Anti-Helicobacter pylori flavonoids from
licorice extract. Life Sci. 71:1449–1463. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Funakoshi-Tago M, Nakamura K, Tsuruya K,
Hatanaka M, Mashino T, Sonoda Y and Kasahara T: The fixed structure
of Licochalcone A by alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone is necessary
for anti-inflammatory activity through the inhibition of NF-kappaB
activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:562–571. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiao XY, Hao M, Yang XY, Ba Q, Li M, Ni
SJ, Wang LS and Du X: Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric
cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression and inducing
apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 302:69–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng Q and Ye M: Chemical analysis of
Chinese herbal medicine Gan-Cao (licorice). J Chromatogr A.
1216:1954–1969. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Feldman M and Grenier D: Cranberry
proanthocyanidins act in synergy with licochalcone A to reduce
Porphyromonas gingivalis growth and virulence properties, and to
suppress cytokine secretion by macrophages. J Appl Microbiol.
113:438–447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Messier C and Grenier D: Effect of
licorice compounds licochalcone A, glabridin and glycyrrhizic acid
on growth and virulence properties of Candida albicans. Mycoses.
54:e801–e806. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Furusawa J, Funakoshi-Tago M, Mashino T,
Tago K, Inoue H, Sonoda Y and Kasahara T: Glycyrrhiza
inflata-derived chalcones, Licochalcone A, Licochalcone B and
Licochalcone D, inhibit phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 in LPS
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:499–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee CS, Kwak SW, Kim YJ, Lee SA, Park ES,
Myung SC, Kim W, Lee MS and Lee JJ: Guanylate cyclase activator
YC-1 potentiates apoptotic effect of licochalcone A on human
epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells via activation of death receptor
and mitochondrial pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 683:54–62. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M,
Decaudin D, Macho A, Hirsch T, Susin SA, Petit PX, Mignotte B and
Kroemer G: Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane
potential and generation of reactive oxygen species in early
programmed cell death. J Exp Med. 182:367–377. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim J, Choi TG, Ding Y, Kim Y, Ha KS, Lee
KH, Kang I, Ha J, Kaufman RJ, Lee J, et al: Overexpressed
cyclophilin B suppresses apoptosis associated with ROS and
Ca2+ homeostasis after ER stress. J Cell Sci.
121:3636–3648. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Santos CX, Tanaka LY, Wosniak J and
Laurindo FR: Mechanisms and implications of reactive oxygen species
generation during the unfolded protein response: Roles of
endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductases, mitochondrial electron
transport, and NADPH oxidase. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:2409–2427.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yan Y, Wei CL, Zhang WR, Cheng HP and Liu
J: Cross-talk between calcium and reactive oxygen species
signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:821–826. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Berridge MJ, Lipp P and Bootman MD: The
versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 1:11–21. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nakagawa T and Yuan J: Cross-talk between
two cysteine protease families. Activation of caspase-12 by calpain
in apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 150:887–894. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Martinez JA, Zhang Z, Svetlov SI, Hayes
RL, Wang KK and Larner SF: Calpain and caspase processing of
caspase-12 contribute to the ER stress-induced cell death pathway
in differentiated PC12 cells. Apoptosis. 15:1480–1493. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan Y, Dourdin N, Wu C, De Veyra T, Elce
JS and Greer PA: Ubiquitous calpains promote caspase-12 and JNK
activation during endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 281:16016–16024. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choi AY, Choi JH, Hwang KY, Jeong YJ, Choe
W, Yoon KS, Ha J, Kim SS, Youn JH, Yeo EJ and Kang I: Licochalcone
A induces apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress via a
phospholipase Cγ1-, Ca(2+)-, and reactive oxygen species-dependent
pathway in HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Apoptosis.
19:682–697. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yuan X, Li D, Zhao H, Jiang J, Wang P, Ma
X, Sun X and Zheng Q: Licochalcone A-induced human bladder cancer
T24 cells apoptosis triggered by mitochondria dysfunction and
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomed Res Int. 2013:4742722013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A,
McMahon J, Vistica D, Warren JT, Bokesch H, Kenney S and Boyd MR:
New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:1107–1112. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hockenbery D, Nuñez G, Milliman C,
Schreiber RD and Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial
membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature.
348:334–346. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jung JI, Lim SS, Choi HJ, Cho HJ, Shin HK,
Kim EJ, Chung WY, Park KK and Park JH: Isoliquiritigenin induces
apoptosis by depolarizing mitochondrial membranes in prostate
cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 17:689–696. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vanden Hoek TL, Li C, Shao Z, Schumacker
PT and Becker LB: Significant levels of oxidants are generated by
isolated cardiomyocytes during ischemia prior to reperfusion. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 29:2571–2583. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reers M, Smith TW and Chen LB: J-aggregate
formation of a carbocyanine as a quantitative fluorescent indicator
of membrane potential. Biochemistry. 30:4480–4486. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carthagena L, Bergamaschi A, Luna JM,
David A, Uchil PD, Margottin-Goguet F, Mothes W, Hazan U, Transy C,
Pancino G and Nisole S: Human TRIM gene expression in response to
interferons. PLoS One. 4:e48942009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rafi MM, Vastano BC, Zhu N, Ho CT, Ghai G,
Rosen RT, Gallo MA and DiPaola RS: Novel polyphenol molecule
isolated from licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra) induces apoptosis,
G2/M cell cycle arrest, and Bcl-2 phosphorylation in tumor cell
lines. J Agric Food Chem. 50:677–684. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang J, Yuan X, Zhao H, Yan X, Sun X and
Zheng Q: Licochalcone A inhibiting proliferation of bladder cancer
T24 cells by inducing reactive oxygen species production. Biomed
Mater Eng. 24:1019–1025. 2014.
|
|
32
|
Kaiser N and Edelman IS: Calcium
dependence of glucocorticoid-induced lymphocytolysis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 74:638–642. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McConkey DJ and Orrenius S: The role of
calcium in the regulation of apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
239:357–366. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sergeev IN: Calcium as a mediator of
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced apoptosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 89–90:419–425. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mekahli D, Bultynck G, Parys JB, De Smedt
H and Missiaen L: Endoplasmic-reticulum calcium depletion and
disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3:a0043172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Matsuzaki S, Hiratsuka T, Kuwahara R,
Katayama T and Tohyama M: Caspase-4 is partially cleaved by calpain
via the impairment of Ca2+ homeostasis under the ER stress.
Neurochem Int. 56:352–356. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|