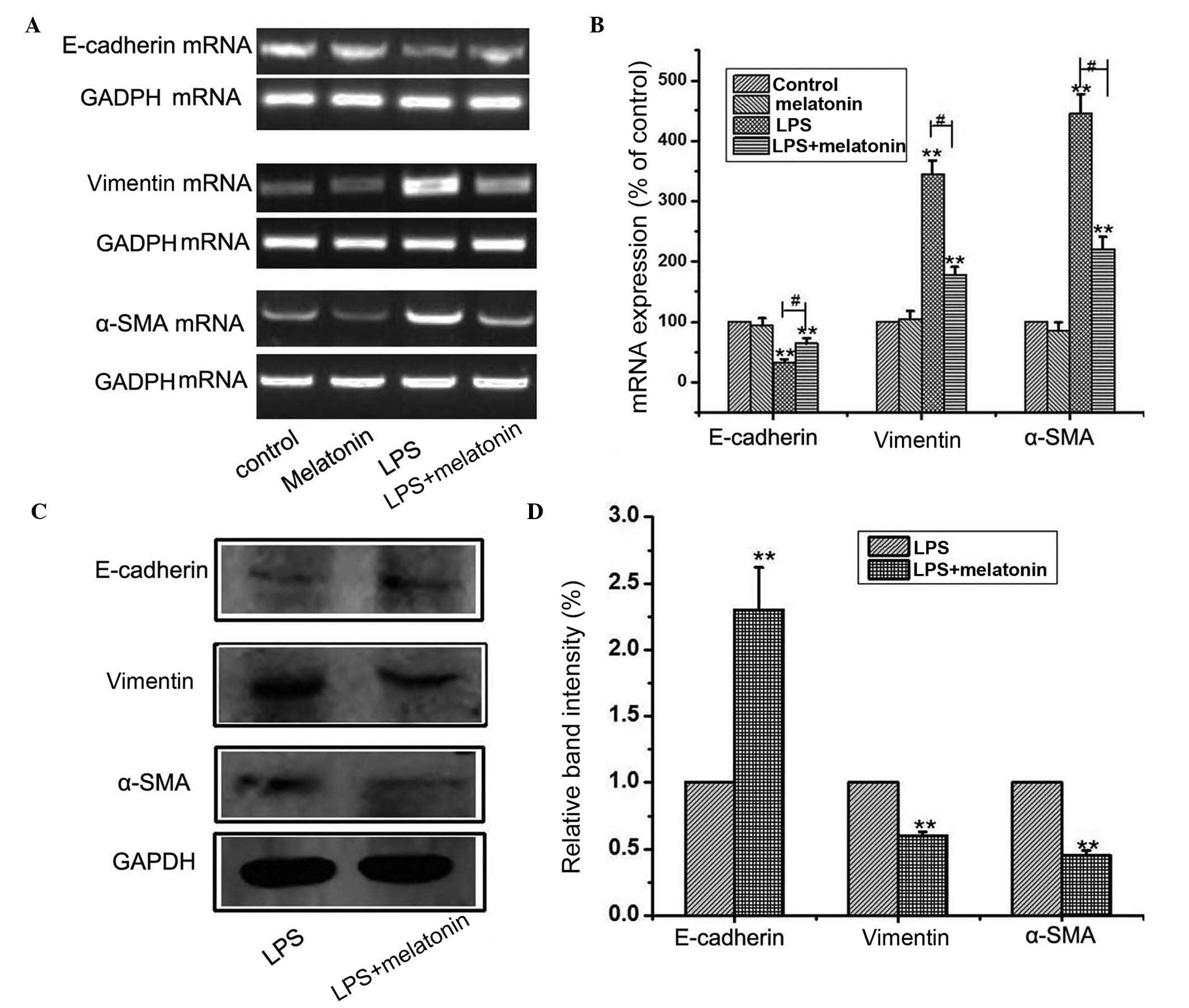
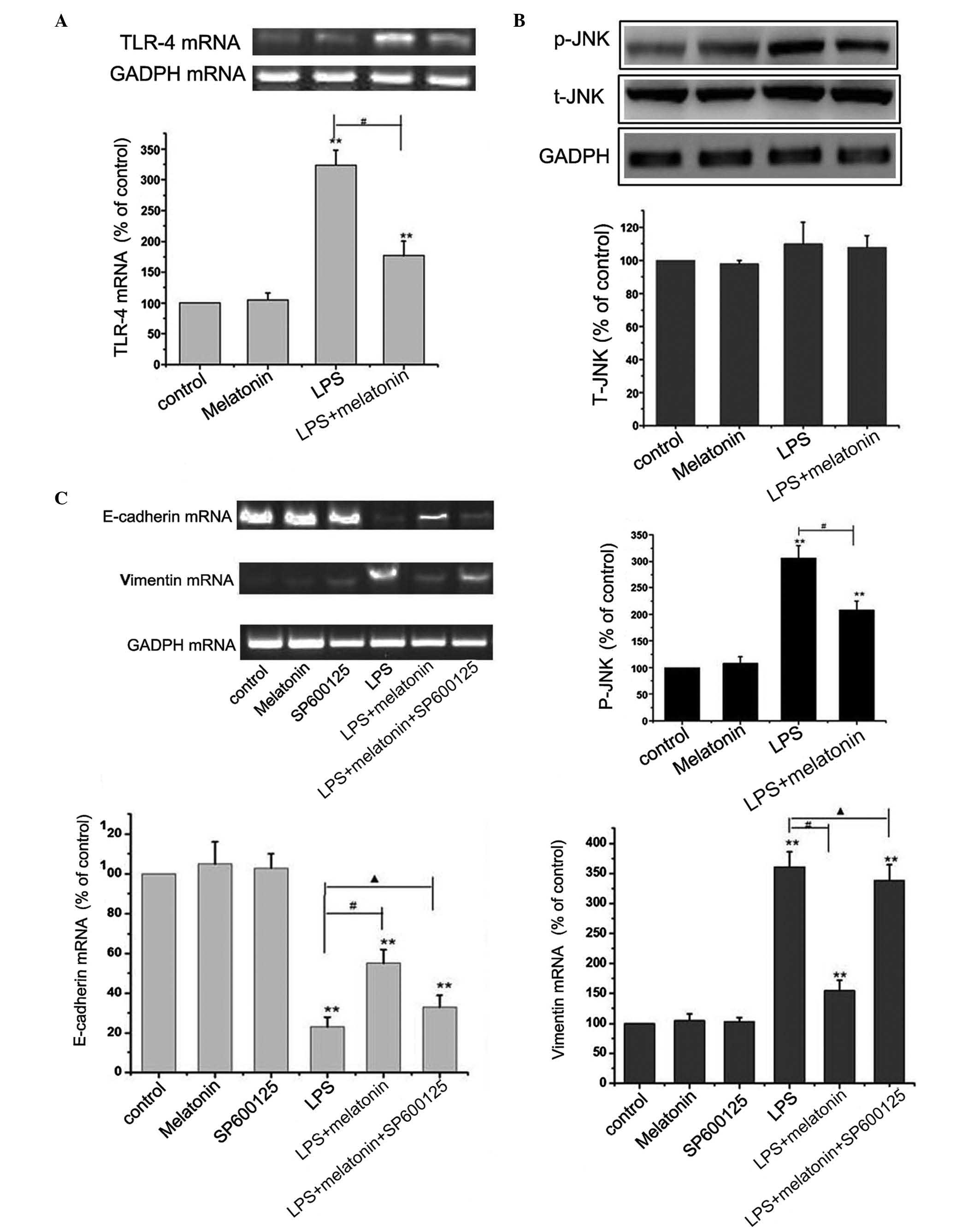
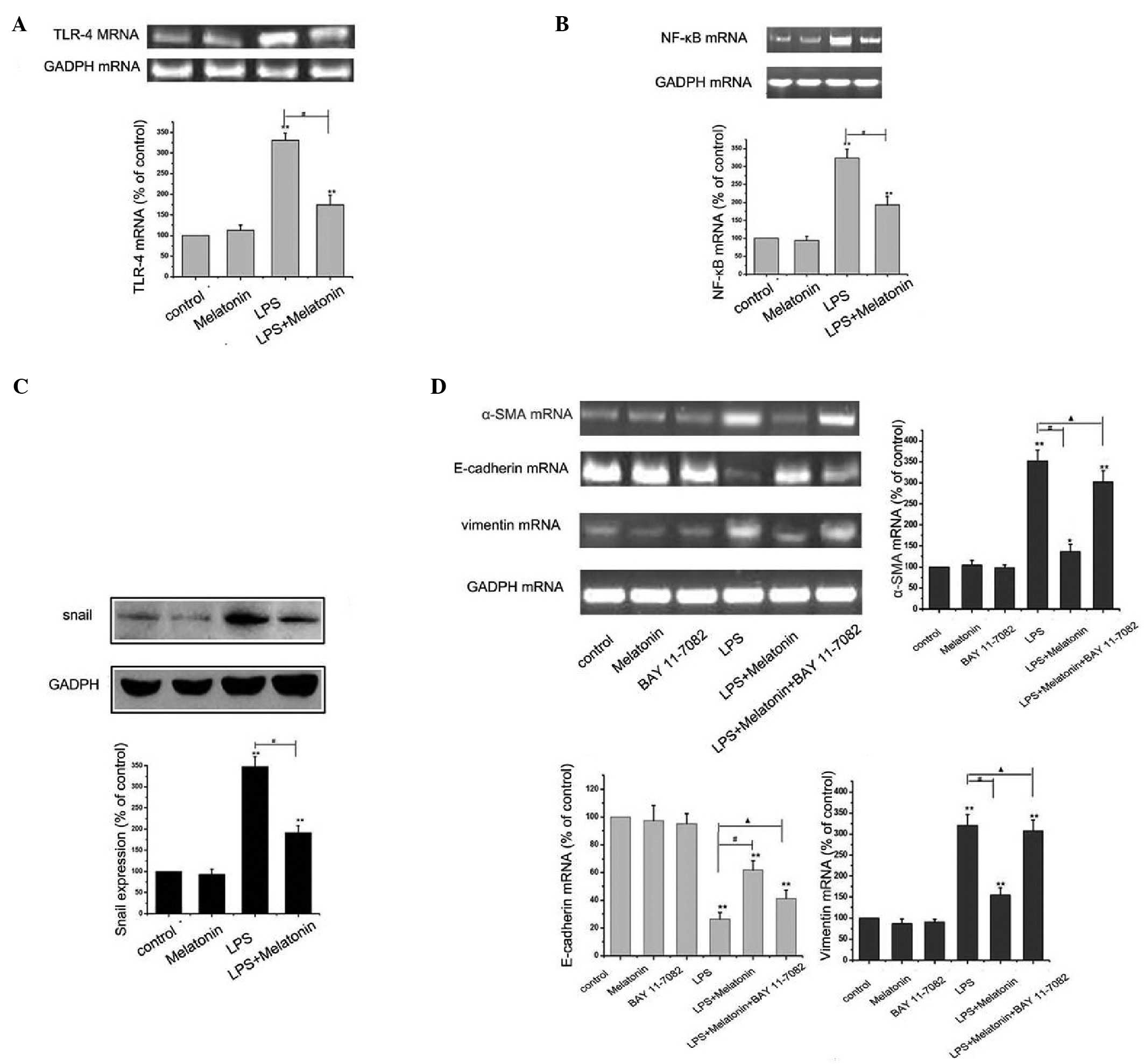
|
1
|
Rastogi A, Linden A and Nissenson AR:
Disease management in chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney
Dis. 15:19–28. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zelmer JL: The economic burden of
end-stage renal disease in Canada. Kidney Int. 72:1122–1129. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Knoll GA and Nichol G: Dialysis, kidney
transplantation, or pancreas transplantation for patients with
diabetes mellitus and renal failure: A decision analysis of
treatment options. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:500–515. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mousavi SS Beladi, Hayati F, Valavi E,
Rekabi F and Mousavi MB: Comparison of survival in patients with
end-stage renal disease receiving hemodialysis versus peritoneal
dialysis. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 26:392–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jain AK, Blake P, Cordy P and Garg AX:
Global trends in rates of peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
23:533–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ueno T, Nakashima A, Doi S, Kawamoto T,
Honda K, Yokoyama Y, Doi T, Higashi Y, Yorioka N, Kato Y, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental peritoneal fibrosis
by suppressing inflammation and inhibiting TGF-β1 signaling. Kidney
Int. 84:297–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Puisieux A, Brabletz T and Caramel J:
Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell
Biol. 16:488–494. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Strippoli R, Moreno-Vicente R, Battistelli
C, Battistelli C, Cicchini C, Noce V, Amicone L, Marchetti A, Del
Pozo MA and Tripodi M: Molecular mechanisms underlying peritoneal
EMT and fibrosis. Stem Cells Int. 35436782016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen MC, Chang WW, Kuan YD, Lin ST, Hsu HC
and Lee CH: Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in mouse melanoma model. Innate Immun. 18:685–693. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang C, Zheng H, He W, Lu G, Li X, Deng Y
and Zeng M: Ghrelin ameliorates the human alveolar epithelial A549
cell apoptosis induced by lipopolysaccharide. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 474:83–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jing YY, Han ZP, Sun K, Zhang SS, Hou J,
Liu Y, Li R, Gao L, Zhao X, Zhao QD, et al: Toll-like receptor 4
signaling promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
hepatocellular carcinoma induced by lipopolysaccharide. BMC Med.
10:982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Esposito E and Cuzzocrea S:
Antiinflammatory activity of melatonin in central nervous system.
Curr Neuropharmacol. 8:228–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Obana-Koshino A, Ono H, Miura J, Sakai M,
Uchida H, Nakamura W, Nohara K, Maruyama Y, Hattori A and Sakai T:
Melatonin inhibits embryonic salivary gland branching morphogenesis
by regulating both epithelial cell adhesion and morphology. PLoS
One. 10:e01199602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pirianov G, Torsney E, Howe F and
Cockerill GW: Rosiglitazone negatively regulates c-Jun N-terminal
kinase and toll-like receptor 4 proinflammatory signalling during
initiation of experimental aortic aneurysms. Atherosclerosis.
225:69–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiong XX, Liu JM, Qiu XY, Pan F, Yu SB and
Chen XQ: Piperlongumine induces apoptotic and autophagic death of
the primary myeloid leukemia cells from patients via activation of
ROS-p38/JNK pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:362–374. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Naugler WE and Karin M: NF-kappaB and
cancer-identifying targets and mechanisms. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
18:19–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gu K, Li MM, Shen J, Liu F, Cao JY, Jin S
and Yu Y: Interleukin-17-induced EMT promotes lung cancer cell
migration and invasion via NF-κB/ZEB1 signal pathway. Am J Cancer
Res. 5:1169–1179. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Houdek P, Polidarová L, Nováková M, Matějů
K, Kubík Š and Sumová A: Melatonin administered during the fetal
stage affects circadian clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus but
not in the liver. Dev Neurobiol. 75:131–144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Pedro N, Martínez-Alvarez RM and
Delgado MJ: Melatonin reduces body weight in goldfish (Carassius
auratus): Effects on metabolic resources and some feeding
regulators. J Pineal Res. 45:32–39. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Plaimee P, Weerapreeyakul N, Barusrux S
and Johns NP: Melatonin potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Prolif.
48:67–77. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carrasco C, Marchena AM, Holguín-Arévalo
MS, Martín-Partido G, Rodríguez AB, Paredes SD and Pariente JA:
Anti-inflammatory effects of melatonin in a rat model of
caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Cell Biochem Funct.
31:585–590. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao H, Wu QQ, Cao LF, Qing HY, Zhang C,
Chen YH, Wang H, Liu RY and Xu DX: Melatonin inhibits endoplasmic
reticulum stress and epithelial-mesenchymal transition during
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. PLoS One.
9:e972662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song J, Kang SM, Lee KM and Lee JE: The
protective effect of melatonin on neural stem cell against
LPS-induced inflammation. Biomed Res Int. 2015:8543592015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aparicio-Soto M, Alarcón-de-la-Lastra C,
Cárdeno A, Sánchez-Fidalgo S and Sanchez-Hidalgo M: Melatonin
modulates microsomal PGE synthase 1 and NF-E2-related
factor-2-regulated antioxidant enzyme expression in LPS-induced
murine peritoneal macrophages. Br J Pharmacol. 171:134–144. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Margetts PJ, Kolb M, Yu L, Hoff CM and
Gauldie J: A chronic inflammatory infusion model of peritoneal
dialysis in rats. Perit Dial Int. 21:(Suppl 3). S368–S372.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nijland R, Hofland T and van Strijp JA:
Recognition of LPS by TLR4: Potential for anti-inflammatory
therapies. Mar Drugs. 12:4260–4273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|