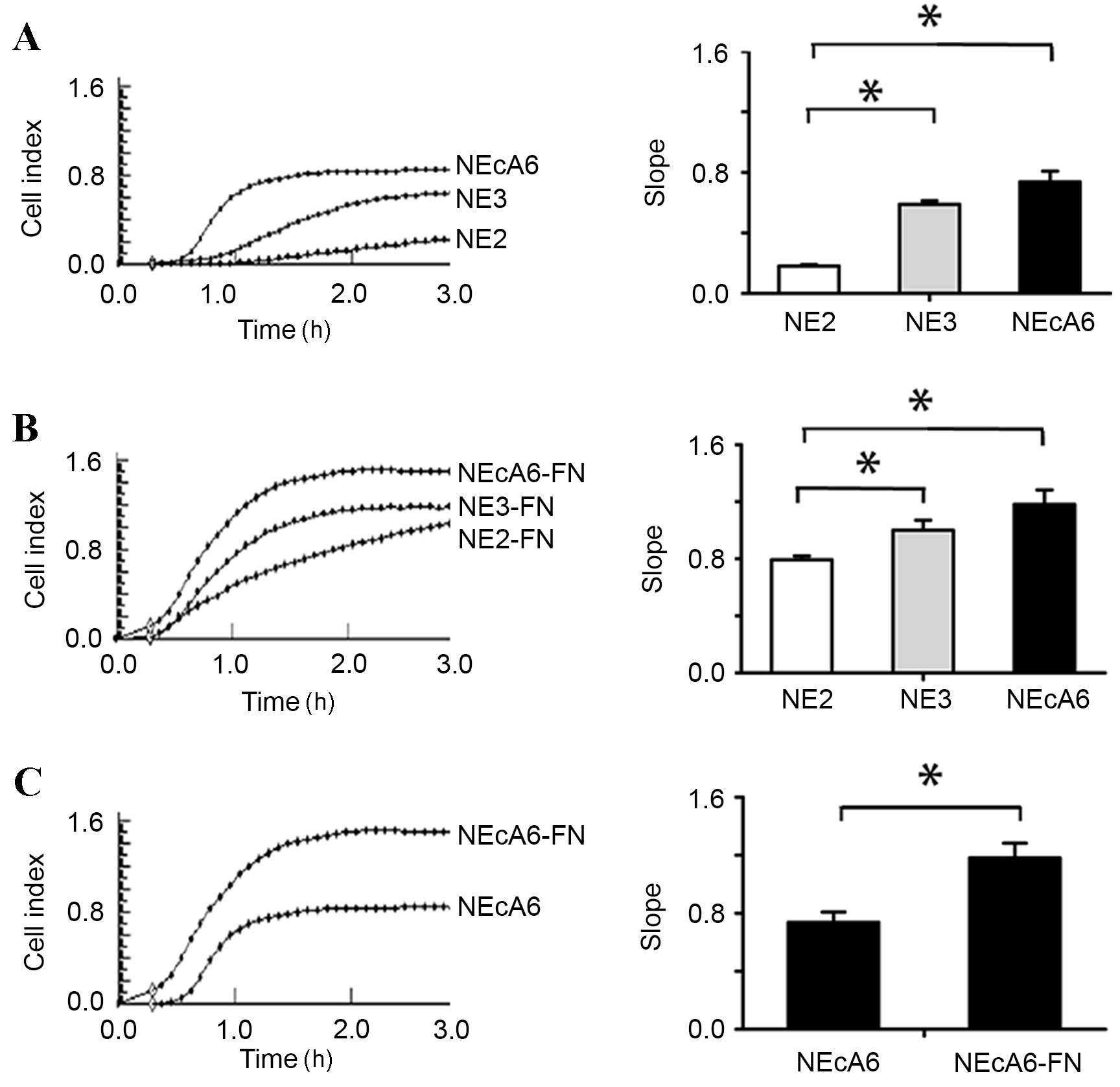
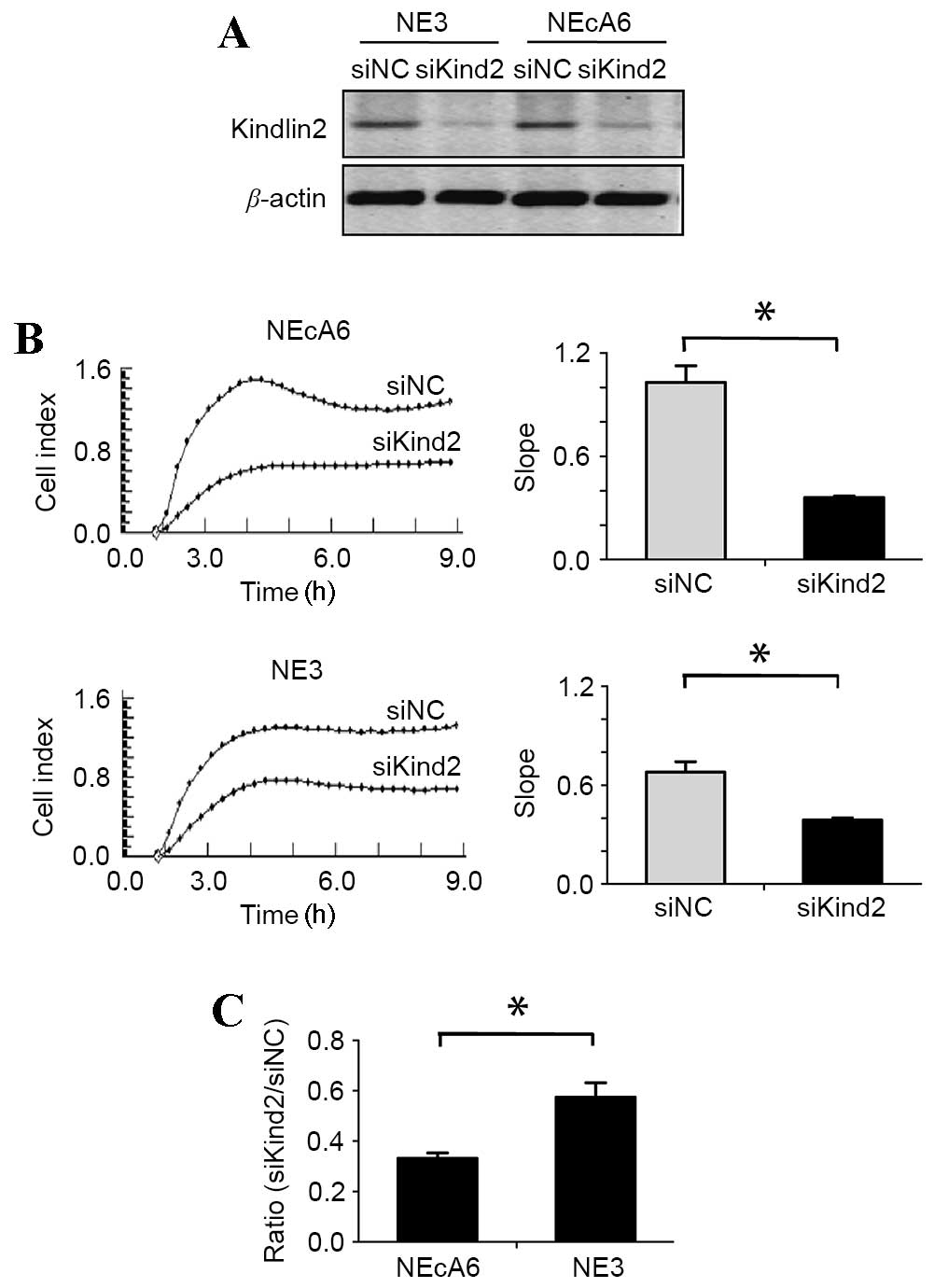
|
1
|
Vicente-Manzanares M, Webb DJ and Horwitz
AR: Cell migration at a glance. J Cell Sci. 118:4917–4919. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Axelrad JE, Lichtiger S and Yajnik V:
Inflammatory bowel disease and cancer: The role of inflammation,
immunosuppression, and cancer treatment. World J Gastroenterol.
22:4794–4801. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mayor R and Etienne-Manneville S: The
front and rear of collective cell migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
17:97–109. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel
RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, Parsons JT and Horwitz AR: Cell
migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science.
302:1704–1709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Etienne-Manneville S: Adherens junctions
during cell migration. Subcell Biochem. 60:225–249. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Turner CE: Paxillin. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 30:955–959. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Friedl P and Wolf K: Tumour-cell invasion
and migration: Diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:362–374. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim DH and Wirtz D: Focal adhesion size
uniquely predicts cell migration. FASEB J. 27:1351–1361. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Clark EA and Brugge JS: Integrins and
signal transduction pathways: The road taken. Science. 268:233–239.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Turner CE, Glenney JR Jr and Burridge K:
Paxillin: A new vinculin-binding protein present in focal
adhesions. J Cell Biol. 111:1059–1068. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brown MC and Turner CE: Paxillin: Adapting
to change. Physiol Rev. 84:1315–1339. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sheppard D: In vivo functions of
integrins: Lessons from null mutations in mice. Matrix Biol.
19:203–209. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Turner CE: Paxillin and focal adhesion
signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2:E231–E236. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Calderwood DA, Campbell ID and Critchley
DR: Talins and kindlins: Partners in integrin-mediated adhesion.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:503–517. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Spillare EA, Wang QS, Sabourin CLK
and Stoner GD: p53-independent down-regulation of cyclin D1 and
p21Waf1 in the process of immortalization of human esophageal
epithelial cells. Int J Oncol. 12:325–328. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shen Z, Cen S, Shen J, Cai W, Xu J, Teng
Z, Hu Z and Zeng Y: Study of immortalization and malignant
transformation of human embryonic esophageal epithelial cells
induced by HPV18 E6E7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 126:589–594. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sashiyama H, Shino Y, Kawamata Y, Tomita
Y, Ogawa N, Shimada H, Kobayashi S, Asano T, Ochiai T and Shirasawa
H: Immortalization of human esophageal keratinocytes by E6 and E7
of human papillomavirus type 16. Int J Oncol. 19:97–103.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Jin Y, Chen X, Jin C, Law S, Tsao
SW and Kwong YL: Cytogenetic aberrations in immortalization of
esophageal epithelial cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 165:25–35.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu L, Qin YR, Xie D, Hu L, Kwong DL,
Srivastava G, Tsao SW and Guan XY: Characterization of a novel
tumor-suppressor gene PLC delta 1 at 3p22 in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 67:10720–10726. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhuang ZH, Tsao SW, Deng W, Wang JD, Xia
HH, He H, Feng HC, Wang LD, Gu Q, Lam SK, et al: Early upregulation
of cyclooxygenase-2 in human papillomavirus type 16 and
telomerase-induced immortalization of human esophageal epithelial
cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1613–1620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao Q, Shen JH, Shen ZY, Wu ZY, Xu XE,
Xie JJ, Wu JY, Huang Q, Lu XF, Li EM and Xu LY: Phosphorylation of
fascin decreases the risk of poor survival in patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem.
58:979–988. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Limame R, Wouters A, Pauwels B, Fransen E,
Peeters M, Lardon F, De Wever O and Pauwels P: Comparative analysis
of dynamic cell viability, migration and invasion assessments by
novel real-time technology and classic endpoint assays. PLoS One.
7:e465362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Atienza JM, Zhu J, Wang X, Xu X and Abassi
Y: Dynamic monitoring of cell adhesion and spreading on
microelectronic sensor arrays. J Biomol Screen. 10:795–805. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheung PY, Deng W, Man C, Tse WW,
Srivastava G, Law S, Tsao SW and Cheung AL: Genetic alterations in
a telomerase-immortalized human esophageal epithelial cell line:
Implications for carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 293:41–51. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie JJ, Xu LY, Zhang HH, Cai WJ, Mai RQ,
Xie YM, Yang ZM, Niu YD, Shen ZY and Li EM: Role of fascin in the
proliferation and invasiveness of esophageal carcinoma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 337:355–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xie JJ, Xu LY, Xie YM, Zhang HH, Cai WJ,
Zhou F, Shen ZY and Li EM: Roles of ezrin in the growth and
invasiveness of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer.
124:2549–2558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mitra SK, Hanson DA and Schlaepfer DD:
Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:56–68. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rondas D, Tomas A and Halban PA: Focal
adhesion remodeling is crucial for glucose-stimulated insulin
secretion and involves activation of focal adhesion kinase and
paxillin. Diabetes. 60:1146–1157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baumann K: Cell adhesion: Extracellular
bonds. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:4042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wrighton KH: Cell adhesion: The ‘ins’ and
‘outs’ of integrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:7522013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Multhaupt HA, Leitinger B, Gullberg D and
Couchman JR: Extracellular matrix component signaling in cancer.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 97:28–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carragher NO and Frame MC: Focal adhesion
and actin dynamics: A place where kinases and proteases meet to
promote invasion. Trends Cell Biol. 14:241–249. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu HP, Xu SQ, Liu L, Shi LY, Cai XK, Lu
WH, Lu B, Su YH and Li YY: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in squamous
dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer
Lett. 198:193–201. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
An Z, Dobra K, Lock JG, Strömblad S,
Hjerpe A and Zhang H: Kindlin-2 is expressed in malignant
mesothelioma and is required for tumor cell adhesion and migration.
Int J Cancer. 127:1999–2008. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deakin NO and Turner CE: Paxillin comes of
age. J Cell Sci. 121:2435–2444. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lawson C and Schlaepfer DD: Integrin
adhesions: Who's on first? What's on second? Connections between
FAK and talin. Cell Adh Migr. 6:302–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schaller MD: Paxillin: A focal
adhesion-associated adaptor protein. Oncogene. 20:6459–6472. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Karaköse E, Schiller HB and Fässler R: The
kindlins at a glance. J Cell Sci. 123:2353–2356. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liao Z, Kato H, Pandey M, Cantor JM,
Ablooglu AJ, Ginsberg MH and Shattil SJ: Interaction of kindlin-2
with integrin β3 promotes outside-in signaling responses by the
αVβ3 vitronectin receptor. Blood. 125:1995–2004. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shen Z, Ye Y, Kauttu T, Seppänen H,
Vainionpää S, Wang S, Mustonen H and Puolakkainen P: Novel focal
adhesion protein kindlin-2 promotes the invasion of gastric cancer
cells through phosphorylation of integrin β1 and β3. J Surg Oncol.
108:106–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang HF, Zhang K, Liao LD, Li LY, Du ZP,
Wu BL, Wu JY, Xu XE, Zeng FM, Chen B, et al: miR-200b suppresses
invasiveness and modulates the cytoskeletal and adhesive machinery
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting
Kindlin-2. Carcinogenesis. 35:292–301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ge YS, Liu D, Jia WD, Li JS, Ma JL, Yu JH
and Xu GL: Kindlin-2: A novel prognostic biomarker for patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 211:198–202. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ren Y, Jin H, Xue Z, Xu Q, Wang S, Zhao G,
Huang J and Huang H: Kindlin-2 inhibited the growth and migration
of colorectal cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 36:4107–4114. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yu Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Zhao T, Ma B, Liu Y,
Fang W, Zhu WG and Zhang H: Kindlin 2 forms a transcriptional
complex with β-catenin and TCF4 to enhance Wnt signalling. EMBO
Rep. 13:750–758. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|