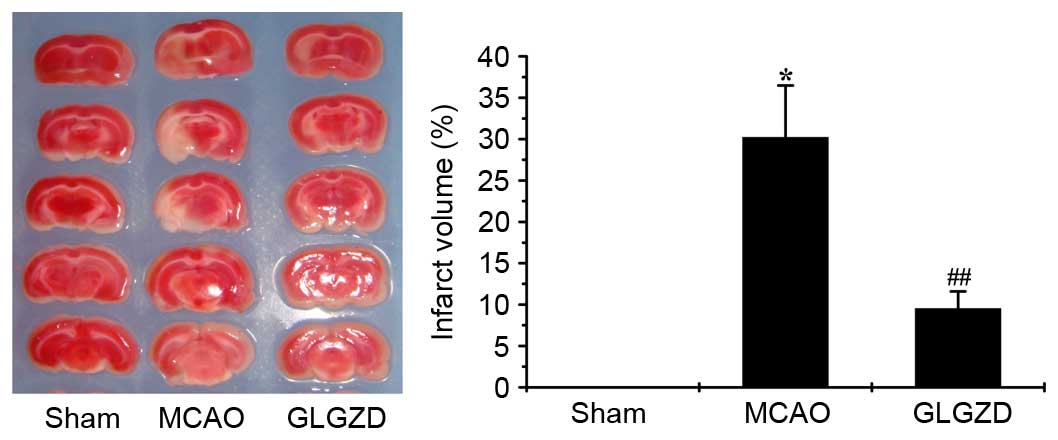
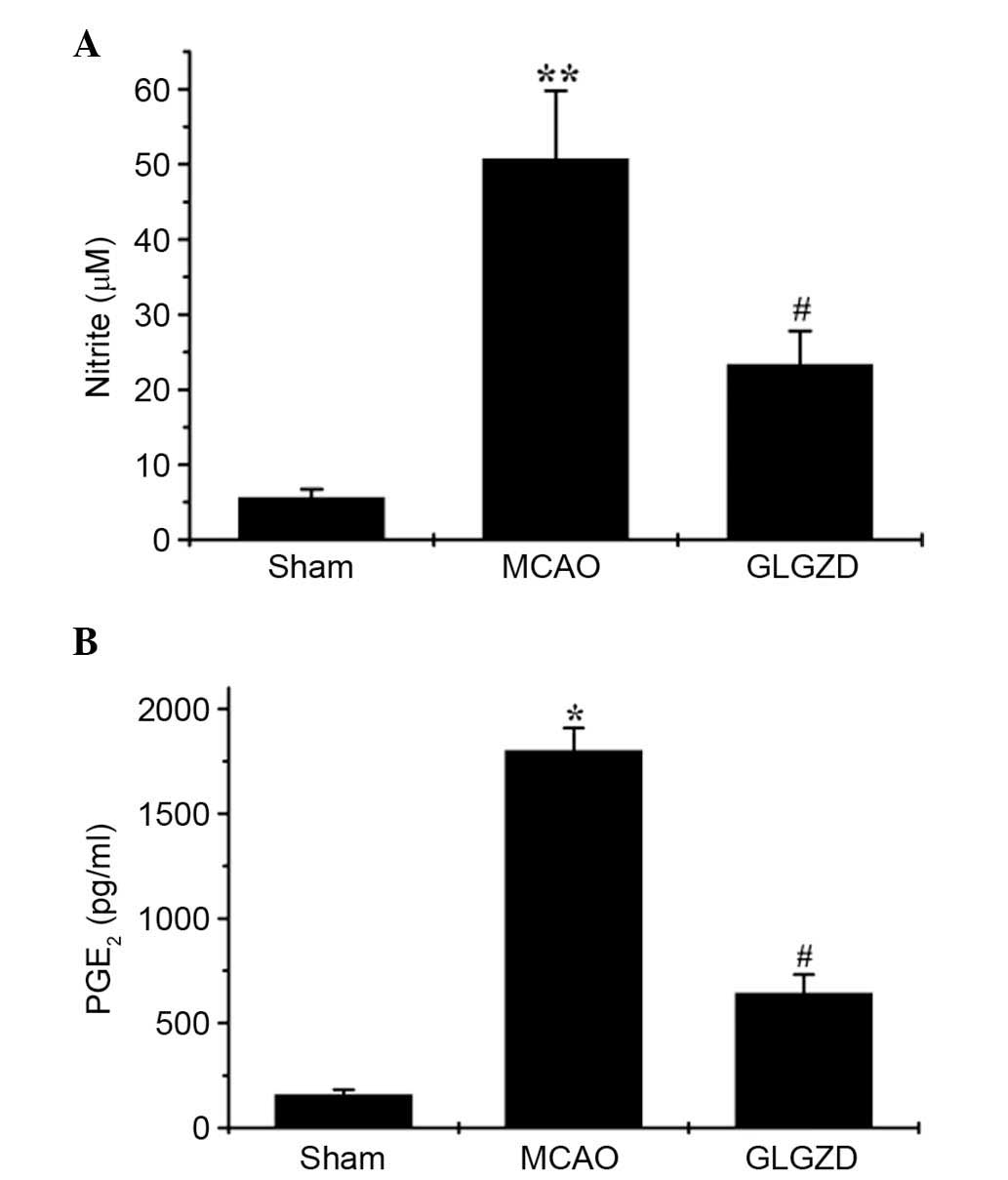
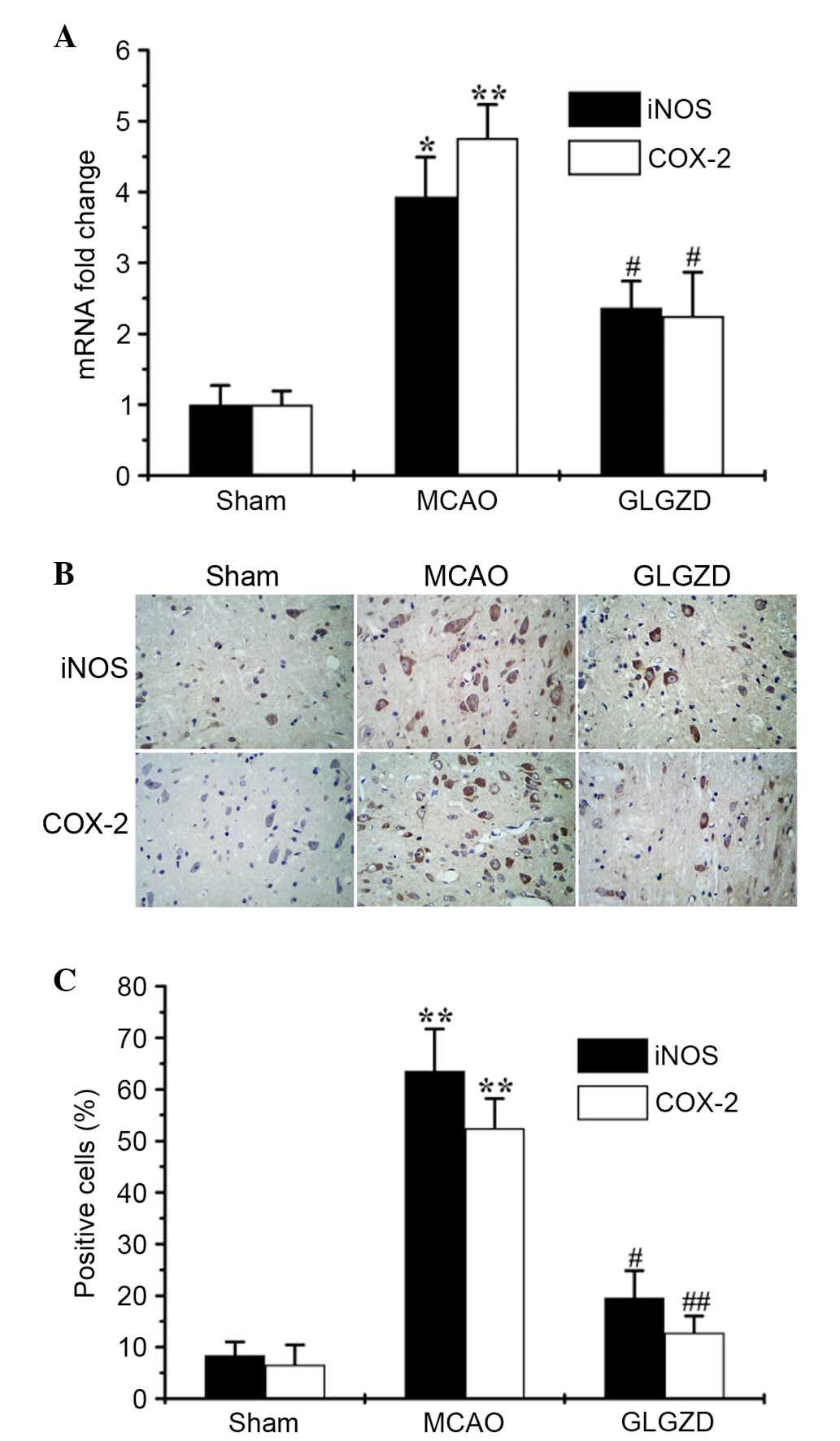
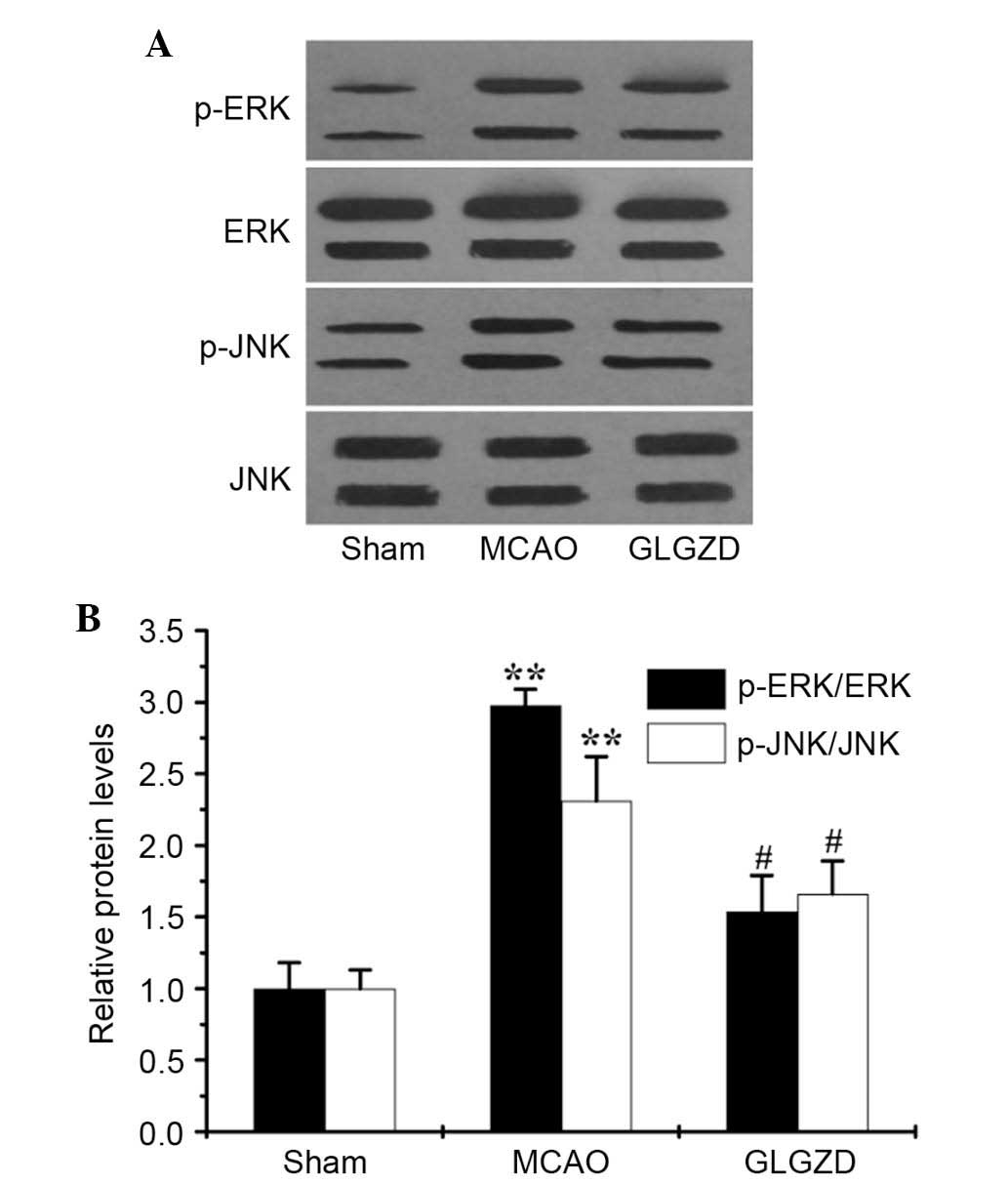
|
1
|
Brown GC and Neher JJ: Inflammatory
neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons.
Mol Neurobiol. 41:242–247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu H, Li Z, Zhu X, Lin R, Lin J, Peng J,
Tao J and Chen L: Gua Lou Gui Zhi decoction suppresses LPS-induced
activation of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in BV-2 murine microglial
cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:1327–1332. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu H, Li Z, Zhu X, Lin R, Peng J, Tao J
and Chen L: GuaLou GuiZhi decoction inhibits LPS-induced microglial
cell motility through the MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
32:1281–1286. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu H, Lin R, Zhu X, Li Z and Chen L:
Anti-inflammatory effects of Gualou Guizhi decoction in transient
focal cerebral ischemic brains. Mol Med Rep. 12:1321–1327.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang J, Tao J, Xue X, Yang S, Han P, Lin
Z, Xu W, Lin J, Peng J and Chen L: Gua Lou Gui Zhi decoction exerts
neuroprotective effects on post-stroke spasticity via the
modulation of glutamate levels and AMPA receptor expression. Int J
Mol Med. 31:841–848. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kovac A, Erickson MA and Banks WA: Brain
microvascular pericytes are immunoactive in culture: Cytokine,
chemokine, nitric oxide and LRP-1 expression in response to
lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroinflammation. 8:1392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Egger T, Schuligoi R, Wintersperger A,
Amann R, Malle E and Sattler W: Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol)
attenuates cyclo-oxygenase 2 transcription and synthesis in
immortalized murine BV-2 microglia. Biochem J. 370:459–467. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Glezer I, Simard AR and Rivest S:
Neuroprotective role of the innate immune system by microglia.
Neuroscience. 29:867–883. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Perry VH, Nicoll JA and Holmes C:
Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 6:193–201.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rock RB and Peterson PK: Microglia as a
pharmacological target in infectious and inflammatory diseases of
the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1:117–126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Minghetti L: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in
inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 63:901–910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Griffiths MR, Gasque P and Neal JW: The
multiple roles of the innate immune system in the regulation of
apoptosis and inflammation in the brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
68:217–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amor S, Puentes F, Baker D and van der
Valk P: Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology.
129:154–169. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lo JY, Kamarudin MN, Hamdi OA, Awang K and
Kadir HA: Curcumenol isolated from Curcuma zedoaria suppresses
Akt-mediated NF-κB activation and p38 MAPK signaling pathway in
LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells. Food Funct. 6:3550–3559.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Banati RB, Gehrmann J, Schubert P and
Kreutzberg GW: Cytotoxicity of microglia. Glia. 7:111–118. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rock RB and Peterson PK: Microglia as a
pharmacological target in infectious and inflammatory diseases of
the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1:117–126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abramson SB, Amin AR, Clancy RM and Attur
M: The role of nitric oxide in tissue destruction. Best Pract Res
Clin Rheumatol. 15:831–845. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boje KM: Nitric oxide neurotoxicity in
neurodegenerative diseases. Front Biosci. 9:763–776. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Minghetti L: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in
inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 63:901–910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Harari OA and Liao JK: NF-kB and innate
immunity in ischemic stroke. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1207:32–40. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee AK, Sung SH, Kim YC and Kim SG:
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase,
TNF-alpha and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on
I-kappaBalpha phosphorylation, C/EBP and AP-1 activation. Br J
Pharmacol. 139:11–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baeuerle PA and Henkel T: Function and
activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol.
12:141–179. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim YJ, Hwang SY, Oh ES, Oh S and Han IO:
IL-1beta, an immediate early protein secreted by activated
microglia, induces iNOS/NO in C6 astrocytoma cells through p38 MAPK
and NF-kappaB pathways. J Neurosci Res. 84:1037–1046. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L and Ai H: Effects of Gua Lou Gui
Zhi decoction on c-fos and c-jun on epileptic Rats. Sichuan Journal
of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 23:21–22. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Yang C, Chen L and Tao J: New usage of a
classical formula-Gua Lou Gui Zhi Decoction. Liaoning Journal of
Traditional Chinese Medicine. 8:166–167. 2012.
|