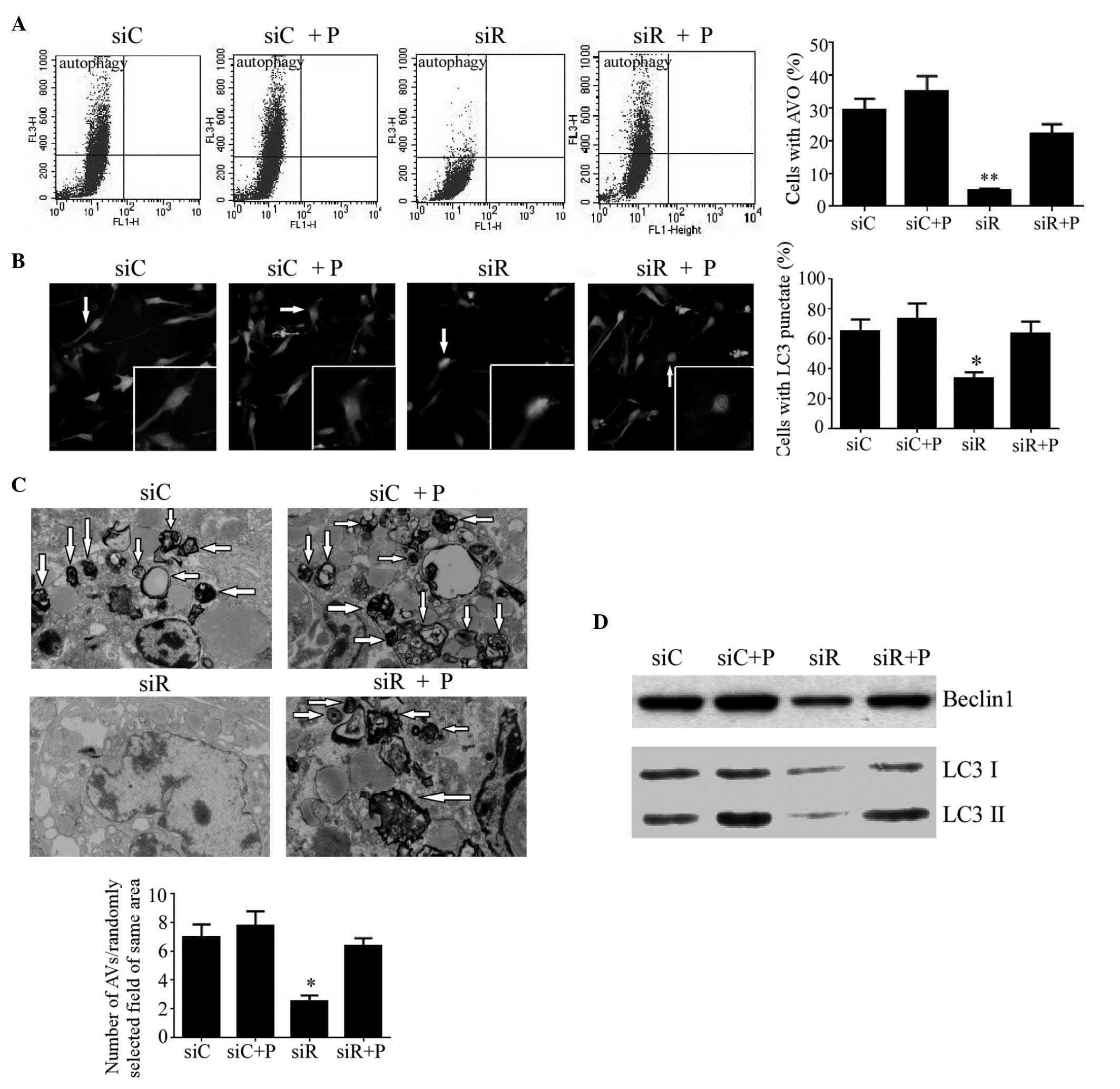
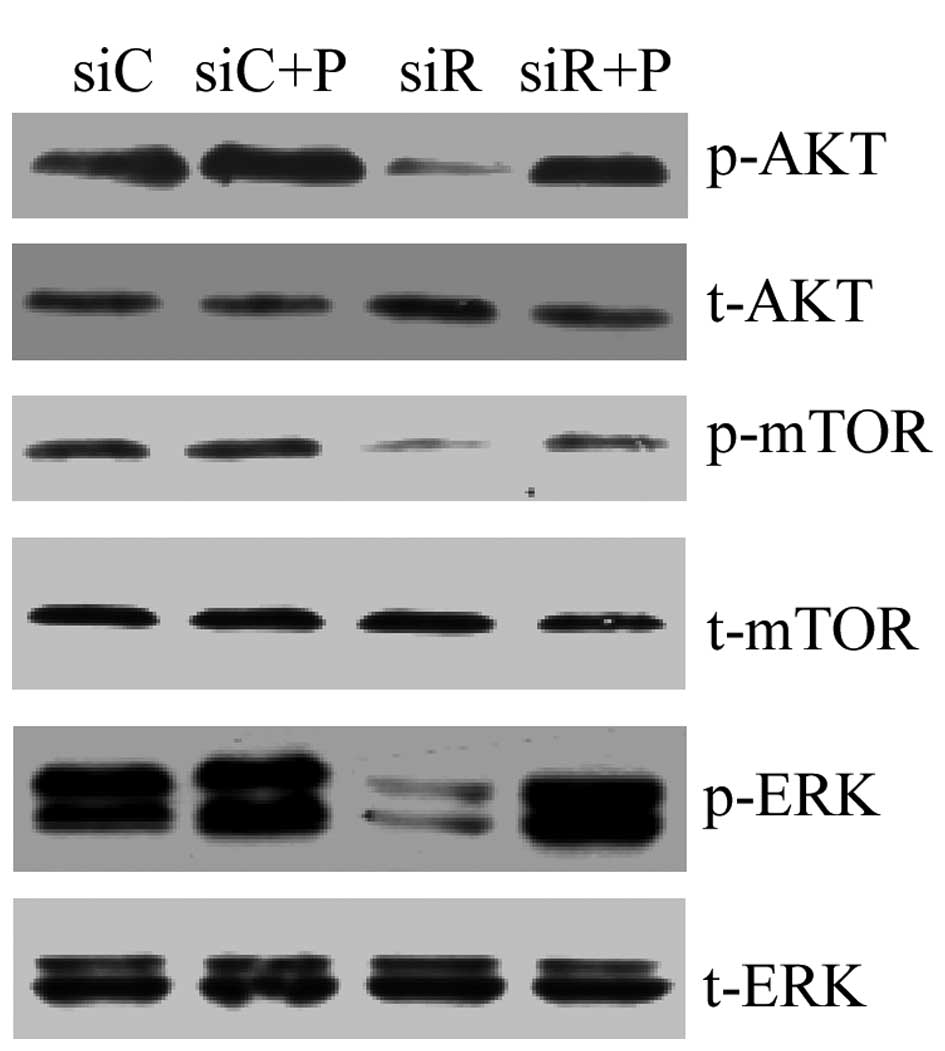
|
1
|
Owens GK, Kumar MS and Wamhoff BR:
Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation
in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 84:767–801. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pyle AL and Young PP: Atheromas feel the
pressure: Biomechanical stress and atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol.
177:4–9. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rudijanto A: The role of vascular smooth
muscle cells on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Acta Med
Indones. 39:86–93. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mack CP: Signaling mechanisms that
regulate smooth muscle cell differentiation. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 31:1495–1505. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jordens I, Marsman M, Kuijl C and Neefjes
J: Rab proteins, connecting transport and vesicle fusion. Traffic.
6:1070–1077. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grosshans BL, Ortiz D and Novick P: Rabs
and their effectors: Achieving specificity in membrane traffic.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:11821–11827. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hutagalung AH and Novick PJ: Role of Rab
GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev.
91:119–149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ravikumar B, Imarisio S, Sarkar S, O'Kane
CJ and Rubinsztein DC: Rab5 modulates aggregation and toxicity of
mutant huntingtin through macroautophagy in cell and fly models of
Huntington disease. J Cell Sci. 121:1649–1660. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang PS, Yin PH, Tseng LM, Yang CH, Hsu
CY, Lee MY, Horng CF and Chi CW: Rab5A is associated with axillary
lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Cancer Sci.
102:2172–2178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu SS, Chen XM, Zheng HX, Shi SL and Li
Y: Knockdown of Rab5a expression decreases cancer cell motility and
invasion through integrin-mediated signaling pathway. J Biomed Sci.
18:582011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Z, Liu XF, Wu HC, Zou SB, Wang JY, Ni
PH, Chen XH and Fan QS: Rab5a overexpression promoting ovarian
cancer cell proliferation may be associated with APPL1-related
epidermal growth factor signaling pathway. Cancer Sci.
101:1454–1462. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fukui K, Tamura S, Wada A, Kamada Y, Igura
T, Kiso S and Hayashi N: Expression of Rab5a in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Possible involvement in epidermal growth factor
signaling. Hepatol Res. 37:957–965. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma Z, Wang H, Wu L, Zhui L, Shi W, Ma D,
Chen Z and Yu B: RNAi-mediated Rab5a suppression inhibits
proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Acta
Cardiol. 65:507–514. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Salabei JK, Cummins TD, Singh M, Jones SP,
Bhatnagar A and Hill BG: PDGF-mediated autophagy regulates vascular
smooth muscle cell phenotype and resistance to oxidative stress.
Biochem J. 451:375–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Butoi E, Gan AM and Manduteanu I:
Molecular and functional interactions among monocytes/macrophages
and smooth muscle cells and their relevance for atherosclerosis.
Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 24:341–355. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garat C, Van Putten V, Refaat ZA, Dessev
C, Han SY and Nemenoff RA: Induction of smooth muscle alpha-actin
in vascular smooth muscle cells by arginine vasopressin is mediated
by c-Jun amino-terminal kinases and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase. J Biol Chem. 275:22537–22543. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hautmann MB, Thompson MM, Swartz EA, Olson
EN and Owens GK: Angiotensin II-induced stimulation of smooth
muscle alpha-actin expression by serum response factor and the
homeodomain transcription factor MHox. Circ Res. 81:600–610. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang L, Zheng J, Du Y, Huang Y, Li J, Liu
B, Liu CJ, Zhu Y, Gao Y, Xu Q, et al: Cartilage oligomeric matrix
protein maintains the contractile phenotype of vascular smooth
muscle cells by interacting with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin. Circ
Res. 106:514–525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Su WC, Chao TC, Huang YL, Weng SC, Jeng KS
and Lai MM: Rab5 and class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase Vps34 are
involved in hepatitis C virus NS4B-induced autophagy. J Virol.
85:10561–10571. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Myllärniemi M, Calderon L, Lemström K,
Buchdunger E and Häyry P: Inhibition of platelet-derived growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits vascular smooth muscle
cell migration and proliferation. FASEB J. 11:1119–1126.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu JC, Lokker NA, Hollenbach S, Apatira M,
Li J, Betz A, Sedlock D, Oda S, Nomoto Y, Matsuno K, et al:
Efficacy of the novel selective platelet-derived growth factor
receptor antagonist CT52923 on cellular proliferation, migration,
and suppression of neointima following vascular injury. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 298:1172–1178. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Du J, Teng RJ, Guan T, Eis A, Kaul S,
Konduri GG and Shi Y: Role of autophagy in angiogenesis in aortic
endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 302:C383–C391. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Slevin M, Krupinski J, Rovira N, Turu M,
Luque A, Baldellou M, Sanfeliu C, de Vera N and Badimon L:
Identification of pro-angiogenic markers in blood vessels from
stroked-affected brain tissue using laser-capture microdissection.
BMC Genomics. 10:1132009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhan Z, Xie X, Cao H, Zhou X, Zhang XD,
Fan H and Liu Z: Autophagy facilitates TLR4-and TLR3-triggered
migration and invasion of lung cancer cells through the promotion
of TRAF6 ubiquitination. Autophagy. 10:257–268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ and Thompson CB:
Autophagy in metazoans: Cell survival in the land of plenty. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:439–448. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Platini F, Pérez-Tomás R, Ambrosio S and
Tessitore L: Understanding autophagy in cell death control. Curr
Pharm Des. 16:101–113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen S, Kepp O, Michaud M, Martins I,
Minoux H, Métivier D, Maiuri MC, Kroemer RT and Kroemer G:
Association and dissociation of autophagy, apoptosis and necrosis
by systematic chemical study. Oncogene. 30:4544–4556. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amaravadi RK: Autophagy-induced tumor
dormancy in ovarian cancer. J Clin Invest. 118:3837–3840.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsieh AC, Liu Y, Edlind MP, Ingolia NT,
Janes MR, Sher A, Shi EY, Stumpf CR, Christensen C, Bonham MJ, et
al: The translational landscape of mTOR signalling steers cancer
initiation and metastasis. Nature. 485:55–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saiki S, Sasazawa Y, Imamichi Y, Kawajiri
S, Fujimaki T, Tanida I, Kobayashi H, Sato F, Sato S, Ishikawa K,
et al: Caffeine induces apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K inhibition. Autophagy. 7:176–187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang RC, Wei Y, An Z, Zou Z, Xiao G,
Bhagat G, White M, Reichelt J and Levine B: Akt-mediated regulation
of autophagy and tumorigenesis through Beclin 1 phosphorylation.
Science. 338:956–959. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shaul YD and Seger R: The MEK/ERK cascade:
From signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1773:1213–1226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang J, Whiteman MW, Lian H, Wang G, Singh
A, Huang D and Denmark T: A non-canonical MEK/ERK signaling pathway
regulates autophagy via regulating Beclin 1. J Biol Chem.
284:21412–21424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|