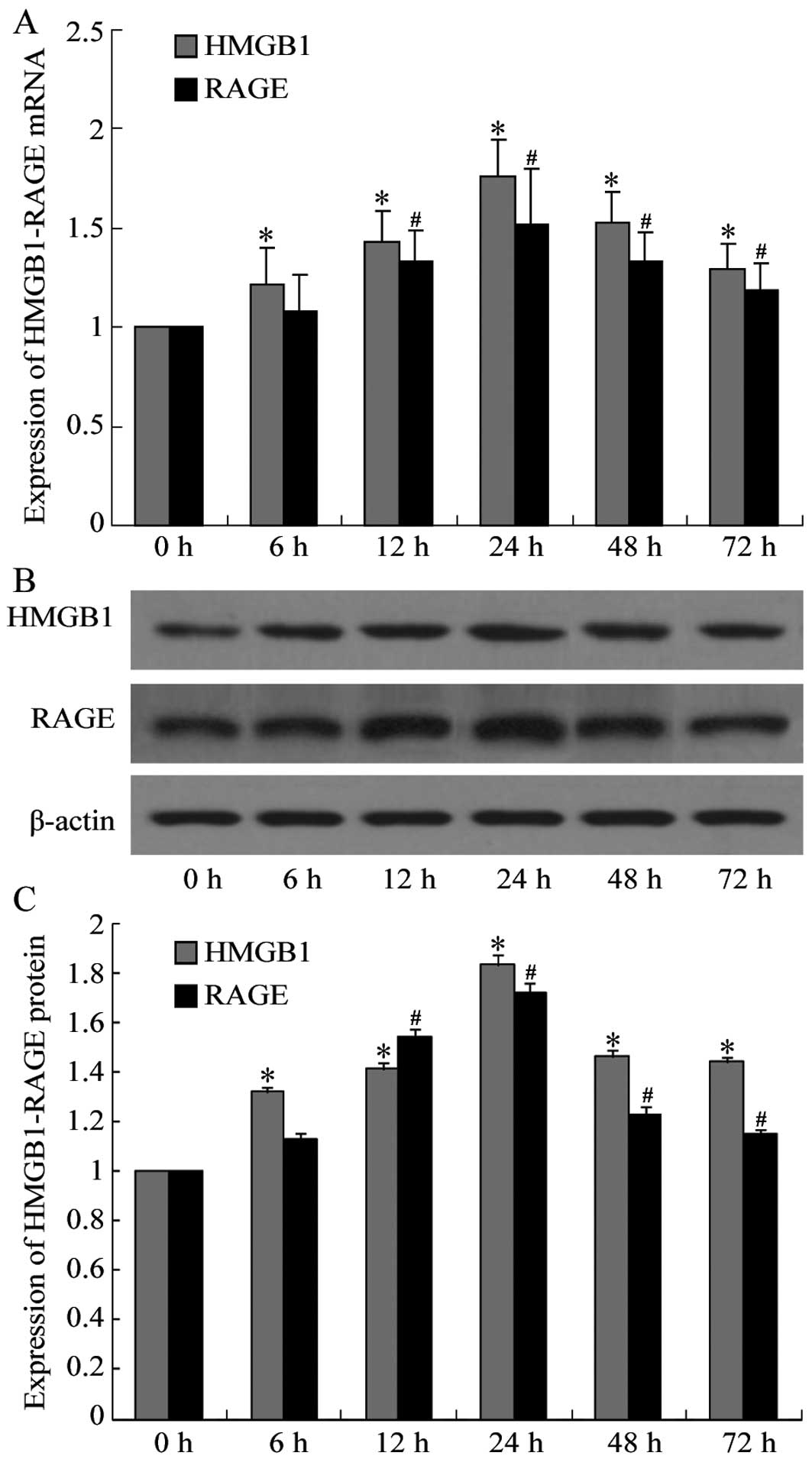
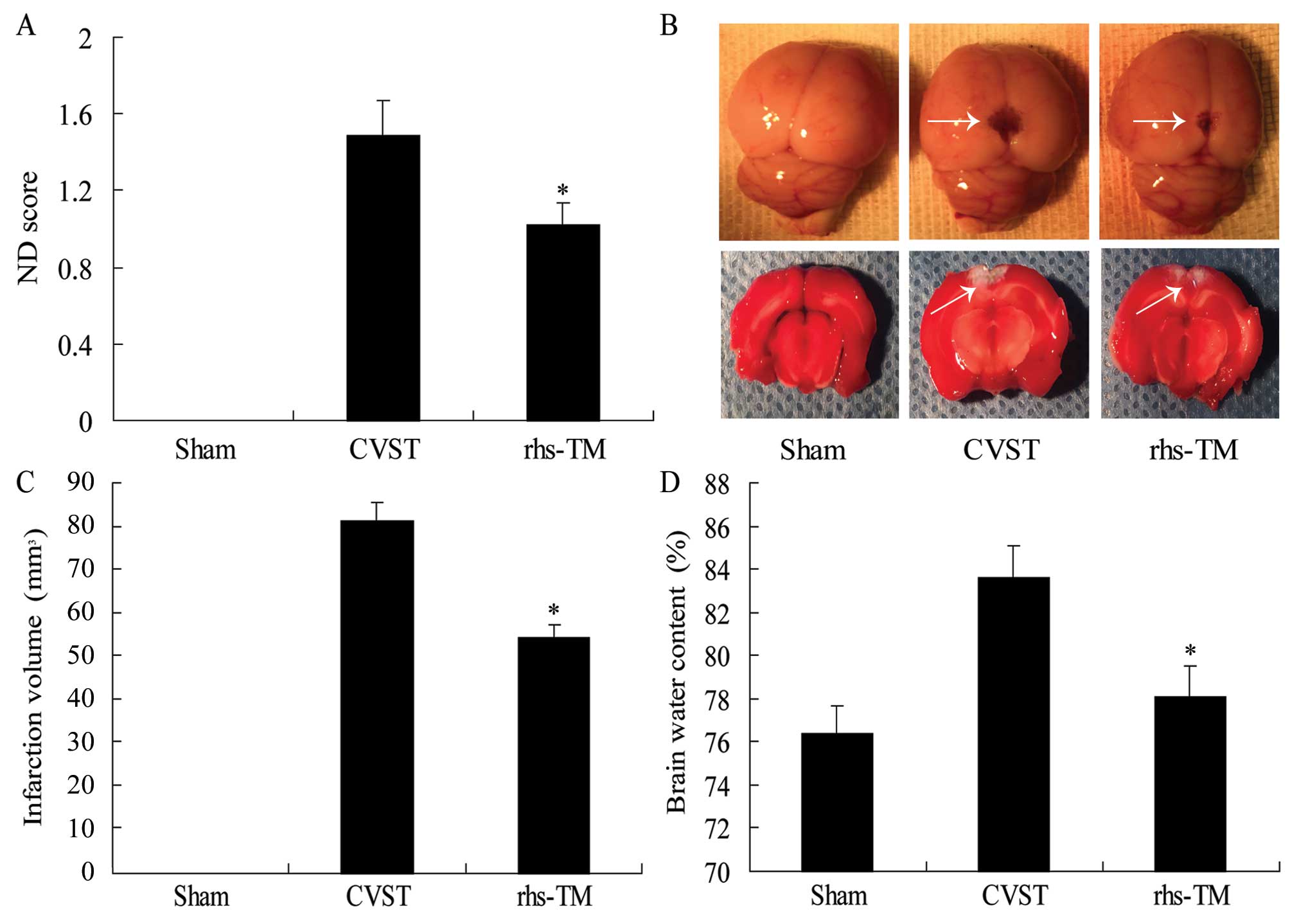
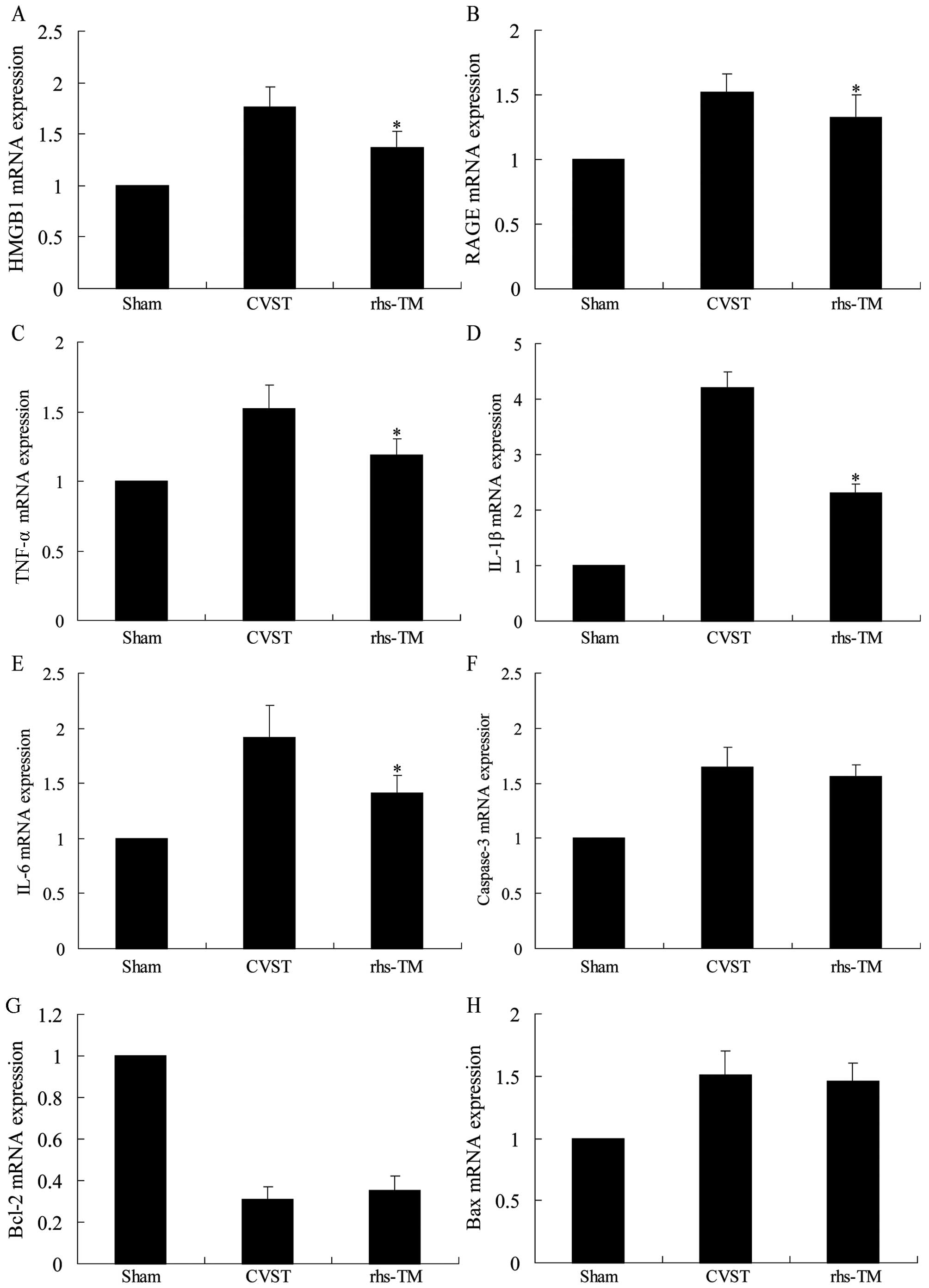
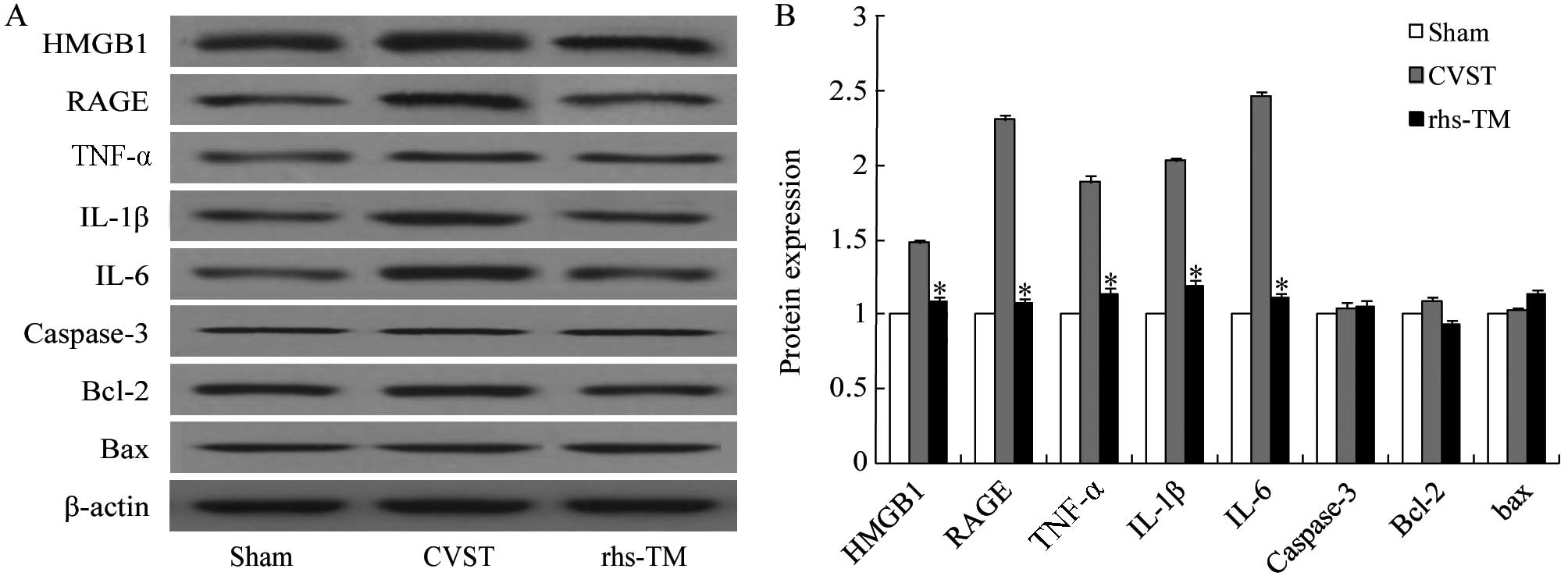
|
1
|
Bousser MG and Ferro JM: Cerebral venous
thrombosis: An update. Lancet Neurol. 6:162–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ruiz-Sandoval JL, Chiquete E,
Bañuelos-Becerra LJ, Torres-Anguiano C, González-Padilla C, Arauz
A, León-Jiménez C, Murillo-Bonilla LM, Villarreal-Careaga J,
Barinagarrementería F, et al: Cerebral venous thrombosis in a
Mexican multicenter registry of acute cerebrovascular disease: The
RENAMEVASC study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 21:395–400. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schaller B and Graf R: Cerebral venous
infarction: The pathophysiological concept. Cerebrovasc Dis.
18:179–188. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guenther G and Arauz A: Cerebral venous
thrombosis: A diagnostic and treatment update. Neurologia.
26:488–498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Camerlingo M, Salvi P, Belloni G, Gamba T,
Cesana BM and Mamoli A: Intravenous heparin started within the
first 3 hours after onset of symptoms as a treatment for acute
nonlacunar hemispheric cerebral infarctions. Stroke. 36:2415–2420.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Esmon CT and Owen WG: Identification of an
endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of
protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:2249–2252. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lane DA, Philippou H and Huntington JA:
Directing thrombin. Blood. 106:2605–2612. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Conway EM, Van de Wouwer M, Pollefeyt S,
Jurk K, Van Aken H, De Vriese A, Weitz JI, Weiler H, Hellings PW,
Schaeffer P, et al: The lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin
confers protection from neutrophil-mediated tissue damage by
suppressing adhesion molecule expression via nuclear factor kappaB
and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Exp Med.
196:565–577. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Su EJ, Geyer M, Wahl M, Mann K, Ginsburg
D, Brohmann H, Petersen KU and Lawrence DA: The thrombomodulin
analog Solulin promotes reperfusion and reduces infarct volume in a
thrombotic stroke model. J Thromb Haemost. 9:1174–1182. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ryang YM, Dang J, Kipp M, Petersen KU,
Fahlenkamp AV, Gempt J, Wesp D, Rossaint R, Beyer C and Coburn M:
Solulin reduces infarct volume and regulates gene-expression in
transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. BMC Neurosci.
12:1132011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang Z, Huang PL, Panahian N, Dalkara T,
Fishman MC and Moskowitz MA: Effect of cerebral ischemia in mice
deficient in neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Science.
265:1883–1885. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weimar C: Diagnosis and treatment of
cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
14:4172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Esmon CT: The protein C pathway. Chest.
124:(Suppl 3). 26S–32S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wenzel J, Assmann JC and Schwaninger M:
Thrombomodulin-a new target for treating stroke at the crossroad of
coagulation and inflammation. Curr Med Chem. 21:2025–2034. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Van de Wouwer M, Plaisance S, De Vriese A,
Waelkens E, Collen D, Persson J, Daha MR and Conway EM: The
lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin interferes with complement
activation and protects against arthritis. J Thromb Haemost.
4:1813–1824. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ito T and Maruyama I: Thrombomodulin:
Protectorate God of the vasculature in thrombosis and infiammation.
J Thromb Haemost. 9:(Suppl 1). S168–S173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lai CH, Shi GY, Lee FT, Kuo CH, Cheng TL,
Chang BI, Ma CY, Hsu FC, Yang YJ and Wu HL: Recombinant hman
thrombomodulin suppresses experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms
induced by calcium chloride in mice. Ann Surg. 258:1103–1110. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Javanmard SH, Shahsavarzadeh T and
Saadatnia M: Soluble thrombomodulin and endothelial cell protein C
receptor levels in patients with cerebral venous and sinus
thrombosis. Eur Neurol. 70:156–158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scaffidi P, Misteli T and Bianchi ME:
Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers
inflammation. Nature. 418:191–195. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andrassy M, Volz HC, Igwe JC, Funke B,
Eichberger SN, Kaya Z, Buss S, Autschbach F, Pleger ST, Lukic IK,
et al: High-mobility group box-1 in ischemia-reperfusion injury of
the heart. Circulation. 117:3216–3226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abeyama K, Stern DM, Ito Y, Kawahara K,
Yoshimoto Y, Tanaka M, Uchimura T, Ida N, Yamazaki Y, Yamada S, et
al: The N-terminal domain of thrombomodulin sequesters
high-mobility group-B1 protein, a novel antiinflammatory mechanism.
J Clin Invest. 115:1267–1274. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsung A, Klune JR, Zhang X, Jeyabalan G,
Cao Z, Peng X, Stolz DB, Geller DA, Rosengart MR and Billiar TR:
HMGB1 release induced by liver ischemia involves Toll-like receptor
4 dependent reactive oxygen species production and calcium-mediated
signaling. J Exp Med. 204:2913–2923. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rauvala H and Rouhiainen A: Physiological
and pathophysiological outcomes of the interactions of HMGB1 with
cell surface receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:164–170. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Yan SF and Stern DM:
The multiligand receptor RAGE as a progression factor amplifying
immune and inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest. 108:949–955.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ito T, Kawahara K, Okamoto K, Yamada S,
Yasuda M, Imaizumi H, Nawa Y, Meng X, Shrestha B, Hashiguchi T and
Maruyama I: Proteolytic cleavage of high mobility group box 1
protein by thrombin-thrombomodulin complexes. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 28:1825–1830. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang H, Meng Z, Zhang C, Zhang P and Wang
Q: Establishing a new rat model of central venous sinus thrombosis
and analyzing its pathophysiological and apoptotic changes. J
Neurosci Methods. 203:130–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|