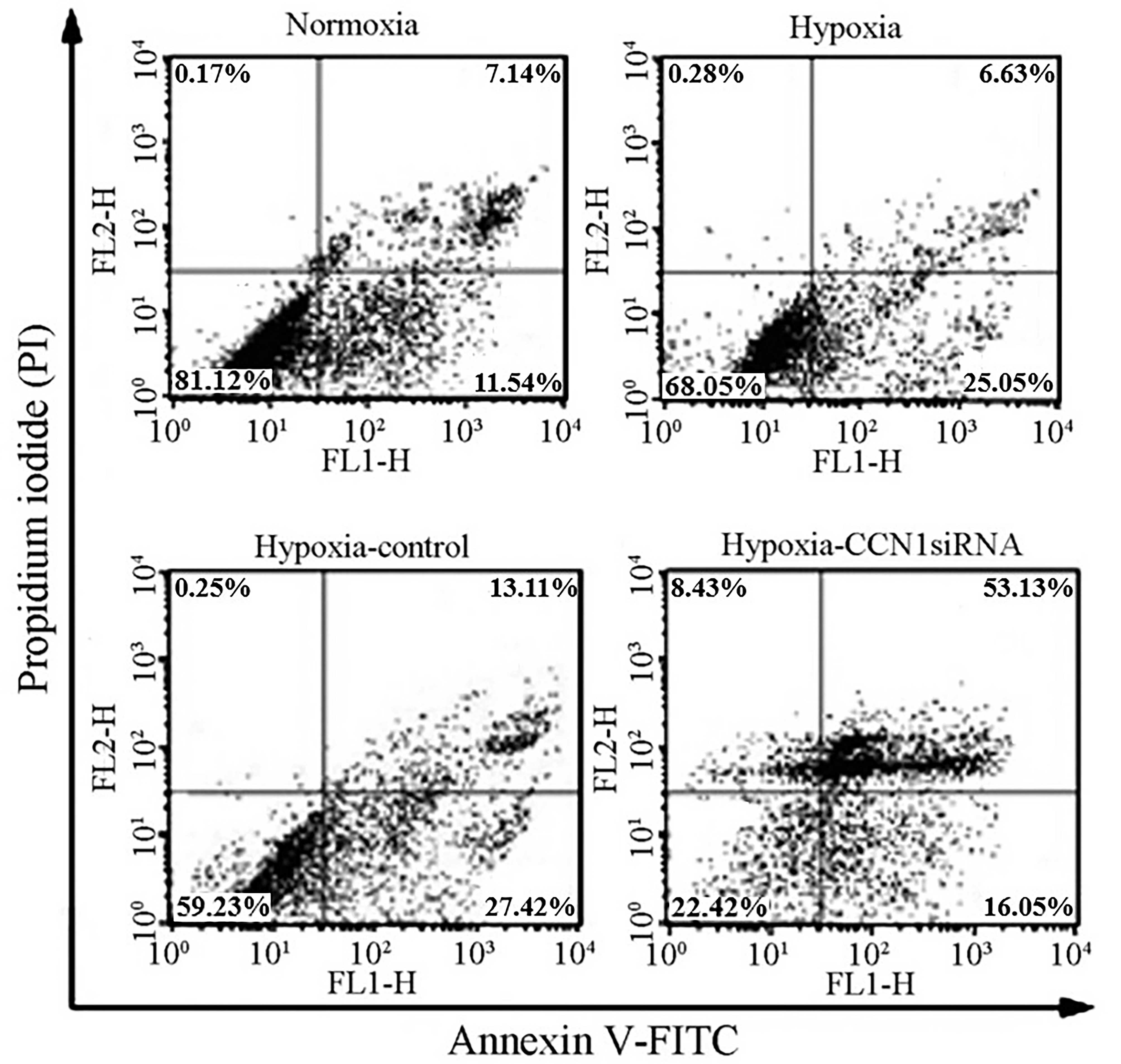
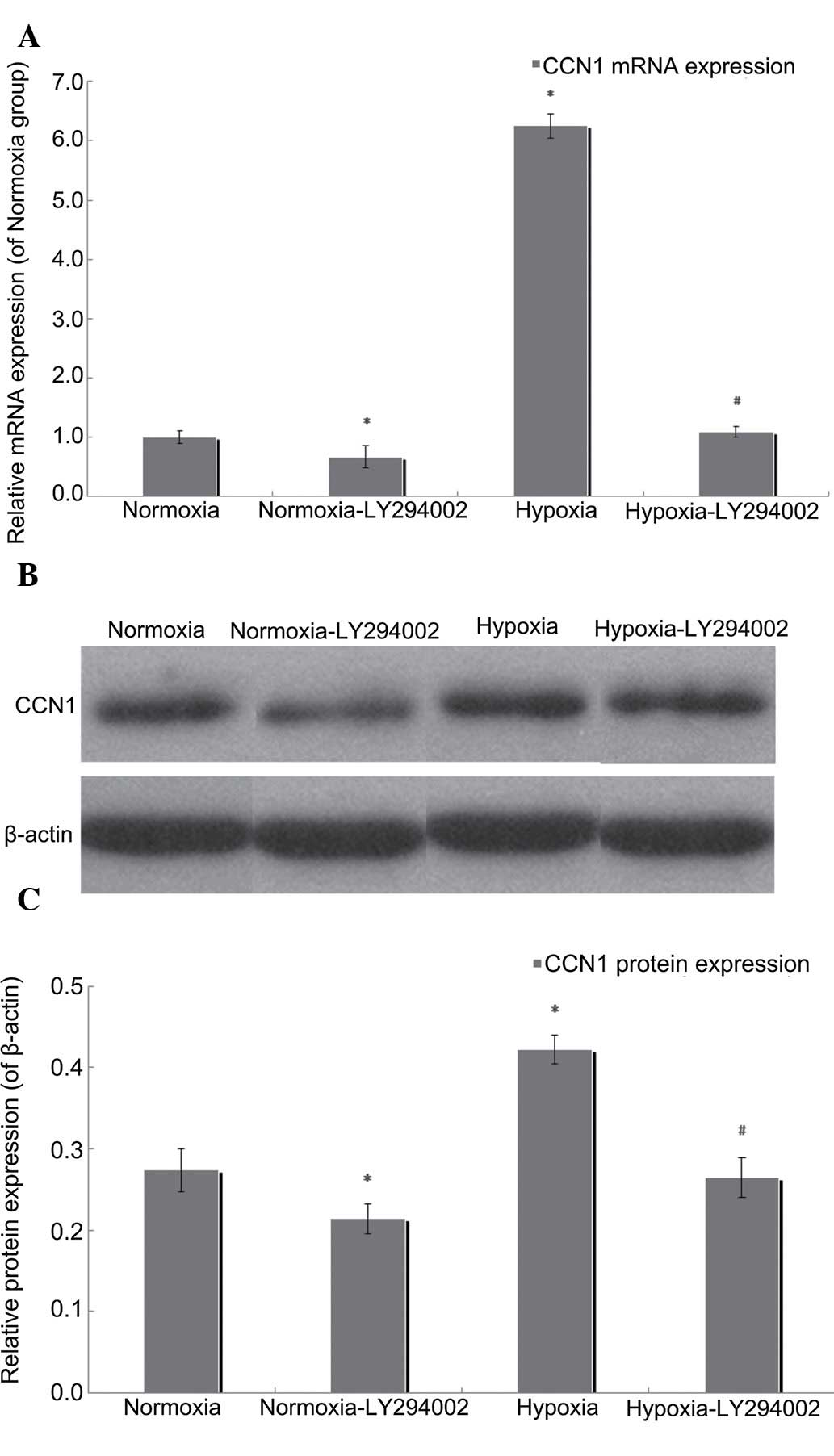
|
1
|
Nyengaard JR, Ido Y, Kilo C and Williamson
JR: Interactions between hyperglycemia and hypoxia: Implications
for diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. 53:2931–2938. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen J and Smith LE: Retinopathy of
prematurity. Angiogenesis. 10:133–140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leask A and Abraham DJ: All in the CCN
family: Essential matricellular signaling modulators emerge from
the bunker. J Cell Sci. 119:4803–4810. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jun JI and Lau LF: The matricellular
protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis
in cutaneous wound healing. Nat Cell Biol. 12:676–685. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yan L and Chaqour B: Cysteine-rich protein
61 (CCN1) and connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) at the
crosshairs of ocular neovascular and fibrovascular disease therapy.
J Cell Commun Signal. 7:253–263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chintalapudi MR, Markiewicz M, Kose N,
Dammai V, Champion KJ, Hoda RS, Trojanowska M and Hsu T: Cyr61/CCN1
and CTGF/CCN2 mediate the proangiogenic activity of VHL-mutant
renal carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:696–703. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meyuhas R, Pikarsky E, Tavor E, Klar A,
Abramovitch R, Hochman J, Lago TG and Honigman A: A Key role for
cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein in hypoxia-mediated
activation of the angiogenesis factor CCN1 (CYR61) in Tumor cells.
Mol Cancer Res. 6:1397–1409. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmitz P, Gerber U, Schütze N, Jüngel E,
Blaheta R, Naggi A, Torri G and Bendas G: Cyr61 is a target for
heparin in reducing MV3 melanoma cell adhesion and migration via
the integrin VLA-4. Thromb Haemost. 110:1046–1054. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haque I, De A, Majumder M, Mehta S,
McGregor D, Banerjee SK, Van Veldhuizen P and Banerjee S: The
matricellular protein CCN1/Cyr61 is a critical regulator of Sonic
Hedgehog in pancreatic carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem.
287:38569–38579. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Long QZ, Zhou M, Liu XG, Du YF, Fan JH, Li
X and He DL: Interaction of CCN1 with αvβ3 integrin induces
P-glycoprotein and confers vinblastine resistance in renal cell
carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 24:810–817. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Emre Y and Imhof BA: Matricellular protein
CCN1/CYR61: A new player in inflammation and leukocyte trafficking.
Semin Immunopathol. 36:253–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang XM, Wang YS, Zhang J, Li Y, Xu JF,
Zhu J, Zhao W, Chu DK and Wiedemann P: Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK
in mediating hypoxia-induced expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in
laser-induced rat choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 50:1873–1879. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
You JJ, Yang CH, Yang CM and Chen MS:
Cyr61 induces the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
via the integrin ανβ3, FAK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB pathways in retinal
vascular endothelial cells. Cell Signal. 26:133–140. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koon HW, Shih DQ, Hing TC, Chen J, Ho S,
Zhao D, Targan SR and Pothoulakis C: Substance P induces CCN1
expression via histone deacetylase activity in human colonic
epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 179:2315–2326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen WG, Peng WX, Shao Y, Xu JF, Dai G,
Zhang Y, Pan FY and Li CJ: Localization and activity of calmodulin
is involved in cell-cell adhesion of tumor cells and endothelial
cells in response to hypoxic stress. Cell Biol Toxicol. 23:323–335.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Zhao T, Yang Z and Li Q: CX3CR1
RNAi inhibits hypoxia-induced microglia activation via p38MAPK/PKC
pathway. Int J Exp Pathol. 95:153–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aubry JP, Blaecke A, Lecoanet-Henchoz S,
Jeannin P, Herbault N, Caron G, Moine V and Bonnefoy JY: Annexin V
used for measuring apoptosis in the early events of cellular
cytotoxicity. Cytometry. 37:197–204. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zou L, Lai H, Zhou Q and Xiao F: Lasting
controversy on ranibizumab and bevacizumab. Theranostics.
1:395–402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Di Y, Zhang YO, Nie QZ and Chen XL:
CCN1/Cyr61-PI3K/AKT signaling promotes retinal neovascularization
in oxygen-induced retinopathy. Int J Mol Med. 36:1507–1518.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brunelle JK and Chandel NS: Oxygen
deprivation induced cell death: An update. Apoptosis. 7:475–482.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin Y, An X, Ye Z, Cully B, Wu J and Li J:
RGS5, a hypoxia-inducible apoptotic stimulator in endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23436–23443. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Distler JH, Hirth A, Kurowska-Stolarska M,
Gay RE, Gay S and Distler O: Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in
the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med. 47:149–161.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Potente M, Gerhardt H and Carmeliet P:
Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell. 146:873–887.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Westenskow PD, Kurihara T, Aguilar E, et
al: Ras pathway inhibition prevents neovascularization by
repressing endothelial cell sprouting. J Clin Invest.
123:4900–4908. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gergely K and Gerinec A: Retinopathy of
prematurity - epidemics, incidence, prevalence, blindness. Bratisl
Lek Listy. 111:514–517. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grote K, Salguero G, Ballmaier M, Dangers
M, Drexler H and Schieffer B: The angiogenic factor CCN1 promotes
adhesion and migration of circulating CD34+ progenitor cells:
Potential role in angiogenesis and endothelial regeneration. Blood.
110:877–885. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu Y, Gao Y, Wang H, Huang L, Qin J, Guo
R, Song M, Yu S, Chen J and Cui B: The matrix protein CCN1 (CYR61)
promotes proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial
progenitor cells. Exp Cell Res. 314:3198–3208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang X, Yu W and Dong F: Cysteine-rich 61
(CYR61) is up-regulated in proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 250:661–668. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
You JJ, Yang CH, Chen MS and Yang CM:
Cysteine-rich 61, a member of the CCN family, as a factor involved
in the pathogenesis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:3447–3455. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou D, Herrick DJ, Rosenbloom J and
Chaqour B: Cyr61 mediates the expression of VEGF, alphav-integrin,
and alpha-actin genes through cytoskeletally based
mechanotransduction mechanisms in bladder smooth muscle cells. J
Appl Physiol (1985). 98:2344–2354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang R, Amir J, Liu H and Chaqour B:
Mechanical strain activates a program of genes functionally
involved in paracrine signaling of angiogenesis. Physiol Genomics.
36:1–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gerszten RE, Friedrich EB, Matsui T, Hung
RR, Li L, Force T and Rosenzweig A: Role of phosphoinositide
3-kinase in monocyte recruitment under flow conditions. J Biol
Chem. 276:26846–26851. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kucharzewska P, Welch JE, Svensson KJ and
Belting M: The polyamines regulate endothelial cell survival during
hypoxic stress through PI3K/AKT and MCL-1. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 380:413–418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hung HS, Wu CC, Chien S and Hsu SH: The
behavior of endothelial cells on polyurethane nanocomposites and
the associated signaling pathways. Biomaterials. 30:1502–1511.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang F, Fang ZF, Hu XQ, Tang L, Zhou SH
and Huang JP: Overexpression of miR-126 promotes the
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells toward endothelial cells
via activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways and release of
paracrine factors. Biol Chem. 394:1223–1233. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin MT, Kuo IH, Chang CC, Chu CY, Chen HY,
Lin BR, Sureshbabu M, Shih HJ and Kuo ML: Involvement of
hypoxia-inducing factor-1alpha-dependent plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 up-regulation in Cyr61/CCN1-induced gastric cancer cell
invasion. J Biol Chem. 283:15807–15815. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Goodwin CR, Lal B, Zhou X, Ho S, Xia S,
Taeger A, Murray J and Laterra J: Cyr61 mediates hepatocyte growth
factor-dependent tumor cell growth, migration, and Akt activation.
Cancer Res. 70:2932–2941. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lin J, Huo R, Wang L, Zhou Z, Sun Y, Shen
B, Wang R and Li N: A novel anti-Cyr61 antibody inhibits breast
cancer growth and metastasis in vivo. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
61:677–687. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
You JJ, Yang CM, Chen MS and Yang CH:
Regulation of Cyr61/CCN1 expression by hypoxia through cooperation
of c-Jun/AP-1 and HIF-1α in retinal vascular endothelial cells. Exp
Eye Res. 91:825–836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|