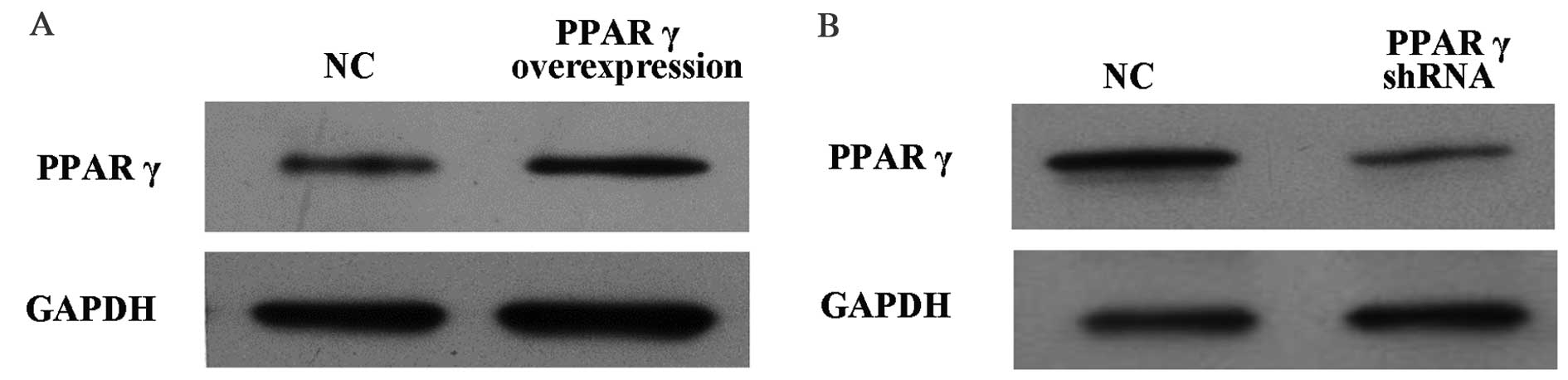
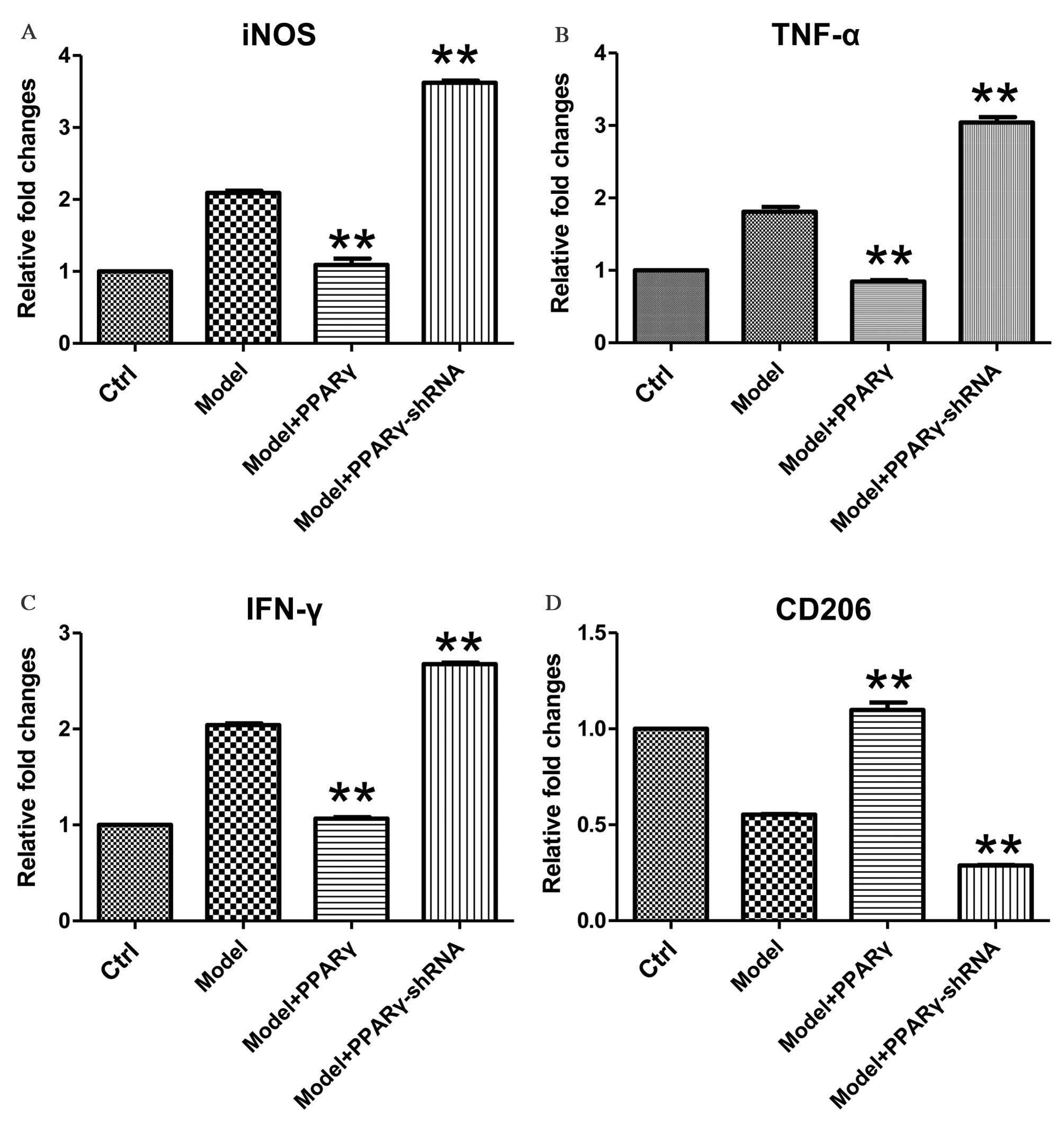
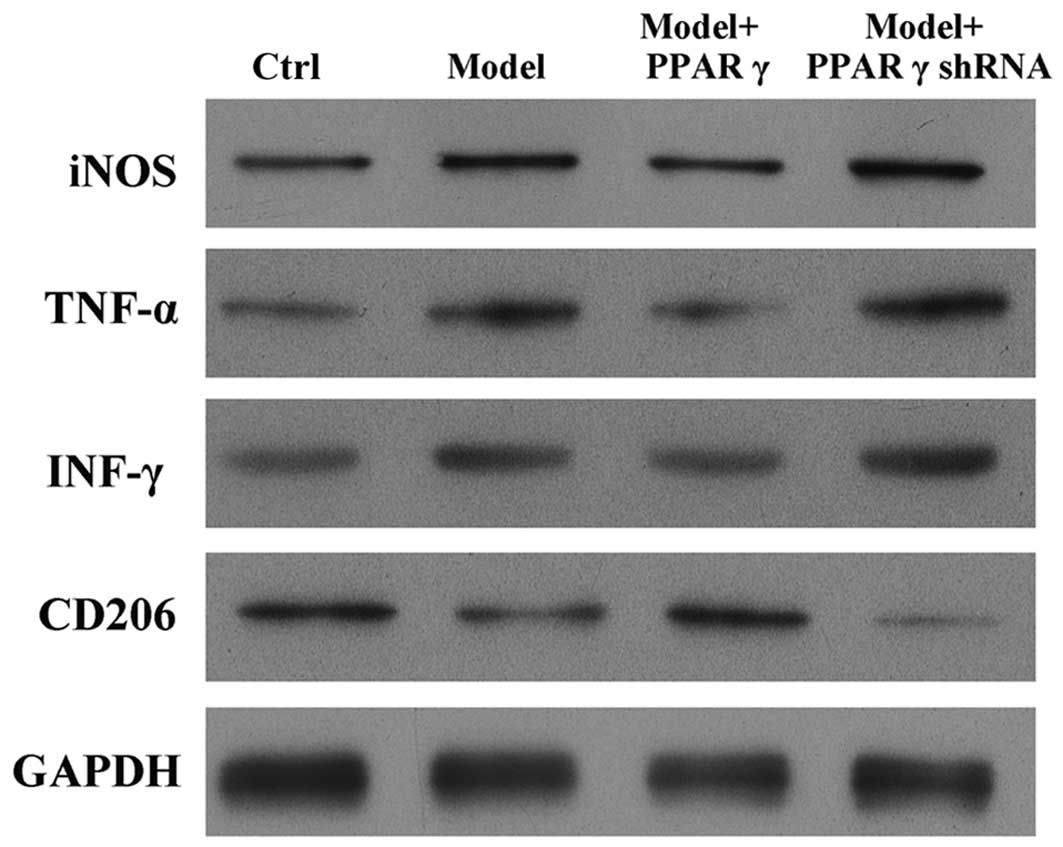
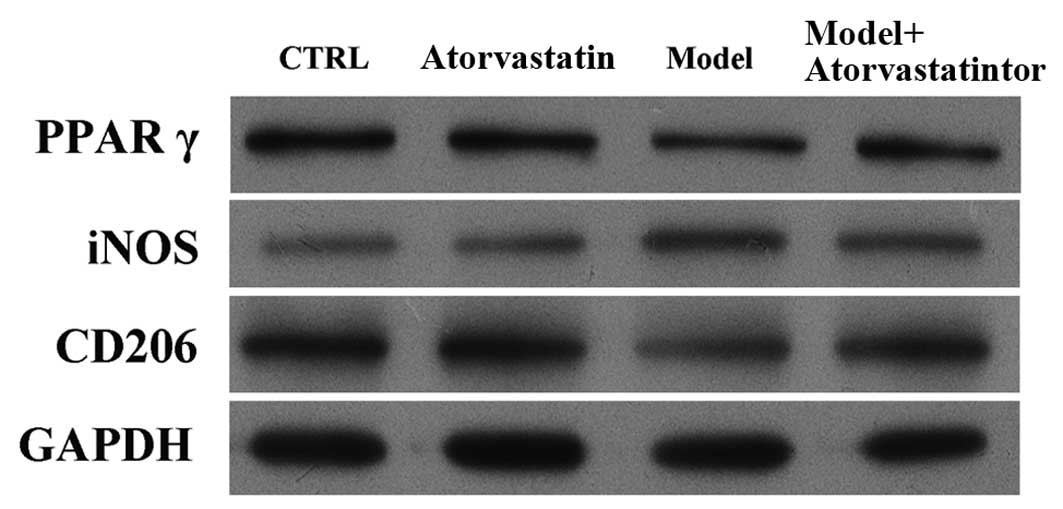
|
1
|
Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ,
Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, Zheng ZJ, Flegal K, O'Donnell C, Kittner S,
et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2006 update: A report
from the American heart association statistics committee and stroke
statistics subcommittee. Circulation. 113:e85–e151. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ricci Z, Cruz D and Ronco C: The RIFLE
criteria and mortality in acute kidney injury: A systematic review.
Kidney Int. 73:538–546. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Groot H and Rauen U:
Ischemia-reperfusion injury: Processes in pathogenetic networks: A
review. Transplant Proc. 39:481–484. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Devarajan P: Update on mechanisms of
ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1503–1520. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bellomo R, Kellum JA and Ronco C: Acute
kidney injury. Lancet. 380:756–766. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Varol C, Mildner A and Jung S:
Macrophages: Development and tissue specialization. Annu Rev
Immunol. 33:643–675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cao Q, Harris DC and Wang Y: Macrophages
in kidney injury, inflammation, and fibrosis. Physiology
(Bethesda). 30:183–194. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bonventre JV and Zuk A: Ischemic acute
renal failure: An inflammatory disease? Kidney Int. 66:480–485.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bonventre JV and Yang L: Cellular
pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest.
121:4210–4221. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simmons EM, Himmelfarb J, Sezer MT,
Chertow GM, Mehta RL, Paganini EP, Soroko S, Freedman S, Becker K,
Spratt D, et al: Plasma cytokine levels predict mortality in
patients with acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 65:1357–1365. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jaber BL, Rao M, Guo D, Balakrishnan VS,
Perianayagam MC, Freeman RB and Pereira BJ: Cytokine gene promoter
polymorphisms and mortality in acute renal failure. Cytokine.
25:212–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kawanishi N, Yano H, Yokogawa Y and Suzuki
K: Exercise training inhibits inflammation in adipose tissue via
both suppression of macrophage infiltration and acceleration of
phenotypic switching from M1 to M2 macrophages in
high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Exerc Immunol Rev. 16:105–118.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mantovani A, Sica A and Locati M: New
vistas on macrophage differentiation and activation. Eur J Immunol.
37:14–16. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goerdt S, Politz O, Schledzewski K, Birk
R, Gratchev A, Guillot P, Hakiy N, Klemke CD, Dippel E, Kodelja V
and Orfanos CE: Alternative versus classical activation of
macrophages. Pathobiology. 67:222–226. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee S, Huen S, Nishio H, Nishio S, Lee HK,
Choi BS, Ruhrberg C and Cantley LG: Distinct macrophage phenotypes
contribute to kidney injury and repair. J Am Soc Nephrol.
22:317–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang J, Jiang ZP, Su N, Fan JJ, Ruan YP,
Peng WX, Li YF and Yu XQ: The role of peritoneal alternatively
activated macrophages in the process of peritoneal fibrosis related
to peritoneal dialysis. Int J Mol Sci. 14:10369–10382. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jo SK, Sung SA, Cho WY, Go KJ and Kim HK:
Macrophages contribute to the initiation of ischaemic acute renal
failure in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 21:1231–1239. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meier CR, Schlienger RG, Kraenzlin ME,
Schlegel B and Jick H: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of
fractures. JAMA. 283:3205–3210. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lewicki M, Ng I and Schneider AG: HMG CoA
reductase inhibitors (statins) for preventing acute kidney injury
after surgical procedures requiring cardiac bypass. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. CD0104802015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zamorskiĭ II and Zeleniuk VG:
Renoprotective effects of statins under the conditions of acute
renal failure, caused by rhabdomyolysis. Biofizika. 59:1027–1030.
2014.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Zhang MX, Meng X, Liu FQ, Yu GS,
Zhang C, Sun T, Wang XP, Li L, Wang YY, et al: Atorvastatin
suppresses LPS-induced rapid upregulation of Toll-like receptor 4
and its signaling pathway in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 300:H1743–H1752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu K, Lei W, Tian J and Li H: Atorvastatin
treatment attenuates renal injury in an experimental model of
ischemia-reperfusion in rats. BMC Nephrol. 15:142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tontonoz P, Hu E and Spiegelman BM:
Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a
lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell. 79:1147–1156. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen CA and Okayama H: Calcium
phosphate-mediated gene transfer: A highly efficient transfection
system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA.
Biotechniques. 6:632–638. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo J, Krause DN, Horne J, Weiss JH, Li X
and Duckles SP: Estrogen-receptor-mediated protection of cerebral
endothelial cell viability and mitochondrial function after
ischemic insult in vitro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:545–554.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brault M, Ray J, Gomez YH, Mantzoros CS
and Daskalopoulou SS: Statin treatment and new-onset diabetes: A
review of proposed mechanisms. Metabolism. 63:735–745. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu X, Li P, Guo Y, Wang H, Leak RK, Chen
S, Gao Y and Chen J: Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics
reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral
ischemia. Stroke. 43:3063–3070. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leitinger N and Schulman IG: Phenotypic
polarization of macrophages in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 33:1120–1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tontonoz P and Spiegelman BM: Fat and
beyond: The diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem.
77:289–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lamers C, Schubert-Zsilavecz M and Merk D:
Therapeutic modulators of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptors (PPAR): A patent review (2008-present). Expert Opin Ther
Pat. 22:803–841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lawrence T and Natoli G: Transcriptional
regulation of macrophage polarization: Enabling diversity with
identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:750–761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wahli W and Michalik L: PPARs at the
crossroads of lipid signaling and inflammation. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 23:351–363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grip O, Janciauskiene S and Lindgren S:
Atorvastatin activates PPAR-γ and attenuates the inflammatory
response in human monocytes. Inflammation Research. 51:58–62. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Planavila A, Laguna JC and Vázquez-Carrera
M: Atorvastatin improves peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
signaling in cardiac hypertrophy by preventing nuclear factor-κB
activation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell
Biology of Lipids. 1687:76–83. 2005.
|