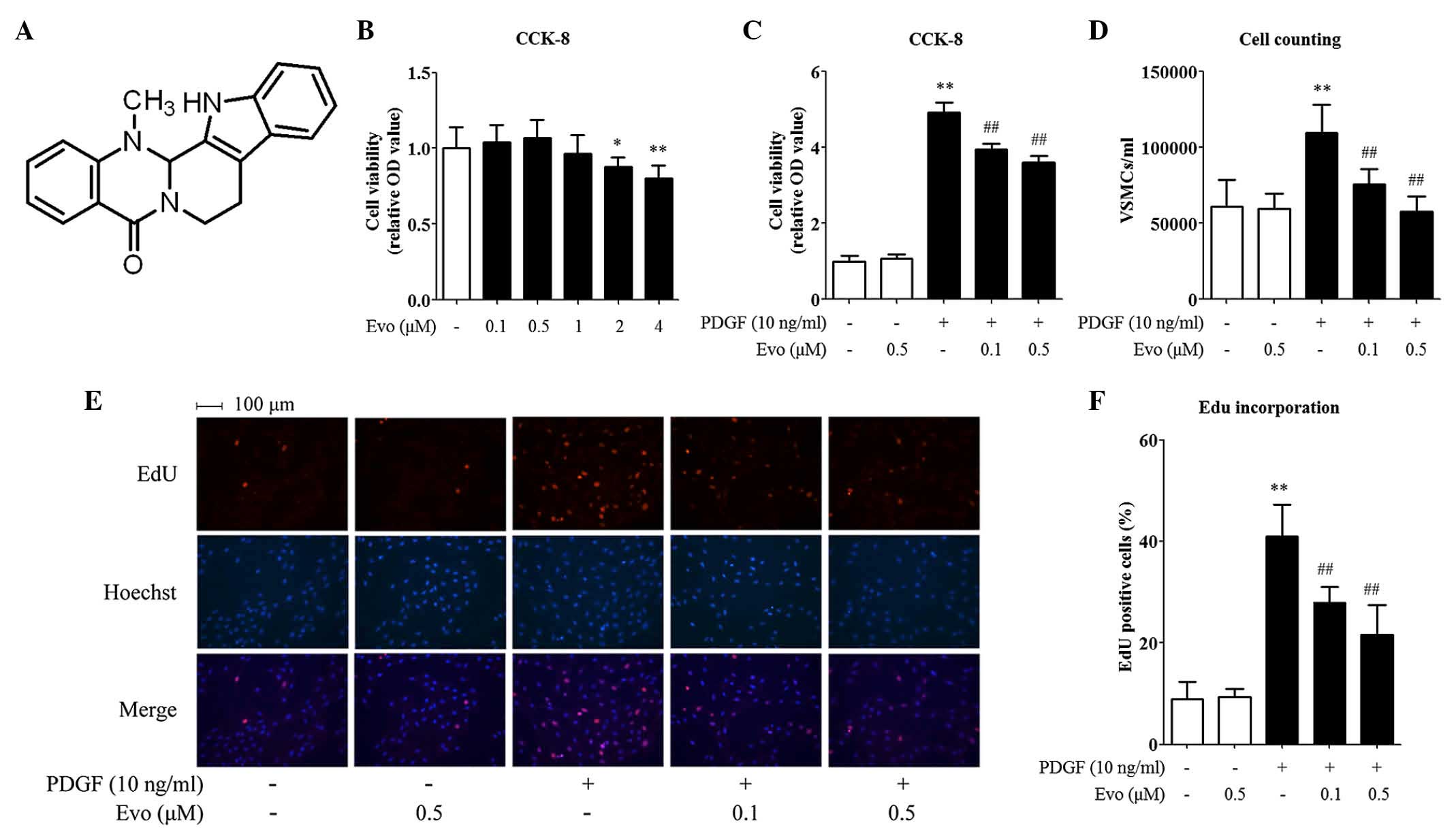
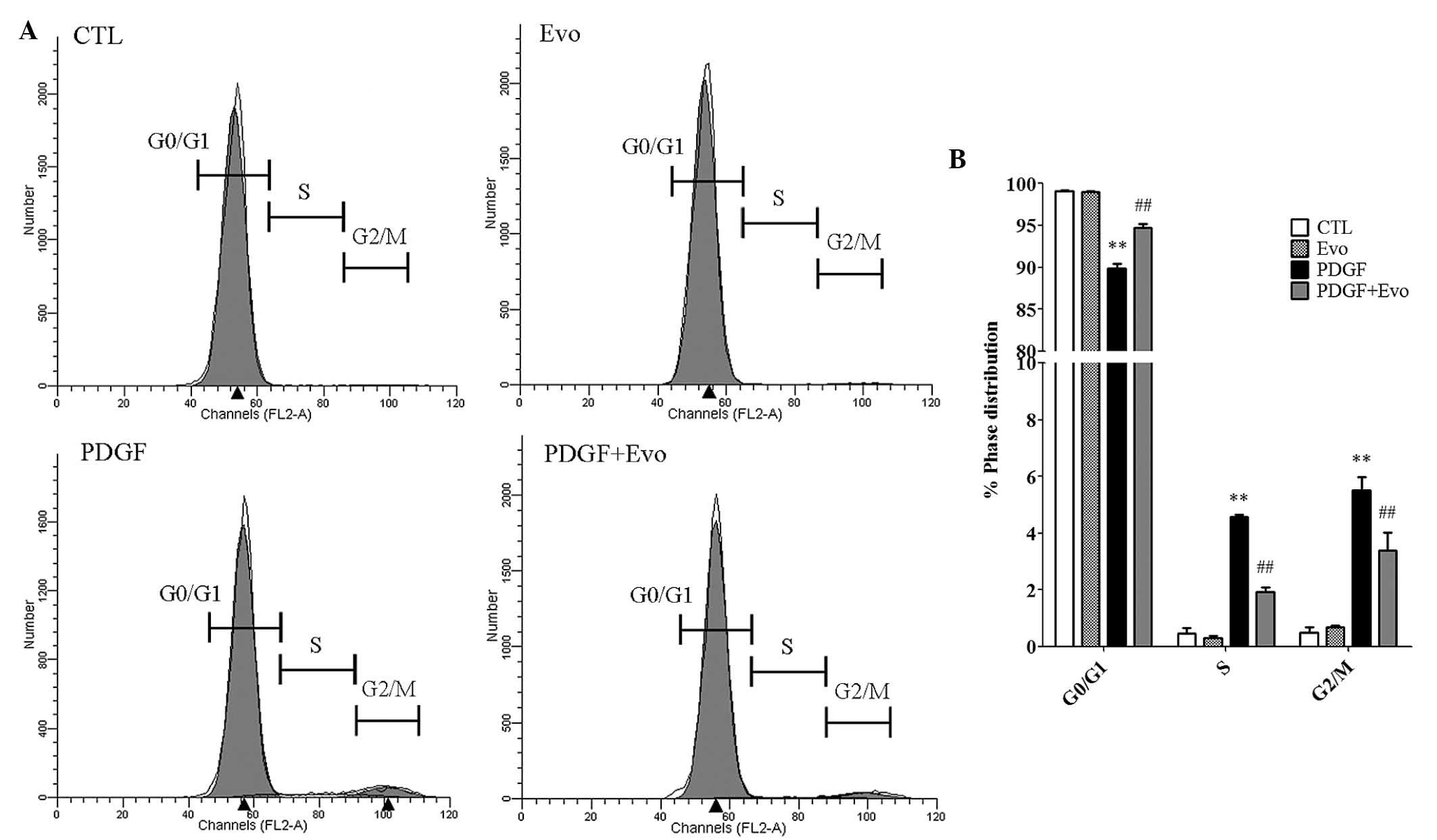
|
1
|
Curcio A, Torella D and Indolfi C:
Mechanisms of smooth muscle cell proliferation and endothelial
regeneration after vascular injury and stenting: Approach to
therapy. Circ J. 75:1287–1296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boucher P and Gotthardt M: LRP and PDGF
signaling: A pathway to atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc Med.
14:55–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rensen SS, Doevendans PA and van Eys GJ:
Regulation and characteristics of vascular smooth muscle cell
phenotypic diversity. Neth Heart J. 15:100–108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park ES, Lee KP, Jung SH, Lee DY, Won KJ,
Yun YP and Kim B: Compound K, an intestinal metabolite of
ginsenosides, inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC proliferation and
migration through G1 arrest and attenuates neointimal hyperplasia
after arterial injury. Atherosclerosis. 228:53–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Palmieri C, Ravani M, Trianni G, Gianetti
J, Vaghetti M, Rizza A, Paradossi U, Beqiri A and Berti S:
Drug-eluting stents versus bare-metal stents in acute ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction. A single-center experience with
long-term follow up. J Invasive Cardiol. 22:151–158.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rosner D, McCarthy N and Bennett M:
Rapamycin inhibits human in stent restenosis vascular smooth muscle
cells independently of pRB phosphorylation and p53. Cardiovasc Res.
66:601–610. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nguyen KT, Shaikh N, Wawro D, Zhang S,
Schwade ND, Eberhart RC and Tang L: Molecular responses of vascular
smooth muscle cells to paclitaxel-eluting bioresorbable stent
materials. J Biomed Mater Res A. 69:513–524. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao FH, Chen YD, Jin ZN and Lu SZ: Are
impaired endothelial progenitor cells involved in the processes of
late in-stent thrombosis and re-endothelialization of drug-eluting
stents? Med Hypotheses. 70:512–514. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fei XF, Wang BX, Li TJ, Tashiro S, Minami
M, Xing DJ and Ikejima T: Evodiamine, a constituent of evodiae
fructus, induces anti-proliferating effects in tumor cells. Cancer
Sci. 94:92–98. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang J and Hu C: Evodiamine: A novel
anti-cancer alkaloid from Evodia rutaecarpa. Molecules.
14:1852–1859. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang L, Liu X, Wu D, Zhang M, Ran G, Bi Y
and Huang H: Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in
SGC7901 human gastric cancer cells by evodiamine. Mol Med Rep.
9:1147–1152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chiou WF, Chou CJ, Shum AY and Chen CF:
The vasorelaxant effect of evodiamine in rat isolated mesenteric
arteries: Mode of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 215:277–283. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hung PH, Lin LC, Wang GJ, Chen CF and Wang
PS: Inhibitory effect of evodiamine on aldosterone release by Zona
glomerulosa cells in male rats. Chin J Physiol. 44:53–57.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heo SK, Yun HJ, Yi HS, Noh EK and Park SD:
Evodiamine and rutaecarpine inhibit migration by light via
suppression of nadph oxidase activation. J Cell Biochem.
107:123–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gordon D, Mohai LG and Schwartz SM:
Induction of polyploidy in cultures of neonatal rat aortic smooth
muscle cells. Circ Res. 59:633–644. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abukhdeir AM and Park BH: P21 and p27:
Roles in carcinogenesis and drug resistance. Expert Rev Mol Med.
10:e192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weiss RH, Joo A and Randour C: p21
(Waf1/Cip1) is an assembly factor required for platelet-derived
growth factor-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. J
Biol Chem. 275:10285–10290. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fang C, Zhang J, Qi D, Fan X, Luo J, Liu L
and Tan Q: Evodiamine induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis via
mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways in H446 and human
small-cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e1152042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Du J, Wang XF, Zhou QM, Zhang TL, Lu YY,
Zhang H and Su SB: Evodiamine induces apoptosis and inhibits
metastasis in MDAMB-231 human breast cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. Oncol Rep. 30:685–694. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rasul A, Yu B, Zhong L, Khan M, Yang H and
Ma T: Cytotoxic effect of evodiamine in SGC-7901 human gastric
adenocarcinoma cells via simultaneous induction of apoptosis and
autophagy. Oncol Rep. 27:1481–1487. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Wu LJ, Tashino S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Protein tyrosine kinase pathway-derived ROS/NO
productions contribute to G2/M cell cycle arrest in
evodiamine-treated human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells. Free Radic
Res. 44:792–802. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cuevas BD, Abell AN and Johnson GL: Role
of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases in signal
integration. Oncogene. 26:3159–3171. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roux PP and Blenis J: ERK and p38
MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with
diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:320–344.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhan Y, Kim S, Izumi Y, Izumiya Y, Nakao
T, Miyazaki H and Iwao H: Role of JNK, p38 and ERK in
platelet-derived growth factor-induced vascular proliferation,
migration and gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
23:795–801. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang L, Liu X, Wu D, Zhang M, Ran G, Bi Y
and Huang H: Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in
SGC7901 human gastric cancer cells by evodiamine. Mol Med Rep.
9:1147–1152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen MC, Yu CH, Wang SW, Pu HF, Kan SF,
Lin LC, Chi CW, Ho LL, Lee CH and Wang PS: Anti-proliferative
effects of evodiamine on human thyroid cancer cell line ARO. J Cell
Biochem. 110:1495–1503. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang J, Cai X, Lu W, Hu C, Xu X, Yu Q and
Cao P: Evodiamine inhibits STAT3 signaling by inducing phosphatase
shatterproof 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
328:243–251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang J, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Nitric oxide activated by p38 and NF-kappaB facilitates
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest under oxidative stress in
evodiamine-treated human melanoma A375-S2 cells. Free Radic Res.
42:1–11. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang T, Wang Y, Kontani Y, Kobayashi Y,
Sato Y, Mori N and Yamashita H: Evodiamine improves diet-induced
obesity in a uncoupling protein-1-independent manner: Involvement
of antiadipogenic mechanism and extracellularly regulated
kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Endocrinology.
149:358–366. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao N, Zhang Z, Jiang BH and Shi X: Role
of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the cell cycle progression of human
prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 310:1124–1132. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duronio V: The life of a cell: Apoptosis
regulation by the PI3K/PKB pathway. Biochem J. 415:333–344. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lim HJ, Lee S, Park JH, Lee KS, Choi HE,
Chung KS, Lee HH and Park HY: PPAR delta agonist L-165041 inhibits
rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via
inhibition of cell cycle. Atherosclerosis. 202:446–454. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Conour JE, Graham WV and Gaskins HR: A
combined in vitro/bioinformatic investigation of redox regulatory
mechanisms governing cell cycle progression. Physiol Genomics.
18:196–205. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pisoschi AM and Pop A: The role of
antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur J
Med Chem. 97:55–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen S, Ding Y, Tao W, Zhang W, Liang T
and Liu C: Naringenin inhibits TNF-alpha induced VSMC proliferation
and migration via induction of HO-1. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:3025–3031. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|