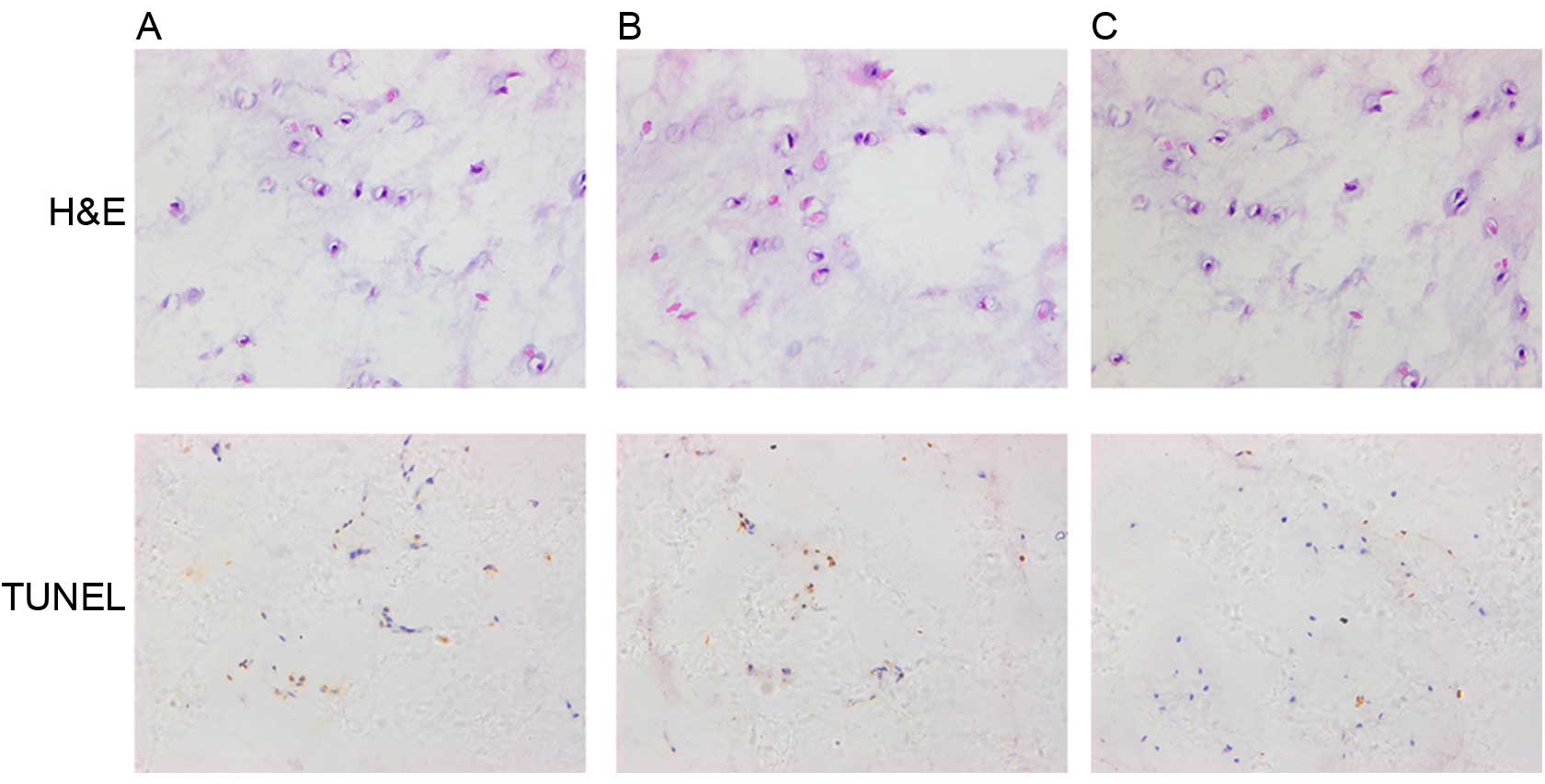
|
1
|
Hoy D, Brooks P, Blyth F and Buchbinder R:
The Epidemiology of low back pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol.
24:769–781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takahashi K, Aoki Y and Ohtori S:
Resolving discogenic pain. Eur Spine J. 17:(Suppl 4). S428–S431.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hillman M, Wright A, Rajaratnam G, Tennant
A and Chamberlain MA: Prevalence of low back pain in the community:
Implications for service provision in Bradford, UK. J Epidemiol
Community Health. 50:347–352. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McMeeken J, Tully E, Stillman B, Nattrass
C, Bygott IL and Story I: The experience of back pain in young
Australians. Man Ther. 6:213–220. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fritzell P, Hägg O, Wessberg P and
Nordwall A: Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group: 2001 Volvo award
winner in clinical studies: Lumbar fusion versus nonsurgical
treatment for chronic low back pain: A multicenter randomized
controlled trial from the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 26:2521–2534; discussion 2532–2534. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, Hoff JT and
McGillicuddy JE: Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or
lumbosacral fusion: Review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 29:1938–1944. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Freemont AJ: The cellular pathobiology of
the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 48:5–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA:
The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human
intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 7:R732–R745.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smith LJ, Nerurkar NL, Choi KS, Harfe BD
and Elliott DM: Degeneration and regeneration of the intervertebral
disc: Lessons from development. Dis Model Mech. 4:31–41. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rannou F, Lee TS, Zhou RH, Chin J, Lotz
JC, Mayoux-Benhamou MA, Barbet JP, Chevrot A and Shyy JY:
Intervertebral disc degeneration: The role of the mitochondrial
pathway in annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis induced by overload. Am
J Pathol. 164:915–924. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao CQ, Liu D, Li H, Jiang LS and Dai LY:
Interleukin-1beta enhances the effect of serum deprivation on rat
annular cell apoptosis. Apoptosis. 12:2155–2161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li F and Ling X: Survivin study: An update
of ‘what is the next wave’? J Cell Physiol. 208:476–486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lechler P, Balakrishnan S, Schaumburger J,
Grässel S, Baier C, Grifka J, Straub RH and Renkawitz T: The
oncofetal gene survivin is re-expressed in osteoarthritis and is
required for chondrocyte proliferation in vitro. BMC Musculoskelet
Disord. 12:1502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bokarewa M, Tarkowski A and Magnusson M:
Pathological survivin expression links viral infections with
pathogenesis of erosive rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol.
66:192–198. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang KS, Yue B and Ma XX: The expression
of survivin and its significance in fetal intervertebral disc.
Qingdao Daxue Yixueyuan Xuebao. 49:205–206. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Yang KS: The expression of survivin and
its significance inintervertebral disc (dissertation). Qingdao
University; 2013
|
|
17
|
Lin Yazhou Yue, Bin Xiang Hongfei, et al:
Survivin is re-expressed in disc degeneration disease and is
required for degenerated nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and
anti-apoptosis in vitro. Mol Med Rep. (In press).
|
|
18
|
Zhou RP, Zhang ZM, Wang L, Huang MJ, Zheng
XC, Cui YN, Yin M, Wang XK, Yao NZ, Chen TY, et al: Establishing a
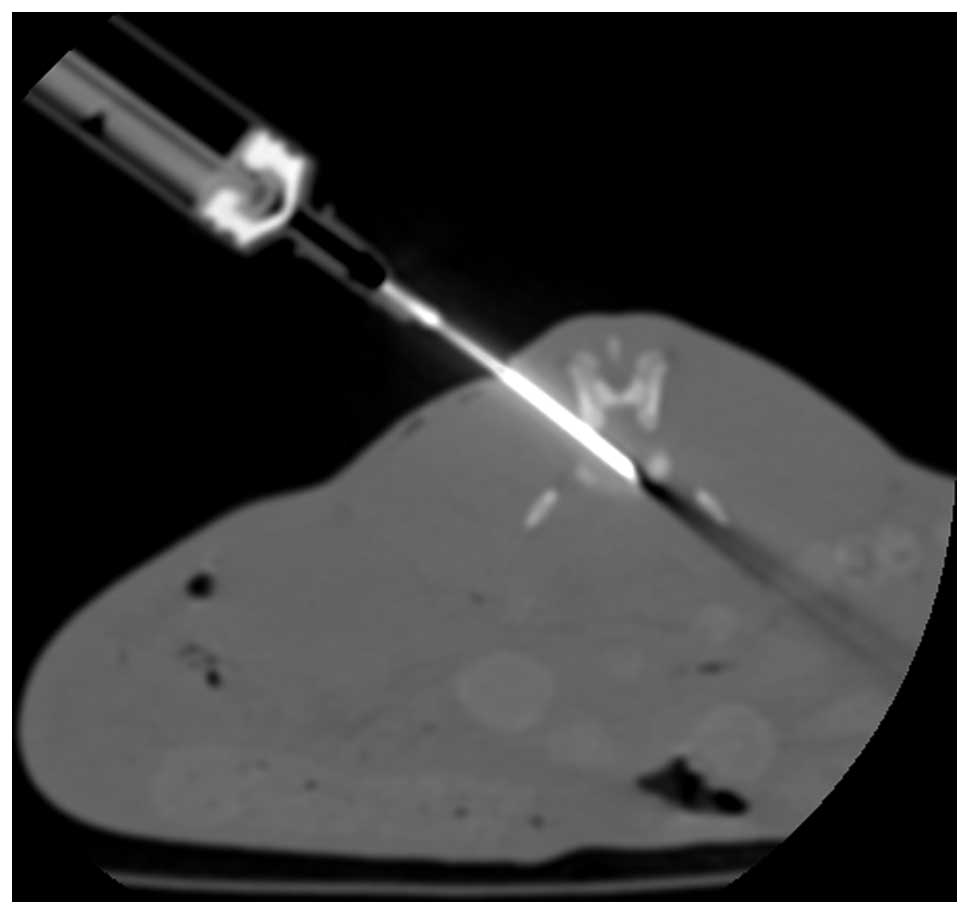
disc degeneration model using computed tomography-guided
percutaneous puncture technique in the rabbit. J Surg Res.
181:e65–e74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kluba T, Niemeyer T, Gaissmaier C and
Gründer T: Human anulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus cells of the
intervertebral disc: Effect of degeneration and culture system on
cell phenotype. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:2743–2748. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elliott DM, Yerramalli CS, Beckstein JI,
Johannessen W and Vresilovic EJ: The effect of relative needle
diameter in puncture and sham injection animal models of
degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:588–596. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kwon YJ: A minimally invasive rabbit model
of progressive and reproducible disc degeneration confirmed by
radiology, gene expression, and histology. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
53:323–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma X, Lin Y, Yang K, Yue B, Xiang H and
Chen B: Effect of lentivirus-mediated survivin transfection on the
morphology and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells derived from
degenerative human disc in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 36:186–194.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sowa G, Westrick E, Pacek C, Coelho P,
Patel D, Vadala G, Georgescu H, Vo N, Studer R and Kang J: In vitro
and in vivo testing of a novel regulatory system for gene therapy
for intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 36:E623–E628. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|