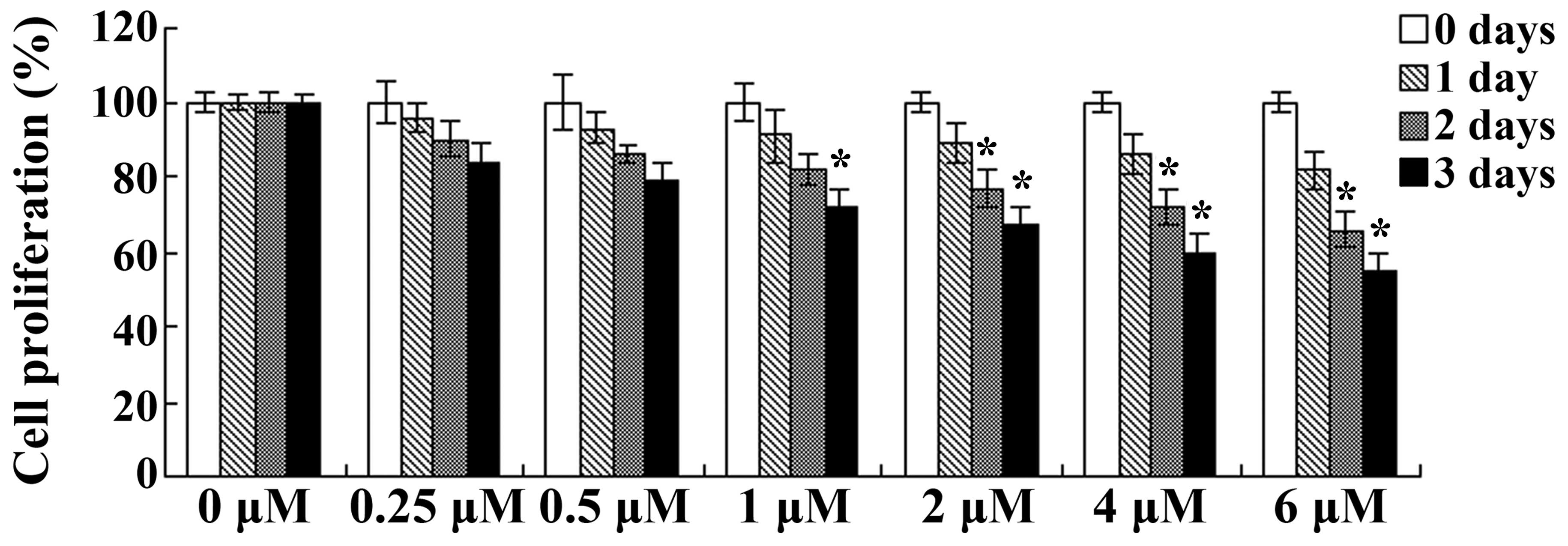
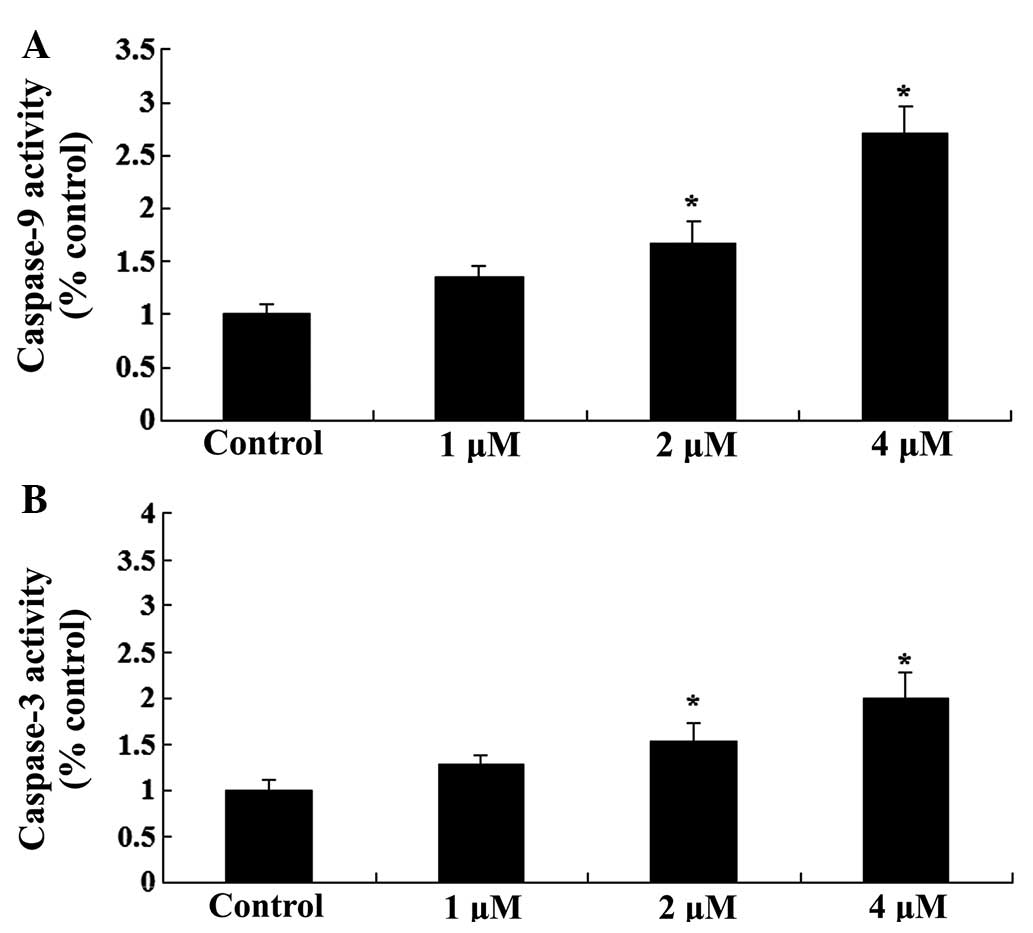
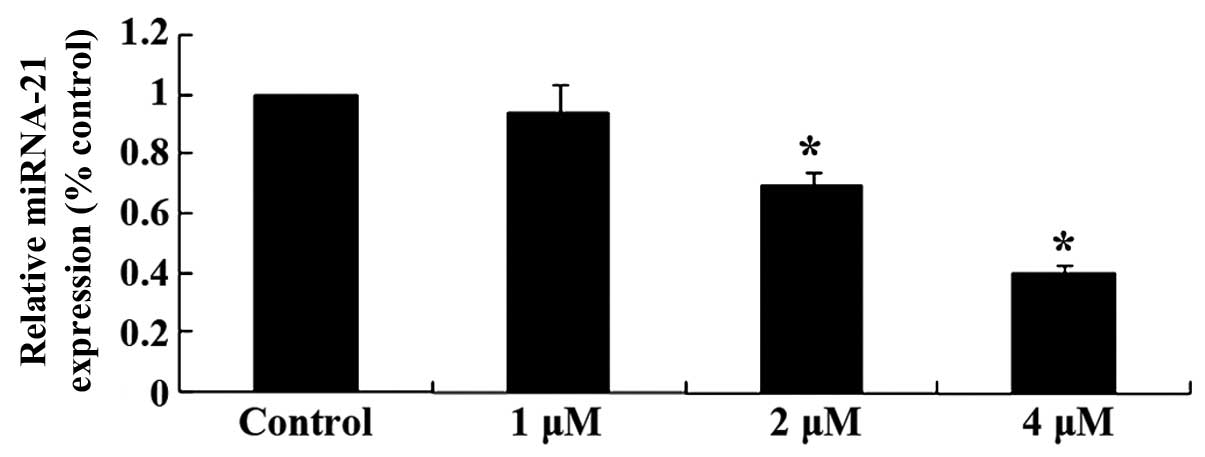
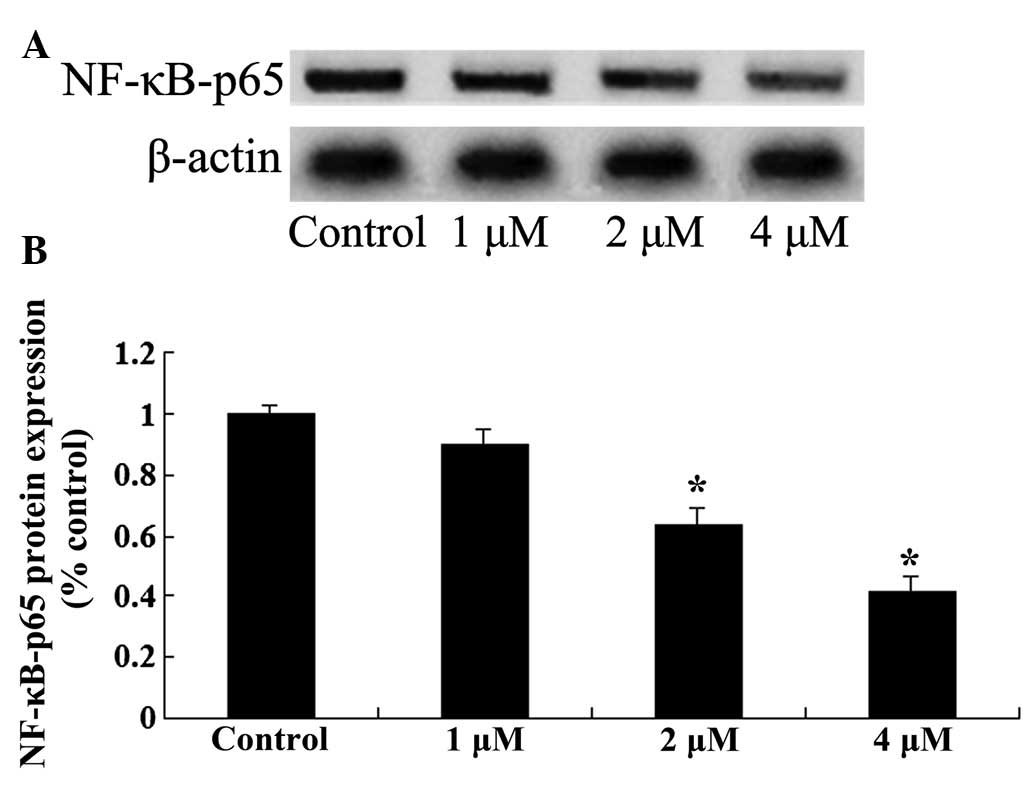
|
1
|
Ren Y, Huang X, Shan B, Wu X, Huang X, Shi
D and Wang H: Adjuvant concurrent chemoradiation followed by
chemotherapy for high-risk endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
140:58–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bao LJ, Jaramillo MC, Zhang ZB, Zheng YX,
Yao M, Zhang DD and Yi XF: Nrf2 induces cisplatin resistance
through activation of autophagy in ovarian carcinoma. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:1502–1513. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krtolica A, Krucher NA and Ludlow JW:
Molecular analysis of selected cell cycle regulatory proteins
during aerobic and hypoxic maintenance of human ovarian carcinoma
cells. Br J Cancer. 80:1875–1883. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li X, Abdel-Mageed AB, Mondal D and Kandil
E: MicroRNA expression profiles in differentiated thyroid cancer, a
review. Int J Clin Exp Med. 6:74–80. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kumarswamy R, Volkmann I and Thum T:
Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease. RNA
Biol. 8:706–713. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bonci D: MicroRNA-21 as therapeutic target
in cancer and cardiovascular disease. Recent Patents Cardiovasc
Drug Discov. 5:156–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Lin B, Hao Y, Qi Y, Zhu L, Li F,
Liu D, Cong J, Zhang S and Iwamori M: Lewis y antigen promotes the
proliferation of ovarian carcinoma-derived RMG-I cells through the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:1542009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zi D, Zhou ZW, Yang YJ, Huang L, Zhou ZL,
He SM, He ZX and Zhou SF: Danusertib induces apoptosis, cell cycle
arrest, and autophagy but inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal
transition involving PI3k/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human
ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 16:27228–27251. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chou CH, Wei LH, Kuo ML, Huang YJ, Lai KP,
Chen CA and Hsieh CY: Up-regulation of interleukin-6 in human
ovarian cancer cell via a Gi/PI3K-Akt/NF-kappaB pathway by
lysophosphatidic acid, an ovarian cancer-activating factor.
Carcinogenesis. 26:45–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Astry B, Venkatesha SH, Laurence A,
Christensen-Quick A, Garzino-Demo A, Frieman MB, O'Shea JJ and
Moudgil KD: Celastrol, a Chinese herbal compound, controls
autoimmune inflammation by altering the balance of pathogenic and
regulatory T cells in the target organ. Clin Immunol. 157:228–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kannaiyan R, Shanmugam MK and Sethi G:
Molecular targets of celastrol derived from Thunder of God Vine:
Potential role in the treatment of inflammatory disorders and
cancer. Cancer Lett. 303:9–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo C, Shibata K, Suzuki S, Kajiyama H,
Senga T, Koya Y, Daimon M, Yamashita M and Kikkawa F: GPC3
expression in mouse ovarian cancer induces GPC3-specific T
cell-mediated immune response through M1 macrophages and suppresses
tumor growth. Oncol Rep. 32:913–921. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakanishi T, Aoki D, Watanabe Y, Ando Y,
Tomotsugu N, Sato Y and Saito T: A Phase II clinical trial of
pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and carboplatin in Japanese
patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian, fallopian tube
or primary peritoneal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 45:422–426. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fruscio R, Colombo N, Lissoni AA, Garbi A,
Fossati R, Ieda' N, Torri V and Mangioni C: A phase II randomised
clinical trial comparing cisplatin, paclitaxel and ifosfamide with
cisplatin, paclitaxel and epirubicin in newly diagnosed advanced
epithelial ovarian cancer: Long-term survival analysis. Br J
Cancer. 98:720–727. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee HW, Jang KS, Choi HJ, Jo A, Cheong JH
and Chun KH: Celastrol inhibits gastric cancer growth by induction
of apoptosis and autophagy. BMB Rep. 47:697–702. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sha M, Ye J, Zhang LX, Luan ZY, Chen YB
and Huang JX: Celastrol induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells
by miR-21 inhibiting PI3K/Akt-NF-κB signaling pathway.
Pharmacology. 93:39–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wolfram J, Suri K, Huang Y, Molinaro R,
Borsoi C, Scott B, Boom K, Paolino D, Fresta M, Wang J, et al:
Evaluation of anticancer activity of celastrol liposomes in
prostate cancer cells. J Microencapsul. 31:501–507. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kiga K, Fukuda-Yuzawa Y, Tanabe M, Tsuji
S, Sasakawa C and Fukao T: Comprehensive silencing of
target-sharing microRNAs is a mechanism for SIRT1 overexpression in
cancer. RNA Biol. 11:1347–1354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mezzanzanica D, Canevari S, Cecco LD and
Bagnoli M: miRNA control of apoptotic programs: Focus on ovarian
cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 11:277–286. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Yu H, Ye L, Jin L, Yu M and Lv Y:
Integrated regulatory mechanisms of miRNAs and targeted genes
involved in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:517–529.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang Y, Yang YB, Zhang XH, Yu XL, Wang ZB
and Cheng XC: MicroRNA-21 gene and cancer. Med Oncol. 30:3762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vaksman O, Tropé C, Davidson B and Reich
R: Exosome-derived miRNAs and ovarian carcinoma progression.
Carcinogenesis. 35:2113–2120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Echevarría-Vargas IM, Valiyeva F and
Vivas-Mejía PE: Upregulation of miR-21 in cisplatin resistant
ovarian cancer via JNK-1/c-Jun pathway. PLoS One. 9:e970942014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bommareddy A, Crisamore K, Fillman S,
Brozena S, Steigerwalt J, Landis T, Vanwert AL and Dwivedi C:
Survivin down-regulation by α-santalol is not mediated through
PI3K-AKT pathway in human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
35:5353–5357. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hussain A, Qazi AK, Mupparapu N, Kumar A,
Mintoo MJ, Mahajan G, Sharma PR, Singh SK, Bharate SB, Zargar MA,
et al: A novel PI3K axis selective molecule exhibits potent tumor
inhibition in colorectal carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. Jan
13–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang JH, Nao JF, Zhang M and He P:
20(s)-ginsenoside Rg3 promotes apoptosis in human ovarian cancer
HO-8910 cells through PI3K/Akt and XIAP pathways. Tumour Biol.
35:11985–11994. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang CH, Ou TT, Yang MY, Huang CC and
Wang CJ: Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn leaves extract inhibits the
angiogenesis and metastasis of breast cancer cells by
downregulation connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) mediated
PI3K/AKT/ERK signaling. J Ethnopharmacol. May 10–2016.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ye Y, Tang X, Sun Z and Chen S:
Upregulated WDR26 serves as a scaffold to coordinate PI3K/AKT
pathway-driven breast cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion.
Oncotarget. Feb 17–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee JH, Won YS, Park KH, Lee MK, Tachibana
H, Yamada K and Seo KI: Celastrol inhibits growth and induces
apoptotic cell death in melanoma cells via the activation
ROS-dependent mitochondrial pathway and the suppression of PI3K/AKT
signaling. Apoptosis. 17:1275–1286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai L, Xu S, Chen W, Li Z, Wang X, Tang H
and Lin Y: Blocking NF-κB and Akt by Hsp90 inhibition sensitizes
Smac mimetic compound 3-induced extrinsic apoptosis pathway and
results in synergistic cancer cell death. Apoptosis. 16:45–54.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu T, Liu D, Liu J, Song JT, Gao SL, Li
H, Hu LH and Liu BR: Effect of NF-κB inhibitors on the
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis of the colon cancer cell line HT-29.
Exp Ther Med. 4:716–722. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Youn GS, Kwon DJ, Ju SM, Rhim H, Bae YS,
Choi SY and Park J: Celastrol ameliorates HIV-1 Tat-induced
inflammatory responses via NF-kappaB and AP-1 inhibition and heme
oxygenase-1 induction in astrocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
280:42–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|