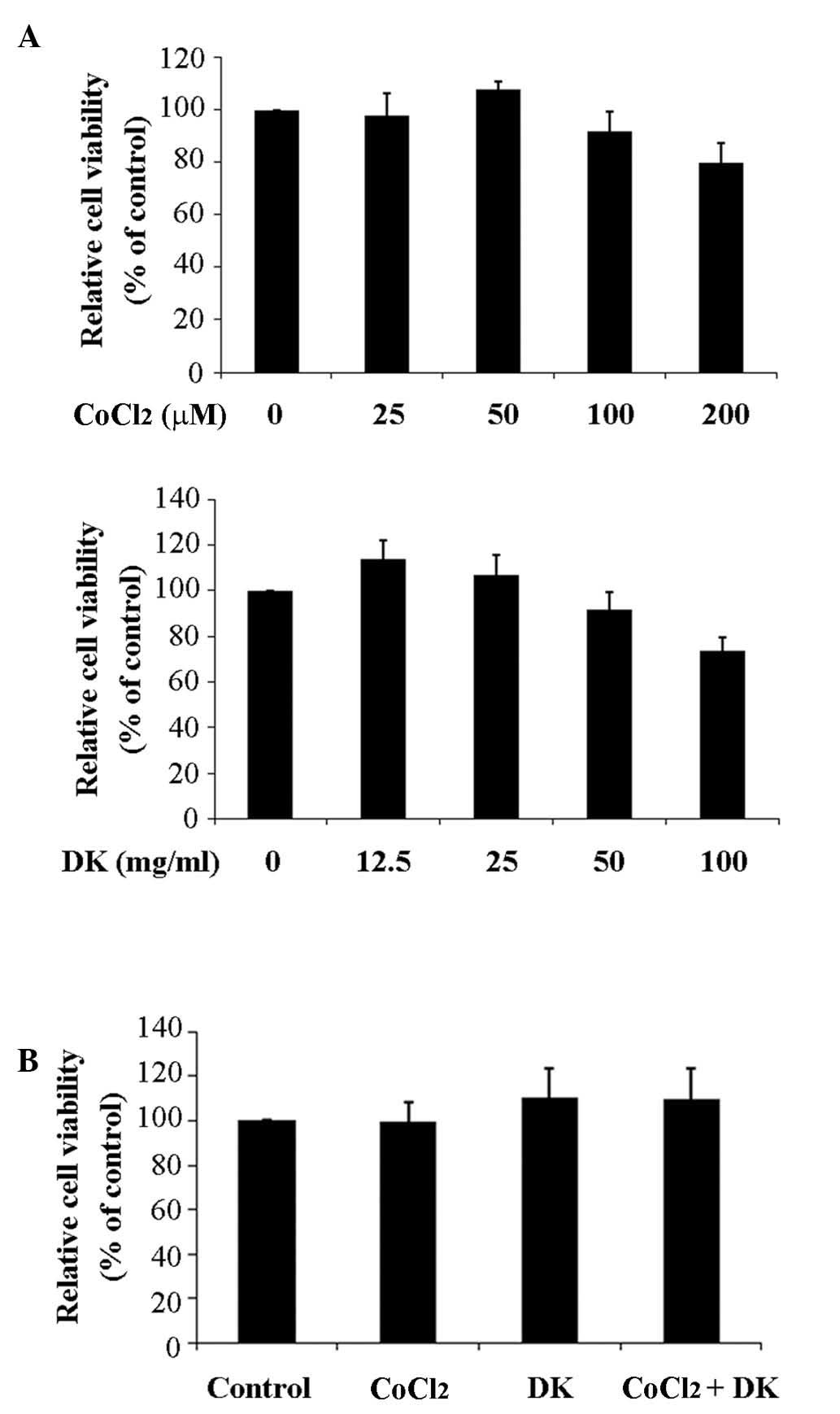
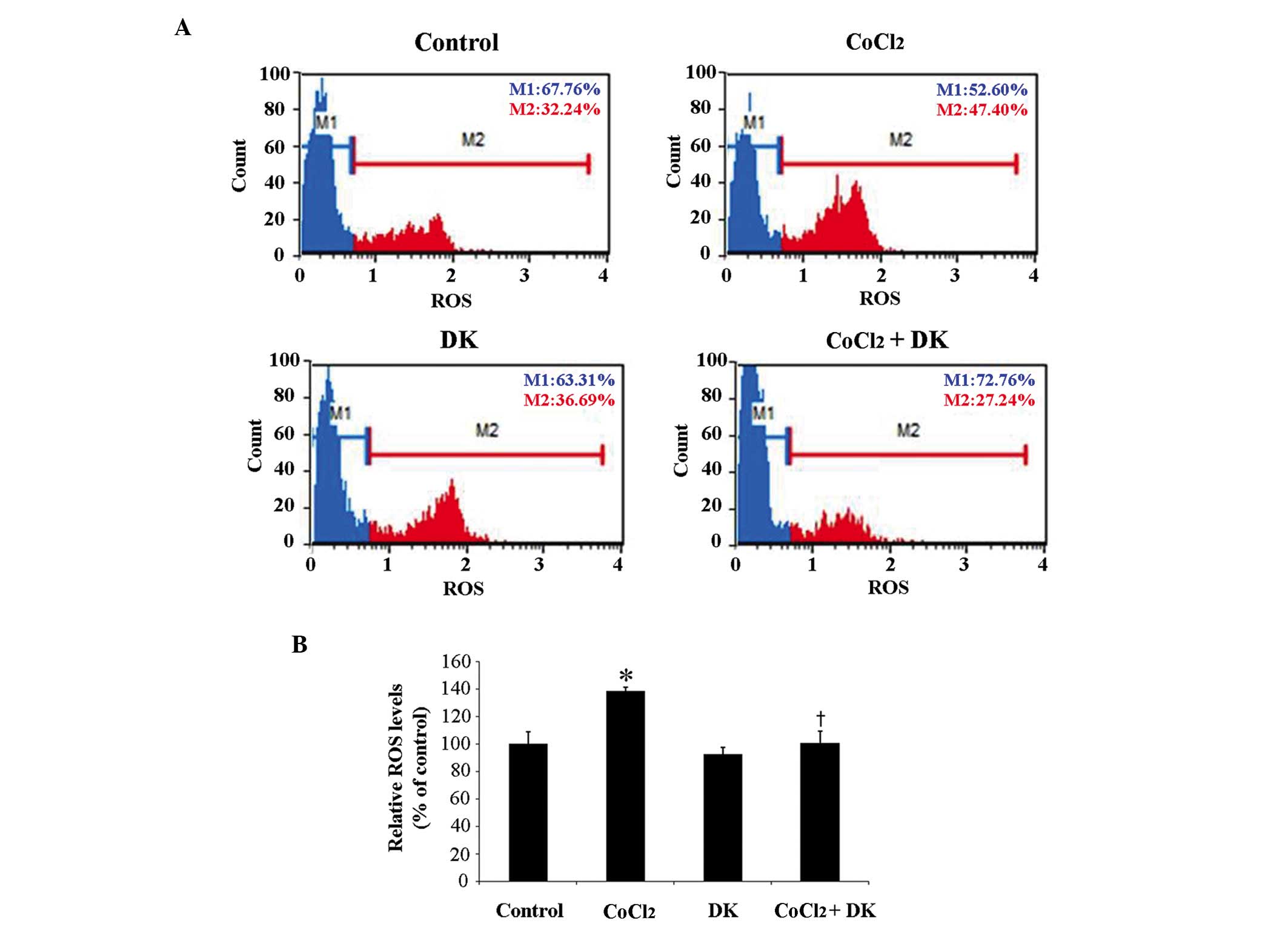
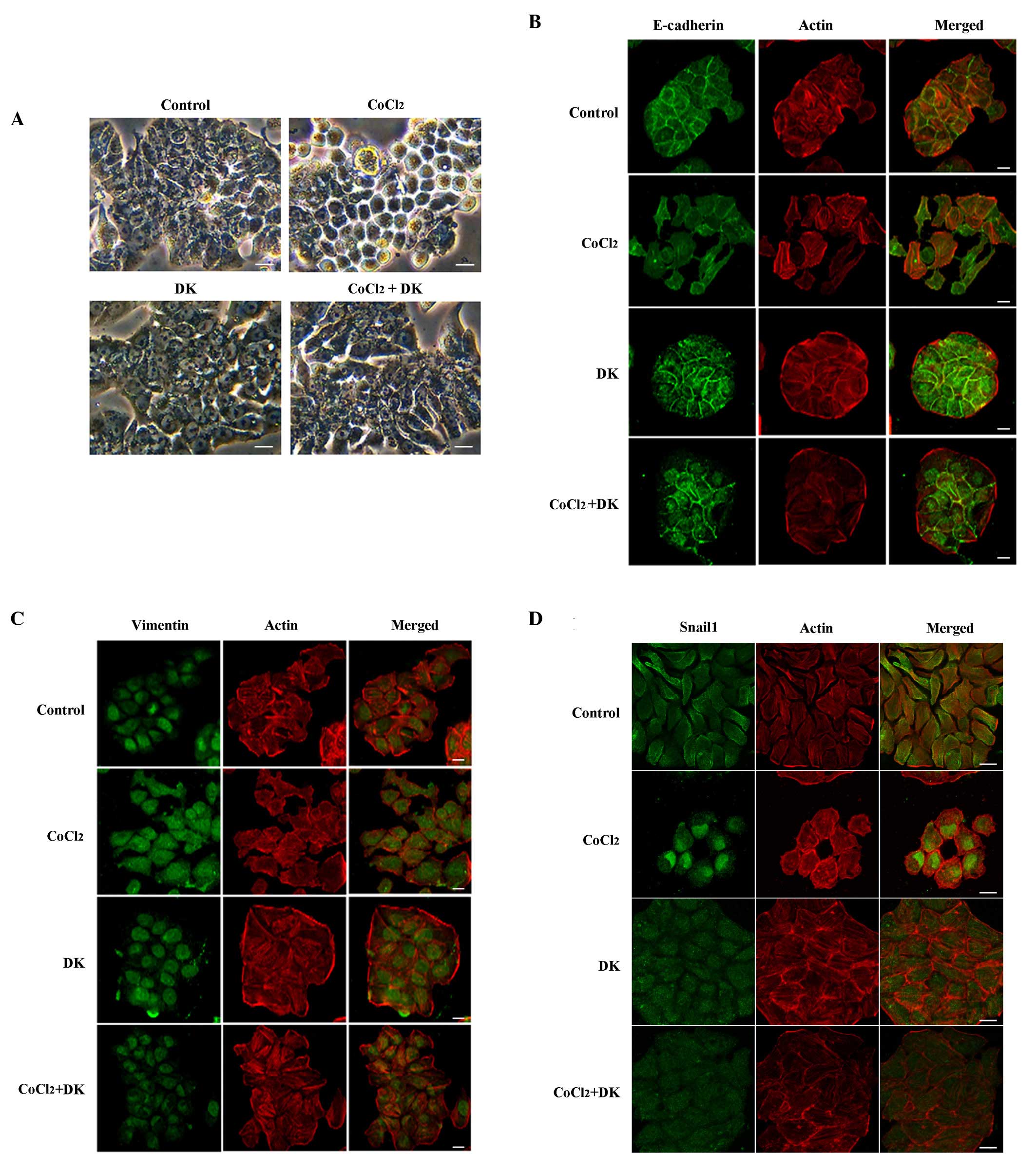
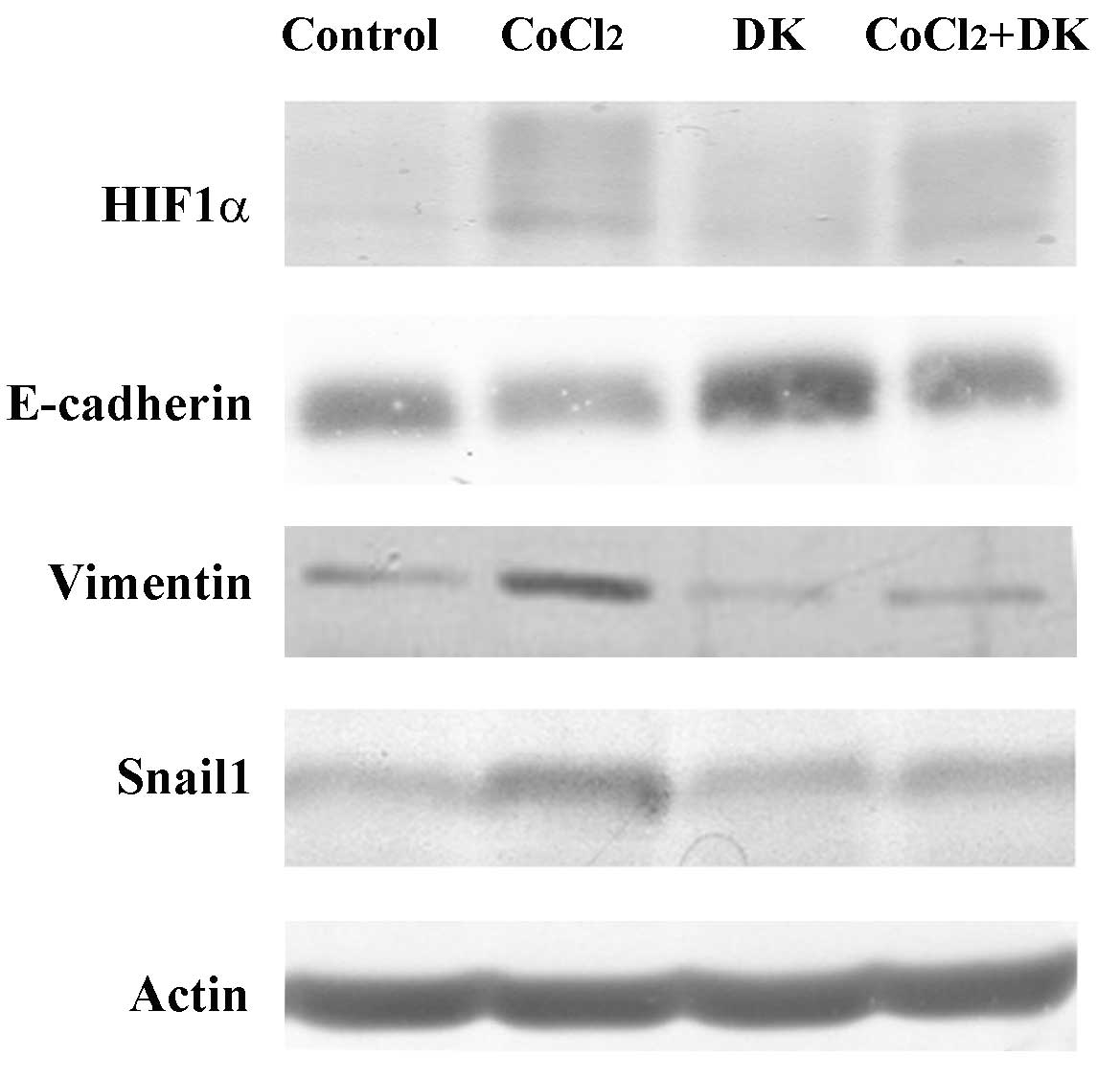
|
1
|
Krishnamachary B, Berg-Dixon S, Kelly B,
Agani F, Feldser D, Ferreira G, Iyer N, LaRusch J, Pak B, Taghavi P
and Semenza GL: Regulation of colon carcinoma cell invasion by
hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cancer Res. 63:1138–1143.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koga F, Kihara K and Neckers L: Inhibition
of cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting the molecular
chaperone heat-shock protein 90. Anticancer Res. 29:797–807.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mendez O, Zavadil J, Esencay M, Lukyanov
Y, Santovasi D, Wang SC, Newcomb EW and Zagzag D: Knock down of
HIF-1alpha in glioma cells reduces migration in vitro and invasion
in vivo and impairs their ability to form tumor spheres. Mol
Cancer. 9:1332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rankin EB and Giaccia AJ: The role of
hypoxia-inducible factors in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ.
15:678–685. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giannoni E, Parri M and Chiarugi P: EMT
and oxidative stress: A bidirectional interplay affecting tumor
malignancy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1248–1263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsai YP and Wu KJ: Hypoxia-regulated
target genes implicated in tumor metastasis. J Biomed Sci.
19:1022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luo Y, He DL, Ning L, Shen SL, Li L and Li
X: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induces the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostatecancer cells.
Chin Med J (Engl). 119:713–718. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Huang G, Li X, Zhang Y, Jiang Y,
Shen J, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhu J, Feng X, et al: Hypoxia induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of SNAI1 by
hypoxia-inducible factor −1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 13:1082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang W, Wu Y, Yan Q, Ma F, Shi X, Zhao Y,
Peng Y, Wang J and Jiang B: Deferoxamine enhances cell migration
and invasion through promotion of HIF-1α expression and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep.
31:111–116. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu LZ, Hu XW, Xia C, He J, Zhou Q, Shi X,
Fang J and Jiang BH: Reactive oxygen species regulate epidermal
growth factor-induced vascular endothelial growth factor and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression through activation of
AKT and P70S6K1 in human ovarian cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med.
41:1521–1533. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao JP, Zhou ZG, Hu HL, Guo Z, Wang T,
Zhen GH and Zhang ZX: The relationships among reactive oxygen
species, hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and cell proliferation in
rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells under hypoxia. Sheng Li
Xue Bao. 59:319–324. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Catalano V, Turdo A, Di Franco S, Dieli F,
Todaro M and Stassi G: Tumor and its microenvironment: A
synergistic interplay. Semin Cancer Biol. 23:522–532. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pettersen EO, Ebbesen P, Gieling RG,
Williams KJ, Dubois L, Lambin P, Ward C, Meehan J, Kunkler IH,
Langdon SP, et al: Targeting tumour hypoxia to prevent cancer
metastasis. from biology, biosensing and technology to drug
development: The METOXIA consortium. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem.
30:689–721. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee SH, Park MH, Heo SJ, Kang SM, Ko SC,
Han JS and Jeon YJ: Dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava inhibits
alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase in vitro and alleviates
postprandial hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.
Food Chem Toxicol. 48:2633–2637. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duan W, Chang Y, Li R, Xu Q, Lei J, Yin C,
Li T, Wu Y, Ma Q and Li X: Curcumin inhibits hypoxia inducible
factor-1α-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HepG2
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:2505–2510.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Krishnamachary B, Zagzag D, Nagasawa H,
Rainey K, Okuyama H, Baek JH and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1-dependent repression of E-cadherin in von hippel-lindau
tumor suppressor-null renal cell carcinoma mediated by TCF3, ZFHX1A
and ZFHX1B. Cancer Res. 66:2725–2731. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chan DA and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia, gene
expression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:333–339. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Evans AJ, Russell RC, Roche O, Burry TN,
Fish JE, Chow VW, Kim WY, Saravanan A, Maynard MA, Gervais ML, et
al: VHL promotes E2 box-dependent E-cadherin transcription by
HIF-mediated regulation of SIP1 and snail. Mol Cell Biol.
27:157–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cannito S, Novo E, Compagnone A, di Bonzo
L Valfre, Busletta C, Zamara E, Paternostro C, Povero D, Bandino A,
Bozzo F, et al: Redox mechanisms switch on hypoxia-dependent
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
29:2267–2278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Christofori G: New signals from the
invasive front. Nature. 441:444–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boyle P and Ferlay J: Mortality and
survival in breast and colorectal cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol.
2:424–425. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Naishadham D, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, Siegel
R, Cokkinides V and Jemal A: State disparities in colorectal cancer
mortality patterns in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 20:1296–1302. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park SJ and Jeon YJ: Dieckol from ecklonia
cava suppresses the migration and invasion of HT1080 cells by
inhibiting the focal adhesion kinase pathway downstream of Rac1-ROS
signaling. Mol Cells. 33:141–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ko SC, Lee M, Lee JH, Lee SH, Lim Y and
Jeon YJ: Dieckol, a phlorotannin isolated from a brown seaweed,
ecklonia cava, inhibits adipogenesis through AMP-activated protein
kinase (AMPK) activation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:1253–1260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Semenza GL: Hydroxylation of HIF-1: Oxygen
sensing at the molecular level. Physiology (Bethesda). 19:176–182.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dehne N, Fuhrmann D and Brüne B:
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) in hormone signaling during health
and disease. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 11:125–135. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koshikawa N, Hayashi J, Nakagawara A and
Takenaga K: Reactive oxygen species-generating mitochondrial DNA
mutation up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha gene
transcription via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt/protein kinase
C/histone deacetylase pathway. J Biol Chem. 284:33185–33194. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan M, Rayoo M, Takano EA, KConFab
Investigators and Fox SB: BRCA1 tumours correlate with a HIF-1alpha
phenotype and have a poor prognosis through modulation of
hydroxylase enzyme profile expression. Br J Cancer. 101:1168–1174.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lan A, Liao X, Mo L, Yang C, Yang Z, Wang
X, Hu F, Chen P, Feng J, Zheng D and Xiao L: Hydrogen sulfide
protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting
ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 cells.
PLoS One. 6:e259212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu D, Li M, Tian Y, Liu J and Shang J:
Luteolin inhibits ROS-activated MAPK pathway in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 122:15–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang F, Liu S, Xi S, Yan L, Wang H, Song Y
and Sun G: Arsenic induces the expressions of angiogenesis-related
factors through PI3K and MAPK pathways in SV-HUC-1 human
uroepithelial cells. Toxicol Lett. 222:303–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and De Herreros A Garcia: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|