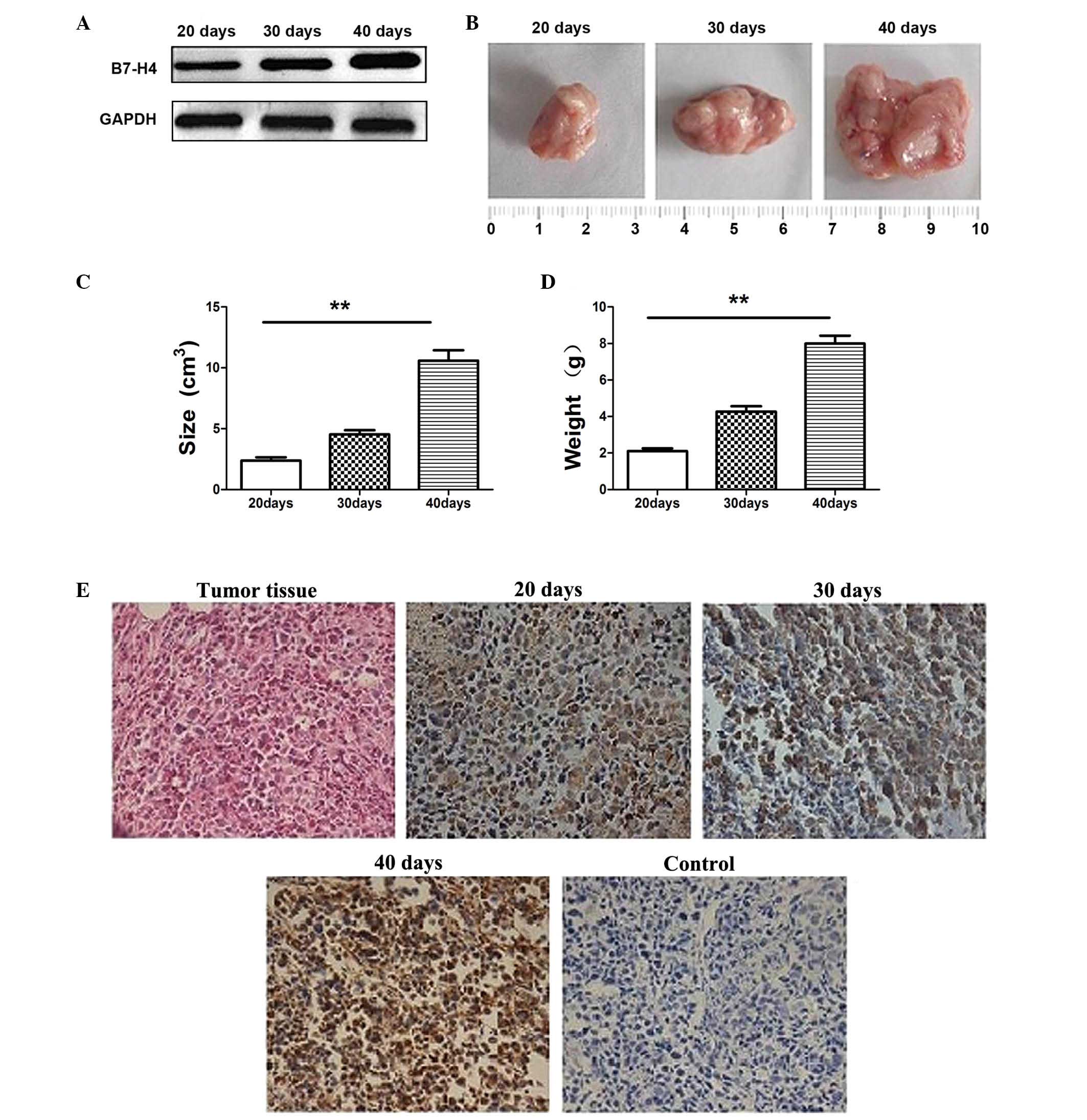
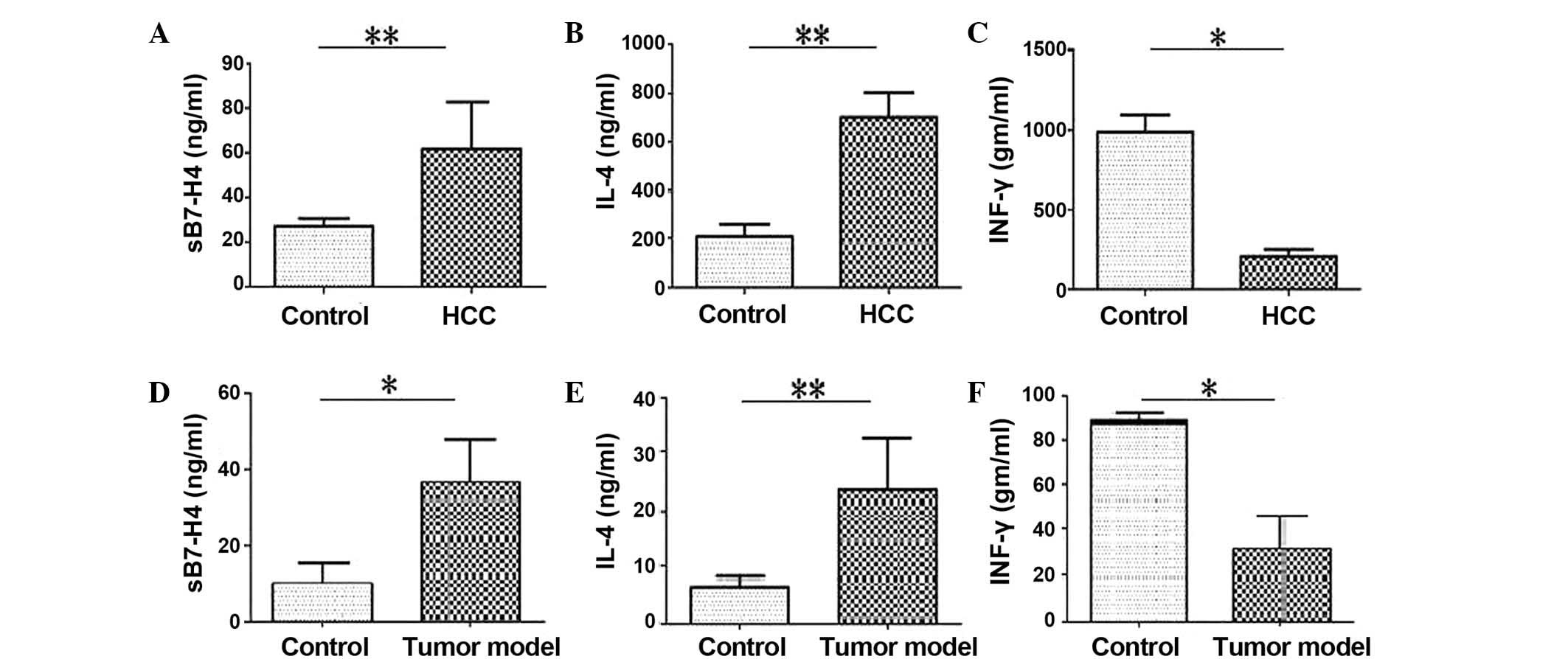
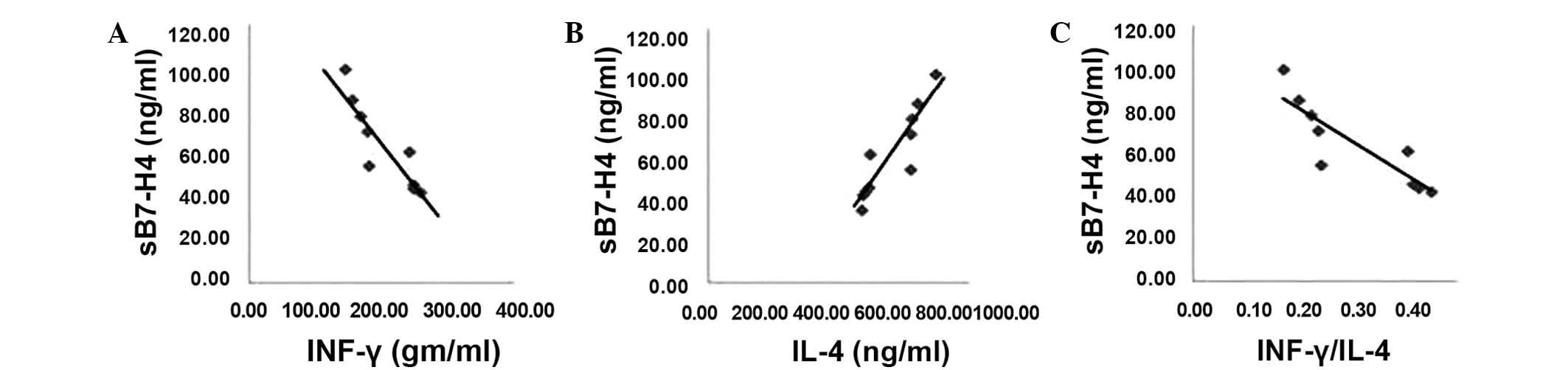
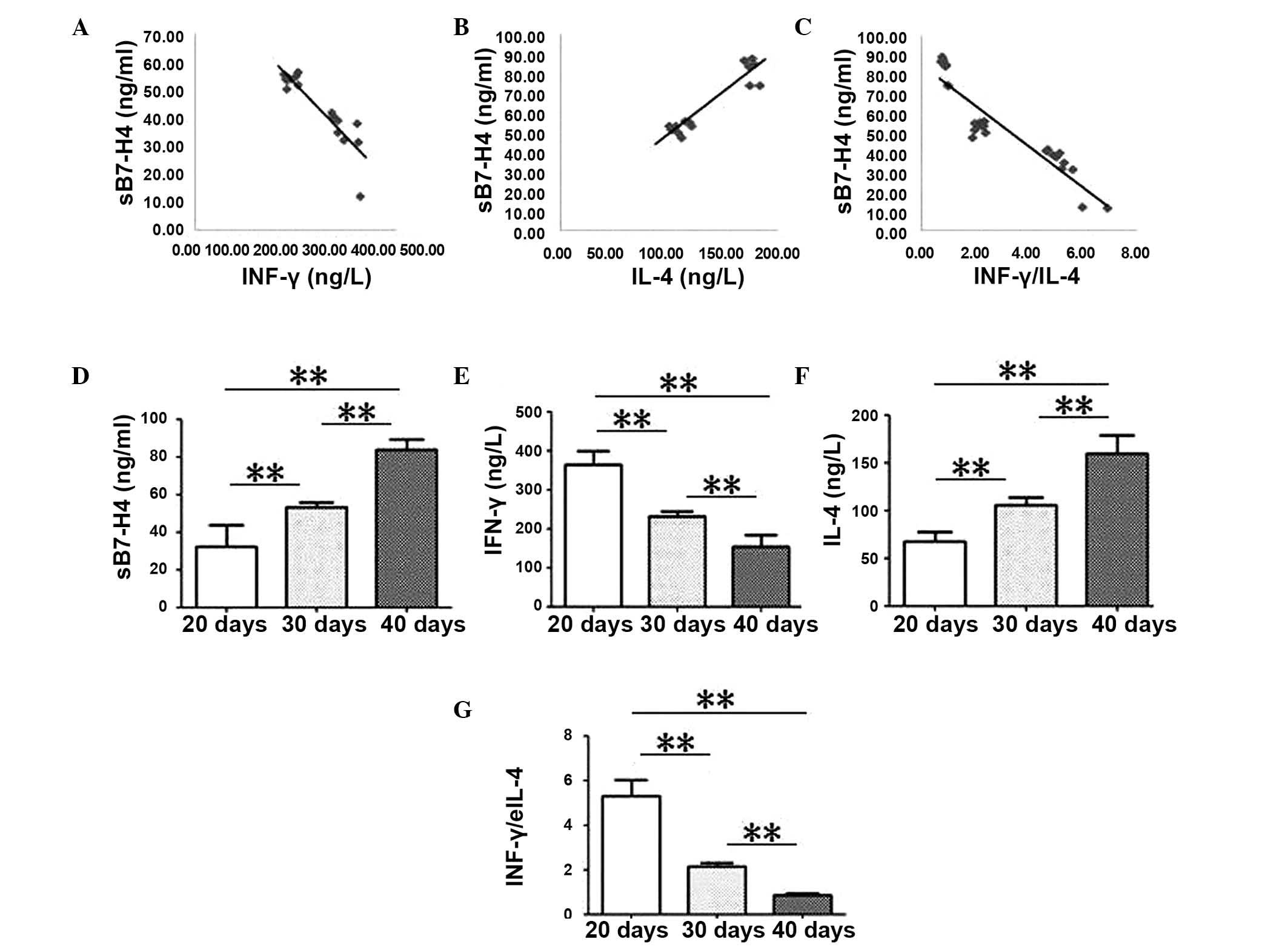
|
1
|
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K
and Thun MJ: Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a
prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N Engl J Med.
348:1625–1638. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM: Global cancer statistics in the
year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2:533–543. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schütte K, Bornschein J and Malfertheiner
P: Hepatocellular carcinoma-epidemiological trends and risk
factors. Dig Dis. 27:80–92. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hawkins MA and Dawson LA: Radiation
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: From palliation to cure.
Cancer. 106:1653–1663. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kudo M, Izumi N, Kokudo N, Matsui O,
Sakamoto M, Nakashima O, Kojiro M and Makuuchi M: HCC Expert Panel
of Japan Society of Hepatology: Management of hepatocellular
carcinoma in Japan: Consensus-based clinical practice guidelines
proposed by the Japan Society of Hepatology (JSH) 2010 updated
version. Dig Dis. 29:339–364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: Practice Guidelines
Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases:
Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 42:1208–1236.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen L: Co-inhibitory molecules of the
B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol.
4:336–347. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sica GL, Choi IH, Zhu G, Tamada K, Wang
SD, Tamura H, Chapoval AI, Flies DB, Bajorath J and Chen L: B7-H4,
a molecule of the B7 family, negatively regulates T cell immunity.
Immunity. 18:849–861. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zang X, Loke P, Kim J, Murphy K, Waitz R
and Allison JP: B7x: A widely expressed B7 family member that
inhibits T cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:10388–10392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prasad DV, Richards S, Mai XM and Dong C:
B7S1, a novel B7 family member that negatively regulates T cell
activation. Immunity. 18:863–873. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Flies DB and Chen L: The new B7s: Playing
a pivotal role in tumor immunity. J Immunother. 30:251–260. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen LJ, Sun J, Wu HY, Zhou SM, Tan Y, Tan
M, Shan BE, Lu BF and Zhang XG: B7-H4 expression associates with
cancer progression and predicts patient's survival in human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
60:1047–1055. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Awadallah NS, Shroyer KR, Langer DA,
Torkko KC, Chen YK, Bentz JS, Papkoff J, Liu W, Nash SR and Shah
RJ: Detection of B7-H4 and p53 in pancreatic cancer: Potential role
as a cytological diagnostic adjunct. Pancreas. 36:200–206. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arigami T, Uenosono Y, Ishigami S,
Hagihara T, Haraguchi N and Natsugoe S: Clinical significance of
the B7-H4 coregulatory molecule as a novel prognostic marker in
gastric cancer. World J Surg. 35:2051–2057. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Geng Y, Wang H, Lu C, Li Q, Xu B, Jiang J
and Wu C: Expression of costimulatory molecules B7-H1, B7-H4 and
Foxp3+ Tregs in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Int J
Clin Oncol. 20:273–281. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao LW, Li C, Zhang RL, Xue HG, Zhang FX,
Zhang F and Gai XD: B7-H1 and B7-H4 expression in colorectal
carcinoma: Correlation with tumor FOXP3(+) regulatory T-cell
infiltration. Acta Histochem. 116:1163–1168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen C, Qu QX, Shen Y, Mu CY, Zhu YB,
Zhang XG and Huang JA: Induced expression of B7-H4 on the surface
of lung cancer cell by the tumor-associated macrophages: A
potential mechanism of immune escape. Cancer Lett. 317:99–105.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jeon H, Vigdorovich V, Garrett-Thomson SC,
Janakiram M, Ramagopal UA, Abadi YM, Lee JS, Scandiuzzi L,
Ohaegbulam KC, Chinai JM, et al: Structure and cancer immunotherapy
of the B7 family member B7x. Cell Rep. 9:1089–1098. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kryczek I, Zou L, Rodriguez P, Zhu G, Wei
S, Mottram P, Brumlik M, Cheng P, Curiel T, Myers L, et al: B7-H4
expression identifies a novel suppressive macrophage population in
human ovarian carcinoma. J Exp Med. 203:871–881. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu J and Paul WE: CD4 T cells: Fates,
functions, and faults. Blood. 112:1557–1569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nieters A, Yuan JM, Sun CL, Zhang ZQ,
Stoehlmacher J, Govindarajan S and Yu MC: Effect of cytokine
genotypes on the hepatitis B virus-hepatocellular carcinoma
association. Cancer. 103:740–748. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ognjanovic S, Yuan JM, Chaptman AK, Fan Y
and Yu MC: Genetic polymorphisms in the cytokine genes and risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma in low-risk non-Asians of USA.
Carcinogenesis. 30:758–762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou D, Gu FM, Gao Q, Li QL, Zhou J and
Miao CH: Effects of anesthetic methods on preserving anti-tumor
T-helper polarization following hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol.
18:3089–3098. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li W, Huang X, Tong H, Wang Y, Zhang T,
Wang W, Dai L, Li T, Lin S and Wu H: Comparison of the regulation
of β-catenin signaling by type I, type II and type III interferons
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 7:e470402012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi IH, Zhu G, Sica GL, Strome SE,
Cheville JC, Lau JS, Zhu Y, Flies DB, Tamada K and Chen L: Genomic
organization and expression analysis of B7-H4, an immune inhibitory
molecule of the B7 family. J Immunol. 171:4650–4654. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tringler B, Liu W, Corral L, Torkko KC,
Enomoto T, Davidson S, Lucia MS, Heinz DE, Papkoff J and Shroyer
KR: B7-H4 overexpression in ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol.
100:44–52. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tringler B, Zhuo S, Pilkington G, Torkko
KC, Singh M, Lucia MS, Heinz DE, Papkoff J and Shroyer KR: B7-H4 is
highly expressed in ductal and lobular breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:1842–1848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Krambeck AE, Thompson RH, Dong H, Lohse
CM, Park ES, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC and Kwon
ED: B7-H4 expression in renal cell carcinoma and tumor vasculature:
Associations with cancer progression and survival. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:10391–10396. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zang X, Thompson RH, Al-Ahmadie HA, Serio
AM, Reuter VE, Eastham JA, Scardino PT, Sharma P and Allison JP:
B7-H3 and B7x are highly expressed in human prostate cancer and
associated with disease spread and poor outcome. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:19458–19463. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shi H, Ji M, Wu J, Zhou Q, Li X, Li Z,
Zheng X, Xu B, Zhao W, Wu C and Jiang J: Serum B7-H4 expression is
a significant prognostic indicator for patients with gastric
cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 12:1882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Simon I, Zhuo S, Corral L, Diamandis EP,
Sarno MJ, Wolfert RL and Kim NW: B7-h4 is a novel membrane-bound
protein and a candidate serum and tissue biomarker for ovarian
cancer. Cancer Res. 66:1570–1575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang C, Li Y and Wang Y: Diagnostic value
of serum B7-H4 for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res.
197:301–306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|