|
1
|
Liang L: The history of cultivation
techniques of Ginkgo biloba in China. Agricultural Archaeology.
1:259–261. 2002.
|
|
2
|
Dias MA, Sampaio AL, Venosa AR, Meneses EA
and Oliveira CA: The chemopreventive effect of Ginkgo biloba
extract 761 against cisplatin ototoxicity: A pilot study. Int
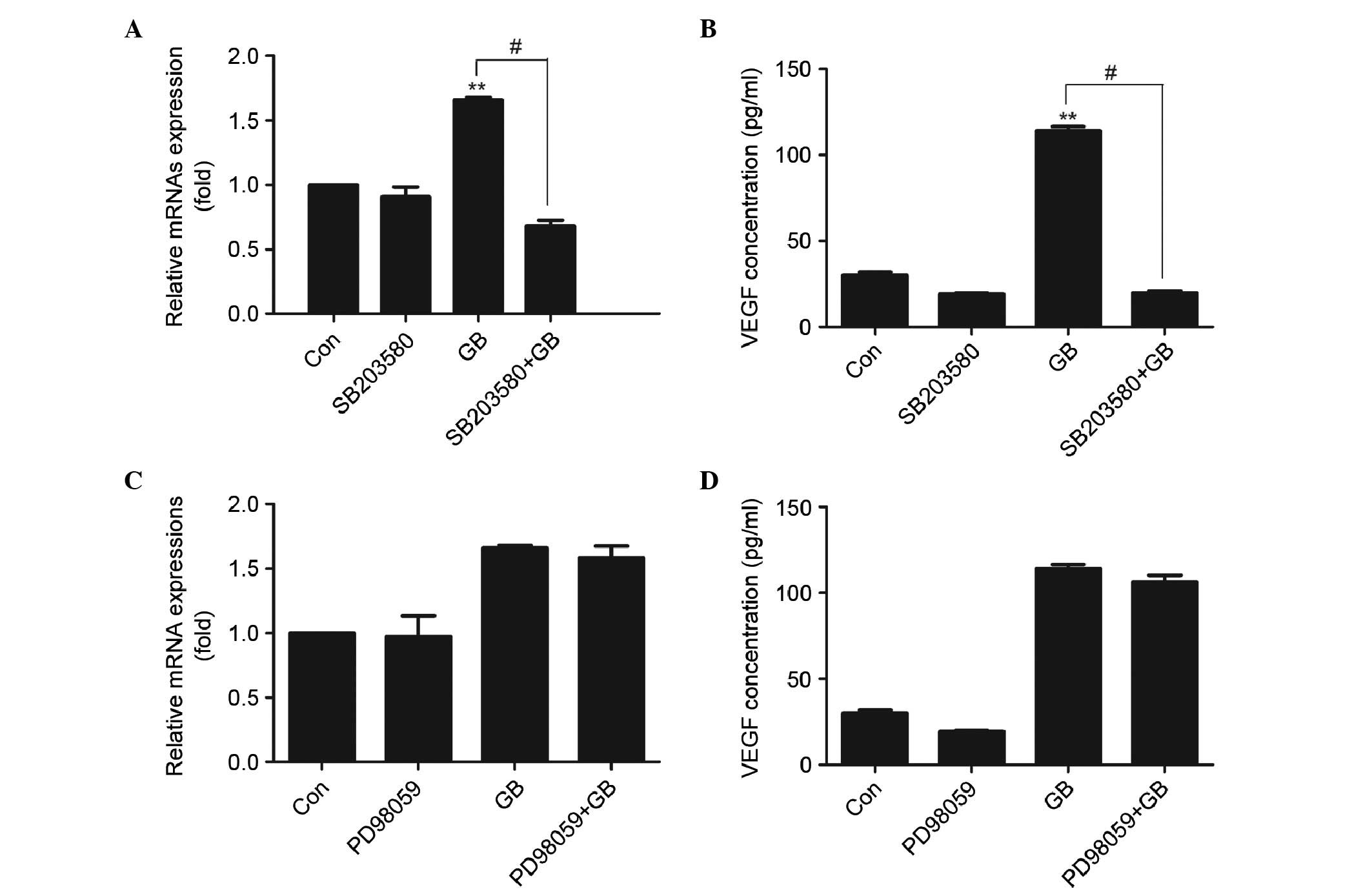
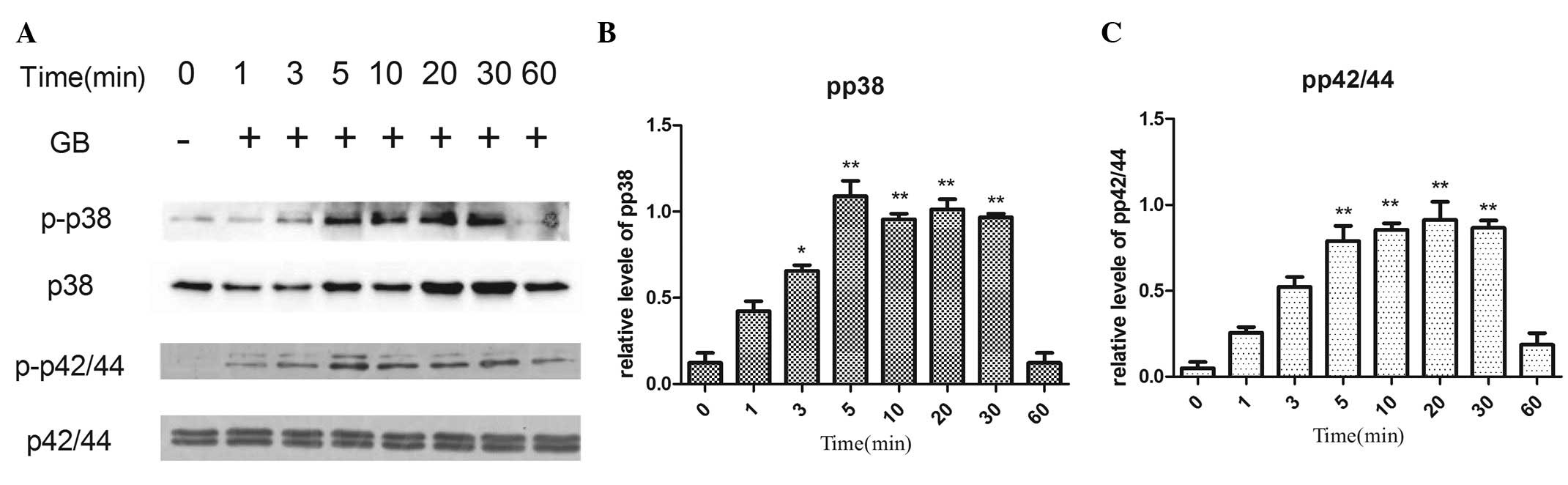
Tinnitus J. 19:12–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shen J, Wang J, Zhao B, Hou J, Gao T and
Xin W: Effects of EGb 761 on nitric oxide and oxygen free radicals,
myocardial damage and arrhythmia in ischemia-reperfusion injury in
vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1406:228–236. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang WR, Hayashi T, Kitagawa H, Sasaki C,
Sakai K, Warita H, Wang JM, Shiro Y, Uchida M and Abe K: Protective
effect of ginkgo extract on rat brain with transient middle
cerebral artery occlusion. Neurol Res. 22:517–521. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ahlemeyer B, Mowes A and Krieglstein J:
Inhibition of serum deprivation- and staurosporine-induced neuronal
apoptosis by Ginkgo biloba extract and some of its constituents.
Eur J Pharmacol. 367:423–430. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Abdel-Wahab BA and Abd El-Aziz SM: Ginkgo
biloba protects against intermittent hypoxia-induced memory
deficits and hippocampal DNA damage in rats. Phytomedicine.
19:444–450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nash KM and Shah ZA: Current perspectives
on the beneficial role of Ginkgo biloba in neurological and
cerebrovascular disorders. Integr Med Insights. 10:1–9. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nabavi SM, Habtemariam S, Daglia M, Braidy
N, Loizzo MR, Tundis R and Navabi SF: Neuroprotective effects of
Ginkgolide B against ischemic stroke: A review of current
literature. Curr Top Med Chem. 15:2222–2232. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li R, Chen B, Wu W, Bao L, Li J and Qi R:
Ginkgolide B suppresses intercellular adhesion molecule-1
expression via blocking nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human
vascular endothelial cells stimulated by oxidized low-density
lipoprotein. J Pharmacol Sci. 110:362–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang M, Qian Y, Guan T, Huang L, Tang X
and Li Y: Different neuroprotective responses of Ginkgolide B and
bilobalide, The Two Ginkgo Components Hyperglycemia. Eur J
Pharmacol. 677:71–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang JYSJMS: Protective effects of
ginkgolide B on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Chin
Pharmacol Bull. 269–272. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Botao Y, Ma J, Xiao W, Xiang Q, Fan K, Hou
J, Wu J and Jing W: Protective effect of ginkgolide B on high
altitude cerebral edema of rats. High Alt Med Biol. 14:61–64. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang Y, Huang B, Sun L, Peng X, Chen X and
Zou X: Ginkgolide B promotes proliferation and functional
activities of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells:
Involvement of Akt/eNOS and MAPK/p38 signaling pathways. Eur Cell
Mater. 21:459–469. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Chin A, Zhang L, Lu J and Wong RW:
The role of traditional Chinese medicines in osteogenesis and
angiogenesis. Phytother Res. 28:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li N, Jiang Y, Wooley PH, Xu Z and Yang
SY: Naringin promotes osteoblast differentiation and effectively
reverses ovariectomy-associated osteoporosis. J Orthop Sci.
18:478–485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huh JE, Yang HR, Park DS, Choi DY, Baek
YH, Cho EM, Cho YJ, Kang-Il K, Kim DY and Lee JD: Puerariae radix
promotes differentiation and mineralization in human
osteoblast-like SaOS-2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 104:345–350. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lamant V, Mauco G, Braquet P, Chap H and
Douste-Blazy L: Inhibition of the metabolism of platelet activating
factor (PAF-acether) by three specific antagonists from Ginkgo
biloba. Biochem Pharmacol. 36:2749–2752. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chan PC, Xia Q and Fu PP: Ginkgo biloba
leave extract: Biological, medicinal and toxicological effects. J
Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 25:211–244.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie H, Cui Z, Wang L, Xia Z, Hu Y, Xian L,
Li C, Xie L, Crane J, Wan M, et al: PDGF-BB secreted by
preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with
osteogenesis. Nat Med. 20:1270–1278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Street J, Winter D, Wang JH, Wakai A,
McGuinness A and Redmond HP: Is human fracture hematoma inherently
angiogenic? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 224–237. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Geiger F, Bertram H, Berger I, Lorenz H,
Wall O, Eckhardt C, Simank HG and Richter W: Vascular endothelial
growth factor gene-activated matrix (VEGF165-GAM) enhances
osteogenesis and angiogenesis in large segmental bone defects. J
Bone Miner Res. 20:2028–2035. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
D'Alimonte I, Nargi E, Mastrangelo F,
Falco G, Lanuti P, Marchisio M, Miscia S, Robuffo I, Capogreco M,
Buccella S, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances in
vitro proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human dental
pulp stem cells. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 25:57–69.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hah YS, Jun JS, Lee SG, Park BW, Kim DR,
Kim UK, Kim JR and Byun JH: Vascular endothelial growth factor
stimulates osteoblastic differentiation of cultured human
periosteal-derived cells expressing vascular endothelial growth
factor receptors. Mol Biol Rep. 38:1443–1450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tan YY, Yang YQ, Chai L, Wong RW and Rabie
AB: Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) on
MC3T3-E1. Orthod Craniofac Res. 13:223–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Deckers MM, Karperien M, van der Bent C,
Yamashita T, Papapoulos SE and Löwik CW: Expression of vascular
endothelial growth factors and their receptors during osteoblast
differentiation. Endocrinology. 141:1667–1674. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tokuda H, Kozawa O, Miwa M and Uematsu T:
p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase but not p44 p42 MAP
kinase is involved in prostaglandin E1-induced vascular endothelial
growth factor synthesis in osteoblasts. J Endocrinol. 170:629–638.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kozawa O, Kawamura H, Hatakeyama D,
Matsuno H and Uematsu T: Endothelin-1 induces vascular endothelial
growth factor synthesis in osteoblasts involvement of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. Cellular Signal. 12:375–380.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tokuda H, Hatakeyama D, Akamatsu S, Tanabe
K, Yoshida M, Shibata T and Kozawa O: Involvement of MAP kinases in
TGF-beta-stimulated vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in
osteoblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 415:117–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen M, Chen PM, Dong QR, Huang Q, She C
and Xu W: p38 signaling in titanium particle-induced MMP-2
secretion and activation in differentiating MC3T3-E1 cells. J
Biomed Mater Res A. 102:2824–2832. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Greenblatt MB, Shim JH, Zou W, Sitara D,
Schweitzer M, Hu D, Lotinun S, Sano Y, Baron R, Park JM, et al: The
p38 MAPK pathway is essential for skeletogenesis and bone
homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:2457–2473. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu Y, Chan E, Wang SX and Li B: Activation
of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for osteoblast
differentiation. Endocrinology. 144:2068–2074. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Thouverey C and Caverzasio J: The p38α
MAPK positively regulates osteoblast function and postnatal bone
acquisition. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3115–3125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|