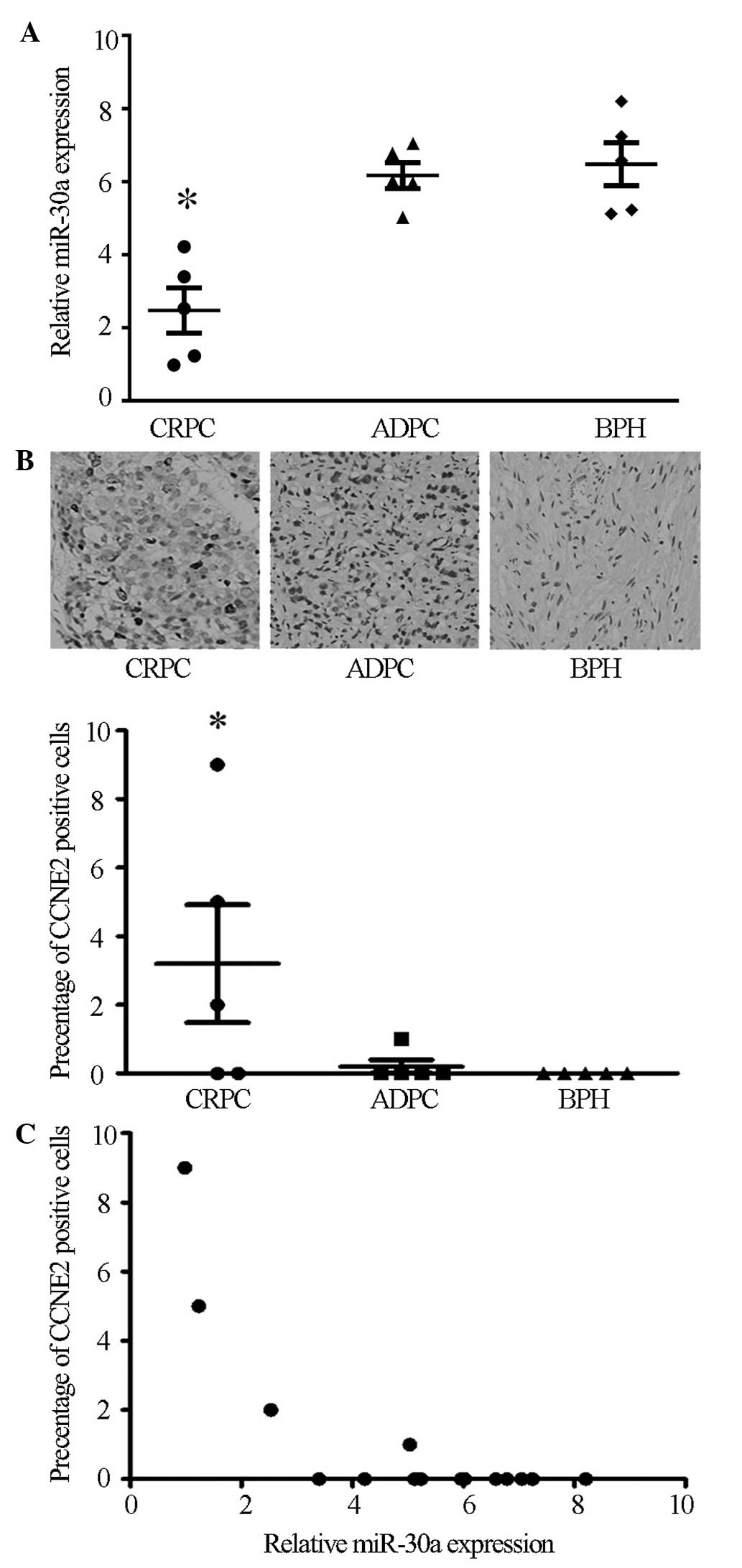
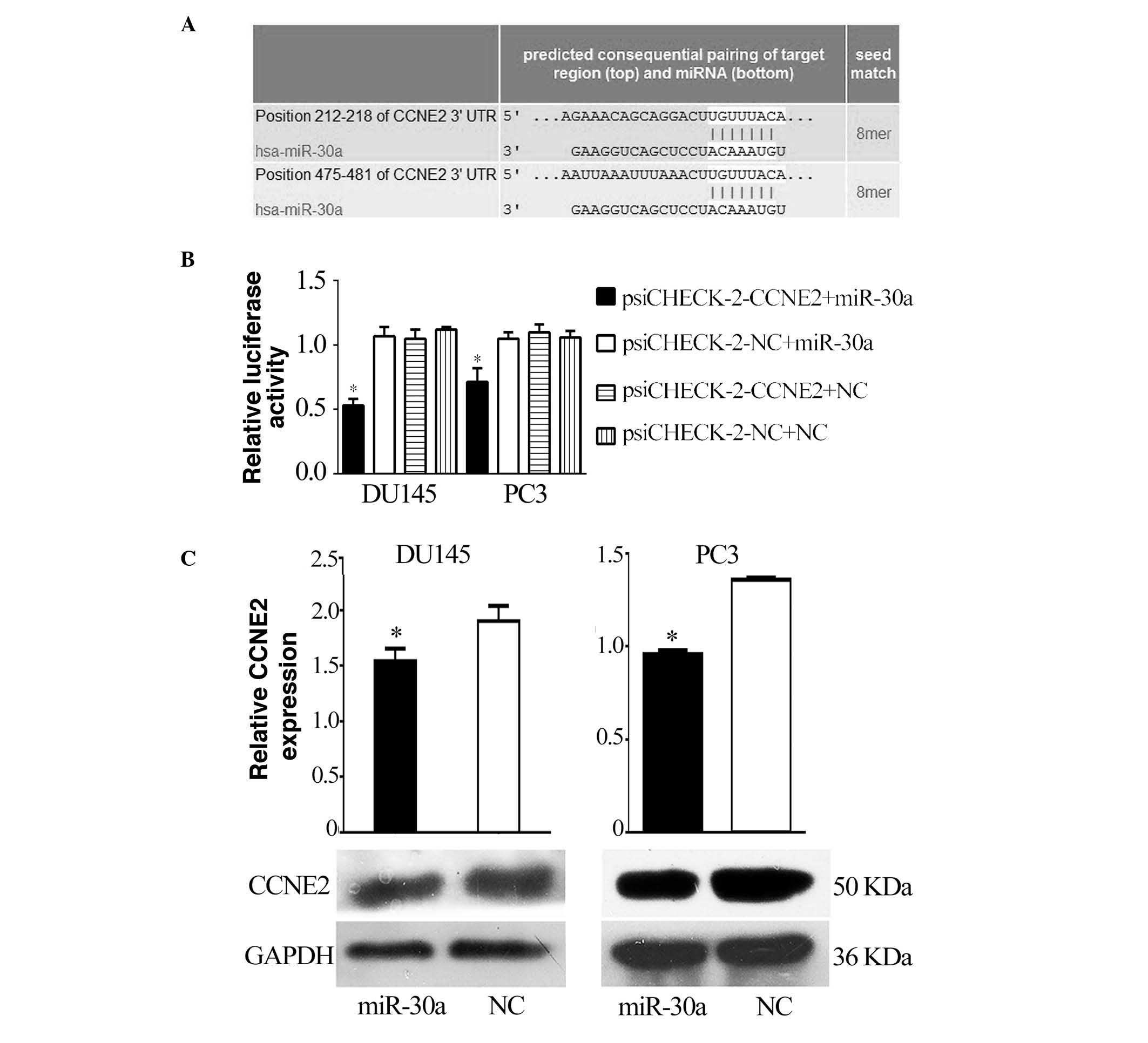
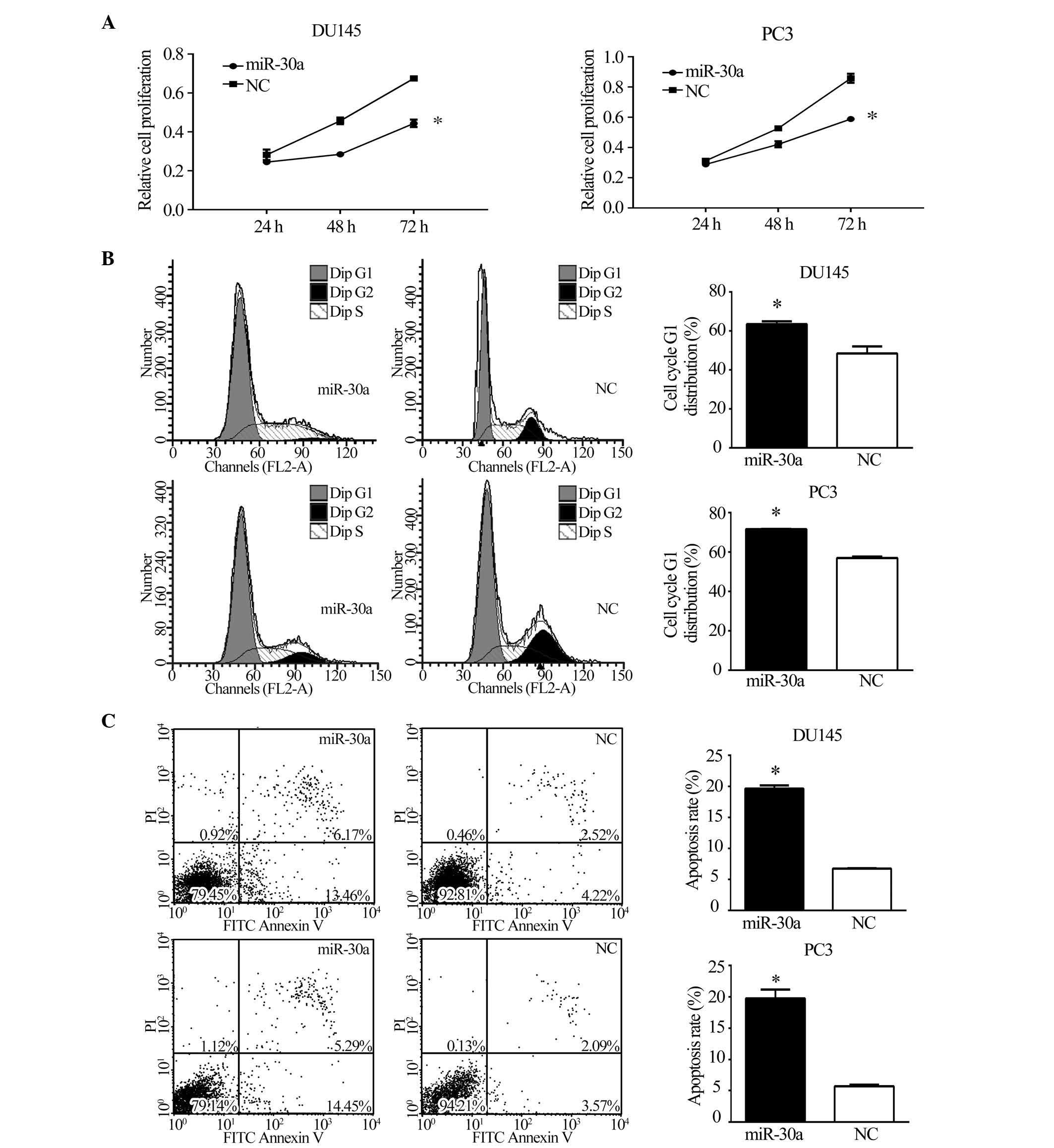
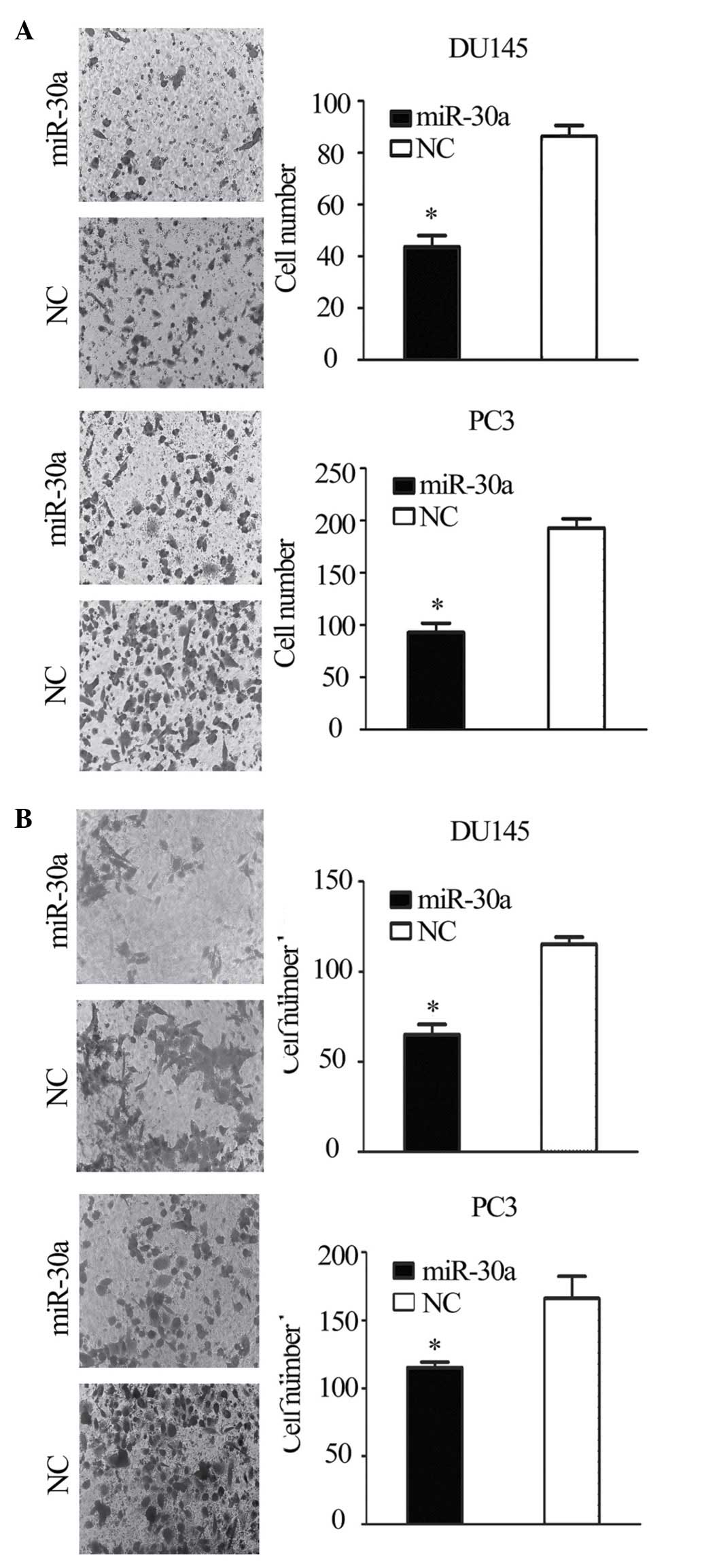
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zhou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feldman BJ and Feldman D: The development
of androgen independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:34–45.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lai EC: MicroRNAs are complementary to
3′UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional
regulation. Nat Genet. 30:363–364. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang L, Xul B, Chen S, Lu K, Liu C, Wang
Y, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Liu D and Chen M: The complex roles of
microRNAS in the metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. J Nanosci
Nanotechnol. 13:3195–3203. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Coppola V, De Maria R and Bonci D:
MicroRNAs and prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F1–F17.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu D, Tao T, Xu B, Chen S, Liu C, Zhang
L, Lu K, Huang Y, Jiang L, Zhang X, et al: MiR-361-5p acts as a
tumor suppressor in prostate cancer by targeting signal transducer
and activator of transcription-6(STAT6). Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 445:151–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
care and use of laboratory animals. 7th edition. National Academy
Press; Washington DC: 1996
|
|
10
|
Xu B, Wang N, Wang X, Tong N, Shao N, Tao
J, Li P, Niu X, Feng N, Zhang L, et al: MiR-146a suppresses tumor
growth and progression by targeting EGFR pathway and in a
p-ERK-dependent manner in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Prostate. 72:1171–1178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ozen M, Creighton CJ, Ozdemir M and
Ittmann M: Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human
prostate cancer. Oncogene. 27:1788–1793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huang QB, Ma X, Zhang X, Liu SW, Ai Q, Shi
TP, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Fan Y, Ni D, et al: Down-Regulated miR-30a in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma correlated with tumor hematogenous
metastasis by targeting angiogenesis-specific DLL4. PLoS One.
8:e672942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kumarswamy R, Mudduluru G, Ceppi P,
Muppala S, Kozlowski M, Niklinski J, Papotti M and Allgayer H:
MicroRNA-30a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by
targeting Snai1 and is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Cancer. 130:2044–2053. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fu J, Xu X, Kang L, Zhou L, Wang S, Lu J,
Cheng L, Fan Z, Yuan B, Tian P, et al: MiR-30a suppresses breast
cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting Eya2. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 445:314–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baraniskin A, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K,
Maghnouj A, Zöllner H, Munding J, Klein-Scory S, Reinacher-Schick
A, Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Schmiegel W and Hahn SA: MiR-30a-5p
suppresses tumor growth in colon carcinoma by targeting DTL.
Carcinogenesis. 33:732–739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jia Z, Wang K, Wang G, Zhang A and Pu P:
MiR-30a-5p antisense oligonucleotide suppresses glioma cell growth
by targeting SEPT7. PLoS One. 8:e550082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kao CJ, Martiniez A, Shi XB, Yang J, Evans
CP, Dobi A, de Vere White RW and Kung HJ: MiR-30 as a tumor
suppressor connects EGF/Src signal to ERG and EMT. Oncogene.
33:2495–2503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Caldon CE and Musgrove EA: Distinct and
redundant functions of cyclin E1 and cyclin E2 in development and
cancer. Cell Div. 5:22010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hwang HC and Clurman BE: Cyclin E in
normal and neoplastic cell cycles. Oncogene. 24:2776–2786. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gudas JM, Payton M, Thukral S, Chen E,
Bass M, Robinson MO and Coats S: Cyclin E2, a novel G1 cyclin that
binds Cdk2 and is aberrantly expressed in human cancers. Mol Cell
Biol. 19:612–622. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Caldon CE, Sergio CM, Burgess A, Deans AJ,
Sutherland RL and Musgrove EA: Cyclin E2 induces genomic
instability by mechanisms distinct from cyclin E1. Cell Cycle.
12:606–617. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Payton M, Scully S, Chung G and Coats S:
Deregulation of cyclin E2 expression and associated kinase activity
in primary breast tumors. Oncogene. 21:8529–8534. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Caldon CE, Sergio CM, Kang J,
Muthukaruppan A, Boersma MN, Stone A, Barraclough J, Lee CS, Black
MA, Miller LD, et al: Cyclin E2 overexpression is associated with
endocrine resistance but not insensitivity to CDK2 inhibition in
human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1488–1499. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder
ME, Timmermans M, Trapman AM, Garcia RR, Arnold M, Goedheer AJ, de
Weerd V, Portengen H, et al: Which cyclin E prevails as prognostic
marker for breast cancer? Results from a retrospective study
involving 635 lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:3319–3328. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Varambally S, Yu J, Laxman B, Rhodes DR,
Mehra R, Tomlins SA, Shah RB, Chandran U, Monzon FA, Becich MJ, et
al: Integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of prostate cancer
reveals signatures of metastatic progression. Cancer Cell.
8:393–406. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu YP, Landsittel D, Jing L, Nelson J, Ren
B, Liu L, McDonald C, Thomas R, Dhir R, Finkelstein S, et al: Gene
expression alterations in prostate cancer predicting tumor
aggression and preceding development of malignancy. J Clin Oncol.
22:2790–2799. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Z, Cho H, Hampton GM and Theodorescu D:
Cdc6 and cyclin E2 are PTEN-regulated genes associated with human
prostate cancer metastasis. Neoplasia. 11:66–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|