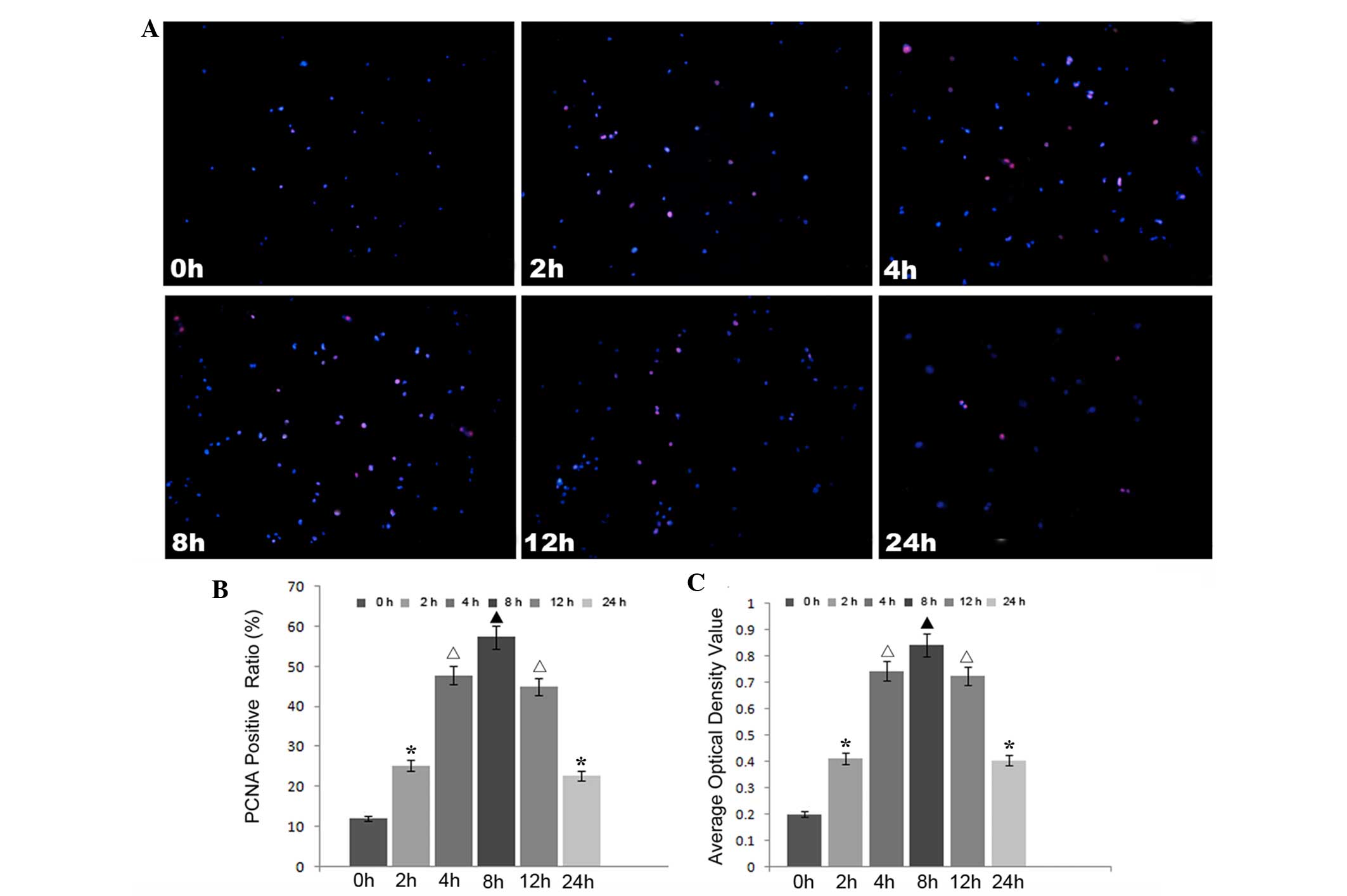
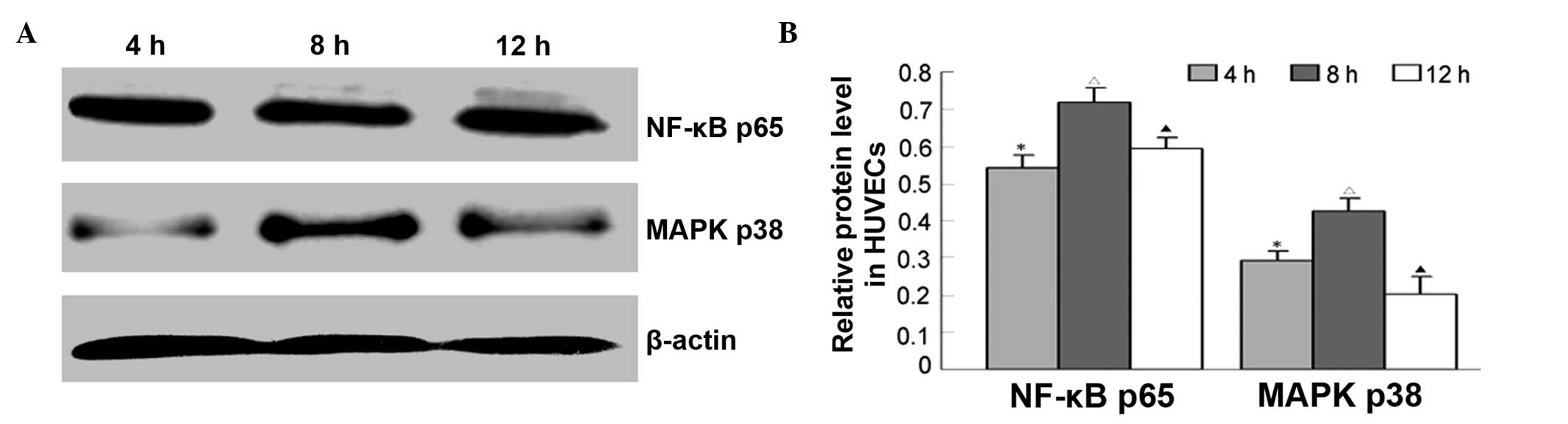
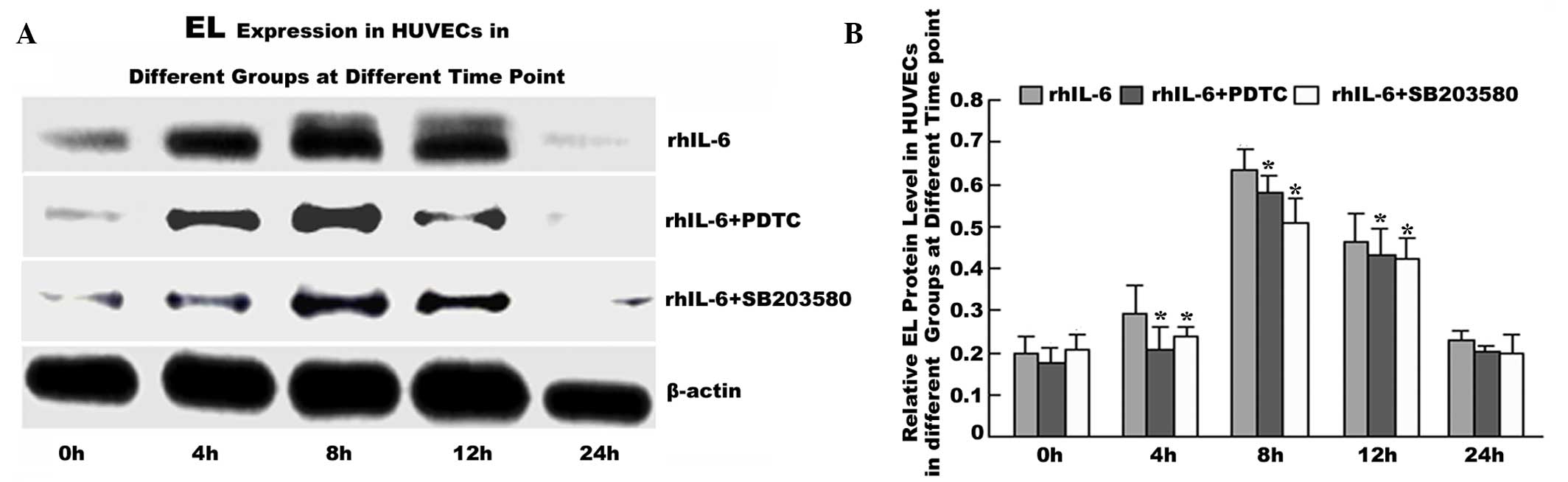
|
1
|
Rattazzi M, Puato M, Faggin E, Bertipaglia
B, Zambon A and Pauletto P: C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in
vascular disease: Culprits or passive bystanders? J Hypertens.
21:1787–1803. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bernberg E, Ulleryd MA, Johansson ME and
Bergström GM: Social disruption stress increases IL-6 levels and
accelerates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Atherosclerosis.
221:359–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nishimoto N: Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid
arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 18:277–281. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barton BE: Interleukin-6 and new
strategies for the treatment of cancer, hyperproliferative diseases
and paraneoplastic syndromes. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 9:737–752.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Smolen JS and Maini RN: Interleukin-6: A
new therapeutic target. Arthritis Res Ther. 8:S52006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL, Mysler
EF, da Silva NA, Alecock E, Woodworth T and Gomez-Reino JJ:
Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease
activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to
disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: The tocilizumab in
combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
therapy study. Arthritis Rheum. 58:2968–2980. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Williams SC: First IL-6-blocking drug
nears approval for rare blood disorder. Nat Med. 19:11932013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jaye M, Lynch KJ, Krawiec J, Marchadier D,
Maugeais C, Doan K, South V, Amin D, Perrone M and Rader DJ: A
novel endothelial-derived lipase that modulates HDL metabolism. Nat
Genet. 21:424–428. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ishida T, Choi S, Kundu RK, Hirata K,
Rubin EM, Cooper AD and Quertermous T: Endothelial lipase is a
major determinant of HDL level. J Clin Invest. 111:347–355. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gordon DJ and Rifkind BM: High-density
lipoproteins-the clinical implications of recent studies. N Engl J
Med. 321:1311–1316. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Broedl UC, Maugeais C, Millar JS, Jin W,
Moore RE, Fuki IV, Marchadier D, Glick JM and Rader DJ: Endothelial
lipase promotes the catabolism of ApoB-containing lipoproteins.
Circ Res. 94:1554–1561. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ishida T, Choi SY, Kundu RK, Spin J,
Yamashita T, Hirata K, Kojima Y, Yokoyama M, Cooper AD and
Quertermous T: Endothelial lipase modulates susceptibility to
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice. J Biol Chem.
279:45085–45092. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jin W, Sun GS, Marchadier D, Octtaviani E,
Glick JM and Rader DJ: Endothelial cells secrete triglyceride
lipase and phospholipase activities in response to cytokines as a
result of endothelial lipase. Circ Res. 92:644–650. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi SY, Hirata K, Ishida T, Quertermous T
and Cooper AD: Endothelial lipase: A new lipase on the block. J
Lipid Res. 43:1763–1769. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L and Ulevitch RJ: A
MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian
cells. Science. 265:808–811. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Monaco C, Andreakos E, Kiriakidis S, Mauri
C, Bicknell C, Foxwell B, Cheshire N, Paleolog E and Feldmann M:
Canonical pathway of nuclear factor kappa B activation selectively
regulates proinflammatory and prothrombotic responses in human
atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 101:5634–5639. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Annema W and Tietge UJ: Role of hepatic
lipase and endothelial lipase in high-density lipoprotein-mediated
reverse cholesterol transport. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:193–205.
2005.
|
|
18
|
Badellino KO, Wolfe ML, Rielly MP and
Rader DJ: Endothelial lipase concentrations are increased in
metabolic syndrome and associated with coronary atherosclerosis.
PLoS Med. 3:e222006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cai G, He G and Qi C: The association
between endothelial lipase 2384A/C gene polymorphism and acute
coronary syndrome in a Chinese population. Mol Biol Rep.
39:9879–9884. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singaraja RR, Sivapalaratnam S, Hovingh K,
Dubé MP, Castro-Perez J, Collins HL, Adelman SJ, Riwanto M, Manz J,
Hubbard B, et al: The impact of partial and complete loss of
function mutations in endothelial lipase on high-density
lipoprotein levels and functionality in humans. Circ Cardiovasc
Genet. 6:54–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Fang YQ, Huang L and Li AM: Correlation
between the expression of endothelial lipase in CECs and the
improved jeopardy score in CAD patients. Chinese Journal of
Critical Care Medicine. 28:5–8. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Hirata K, Ishida T, Matsushita H, Tsao PS
and Quertermous T: Regulated expression of endothelial cell-derived
lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 272:90–93. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin W, Sun GS, Marchadier D, Octtaviani E,
Glick JM and Rader DJ: Endothelial cells secrete triglyceride
lipase and phospholipase activities in response to cytokines as a
result of endothelial lipase. Circ Res. 92:644–650. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Badellino KO, Wolfe ML, Reilly MP and
Rader DJ: Endothelial lipase is increased in vivo by inflammation
in humans. Circulation. 117:678–685. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paradis ME, Badellino KO, Rader DJ,
Deshaies Y, Couture P, Archer WR, Bergeron N and Lamarche B:
Endothelial lipase is associated with inflammation in humans. J
Lipid Res. 47:2808–2813. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yogi A, Callera GE, Aranha AB, Antunes TT,
Graham D, McBride M, Dominiczak A and Touyz RM:
Sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced inflammation involves receptor
tyrosine kinase transactivation in vascular cells: Upregulation in
hypertension. Hypertension. 57:809–818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gerthoffer WT: Mechanisms of vascular
smooth muscle cell migration. Circ Res. 100:607–621. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jacobsen JC, Mulvany MJ and
Holstein-Rathlou NH: A mechanism for arteriolar remodeling based on
maintenance of smooth muscle cell activation. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 294:R1379–R1389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Paravicini TM, Montezano AC, Yusuf H and
Touyz RM: Activation of vascular p38 MAPK by mechanical stretch is
independent of c-Src and NADPH oxidase: Influence of hypertension
and angiotensin II. J Am Soc Hypertension. 6:169–178. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Oeckinghaus A and Ghosh S: The NF-kappaB
family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0000342009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Brand K, Page S, Rogler G, Bartsch A,
Brandl R, Knuechel R, Page M, Kaltschmidt C and Baeuerle PA:
Activated transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B is present in
the atherosclerotic lesion. J Clin Invest. 97:1715–1722. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hajra L, Evans AI, Chen M, Hyduk SJ,
Collins T and Cybulsky MI: The NF-kappa B signal transduction
pathway in aortic endothelial cells is primed for activation in
regions predisposed to atherosclerotic lesion formation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 97:9052–9057. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cao Y, Zhou X, Liu H, Zhang Y, Yu X and
Liu C: The NF-κB pathway: Regulation of the instability of
atherosclerotic plaques activated by Fg, Fb and FDPs. Mol Cell
Biochem. 383:29–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|