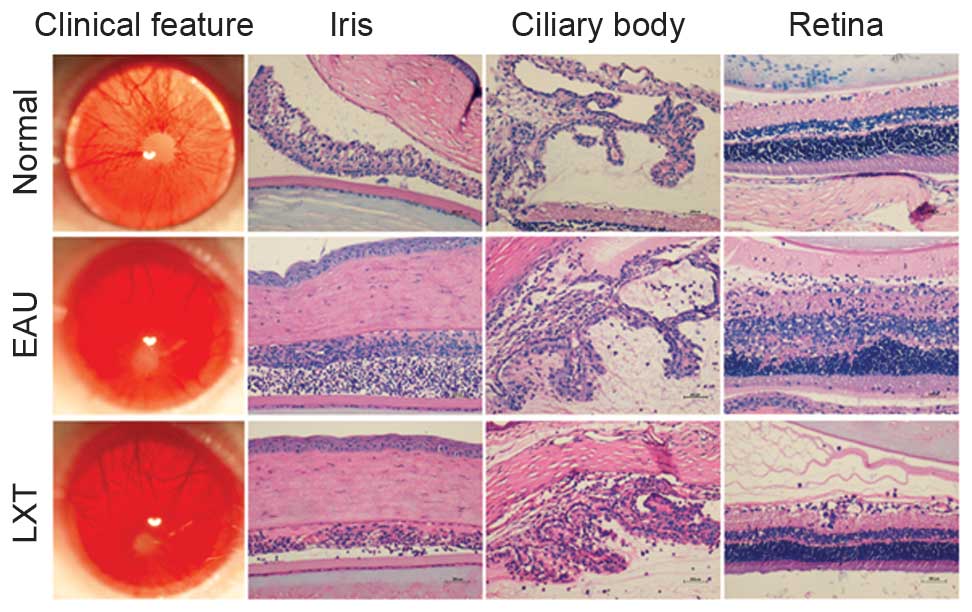
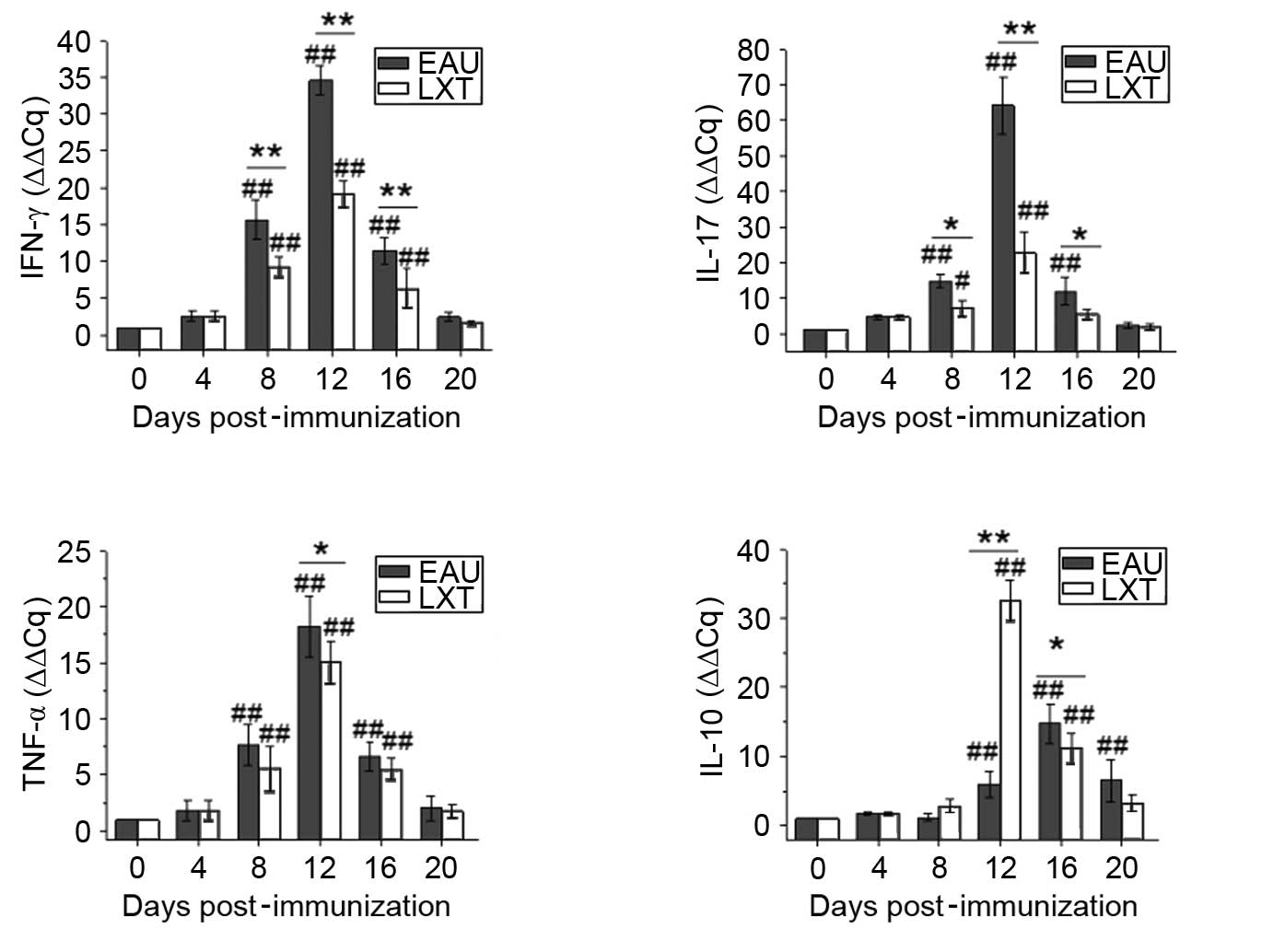
|
1
|
Caspi RR: A look at autoimmunity and
inflammation in the eye. J Clin Invest. 120:3073–3083. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fang CB, Zhou DX, Zhan SX, He Y, Lin Z,
Huang C and Li J: Amelioration of experimental autoimmune uveitis
by leflunomide in Lewis rats. PLoS One. 8:e620712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guo D, Gu P, Liu Z, Tang K, Du Y and Bi H:
Proteomic analysis of rat plasma with experimental autoimmune
uveitis based on label-free liquid chromatography-tandem mass
spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life
Sci. 976–977:84–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guo D, Li J, Liu Z, Tang K, Song H and Bi
H: Characterization of microRNA expression profiling in peripheral
blood lymphocytes in rats with experimental autoimmune uveitis.
Inflamm Res. 64:683–696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Trinh L, Brignole-Baudouin F, Pauly A,
Liang H, Houssier M and Baudouin C: Th1- and Th2-related chemokine
and chemokine receptor expression on the ocular surface in
endotoxin-induced uveitis. Mol Vis. 14:2428–2434. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luger D, Silver PB, Tang J, Cua D, Chen Z,
Iwakura Y, Bowman EP, Sgambellone NM, Chan CC and Caspi RR: Either
a Th17 or a Th1 effector response can drive autoimmunity:
Conditions of disease induction affect dominant effector category.
J Exp Med. 205:799–810. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Horai R and Caspi RR: Cytokines in
autoimmune uveitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 31:733–744. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanz-Marco E, Garces M, Sempere A and
Diaz-Llopis M: CD4/CD8 ratio in aqueous humor in Uveitis. Ocul
Immunol Inflamm. 21:408–409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kojima K, Maruyama K, Inaba T, Nagata K,
Yasuhara T, Yoneda K, Sugita S, Mochizuki M and Kinoshita S: The
CD4/CD8 ratio in vitreous fluid is of high diagnostic value in
sarcoidosis. Ophthalmology. 119:2386–2392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Davis JL, Ruiz P Jr, Shah M and Mandelcorn
ED: Evaluation of the reactive T-cell infiltrate in uveitis and
intraocular lymphoma with flow cytometry of vitreous fluid (an
American Ophthalmological Society thesis). Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc.
110:117–129. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Wang CH, Cheng XM, Bligh SW, White KN,
Branford-White CJ and Wang ZT: Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability
of gentiopicroside from decoctions of Gentianae and Longdan Xiegan
Tang after oral administration in rats - comparison with
gentiopicroside alone. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 44:1113–1117. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng HY, Huang HH, Yang CM, Lin LT and
Lin CC: The in vitro anti-herpes simplex virus type-1 and type-2
activity of Long Dan Xie Gan Tan, a prescription of traditional
Chinese medicine. Chemotherapy. 54:77–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lai SC, Chen KM, Chang YH and Lee HH:
Comparative efficacies of albendazole and the Chinese herbal
medicine long-dan-xie-gan-tan, used alone or in combination, in the
treatment of experimental eosinophilic meningitis induced by
Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 102:143–150.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee TY and Chang HH: Longdan Xiegan Tang
has immuno-modulatory effects on CD4+CD25+ T cells and attenuates
pathological signs in MRL/lpr mice. Int J Mol Med. 25:677–685.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ou YY, Cao SX and Zhang J: Clinical
experience of decoction of gentian for purging liver fire
applicated in ophthalmology. Liao Ning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao.
10:123–124. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
16
|
Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. (NIH Publication No. 80-23). Washington, D.C: National
Academy Press; 1996
|
|
17
|
The Association for Research in Vision and
Opthamology: Statement for the use of animals in ophthalmic and
visual research. http://www.arvo.org/About_ARVO/Policies/Statement_for_the_Use_of_Animals_in_Ophthalmic_and_Visual_Research/.
Accessed Jun 1, 2016.
|
|
18
|
Chinese Pharmacopeia. China Medical
Science Press; Beijing, China: 2010
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zaidi AA, Ying GS, Daniel E, Gangaputra S,
Rosenbaum JT, Suhler EB, Thorne JE, Foster CS, Jabs DA, Levy-Clarke
GA, et al: Hypopyon in patients with uveitis. Ophthalmology.
117:366–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Agarwal RK, Silver PB and Caspi RR: Rodent
models of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Methods Mol Biol.
900:443–469. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Raveney BJ, Copland DA, Dick AD and
Nicholson LB: TNFR1-dependent regulation of myeloid cell function
in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. J Immunol. 183:2321–2329.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kerr EC, Raveney BJ, Copland DA, Dick AD
and Nicholson LB: Analysis of retinal cellular infiltrate in
experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis reveals multiple regulatory
cell populations. J Autoimmun. 31:354–361. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caspi RR: Th1 and Th2 responses in
pathogenesis and regulation of experimental autoimmune
uveoretinitis. Int Rev Immunol. 21:197–208. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Crane IJ, Xu H, Wallace C, Manivannan A,
Mack M, Liversidge J, Marquez G, Sharp PF and Forrester JV:
Involvement of CCR5 in the passage of Th1-type cells across the
blood-retina barrier in experimental autoimmune uveitis. J Leukoc
Biol. 79:435–443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva
R, Wang YH, Wang Y, Hood L, Zhu Z, Tian Q and Dong C: A distinct
lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing
interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 6:1133–1141. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A,
Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Sudo K and Iwakura Y: IL-17 plays an
important role in the development of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 177:566–573. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM,
Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA and
Cua DJ: IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces
autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 201:233–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cui Y, Shao H, Lan C, Nian H, O'Brien RL,
Born WK, Kaplan HJ and Sun D: Major role of gamma delta T cells in
the generation of IL-17+ uveitogenic T cells. J Immunol.
183:560–567. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zuo A, Liang D, Shao H, Born WK, Kaplan HJ
and Sun D: In vivo priming of IL-17(+) uveitogenic T
cells is enhanced by Toll ligand receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 agonists
via γδ T cell activation. Mol Immunol. 50:125–133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peng Y, Han G, Shao H, Wang Y, Kaplan HJ
and Sun D: Characterization of IL-17+ interphotoreceptor
retinoid-binding protein-specific T cells in experimental
autoimmune uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 48:4153–4161. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tian Q, Bi H, Cui Y, Guo D, Xie X, Su W
and Wang X: Qing-kailing injection alleviates experimental
autoimmune uveitis in rats via inhibiting Th1 and Th17 effector
cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:1991–1996. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Agarwal RK, Horai R, Viley AM, Silver PB,
Grajewski RS, Su SB, Yazdani AT, Zhu W, Kronenberg M, Murray PJ, et
al: Abrogation of anti-retinal autoimmunity in IL-10 transgenic
mice due to reduced T cell priming and inhibition of disease
effector mechanisms. J Immunol. 180:5423–5429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shao J, Tian L, Lei B, Wei L, Yang Y,
Kijlstra A and Yang P: AAV2-mediated subretinal gene transfer of
mIL-27p28 attenuates experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in mice.
PLoS One. 7:e377732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|