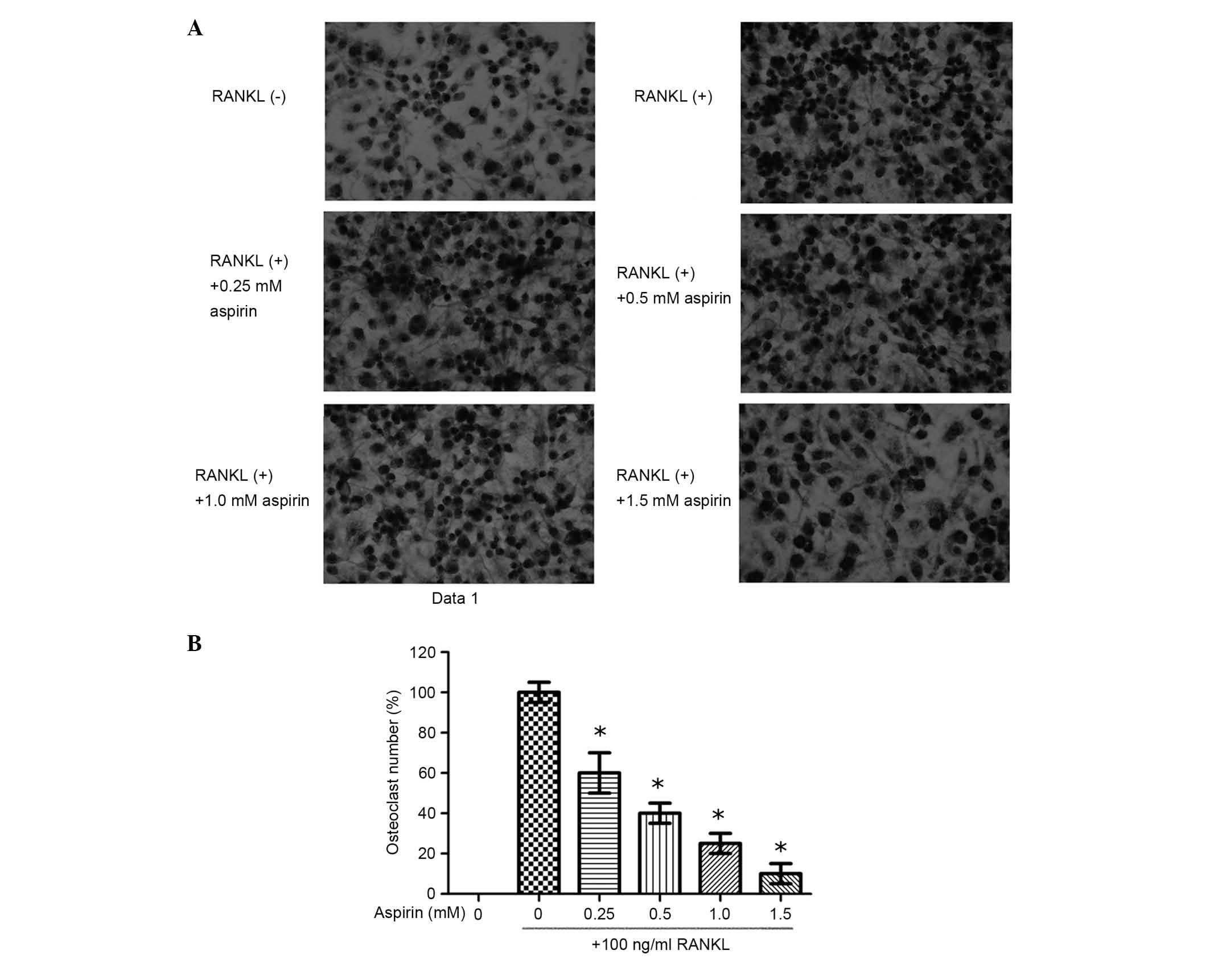
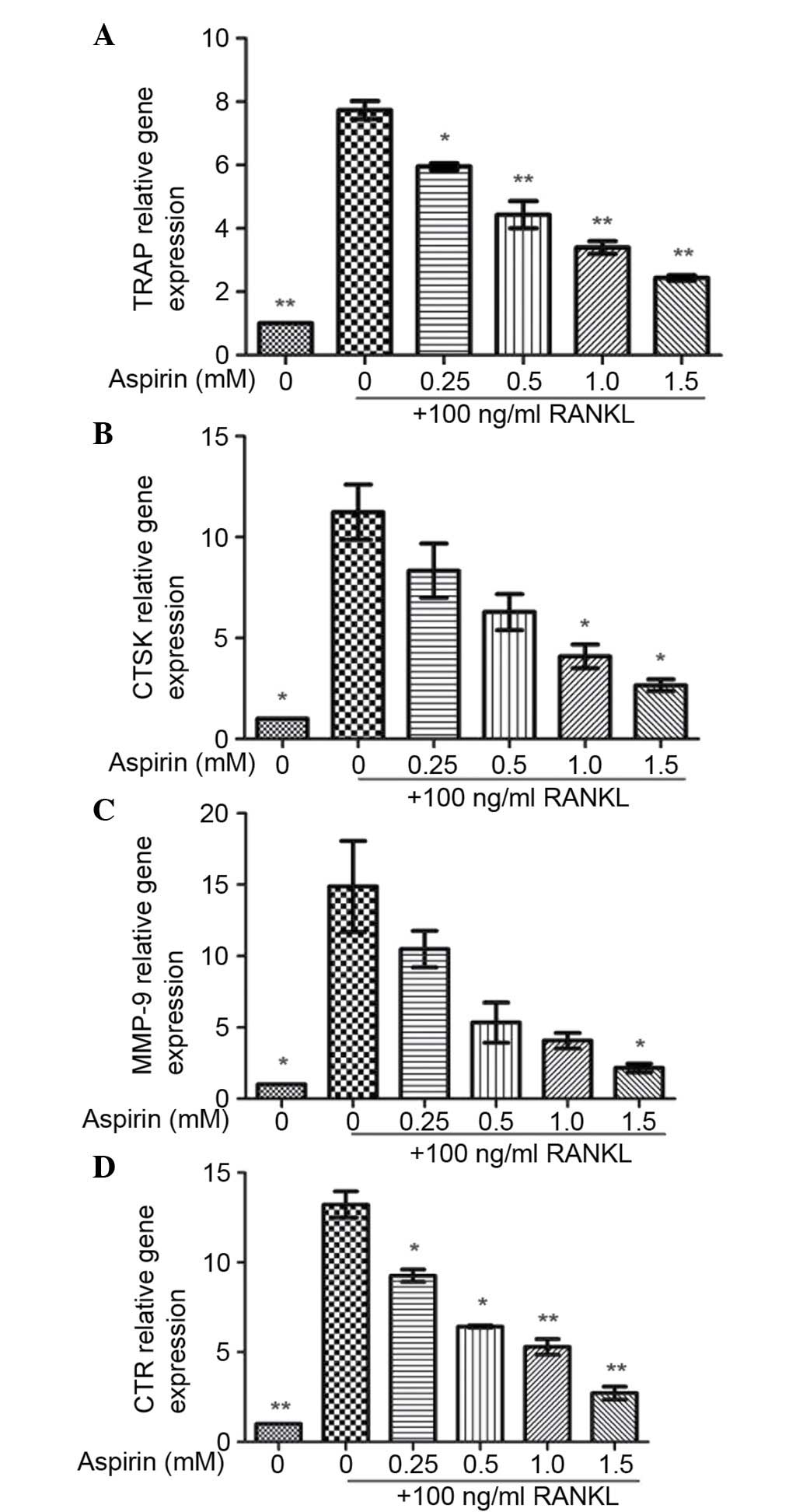
|
1
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Armstrong AP, Tometsko ME, Glaccum M,
Sutherland CL, Cosman D and Dougall WC: A RANK/TRAF6-dependent
signal transduction pathway is essential for osteoclast
cytoskeletal organization and resorptive function. J Biol Chem.
277:44347–44356. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei S, Teitelbaum SL, Wang MW and Ross FP:
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa b ligand activates
nuclear factor-kappa b in osteoclast precursors. Endocrinology.
142:1290–1295. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Saito T, Osada H and
Tsujimoto M: Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor
activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL). J Biol Chem.
275:31155–31161. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
David JP, Sabapathy K, Hoffmann O,
Idarraga MH and Wagner EF: JNK1 modulates osteoclastogenesis
through both c-Jun phosphorylation-dependent and -independent
mechanisms. J Cell Sci. 115:4317–4325. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee SE, Woo KM, Kim SY, Kim HM, Kwack K,
Lee ZH and Kim HH: The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38, and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved
inosteoclast differentiation. Bone. 30:71–77. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K, Kim S, Suematsu
A, Kobayashi E, Iwata T, Ohnishi H, Matozaki T, Kodama T, et al:
Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with
RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature. 428:758–763. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baltas CS, Balanika AP, Raptou PD, Tournis
S and Lyritis GP; Hellenic guidelines on bone densitometry working
group: Clinical practice guidelines proposed by the Hellenic
Foundation of Osteoporosis for the management of osteoporosis based
on DXA results. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 5:388–392.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Valverde P: Pharmacotherapies to manage
bone loss-associated diseases: A quest for the perfect
benefit-to-risk ratio. Curr Med Chem. 15:284–304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L and Seeram NP: Further investigation
into maple syrup yields 3 new lignans, a new phenylpropanoid, and
26 other phytochemicals. J Agric Food Chem. 59:7708–7716. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bauer DC, Orwoll ES, Fox KM, Vogt TM, Lane
NE, Hochberg MC, Stone K and Nevitt MC: Aspirin and NSAID use in
older women: Effect on bone mineral density and fracture risk.
Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. J Bone Miner Res.
11:29–35. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen ZW, Wu ZX, Sang HX, Qin GL, Wang LS,
Feng J, Wang J, Li XJ, Wang JC and Zhang D: Effect of aspirin
administration for the treatment of osteoporosis in ovariectomized
rat model. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 91:925–929. 2011.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Raisz LG: Pathogenesis of osteoporosis:
Concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 115:3318–3325.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grigoriadis AE, Wang ZQ, Cecchini MG,
Hofstetter W, Felix R, Fleisch HA and Wagner EF: c-Fos: A key
regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone
remodeling. Science. 266:443–448. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mansky KC, Sankar U, Han J and Ostrowski
MC: Microphthalmia transcription factor is a target of the p38 MAPK
pathway in response to receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand
signaling. J Biol Chem. 277:11077–11083. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gingery A, Bradley E, Shaw A and Oursler
MJ: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase coordinately activates the
MEK/ERK and AKT/NFkappaB pathways to maintain osteoclast survival.
J Cell Biochem. 89:165–179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mohamed SG, Sugiyama E, Shinoda K, Taki H,
Hounoki H, Abdel-Aziz HO, Maruyama M, Kobayashi M, Ogawa H and
Miyahara T: Interleukin-10 inhibits RANKL-mediated expression of
NFATc1 in part via suppression of c-Fos and c-Jun in RAW264.7 cells
and mouse bone marrow cells. Bone. 41:592–602. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Anusaksathien O, Laplace C, Li X, Ren Y,
Peng L, Goldring SR and Galson DL: Tissue-specific and ubiquitous
promoters direct the expression of alternatively spliced
transcripts from the calcitonin receptor gene. J Biol Chem.
276:22663–22674. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Motyckova G, Weilbaecher KN, Horstmann M,
Rieman DJ, Fisher DZ and Fisher DE: Linking osteopetrosis and
pycnodysostosis: Regulation of cathepsin K expression by the
microphthalmia transcription factor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:5798–5803. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reddy SV, Hundley JE, Windle JJ, Alcantara
O, Linn R, Leach RJ, Boldt DH and Roodman GD: Characterization of
the mouse tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) gene promoter.
J Bone Miner Res. 10:601–606. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choi HJ, Park YR, Nepal M, Choi BY, Cho
NP, Choi SH, Heo SR, Kim HS, Yang MS and Soh Y: Inhibition of
osteoclastogenic differentiation by Ikarisoside A in RAW 264.7
cells via JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol.
636:28–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bharti AC, Takada Y and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) inhibits receptor activator of
NF-kappa B ligand-induced NF-kappa B activation in osteoclast
precursors and suppresses osteoclastogenesis. J Immunol.
172:5940–5947. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghosh S and Karin M: Missing pieces in the
NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 109(Suppl): S81–S96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karin M, Yamamoto Y and Wang QM: The IKK
NF-kappa B system: A treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 3:17–26. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|