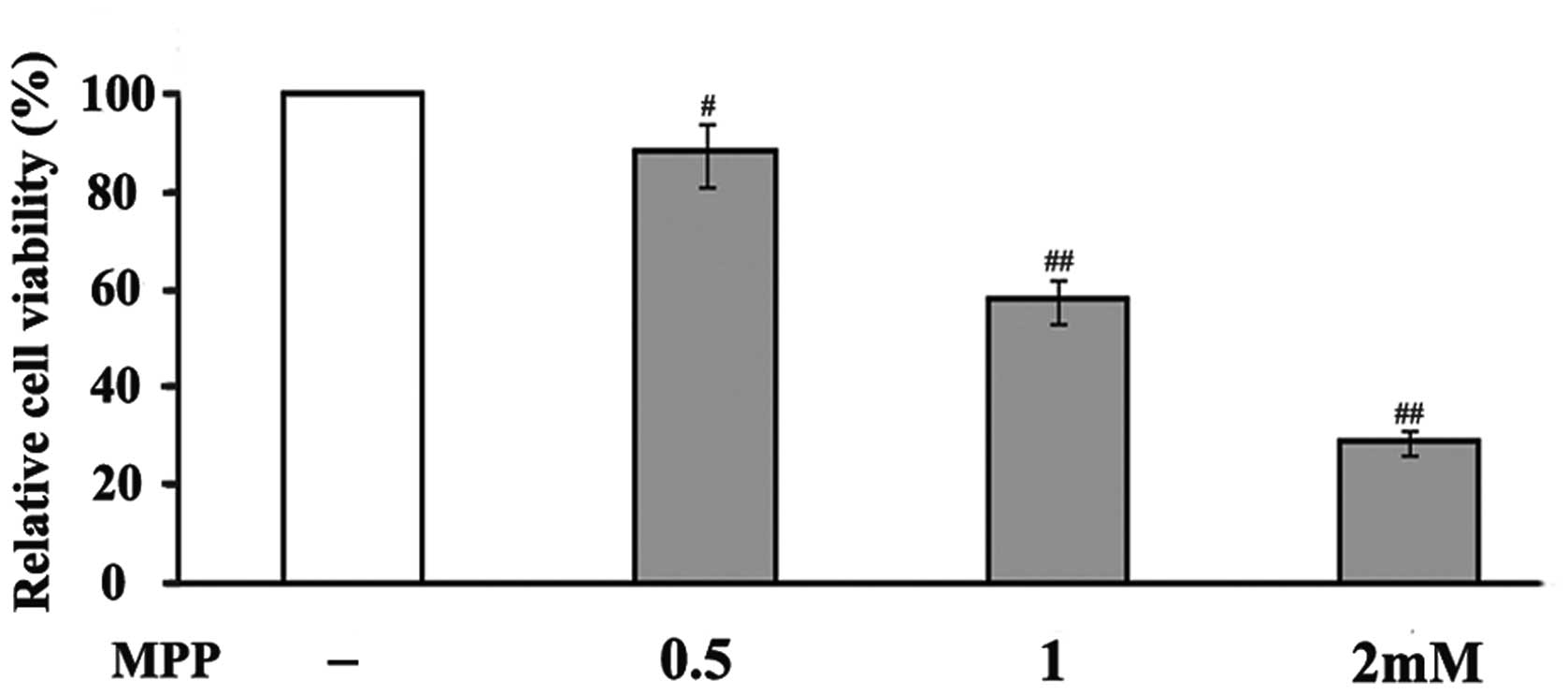
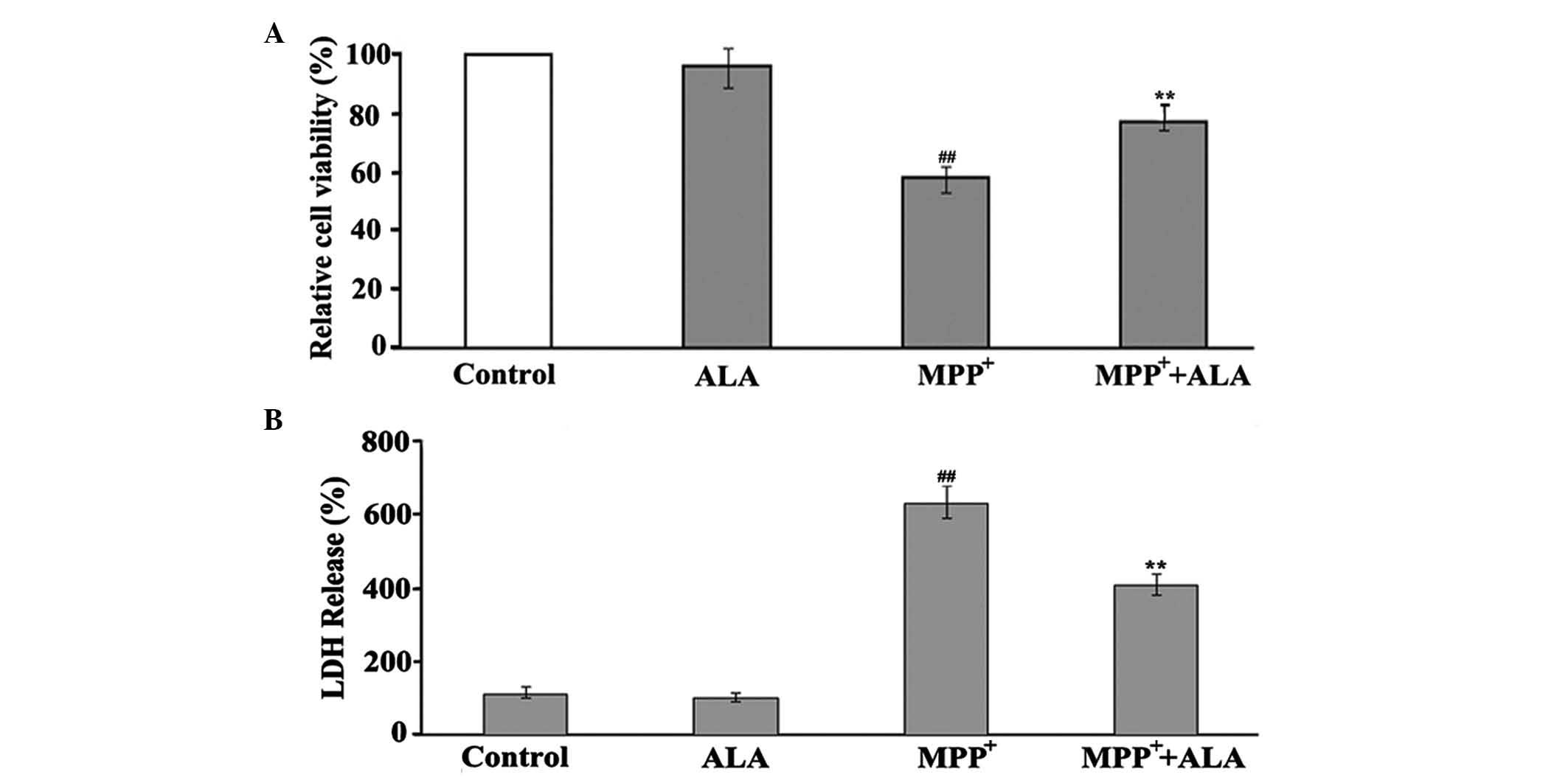
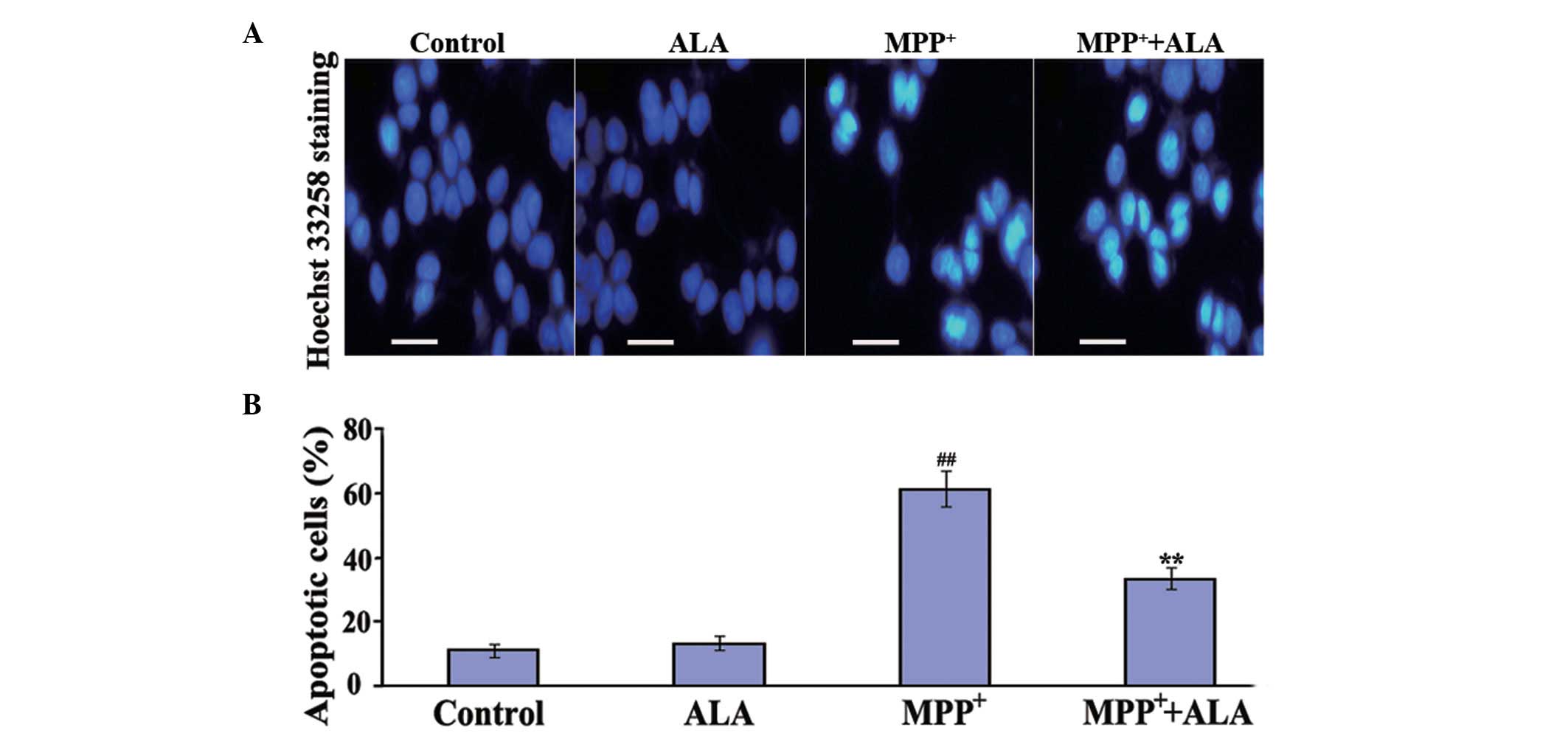
|
1
|
de Lau LM and Breteler MM: Epidemiology of
Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 5:525–535. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alam ZI, Jenner A, Daniel SE, Lees AJ,
Cairns N, Marsden CD, Jenner P and Halliwell B: Oxidative DNA
damage in the parkinsonian brain: An apparent selective increase in
8-hydroxyguanine levels in substantia nigra. J Neurochem.
69:1196–1203. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mandir AS, Przedborski S, Jackson-Lewis V,
Wang ZQ, Simbulan-Rosenthal CM, Smulson ME, Hoffman BE, Guastella
DB, Dawson VL and Dawson TM: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
activation mediates 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
(MPTP)-induced parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:5774–5779.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moldovan GL, Pfander B and Jentsch S:
PCNA, the maestro of the replication fork. Cell. 129:665–679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mailand N, Gibbs-Seymour I and
Bekker-Jensen S: Regulation of PCNA-protein interactions for genome
stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:269–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li DW, Li GR, Zhang BL, Feng JJ and Zhao
H: Damage to dopaminergic neurons is mediated by proliferating cell
nuclear antigen through the p53 pathway under conditions of
oxidative stress in a cell model of Parkinson's disease. Int J Mol
Med. 37:429–435. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Burkovics P, Hajdú I, Szukacsov V, Unk I
and Haracska L: Role of PCNA-dependent stimulation of
3′-phosphodiesterase and 3′-5′ exonuclease activities of human Ape2
in repair of oxidative DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:4247–4255.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amoroso A, Concia L, Maggio C, Raynaud C,
Bergounioux C, Crespan E, Cella R and Maga G: Oxidative DNA damage
bypass in Arabidopsis thaliana requires DNA polymerase λ and
proliferating cell nuclear antigen 2. Plant Cell. 23:806–822. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shay KP, Moreau RF, Smith EJ, Smith AR and
Hagen TM: Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1790:1149–1160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wollin SD and Jones PJ: Alpha-lipoic acid
and cardiovascular disease. J Nutr. 133:3327–3330. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McNeilly AM, Davison GW, Murphy MH, Nadeem
N, Trinick T, Duly E, Novials A and McEneny J: Effect of α-lipoic
acid and exercise training on cardiovascular disease risk in
obesity with impaired glucose tolerance. Lipids Health Dis.
10:2172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stanković MN, Mladenović D, Ninković M,
Ethuričić I, Sobajić S, Jorgačević B, de Luka S, Vukicevic RJ and
Radosavljević TS: The effects of α-lipoic acid on liver oxidative
stress and free fatty acid composition in methionine-choline
deficient diet-induced NAFLD. J Med Food. 17:254–261. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hatami S, Zavareh S, Salehnia M,
Lashkarbolouki T, Ghorbanian MT and Karimi I: Total oxidative
status of mouse vitrified pre-antral follicles with pre-treatment
of alpha lipoic acid. Iran Biomed J. 18:181–188. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Showkat A, Bastnagel WR and Hudson JQ:
Effect of α-lipoic acid on oxidative stress in end-stage renal
disease patients receiving intravenous iron. ISRN Nephrol.
2014:6345152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, Meissner
HP, Lobisch M, Schütte K and Gries FA: Treatment of symptomatic
diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the anti-oxidant alpha-lipoic
acid. A 3-week multicentre randomized controlled trial (ALADIN
Study). Diabetologia. 38:1425–1433. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, Hasche
H, Lobisch M, Schütte K, Kerum G and Malessa R: Treatment of
symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant
alpha-lipoic acid: A 7-month multicenter randomized controlled
trial (ALADIN III Study). ALADIN III study group. Alpha-lipoic acid
in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 22:1296–1301. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sancheti H, Kanamori K, Patil I, Brinton R
Diaz, Ross BD and Cadenas E: Reversal of metabolic deficits by
lipoic acid in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease: A 13C NMR study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 34:288–296.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mansoor S, Gupta N, Luczy-Bachman G, Limb
GA, Kuppermann BD and Kenney MC: Protective effects of lipoic acid
on chrysene-induced toxicity on Müller cells in vitro. Mol Vis.
19:25–38. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li DW, Li GR, Lu Y, Liu ZQ, Chang M, Yao
M, Cheng W and Hu LS: α-lipoic acid protects dopaminergic neurons
against MPP+-induced apoptosis by attenuating reactive oxygen
species formation. Int J Mol Med. 32:108–114. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morris GF, Bischoff JR and Mathews MB:
Transcriptional activation of the human proliferating-cell nuclear
antigen promoter by p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:895–899. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shivakumar CV, Brown DR, Deb S and Deb SP:
Wild-type human p53 transactivates the human proliferating cell
nuclear antigen promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 15:6785–6793. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martin LJ: p53 is abnormally elevated and
active in the CNS of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Neurobiol Dis. 7:613–622. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duan W, Zhu X, Ladenheim B, Yu QS, Guo Z,
Oyler J, Cutler RG, Cadet JL, Greig NH and Mattson MP: p53
inhibitors preserve dopamine neurons and motor function in
experimental parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 52:597–606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Forno LS: Neuropathology of Parkinson's
disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 55:259–272. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dias V, Junn E and Mouradian MM: The role
of oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis.
3:461–491. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Montine KS, Quinn JF, Zhang J, Fessel JP,
Roberts LJ II, Morrow JD and Montine TJ: Isoprostanes and related
products of lipid peroxidation in neurodegenerative diseases. Chem
Phys Lipids. 128:117–124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sadrzadeh SM and Saffari Y: Iron and brain
disorders. Am J Clin Pathol. 121:(Suppl). S64–S70. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jomova K and Valko M: Advances in
metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology.
283:65–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nagatsu T and Sawada M: Molecular
mechanism of the relation of monoamine oxidase B and its inhibitors
to Parkinson's disease: Possible implications of glial cells. J
Neural Transm Suppl. 53–65. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Núñez MT, Urrutia P, Mena N, Aguirre P,
Tapia V and Salazar J: Iron toxicity in neurodegeneration.
Biometals. 25:761–776. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goraca A, Huk-Kolega H, Piechota A,
Kleniewska P, Ciejka E and Skibska B: Lipoic acid-biological
activity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Rep. 63:849–858.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Panigrahi M, Sadguna Y, Shivakumar BR,
Kolluri SV, Roy S, Packer L and Ravindranath V: Alpha-Lipoic acid
protects against reperfusion injury following cerebral ischemia in
rats. Brain Res. 717:184–188. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Arivazhagan P, Shila S, Kumaran S and
Panneerselvam C: Effect of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on the status of
lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in various brain regions
of aged rats. Exp Gerontol. 37:803–811. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: Dissecting
p53-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 13:994–1002. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Culmsee C and Mattson MP: p53 in neuronal
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:761–777. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mandir AS, Simbulan-Rosenthal CM, Poitras
MF, Lumpkin JR, Dawson VL, Smulson ME and Dawson TM: A novel in
vivo post-translational modification of p53 by PARP-1 in
MPTP-induced parkinsonism. J Neurochem. 83:186–192. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nair VD: Activation of p53 signaling
initiates apoptotic death in a cellular model of Parkinson's
disease. Apoptosis. 11:955–966. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Biswas SC, Ryu E, Park C, Malagelada C and
Greene LA: Puma and p53 play required roles in death evoked in a
cellular model of Parkinson disease. Neurochem Res. 30:839–845.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nakaso K, Yoshimoto Y, Yano H, Takeshima T
and Nakashima K: p53-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction by
proteasome inhibition in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Lett.
354:213–216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Busse E, Zimmer G, Schopohl B and
Kornhuber B: Influence of alpha-lipoic acid on intracellular
glutathione in vitro and in vivo. Arzneimittelforschung.
42:829–831. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Talebi A, Zavareh S, Kashani MH,
Lashgarbluki T and Karimi I: The effect of alpha lipoic acid on the
developmental competence of mouse isolated preantral follicles. J
Assist Reprod Genet. 29:175–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Packer L, Witt EH and Tritschler HJ:
Alpha-Lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med.
19:227–250. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Packer L, Tritschler HJ and Wessel K:
Neuroprotection by the metabolic antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid.
Free Radic Biol Med. 22:359–378. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|