|
1
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pieraccini S, Saladino G, Sironi M,
Francescato P, Cattaneo MG, Vicentini LM, Speranza G and Manitto P:
A molecular dynamics study of an endostatin-derived peptide with
antiangiogenic activity and of its mutants. Chem Phys Lett.
455:311–315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang Z, Dabrosin C, Yin X, Fuster MM,
Arreola A, Rathmell WK, Generali D, Nagaraju GP, El-Rayes B,
Ribatti D, et al: Broad targeting of angiogenesis for cancer
prevention and therapy. Semi Cancer Biol. 35(Suppl): S224–S243.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shimizu K and Oku N: Cancer
anti-angiogenic therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 27:599–605. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N,
Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR and Folkman J:
Endostatin: An endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell. 88:277–285. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zatterstrom UK, Felbor U, Fukai N and
Olsen BR: Collagen XVIII/endostatin structure and functional role
in angiogenesis. Cell Struct Funct. 25:97–101. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dhanabal M, Ramchandran R, Waterman MJ, Lu
H, Knebelmann B, Segal M and Sukhatme VP: Endostatin induces
endothelial cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 274:11721–11726. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rehn M, Veikkkola T, Kukk-Valdre E,
Nakamura H, Ilmonen M, Lombardo C, Pihlajaniemi T, Alitalo K and
Vuori K: Interaction of endostatin with integrins implicated in
angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:1024–1029. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim YM, Hwang S, Kim YM, Pyunn BJ, Kim TY,
Lee ST, Gho YS and Kwon YG: Endostatin blocks vascular endthelial
growth factor-mediated signaling via direct interaction with
KDR/Flk-1. J Biol Chem. 277:27872–27879. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hanai J, Dhanabal M, Karumanchi SA,
Albanese C, Waterman M, Chan B, Ramchandran R, Pestell R and
Sukhatme VP: Endostatin causes G1 arrest of endothelial cells
through inhibition of cyclin D1. J Biol Chem. 277:16464–16469.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim YM, Jang JW, Lee OH, Yeon J, Choi EY,
Kim KW, Lee ST and Kwon YG: Endostatin inhibits endothelial and
tumor cellular invasion by blocking the activation and catalytic
activity of matrix metalloproteinase. Cancer Res. 60:5410–5413.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee SJ, Jang JW, Kim YM, Lee HI, Jeon JY,
Kwon YG and Lee ST: Endostatin binds to the catalytic domain of
matrix metalloproteinase-2. FEBS Lett. 519:147–152. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Foda HD and Zucker S: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis.
Drug Discov Today. 6:478–482. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hellström-Lindahl E, Ravid R and Nordberg
A: Age-dependent decline of neprilysin in Alzheimer's disease and
normal brain: Inverse correlation with A beta levels. Neurobiol
Aging. 29:210–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bunn PA Jr, Helfrich BA, Brenner DG, Chan
DC, Dykes DJ, Cohen AJ and Miller YE: Effects of recombinant
neutral endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11.) on the growth of lung cancer
cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 4:2849–2858.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Usmani BA, Harden B, Maitland NJ and
Turner AJ: Differential expression of neutral endopeptidase-24.11
(neprilysin) and endothelin-converting enzyme in human prostate
cancer cell lines. Clin Sci (Lond). 103(Suppl 48): 314S–317S. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Renneberg H, Albrecht M, Kurek R, Krause
E, Lottspeich F, Aumüller G and Wilhelm B: Identification and
characterization of neutral endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) from human
prostasomes-localization in prostatic tissue and cell lines.
Prostate. 46:173–183. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Albrecht M, Doroszewicz J, Gillen S, Gomes
I, Wilhelm B, Stief T and Aumüller G: Proliferation of prostate
cancer cells and activity of neutral endopeptidase is regulated by
bombesin and IL-Ibeta with IL-1beta acting as a modulator of
cellular differentiation. Prostate. 58:82–94. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Burns DM, Walker B, Gray J and Nelson J:
Breast cancer cell associated endopeptidase EC 24.11 modulates
proliferative response to bombesin. Br J Cancer. 79:214–220. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seals DF and Courtneidge SA: The ADAMs
family of metalloproteinases: Multidomain proteins with multiple
functions. Genes Dev. 17:7–30. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Van der Vorst EP, Keijbeck AA, de Winther
MP and Donners MM: A disintegrin and metalloproteases: Molecular
scissors in angiogenesis, inflammation and atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis. 224:302–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mochizuki S and Okada Y: ADAMs in cancer
cell proliferation and progression. Cancer Sci. 98:621–628. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Erin N, Zhao W, Bylander J, Chase G and
Clawson G: Capsaicin induced inactivation of sensory neurons
promotes a more aggressive gene expression phenotype in breast
cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 99:351–364. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sumner SC, Gallagher KS, Davis DG, Covell
DG, Jernigan RL and Ferretti JA: Conformational analysis of the
tachykinins in solution: Substance P and physalaemin. J Biomol
Struct Dyn. 8:687–707. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kurtz MM, Wang R, Clements MK, Cascieria
MA, Austin CP, Cunningham BR, Chicchia GG and Liu Q:
Identification, localization and receptor characterization of novel
mammalian substance P-like peptides. Gene. 296:205–212. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Koon HW and Pothoulakis C:
Immunomodulatory properties of substance P: The gastrointestinal
system as a model. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1088:23–40. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schäffer M, Beiter T, Becker HD and Hunt
TK: Neuropeptides: Mediators of inflammation and tissue repair?
Arch Surg. 133:1107–1116. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Muangman P, Tamura RN, Muffley LA, Isik
FF, Scott JR, Xie C, Kegel G, Sullivan SR, Liang Z and Gibran NS:
Substance P enhances wound closure in nitric oxide synthase
knockout mice. J Surg Res. 153:201–209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Chappa AK, Audus KL and Lunte SM:
Characteristics of substance P transport across the blood-brain
barrier. Pharm Res. 23:1201–1208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Esteban F, Gonzalez-Moles MA, Castro D,
Martin-Jaen Mdel M, Redondo M, Ruiz-Avila I and Muñoz M: Expression
of substance P and neurokinin-1-receptor in laryngeal cancer:
Linking chronic inflammation to cancer promotion and progression.
Histopathology. 54:258–260. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Erin N and Ulusoy O: Differentiation of
neuronal from non-neuronal substance P. Regul Pept. 152:108–113.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
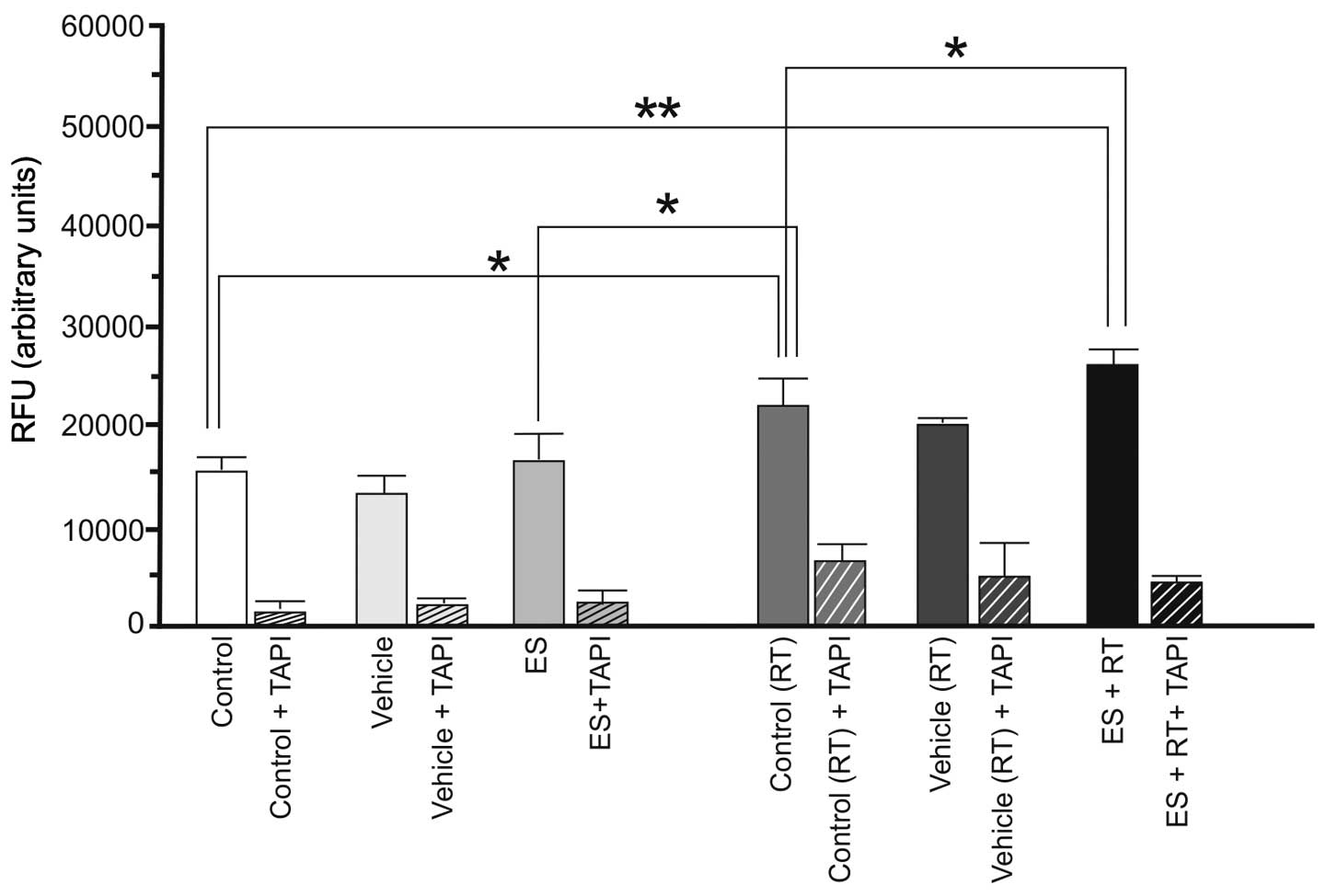
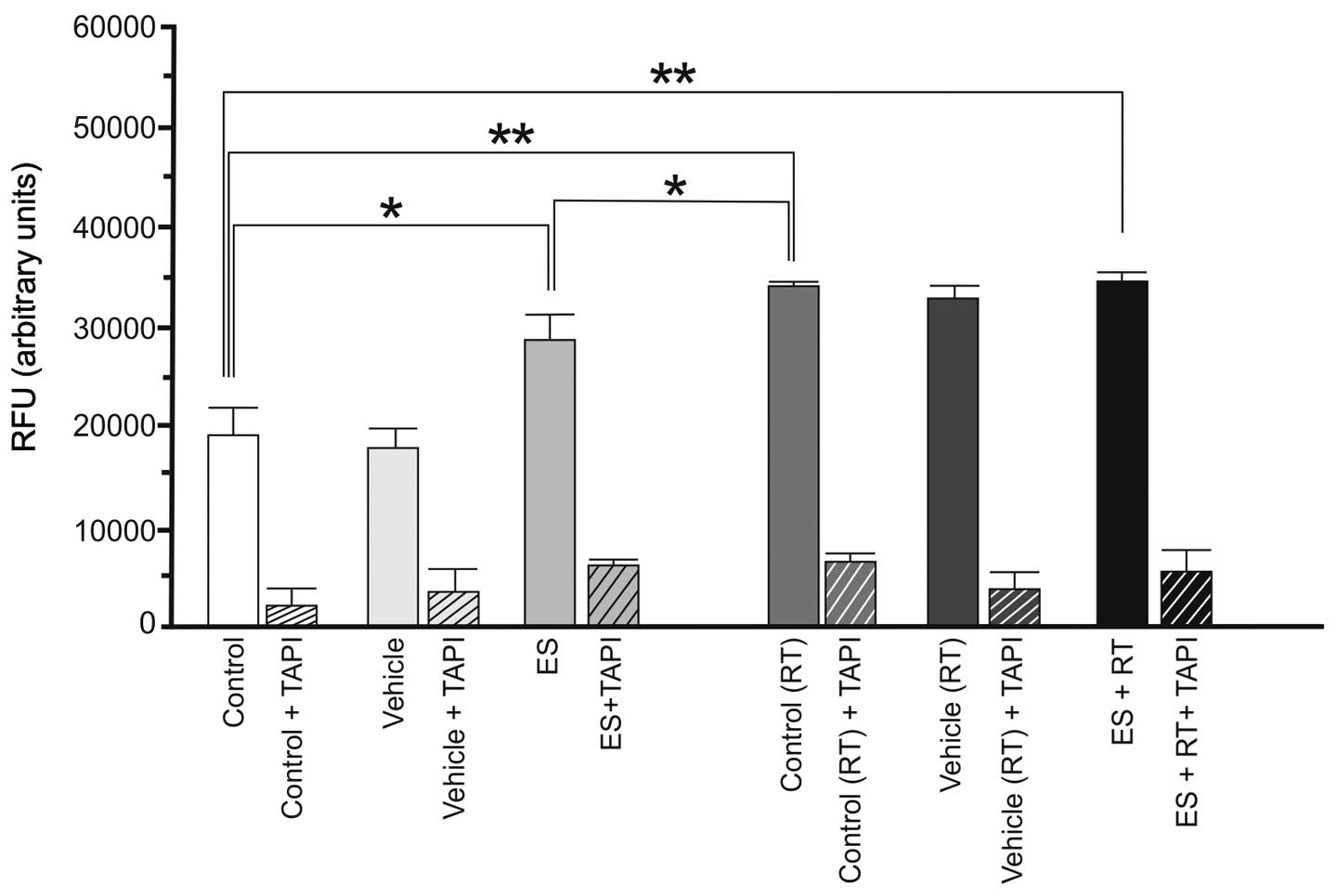
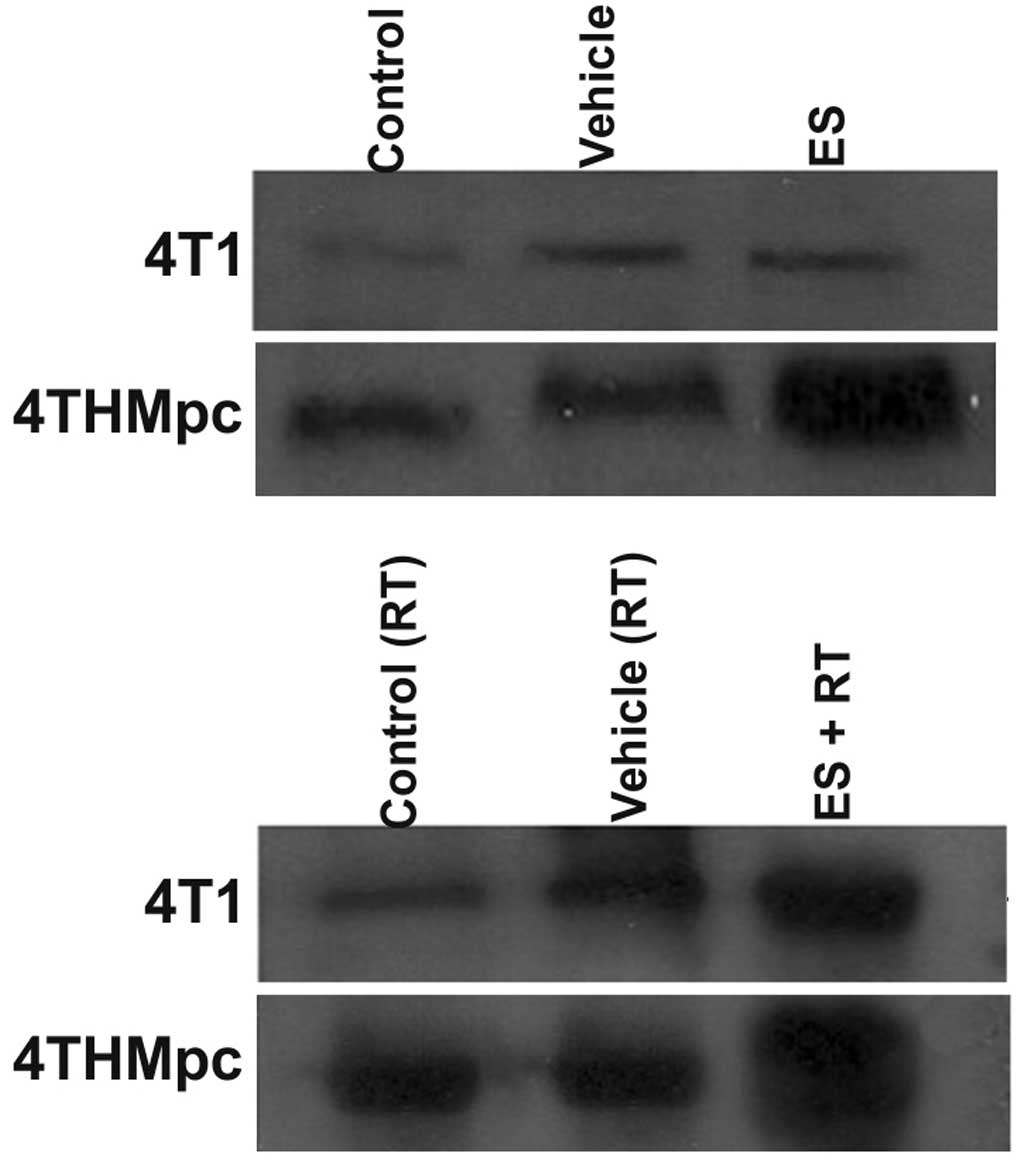
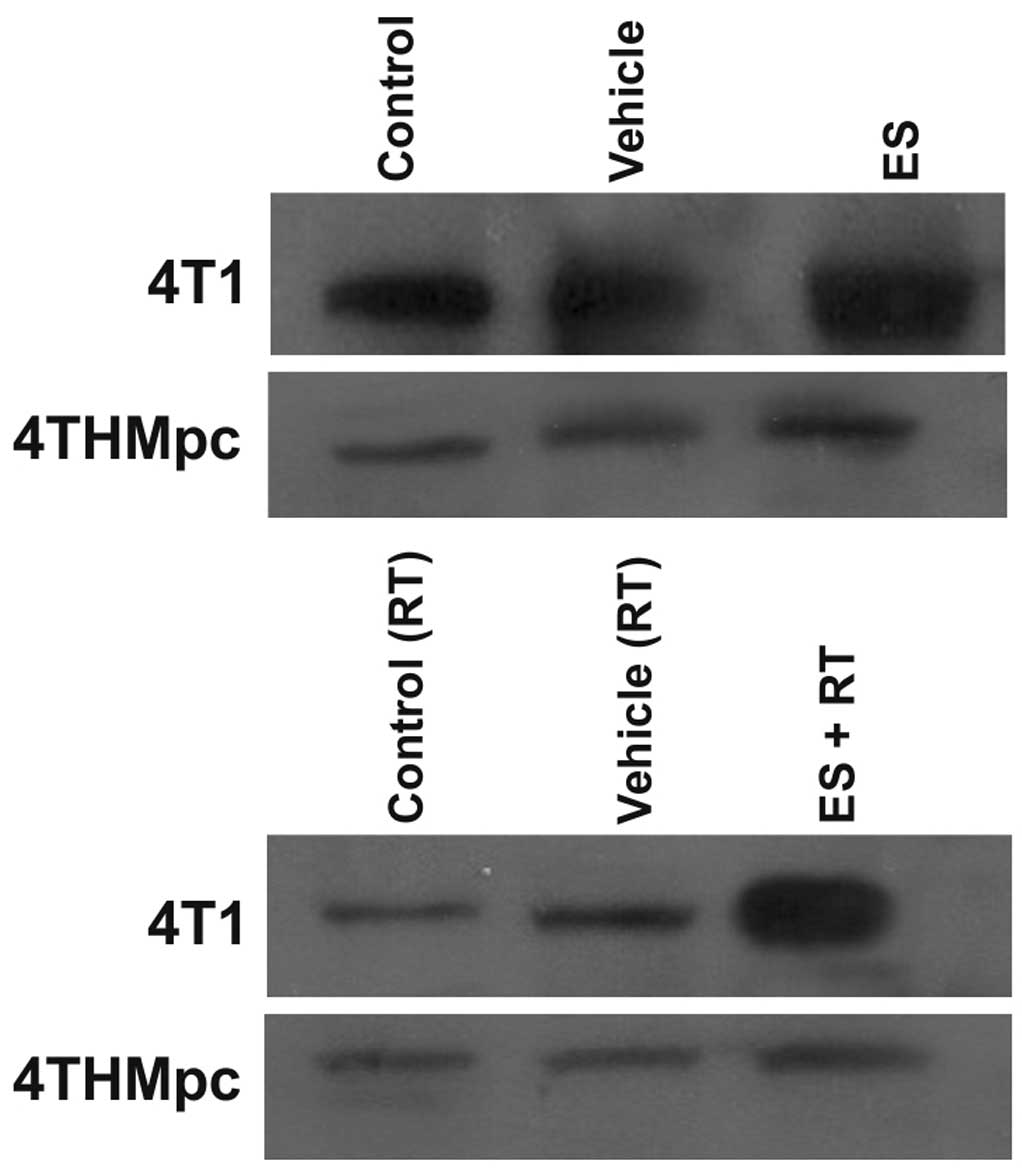
Arslan Aydemir E, Simsek Oz E, Fidan
Korcum A and Fiskin K: Endostatin enhances radioresponse in breast
cancer cells via alteration of substance P levels. Oncol Lett.
2:879–886. 2011.
|
|
33
|
Carpenter TC and Stenmark KR: Hypoxia
decreases lung neprilysin express and increases pulmonary vascular
leak. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 281:L941–L948.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shichiri M and Hirata Y: Antiangiogenesis
signals by endostatin. FASEB J. 15:1044–1053. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kranenburga O, Kroon-Batenburgb LM,
Reijerkerka A, Wuc YP, Voesta EE and Gebbinka MF: Recombinant
endostatin forms amyloid fibrils that bind and are cytotoxic to
murine neuroblastoma cells in vitro. FEBS Lett. 539:149–155. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dkhissi F, Lu H, Sorıa C, Opolon P,
Griscelli F, Liu H, Khattar P, Mishal Z, Perricaudet M and Li H:
Endostatin exhibits a direct antitumor effect in addition to its
antiangiogenic activity in colon cancer cells. Hum Gene Ther.
14:997–1008. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hanai J, Gloy J, Karumanchi SA, Kale S,
Tang J, Hu G, Chan B, Ramchandran R, Jha V, Sukhatme VP and Sokol
S: Endostatin is a potential inhibitor of Wnt signaling. J Cell
Biol. 158:529–539. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hajitou A, Grignet C, Devy L, Berndt S,
Blacher S, Deroanne CF, Bajou K, Fong T, Chiang Y, Foidart JM and
Noël A: The antitumoral effect of endostatin and angiostatin is
associated with a down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor expression in tumor cells. FASEB J. 16:1802–1804.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Verhoef C, de Wilt JH and Verheul HM:
Angiogenesis inhibitors: Perspectives for medical, surgical and
radiation oncology. Curr Pharma Design. 12:2623–2630. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Higgins GS, O'Cathail SM, Muschel RJ and
McKenna WG: Drug radiotherapy combinations: Review of previous
failures and reasons for future optimism. Cancer Treat Rev.
41:105–113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Teicher BA: A systems approach to cancer
therapy. (Antioncogenics + standard cytotoxics→mechanism(s) of
interaction). Cancer Metastasis Rev. 15:247–272. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zips D, Krause M, Hessel F, Westphal J,
Brüchner K, Eicheler W, Dörfler A, Grenman R, Petersen C, Haberey M
and Baumann M: Experimental study on different combination
schedules of VEGF-receptor inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584 and
fractionated irradiation. Anticancer Res. 23:3869–3876.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kaliski A, Maggiorella L, Cengel KA, Mathe
D, Rouffiac V, Opolon P, Lassau N, Bourhis J and Deutsch E:
Angiogenesis and tumor growth inhibition by a matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitor targeting radiation-induced invasion.
Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1717–1728. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dass CR, Tran TM and Choong PF:
Angiogenesis Inhibitors and the need for anti-angiogenic
therapeutics. J Dent Res. 86:927–936. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luo W, Sharif TR and Sharif M: Substance
P-induced mitogenesis in human astrocytoma cells correlates with
activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathway. Cancer Res. 56:4983–4991. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Muñoz M, Pérez A, Rosso M, Zamarriego C
and Rosso R: Antitumoral action of the neurokinin-1 receptor
antagonist L-733 060 on human melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res.
14:183–188. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Walsh DT, Weg VB, Williams TJ and
Nourshargh S: Substance P induced inflammatory responses in
guinea-pig skin: The effect of specific NK1 receptor antagonists
and the role of endogenous mediators. Br J Pharmacol.
114:1343–1350. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Musumecia G, Coleman R, Imbesi R, Magro G,
Parenti R, Szychlinska MA, Scuderi R, Cinà CS, Castorina S and
Castrogiovanni P: ADAM-10 could mediate cleavage of N-cadherin
promoting apoptosis in human atherosclerotic lesions leading to
vulnerable plaque: A morphological and immunohistochemical study.
Acta Histochem. 116:1148–1158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Reiss K and Saftig P: The 'a disintegrin
and metalloprotease' (ADAM) family of sheddases: Physiological and
cellular functions. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 20:126–137. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li B, Yu D and Xu Z: Activated protein C
inhibits amyloid β production via promoting expression of ADAM-10.
Brain Res. 1545:35–44. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jones AV, Lambert DW, Speight PM and
Whawell SA: ADAM 10 is over expressed in oral squamous cell
carcinoma and contributes to invasive behaviour through a
functional association with αvβ6 integrin. FEBS Lett.
587:3529–3534. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Şimşek E, Aydemir E, Korcum AF and Fişkin
K: Thalidomide combined with irradiation alters the activity of two
proteases. Mol Med Rep. 11:1535–1541. 2015.
|
|
53
|
von Lueder TG, Atar D and Kruma H: Current
role of neprilysin inhibitors in hypertension and heart failure.
Pharmacol Ther. 144:41–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bayés-Genís A, Barallat J, Galán A, de
Antonio M, Domingo M, Zamora E, Urrutia A and Lupón J: Soluble
neprilysin is predictive of cardiovascular death and heart failure
hospitalization in heart failure patients. J Am Coll Cardiol.
65:657–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cohen AJ, Bunn PA, Franklin W, Magill-Solc
C, Hartmann C, Helfrich B, Gilman L, Folkvord J, Helm K and Miller
YE: Neutral endopeptidase: Variable expression in human lung,
inactivation in lung cancer, and modulation of peptide-induced
calcium flux. Cancer Res. 56:831–839. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Göhring B, Holzhausen HJ, Meye A,
Heynemann H, Rebmann U, Langner J and Riemann D: Endopeptidase
24.11/CD10 is down-regulated in renal cell cancer. Int J Mol Med.
2:409–414. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sato Y, Itoh F, Hinoda Y, Ohe Y, Nakagawa
N, Ueda R, Yachi A and Imai K: Expression of CD10/neutral
endopeptidase in normal and malignant tissues of the human stomach
and colon. J Gastroenterol. 31:12–17. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dragović T, Deddish PA, Tan F, Weber G and
Erdös EG: Increased expression of neprilysin (neutral endopeptidase
24.11) in rat and human hepatocellular carcinomas. Lab Invest.
70:107–113. 1994.
|
|
59
|
Dragovic T, Sekosan M, Becker RP and Erdös
EG: Detection of neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (neprilysin) in human
hepatocellular carcinomas by immunocytochemistry. Anticancer Res.
17:3233–3238. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Esteban F, Muñoz M, González-Moles MA and
Rosso M: A role for substance P in cancer promotion and
progression: A mechanism to counteract intracellular death signals
following oncogene activation or DNA damage. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:137–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Langdon S, Sethi T, Ritchie A, Muir M,
Smyth J and Rozengurt E: Broad spectrum neuropeptide antagonists
inhibit the growth of small celllung cancer in vivo. Cancer Res.
52:4554–4557. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Reeve JG and Bleehen NM:
D-Arg1, D-Phe5, D-Trp7,9,
Leu11 substance P induces apoptosis in lung cancer cell
lines in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 199:1313–1319. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Seckl MJ, Higgins T, Widmer F and
Rozengurt E: D-Arg1, D-Trp5,7,9,
Leu11 substance P: A novel potent inhibitor of signal
transduction and growth in vitro and in vivo in small cell lung
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 57:51–54. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Woll PJ and Rozengurt E:
D-Arg1, D-Phe5, D-Trp7,9,
Leu11 substance P, a potent bombesin antagonist in
murine Swiss 3T3 cells, inhibits the growth of human small cell
lung cancer cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:1859–1863.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Palma C, Bigioni M, Irrissuto C, Nardelli
F, Maggi CA and Manzini S: Anti-tumour activity of tachykinin NK1
receptor antagonists on human glioma U373 MG xenograft. Br J
Cancer. 82:480–487. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gross K, Karagiannides I, Thomou T, Koon
HW, Bowe C, Kim H, Giorgadze N, Tchkonia T, Pirtskhalava T,
Kirkland JL and Pothoulakis C: Substance P promotes expansion of
human mesenteric preadipocytes through proliferative and
antiapoptotic pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
296:G1012–G1019. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|