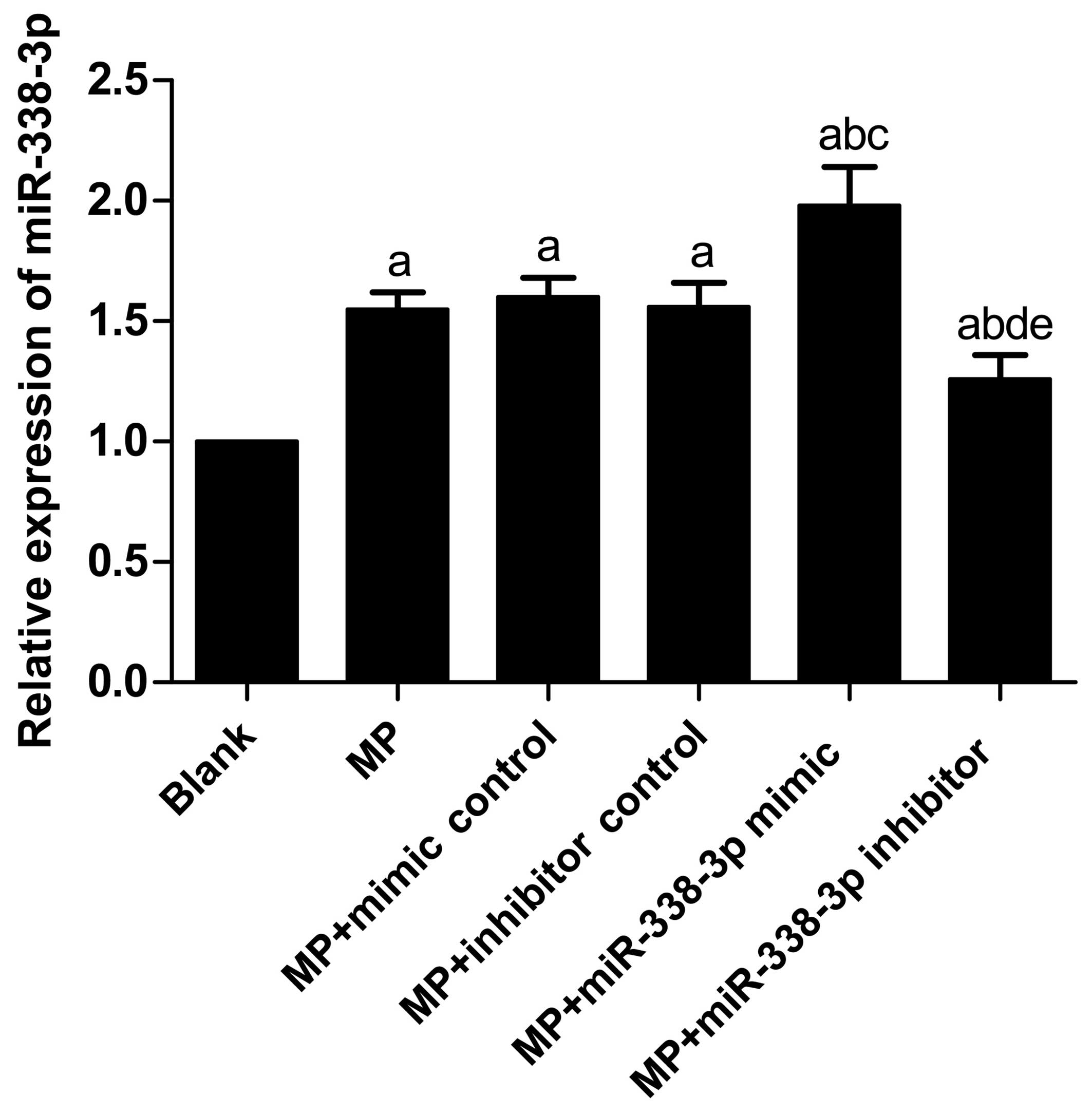
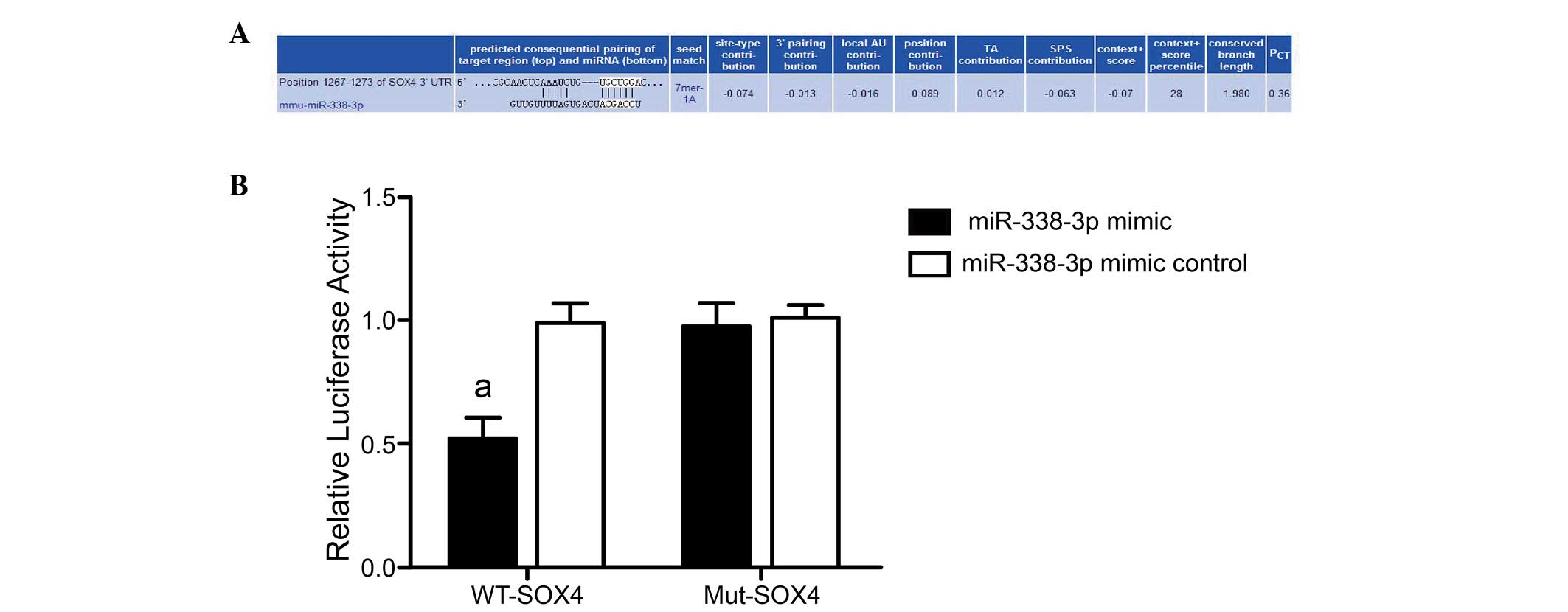
|
1
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 774:1–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu B, Qian T, Wang Y, Zhou S, Ding G, Ding
F and Gu X: miR-182 inhibits Schwann cell proliferation and
migration by targeting FGF9 and NTM, respectively at an early stage
following sciatic nerve injury. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:10356–10365.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahmann S, Martin M, Schulte JH, Köster J,
Marschall T and Schramm A: Identifying transcriptional miRNA
biomarkers by integrating high-throughput sequencing and real-time
PCR data. Methods. 59:154–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gurtan AM and Sharp PA: The role of miRNAs
in regulating gene expression networks. J Mol Biol. 425:3582–3600.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kong X, Xu X, Yan Y, Guo F, Li J, Hu Y,
Zhou H and Xun Q: Estrogen regulates the tumour suppressor
MiRNA-30c and its target gene, MTA-1, in endometrial cancer. PLoS
One. 9:e908102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fiori E, Babicola L, Andolina D, Coassin
A, Pascucci T, Patella L, Han YC, Ventura A and Ventura R:
Neurobehavioral alterations in a genetic murine model of Feingold
Syndrome 2. Behav Genet. 45:547–559. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Zhang J, Carver B,
Haveman WJ and Pandolfi PP: A coding-independent function of gene
and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature.
465:1033–1038. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sayed D and Abdellatif M: MicroRNAs in
development and disease. Physiol Rev. 91:827–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takahashi RU, Miyazaki H and Ochiya T: The
Roles of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 7:598–616.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dahiya N and Atreya CD: MicroRNAs and
Major Blood-borne Infectious Viral Diseases. Microrna. 2:212–218.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bimonte S, Barbieri A, Rea D, Palma G,
Luciano A, Cuomo A, Arra C and Izzo F: Morphine promotes tumor
angiogenesis and increases breast cancer progression. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:1615082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nomura Y, Kawaraguchi Y, Sugimoto H,
Furuya H and Kawaguchi M: Effects of morphine and fentanyl on
5-fluorouracil sensitivity in human colon cancer HCT116 cells. J
Anesth. 28:298–301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gonzalez-Nunez V, Noriega-Prieto JA and
Rodriguez RE: Morphine modulates cell proliferation through mir133b
&mir128 in the neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:566–572. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zheng H, Zeng Y, Chu J, Kam AY, Loh HH and
Law PY: Modulations of NeuroD activity contribute to the
differential effects of morphine and fentanyl on dendritic spine
stability. J Neurosci. 30:8102–8110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sanchez-Simon FM, Zhang XX, Loh HH, Law PY
and Rodriguez RE: Morphine regulates dopaminergic neuron
differentiation via miR-133b. Mol Pharmacol. 78:935–942. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nadeau SE: Opioids for chronic noncancer
pain: To prescribe or not to prescribe-What is the question?
Neurology. 85:646–651. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oosten AW, Oldenmenger WH, Mathijssen RH
and van der Rijt CC: A systematic review of prospective studies
reporting adverse events of commonly used opioids for
Cancer-Related Pain: A call for the use of standardized outcome
measures. J Pain. 16:935–946. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li MC, Yu JH, Yu SS, Chi YY and Xiang YB:
MicroRNA-873 Inhibits Morphine-Induced Macrophage Apoptosis by
Elevating A20 Expression. Pain Med. 16:1993–1999. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He Y, Yang C, Kirkmire CM and Wang ZJ:
Regulation of opioid tolerance by let-7 family microRNA targeting
the mu opioid receptor. J Neurosci. 30:10251–10258. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng Y, Liu YM, Li LC, Wang LL and Wu XL:
MicroRNA-338 inhibits growth, invasion and metastasis of gastric
cancer by targeting NRP1 expression. PLoS One. 9:e944222014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo B, Liu L, Yao J, Ma R, Chang D, Li Z,
Song T and Huang C: miR-338-3p suppresses gastric cancer
progression through a PTEN-AKT axis by targeting P-REX2a. Mol
Cancer Res. 12:313–321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wood MM and Cousins MJ: Iatrogenic
neurotoxicity in cancer patients. Pain. 39:1–3. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(t)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rogler CE, Levoci L, Ader T, Massimi A,
Tchaikovskaya T, Norel R and Rogler LE: MicroRNA-23b cluster
microRNAs regulate transforming growth factor-beta/bone
morphogenetic protein signaling and liver stem cell differentiation
by targeting Smads. Hepatology. 50:575–584. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Osnes T, Sandstad O, Skar V, Osnes M and
Kierulf P: Total protein in common duct bile measured by
acetonitrile precipitation and a micro bicinchoninic acid (BCA)
method. Scand J Clin Lad Invest. 53:757–763. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li P, Chen X, Su L, Li C, Zhi Q, Yu B,
Sheng H, Wang J, Feng R, Cai Q, et al: Epigenentic silencing of
miR-338-3p contributed to tumorigenicity in gastric cancer by
targeting SSX2IP. PLoS One. 8:e667822013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen X, Pan M, Han L, Lu H, Hao X and Dong
Q: miR-338-3p suppresses neuroblastoma proliferation, invasion and
migration through targeting PREX2a. FEBS Lett. 587:3729–3737. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gunes S, Yegin Z, Sullu Y, Buyukalpelli R
and Bagci H: SOX4 expression levels in urothelial bladder
carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 207:423–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y, Wang X, Huang Y, Chen Y, Zhao G,
Yao Q, Jin C, Huang Y, Liu X and Li G: Down-regulated SOX4
expression suppresses cell proliferation, metastasis and induces
apoptosis in Xuanwei female lung cancer patients. J Cell Biochem.
116:1007–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jang SM, Kang EJ, Kim JW, Kim CH, An JH
and Choi KH: Transcription factor Sox4 is required for
PUMA-mediated apoptosis induced by histone deacetylase inhibitor,
TSA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 438:445–451. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu LW, Lu J, Wang XH, Fu SK, Li Q and Lin
FQ: Neuronal apoptosis in morphine addiction and its molecular
mechanism. Int J Clin Exp Med. 6:540–545. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li MD and van der Vaart AD: MicroRNAs in
addiction: Adaptation's middlemen? Mol Psychiatry. 16:1159–1168.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dreyer JL: New insights into the roles of
microRNAs in drug addiction and neuroplasticity. Genome Med.
2:922010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hollander JA, Im HI, Amelio AL, Kocerha J,
Bali P, Lu Q, Willoughby D, Wahlestedt C, Conkright MD and Kenny
PJ: Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB
signalling. Nature. 466:197–202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rodríguez RE: Morphine and microRNA
Activity: Is There a Relation with Addiction? Front Genet.
3:2232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|