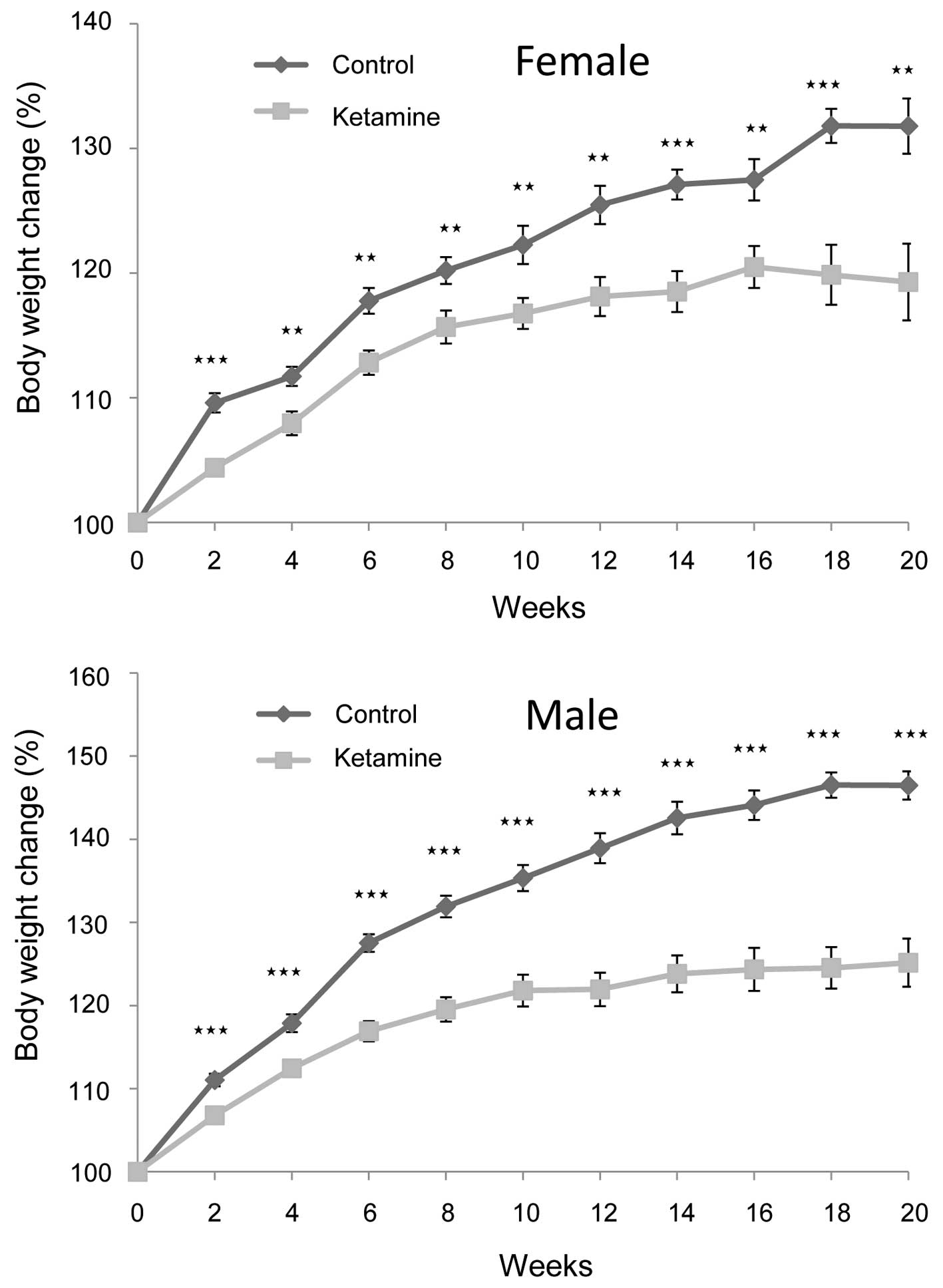
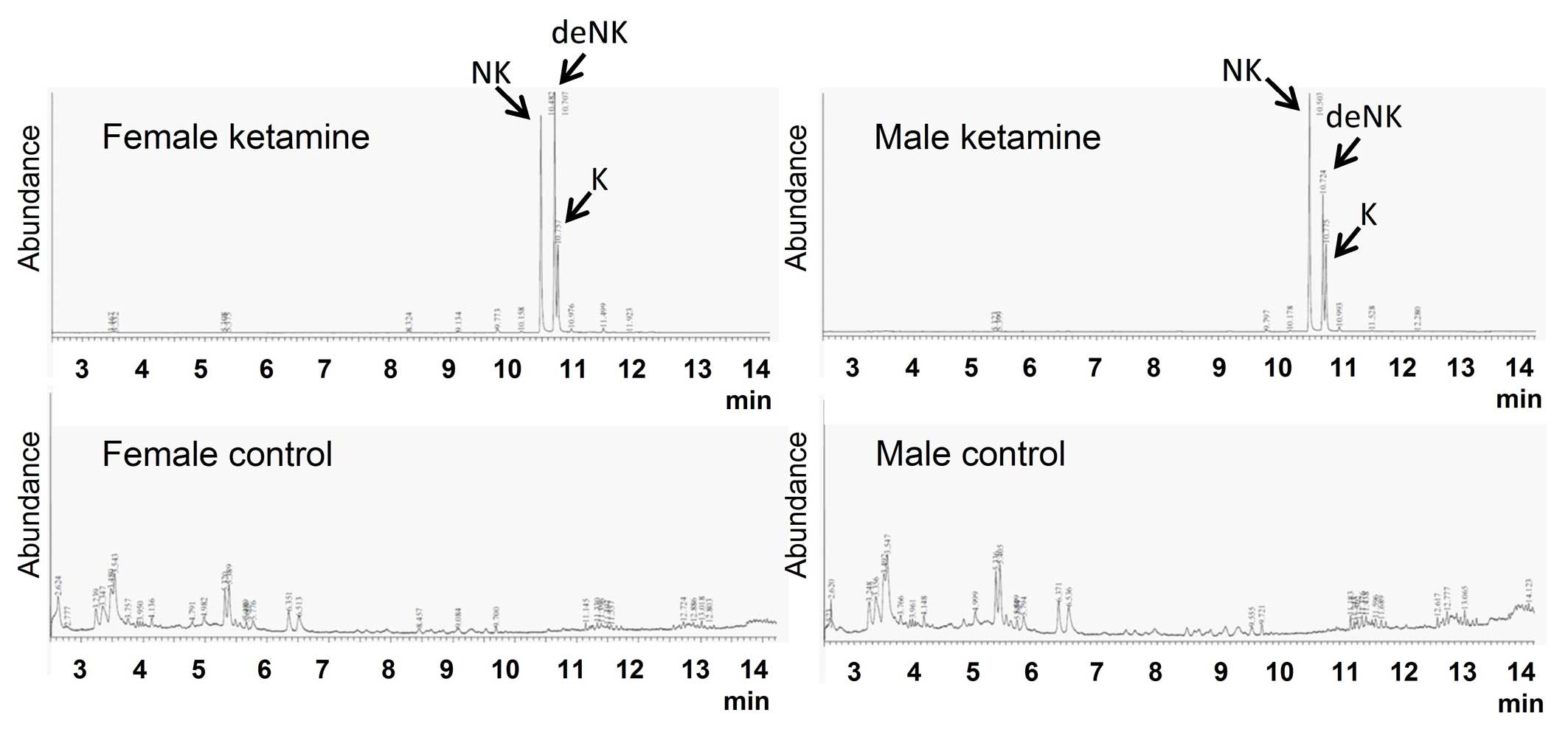
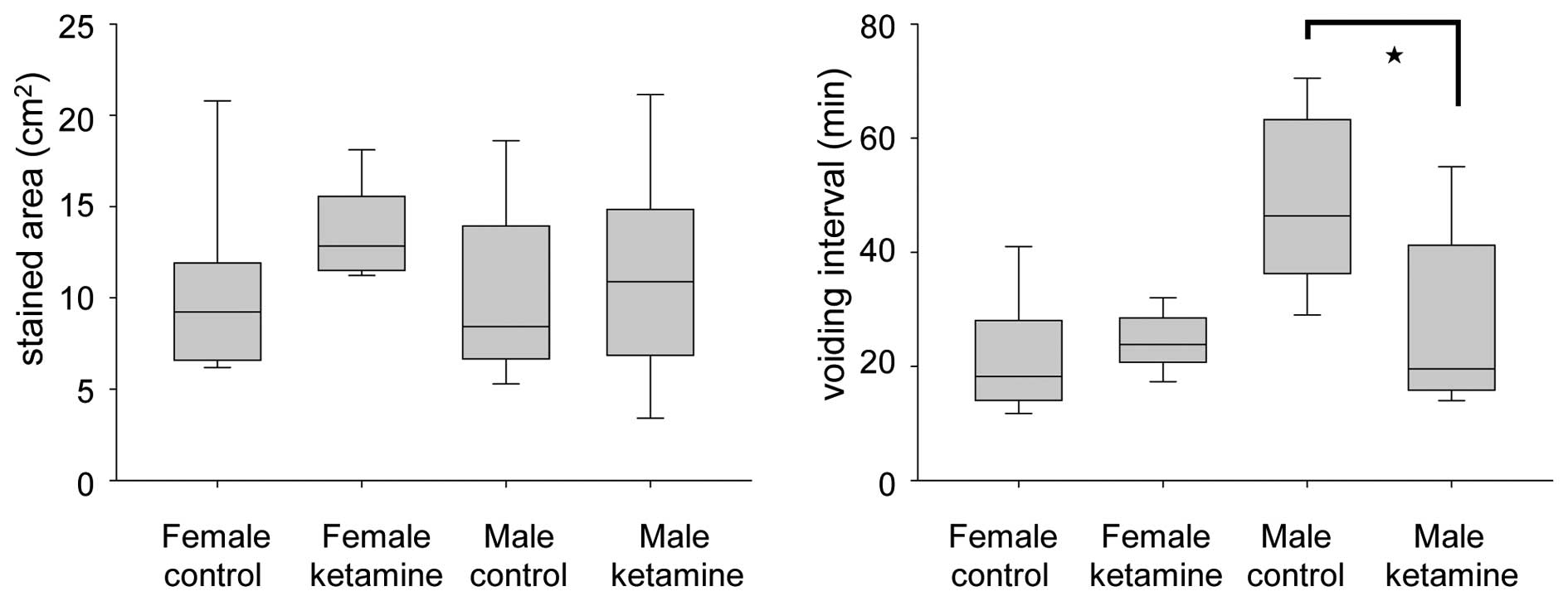
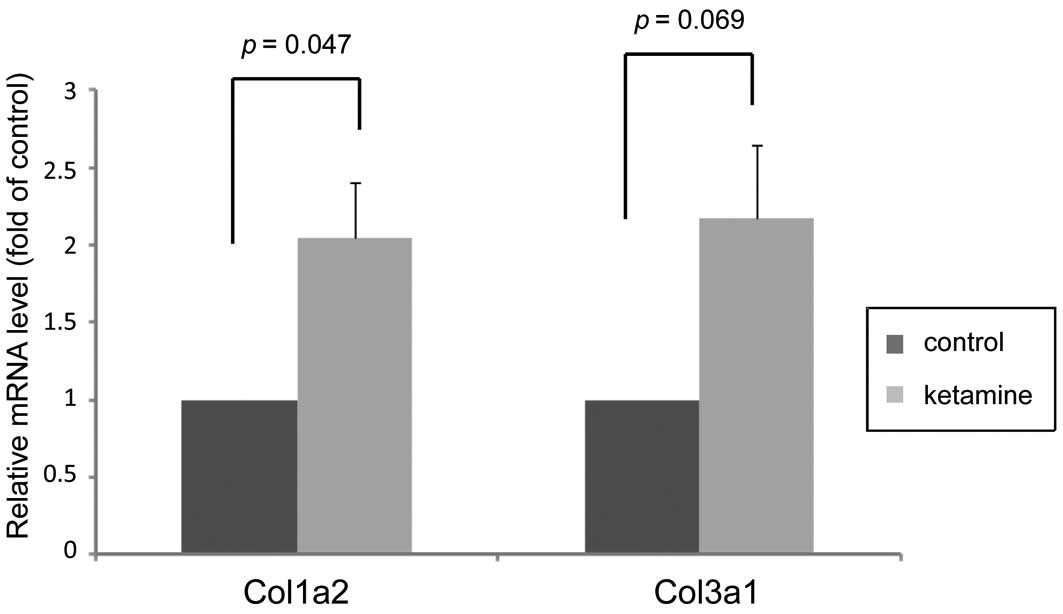
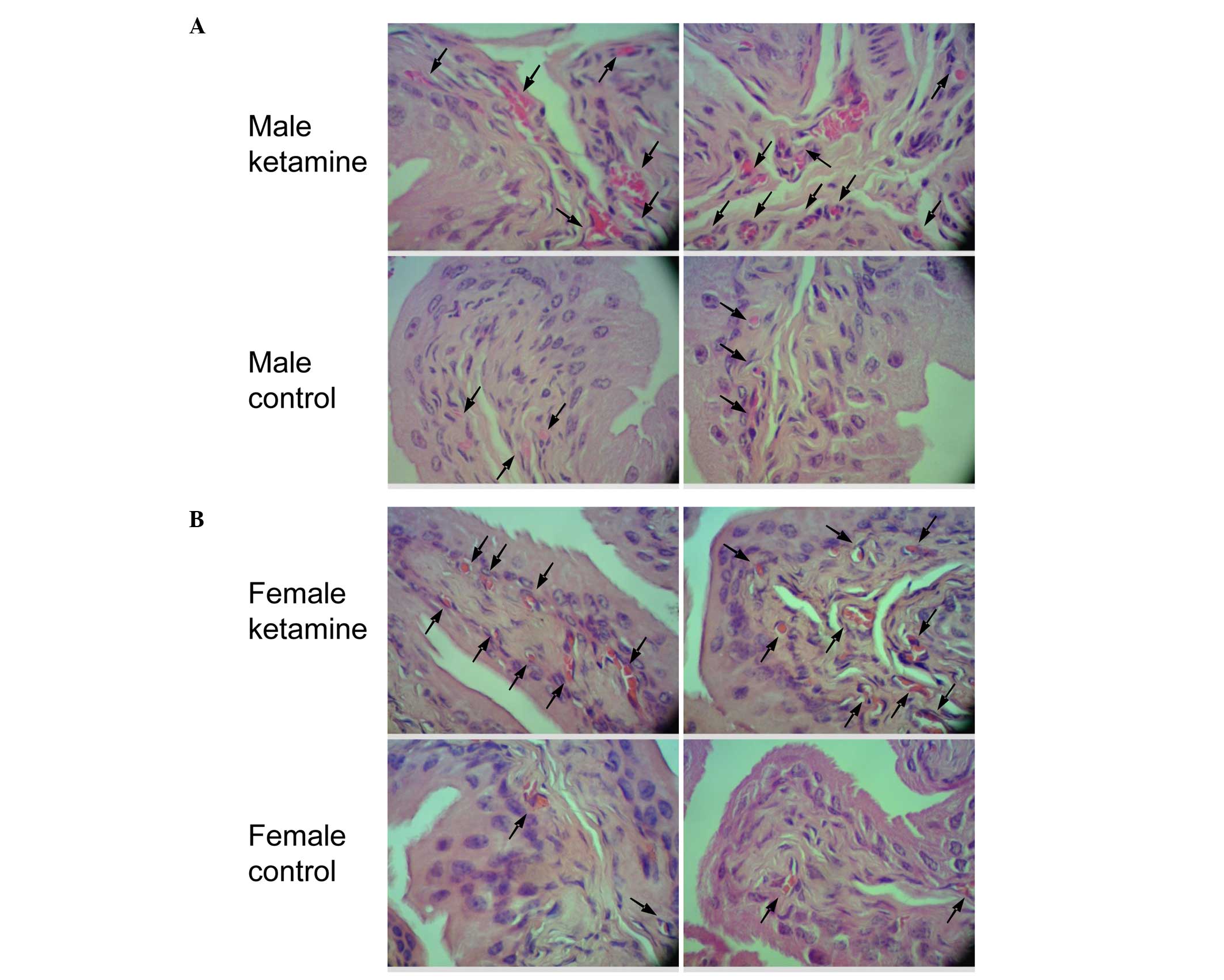
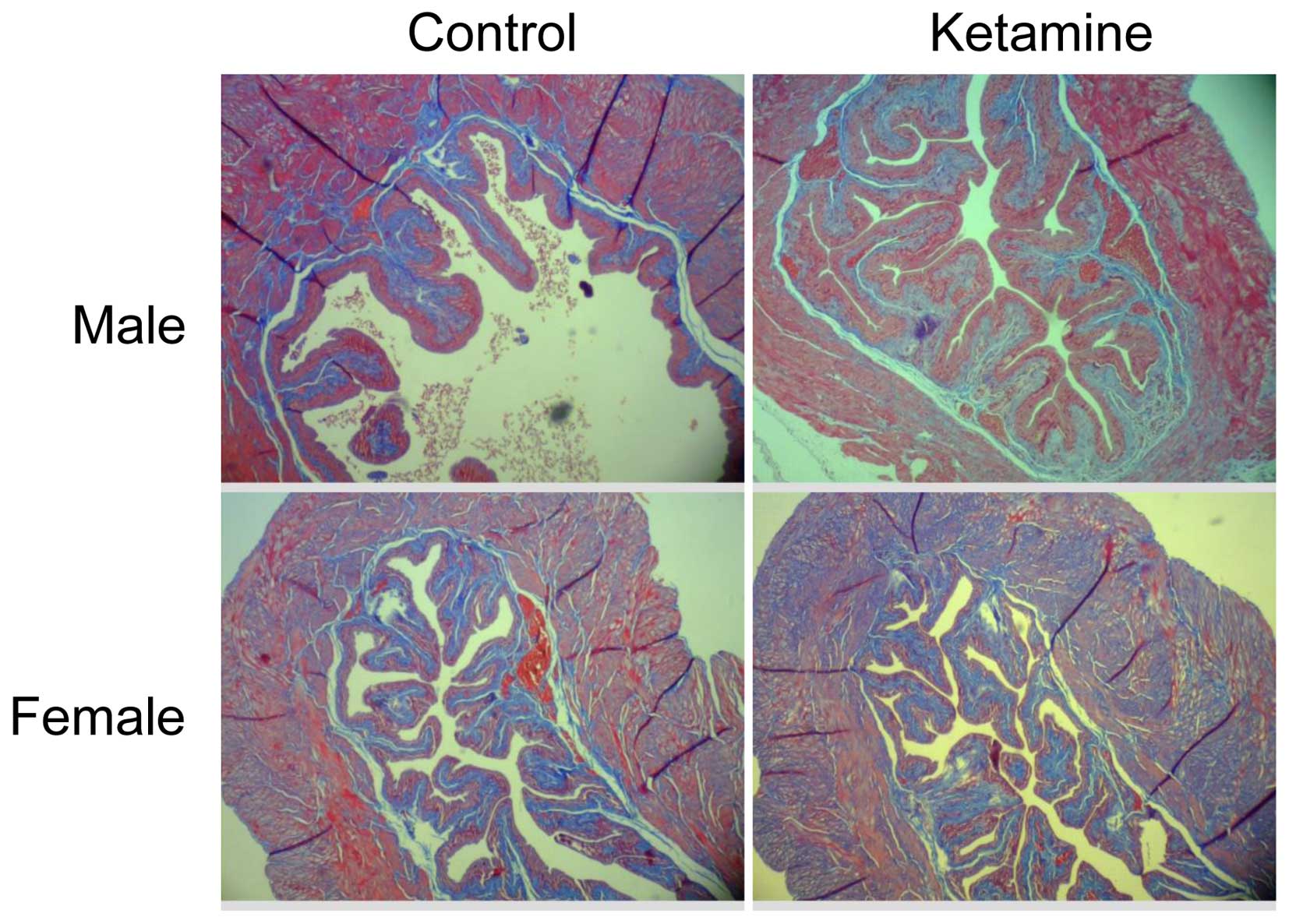
|
1
|
Domino EF, Chodoff P and Corssen G:
Pharmacologic Effects of Ci-581, a new dissociative anesthetic, in
man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 6:279–291. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shahani R, Streutker C, Dickson B and
Stewart RJ: Ketamine-associated ulcerative cystitis: A new clinical
entity. Urology. 69:810–812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chu PS, Kwok SC, Lam KM, Chu TY, Chan SW,
Man CW, Ma WK, Chui KL, Yiu MK, Chan YC, et al: 'Street
ketamine'-associated bladder dysfunction: A report of ten cases.
Hong Kong Med J. 13:311–313. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chu PS, Ma WK, Wong SC, Chu RW, Cheng CH,
Wong S, Tse JM, Lau FL, Yiu MK and Man CW: The destruction of the
lower urinary tract by ketamine abuse: A new syndrome? BJU Int.
102:1616–1622. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chuang SM, Liu KM, Li YL, Jang MY, Lee HH,
Wu WJ, Chang WC, Levin RM and Juan YS: Dual involvements of
cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase expressions in
ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis in rat bladder. Neurourol
Urodyn. 32:1137–1143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yeung LY, Rudd JA, Lam WP, Mak YT and Yew
DT: Mice are prone to kidney pathology after prolonged ketamine
addiction. Toxicol Lett. 191:275–278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Juan YS, Lee YL, Long CY, Wong JH, Jang
MY, Lu JH, Wu WJ, Huang YS, Chang WC and Chuang SM: Translocation
of NF-kB and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 are enhanced by
ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis in rat bladder. Am J Pathol.
185:2269–2285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meng E, Chang HY, Chang SY, Sun GH, Yu DS
and Cha TL: Involvement of purinergic neurotransmission in ketamine
induced bladder dysfunction. J Urol. 186:1134–1141. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gu D, Huang J, Shan Z, Yin Y, Zheng S and
Wu P: Effects of long-term ketamine administration on rat bladder
protein levels: A proteomic investigation using two-dimensional
difference gel electrophoresis system. Int J Urol. 20:1024–1031.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sangkum P, Gokce A, Tan RB, Bouljihad M,
Kim H, Mandava SH, Saleem SN, Lasker GF, Yafi FA, Abd Elmageed ZY,
et al: Transforming growth factor-β1 induced urethral fibrosis in a
rat model. J Urol. 194:820–827. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen CH, Wang ST, Lee YR, Liu SY, Li YZ,
Wu JD, Chen YJ and Liu YW: Biological effect of ketamine in
urothelial cell lines and global gene expression analysis in the
bladders of ketamine-injected mice. Mol Med Rep. 11:887–895.
2015.
|
|
12
|
Tsai TH, Cha TL, Lin CM, Tsao CW, Tang SH,
Chuang FP, Wu ST, Sun GH, Yu DS and Chang SY: Ketamine-associated
bladder dysfunction. Int J Urol. 16:826–829. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Veilleux-Lemieux D, Castel A, Carrier D,
Beaudry F and Vachon P: Pharmacokinetics of ketamine and xylazine
in young and old Sprague-Dawley rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci.
52:567–570. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu CH, Huang MH, Wang SM, Lin CC and Liu
RH: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of ketamine and
its metabolites-a comparative study on the utilization of different
derivatization groups. J Chromatogr A. 1157:336–351. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sugino Y, Kanematsu A, Hayashi Y, Haga H,
Yoshimura N, Yoshimura K and Ogawa O: Voided stain on paper method
for analysis of mouse urination. Neurourol Urodyn. 27:548–552.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deveaud CM, Macarak EJ, Kucich U, Ewalt
DH, Abrams WR and Howard PS: Molecular analysis of collagens in
bladder fibrosis. J Urol. 160:1518–1527. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Corazza O, Assi S and Schifano F: From
'Special K' to 'Special M': The evolution of the recreational use
of ketamine and methoxetamine. CNS Neurosci Ther. 19:454–460. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reyes-Gordillo K, Shah R,
Arellanes-Robledo J, Hernández-Nazara Z, Rincón-Sánchez AR, Inagaki
Y, Rojkind M and Lakshman MR: Mechanisms of action of acetaldehyde
in the up-regulation of the human α2(I) collagen gene in hepatic
stellate cells: Key roles of Ski, SMAD3, SMAD4, and SMAD7. Am J
Pathol. 184:1458–1467. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wong L, Hutson PR and Bushman W: Prostatic
inflammation induces fibrosis in a mouse model of chronic bacterial
infection. PloS One. 9:e1007702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stadelmann WK, Digenis AG and Tobin GR:
Physiology and healing dynamics of chronic cutaneous wounds. Am J
Surg. 176(Suppl 2A): S26–S38. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Broughton G II, Janis JE and Attinger CE:
The basic science of wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 117(Suppl
7): S12–S34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Cellular
mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. 1. Common and organ-specific
mechanisms associated with tissue fibrosis. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 304:C216–C225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Seki E, de Minicis S, Inokuchi S, Taura K,
Miyai K, van Rooijen N, Schwabe RF and Brenner DA: CCR2 promotes
hepatic fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 50:185–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moore BB, Kolodsick JE, Thannickal VJ,
Cooke K, Moore TA, Hogaboam C, Wilke CA and Toews GB: CCR2-mediated
recruitment of fibrocytes to the alveolar space after fibrotic
injury. Am J Pathol. 166:675–684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ong VH, Carulli MT, Xu S, Khan K, Lindahl
G, Abraham DJ and Denton CP: Cross-talk between MCP-3 and TGFbeta
promotes fibroblast collagen biosynthesis. Exp Cell Res.
315:151–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Graham GJ and Locati M: Regulation of the
immune and inflammatory responses by the 'atypical' chemokine
receptor D6. J Pathol. 229:168–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shi-Wen X, Rodríguez-Pascual F, Lamas S,
Holmes A, Howat S, Pearson JD, Dashwood MR, du Bois RM, Denton CP,
Black CM, et al: Constitutive ALK5-independent c-Jun N-terminal
kinase activation contributes to endothelin-1 overexpression in
pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence of an autocrine endothelin loop
operating through the endothelin A and B receptors. Mol Cell Biol.
26:5518–5527. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Swigris JJ and Brown KK: The role of
endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
BioDrugs. 24:49–54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Krönke G, Reich N, Scholtysek C,
Akhmetshina A, Uderhardt S, Zerr P, Palumbo K, Lang V, Dees C,
Distler O, et al: The 12/15-lipoxygenase pathway counteracts
fibroblast activation and experimental fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:1081–1087. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tonnesen MG, Feng X and Clark RA:
Angiogenesis in wound healing. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc.
5:40–46. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shellenberger TD, Wang M, Gujrati M,
Jayakumar A, Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Ioannides CG, Efferson CL,
El-Naggar AK, Roberts D, et al: BRAK/CXCL14 is a potent inhibitor
of angiogenesis and a chemotactic factor for immature dendritic
cells. Cancer Res. 64:8262–8270. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ye X, Wang Y, Cahill H, Yu M, Badea TC,
Smallwood PM, Peachey NS and Nathans J: Norrin, frizzled-4, and
Lrp5 signaling in endothelial cells controls a genetic program for
retinal vascularization. Cell. 139:285–298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma MZ, Zhuang C, Yang XM, Zhang ZZ, Ma H,
Zhang WM, You H, Qin W, Gu J, Yang S, et al: CTHRC1 acts as a
prognostic factor and promotes invasiveness of gastrointestinal
stromal tumors by activating Wnt/PCP-Rho signaling. Neoplasia.
16:265–278. 278.e1–e13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou Y, Lee JY, Lee CM, Cho WK, Kang MJ,
Koff JL, Yoon PO, Chae J, Park HO, Elias JA and Lee CG:
Amphiregulin, an epidermal growth factor receptor ligand, plays an
essential role in the pathogenesis of transforming growth
factor-β-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Biol Chem. 287:41991–42000.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Perugorria MJ, Latasa MU, Nicou A,
Cartagena-Lirola H, Castillo J, Goñi S, Vespasiani-Gentilucci U,
Zagami MG, Lotersztajn S, Prieto J, et al: The epidermal growth
factor receptor ligand amphiregulin participates in the development
of mouse liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 48:1251–1261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu YJ, Xu Y and Yu Q: Full-length
ADAMTS-1 and the ADAMTS-1 fragments display pro- and antimetastatic
activity, respectively. Oncogene. 25:2452–2467. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|