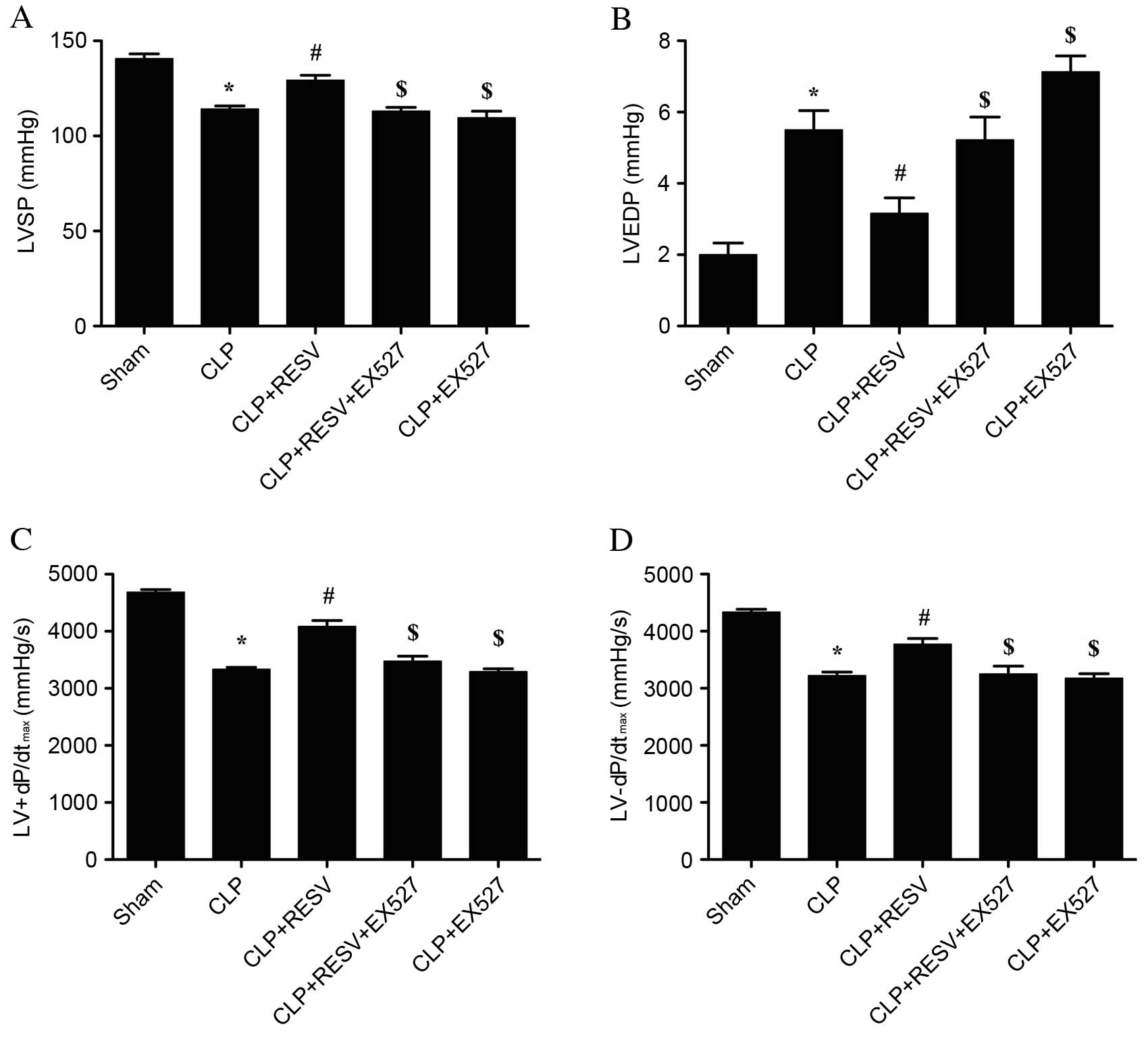
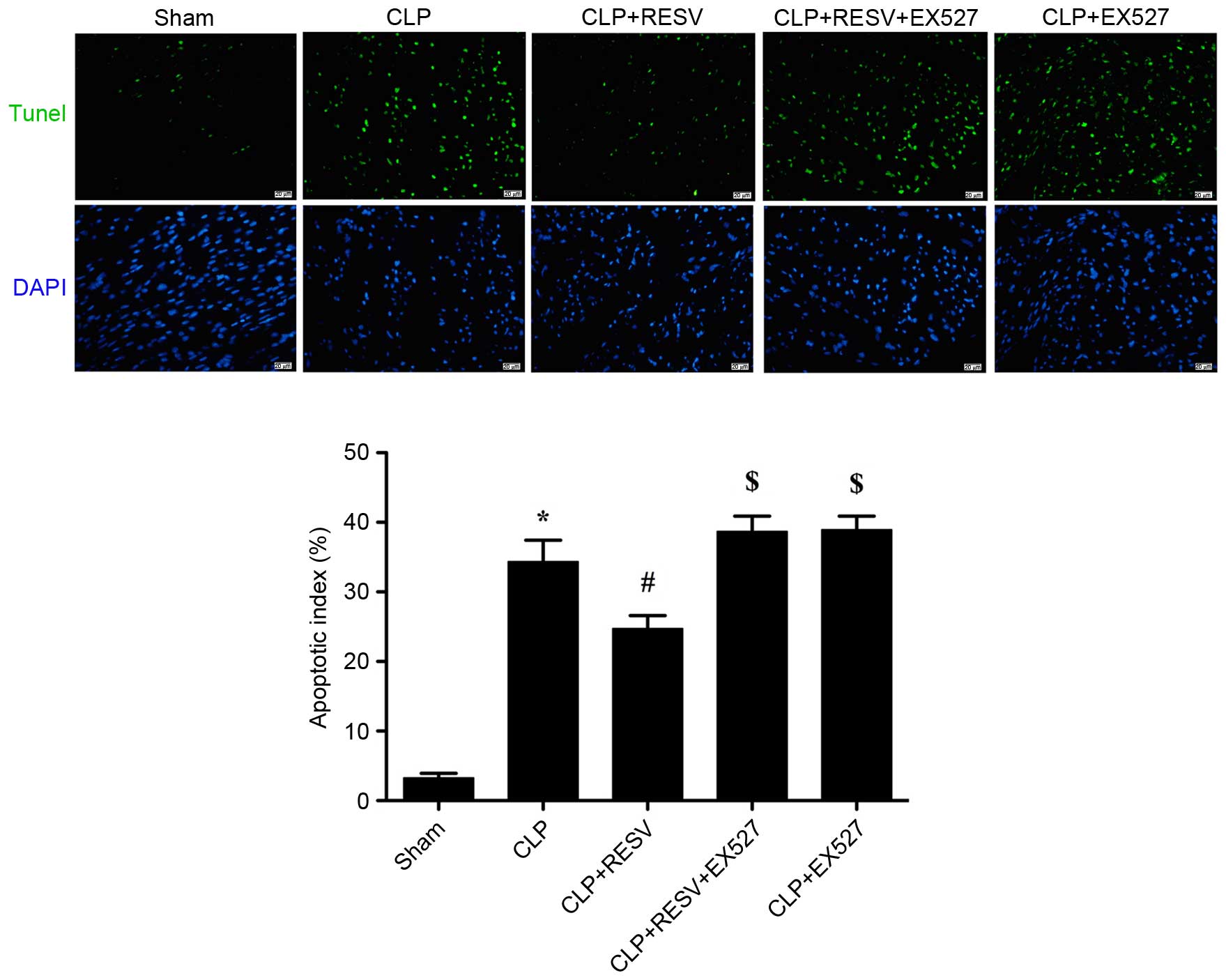
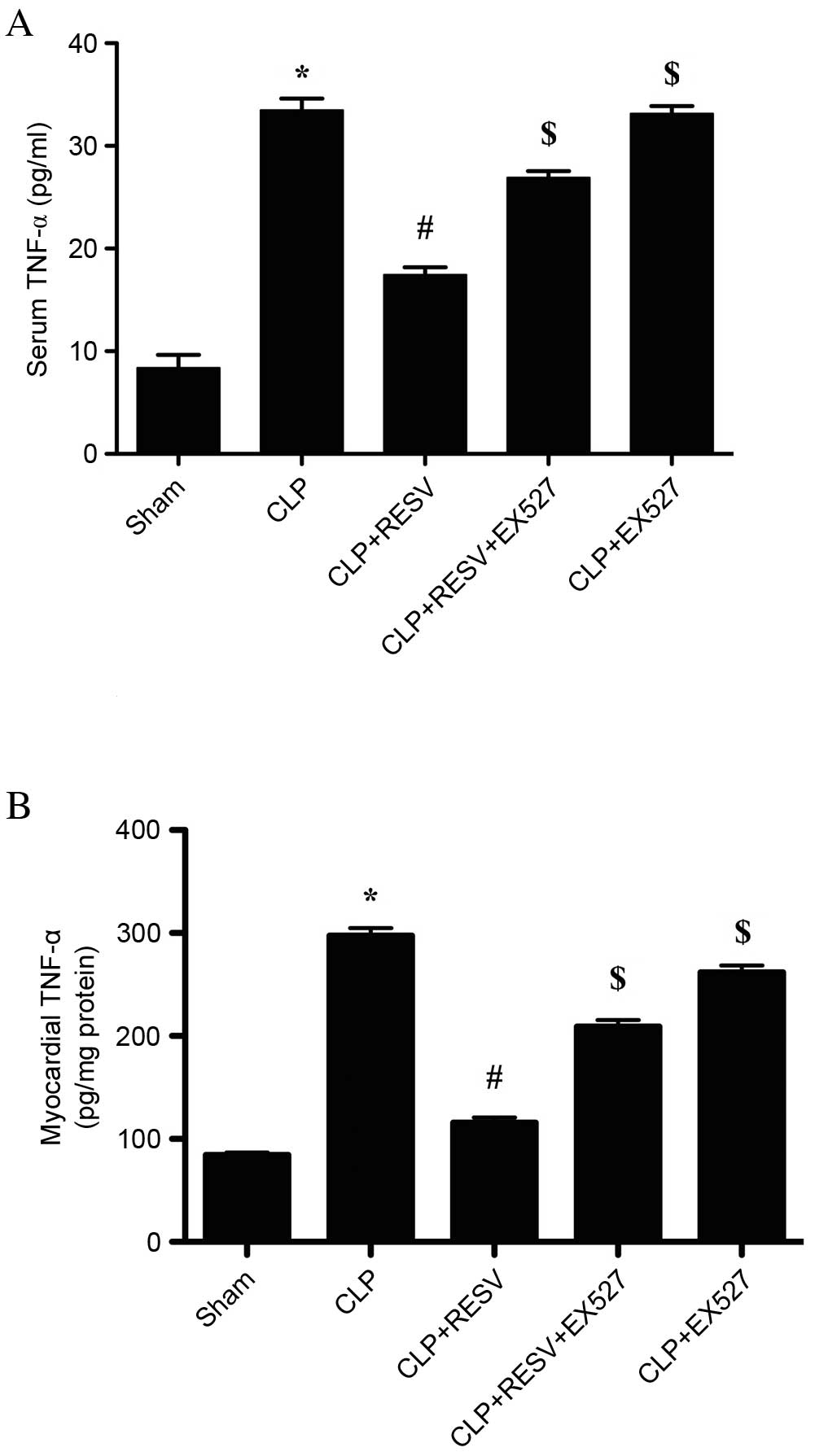
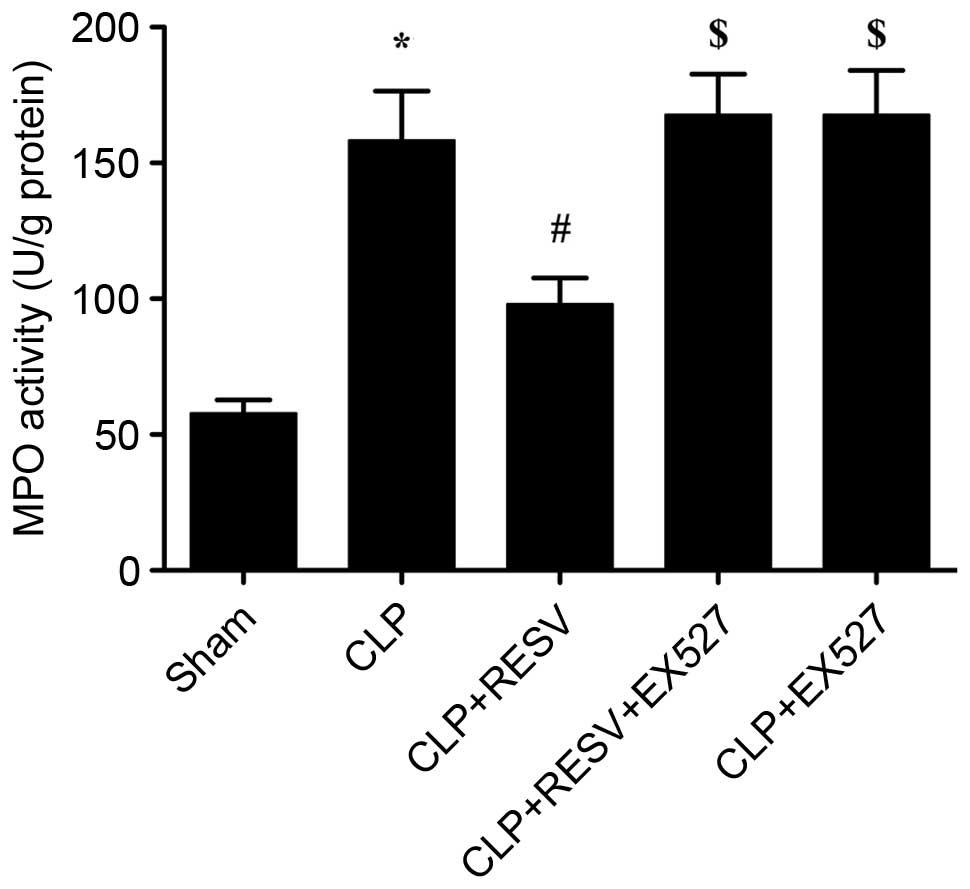
|
1
|
Annane D, Bellissant E and Cavaillon JM:
Septic shock. Lancet. 365:63–78. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Frolkis I, Klein Y, Locker C, Adi N, Dahan
E, Uretzsky G, Shapira I and Sorkine P: Vipera aspis venom reduces
lethality and down-regulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha in a rat
model of LPS-induced sepsis. Cytokine. 49:319–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J,
Clermont G, Carcillo J and Pinsky MR: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 29:1303–1310. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D,
Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke
R, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for
management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care
Med. 39:165–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
An R, Zhao L, Xi C, Li H, Shen G, Liu H,
Zhang S and Sun L: Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac
dysfunction via a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Basic Res Cardiol.
111:82016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rudiger A and Singer M: Mechanisms of
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 35:1599–1608.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Court O and Kumar A, Parrillo JE and Kumar
A: Clinical review: Myocardial depression in sepsis and septic
shock. Crit Care. 6:500–508. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van der Poll T and van Deventer SJ:
Cytokines and anticytokines in the pathogenesis of sepsis. Infect
Dis Clin North Am. 13:413–426, ix. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Borra MT, Smith BC and Denu JM: Mechanism
of human SIRT1 activation by resveratrol. J Biol Chem.
280:17187–17195. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li YG, Zhu W, Tao JP, Xin P, Liu MY, Li JB
and Wei M: Resveratrol protects cardiomyocytes from oxidative
stress through SIRT1 and mitochondrial biogenesis signaling
pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 438:270–276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu BL, Zhang X, Zhang W and Zhen HN: New
enlightenment of French Paradox: Resveratrol's potential for cancer
chemoprevention and anti-cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
6:1833–1836. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smeding L, Leong-Poi H, Hu P, Shan Y,
Haitsma JJ, Horvath E, Furmli S, Masoom H, Kuiper JW, Slutsky AS,
et al: Salutary effect of resveratrol on sepsis-induced myocardial
depression. Crit Care Med. 40:1896–1907. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu W, Lu Y, Yao J, Li Z, Chen Z, Wang G,
Jing H, Zhang X, Li M, Peng J and Tian X: Novel role of
resveratrol: Suppression of high-mobility group protein box 1
nucleocytoplasmic translocation by the upregulation of sirtuin 1 in
sepsis-induced liver injury. Shock. 42:440–447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu F, Burk D, Gao Z, Yin J, Zhang X, Weng
J and Ye J: Angiogenic deficiency and adipose tissue dysfunction
are associated with macrophage malfunction in SIRT1-/− mice.
Endocrinology. 153:1706–1716. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Motta MC, Divecha N, Lemieux M, Kamel C,
Chen D, Gu W, Bultsma Y, McBurney M and Guarente L: Mammalian SIRT1
represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell. 116:551–563. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo R, Liu W, Liu B, Zhang B, Li W and Xu
Y: SIRT1 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy: An insight into endoplasmic reticulum stress
response mechanism. Int J Cardiol. 191:36–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao R, Ma Z, Hu Y, Chen J, Shetty S and Fu
J: Sirt1 restrains lung inflammasome activation in a murine model
of sepsis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 308:L847–L853. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arnhold J: Properties, functions, and
secretion of human myeloperoxidase. Biochemistry (Mosc). 69:4–9.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thom SR, Milovanova TN, Bogush M, Yang M,
Bhopale VM, Pollock NW, Ljubkovic M, Denoble P, Madden D, Lozo M
and Dujic Z: Bubbles, microparticles, and neutrophil activation:
Changes with exercise level and breathing gas during open-water
SCUBA diving. J Appl Physiol (1985). 114:1396–1405. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mallat Z, Hugel B, Ohan J, Lesèche G,
Freyssinet JM and Tedgui A: Shed membrane microparticles with
procoagulant potential in human atherosclerotic plaques: A role for
apoptosis in plaque thrombogenicity. Circulation. 99:348–353. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Angus DC and van der Poll T: Severe sepsis
and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 369:840–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Calis J, van Woensel J and Lemson J:
Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 369:20622013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Merx MW and Weber C: Sepsis and the heart.
Circulation. 116:793–802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stanley WC, Recchia FA and Lopaschuk GD:
Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart.
Physiol Rev. 85:1093–1129. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sharshar T, Gray F, de la Grandmaison G
Lorin, Hopkinson NS, Ross E, Dorandeu A, Orlikowski D, Raphael JC,
Gajdos P and Annane D: Apoptosis of neurons in cardiovascular
autonomic centres triggered by inducible nitric oxide synthase
after death from septic shock. Lancet. 362:1799–1805. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Qin W, Qiu X, Cao J, Liu D and Sun
B: A novel role of exogenous carbon monoxide on protecting cardiac
function and improving survival against sepsis via mitochondrial
energetic metabolism pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 10:777–788. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zou X, Xu J, Yao S, Li J, Yang Y and Yang
L: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in HL-1 cardiomyocytes. Exp
Physiol. 99:1348–1358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang T, Yan T, Du J, Wang S and Yang H:
Apigenin attenuates heart injury in lipopolysaccharide-induced
endotoxemic model by suppressing sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine
1-phosphate signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 233:46–55. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Antonucci E, Fiaccadori E, Donadello K,
Taccone FS, Franchi F and Scolletta S: Myocardial depression in
sepsis: From pathogenesis to clinical manifestations and treatment.
J Crit Care. 29:500–511. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vincent JL, Bakker J, Marécaux G,
Schandene L, Kahn RJ and Dupont E: Administration of anti-TNF
antibody improves left ventricular function in septic shock
patients. Results of a pilot study. Chest. 101:810–815. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu X, Zhang B, Fan R, Zhao L, Wang Y,
Zhang S, Kaye AD, Huang L and Pei J: U50, 488H inhibits neutrophil
accumulation and TNF-α induction induced by ischemia-reperfusion in
rat heart. Cytokine. 56:503–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Unnewehr H, Rittirsch D, Sarma JV, Zetoune
F, Flierl MA, Perl M, Denk S, Weiss M, Schneider ME, Monk PN, et
al: Changes and regulation of the C5a receptor on neutrophils
during septic shock in humans. J Immunol. 190:4215–4225. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kolgazi M, Sener G, Cetinel S, Gedik N and
Alican I: Resveratrol reduces renal and lung injury caused by
sepsis in rats. J Surg Res. 134:315–321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Holthoff JH, Wang Z, Seely KA, Gokden N
and Mayeux PR: Resveratrol improves renal microcirculation,
protects the tubular epithelium, and prolongs survival in a mouse
model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int.
81:370–378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hao E, Lang F, Chen Y, Zhang H, Cong X,
Shen X and Su G: Resveratrol alleviates endotoxin-induced
myocardial toxicity via the Nrf2 transcription factor. PLoS One.
8:e694522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang X, Buechler NL, Yoza BK, McCall CE
and Vachharajani VT: Resveratrol attenuates microvascular
inflammation in sepsis via SIRT-1-Induced modulation of adhesion
molecules in ob/ob mice. Obesity (Silver Spring). 23:1209–1217.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bishayee A, Waghray A, Barnes KF, Mbimba
T, Bhatia D, Chatterjee M and Darvesh AS: Suppression of the
inflammatory cascade is implicated in resveratrol chemoprevention
of experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. Pharm Res. 27:1080–1091.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z,
Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P,
Elliott P, et al: Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and
protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and
PGC-1alpha. Cell. 127:1109–1122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun W, Wang W, Kim J, Keng P, Yang S,
Zhang H, Liu C, Okunieff P and Zhang L: Anti-cancer effect of
resveratrol is associated with induction of apoptosis via a
mitochondrial pathway alignment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 614:179–186.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Daitoku H, Hatta M, Matsuzaki H, Aratani
S, Ohshima T, Miyagishi M, Nakajima T and Fukamizu A: Silent
information regulator 2 potentiates Foxo1-mediated transcription
through its deacetylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:10042–10047. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kalle AM, Mallika A, Badiger J, Alinakhi
Talukdar P and Sachchidanand: Inhibition of SIRT1 by a small
molecule induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 401:13–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo S, Yao Q, Ke Z, Chen H, Wu J and Liu
C: Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced oxidative stress and
cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AMPK. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
412:85–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang R, Liu YY, Liu XY, Jia SW, Zhao J,
Cui D and Wang L: Resveratrol protects neurons and the myocardium
by reducing oxidative stress and ameliorating mitochondria damage
in a cerebral ischemia rat model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:854–864.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin Y, Zhu J, Zhang X, Wang J, Xiao W, Li
B, Jin L, Lian J, Zhou L and Liu J: Inhibition of cardiomyocytes
hypertrophy by resveratrol is Associated with Amelioration of
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 39:780–789.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|