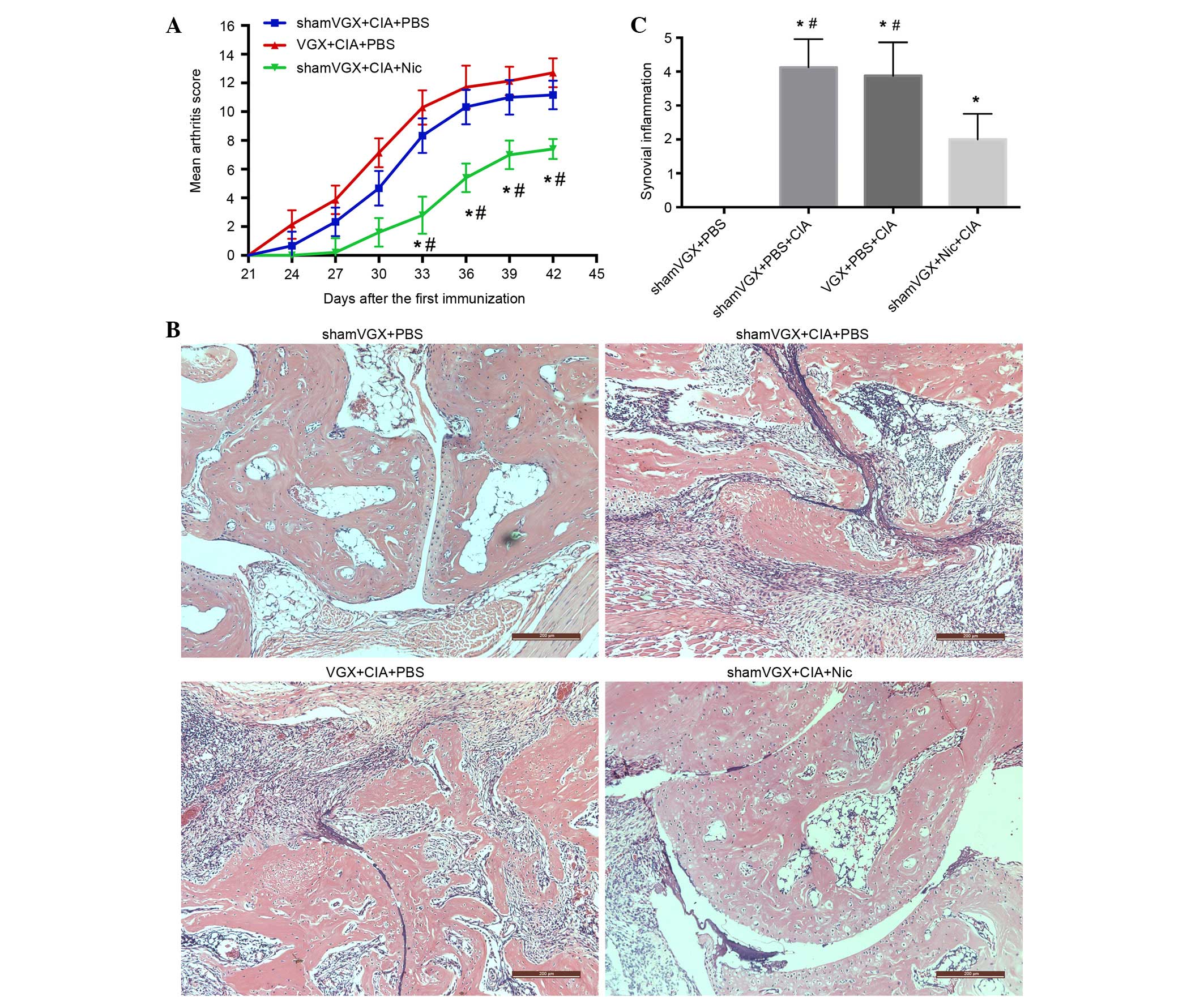
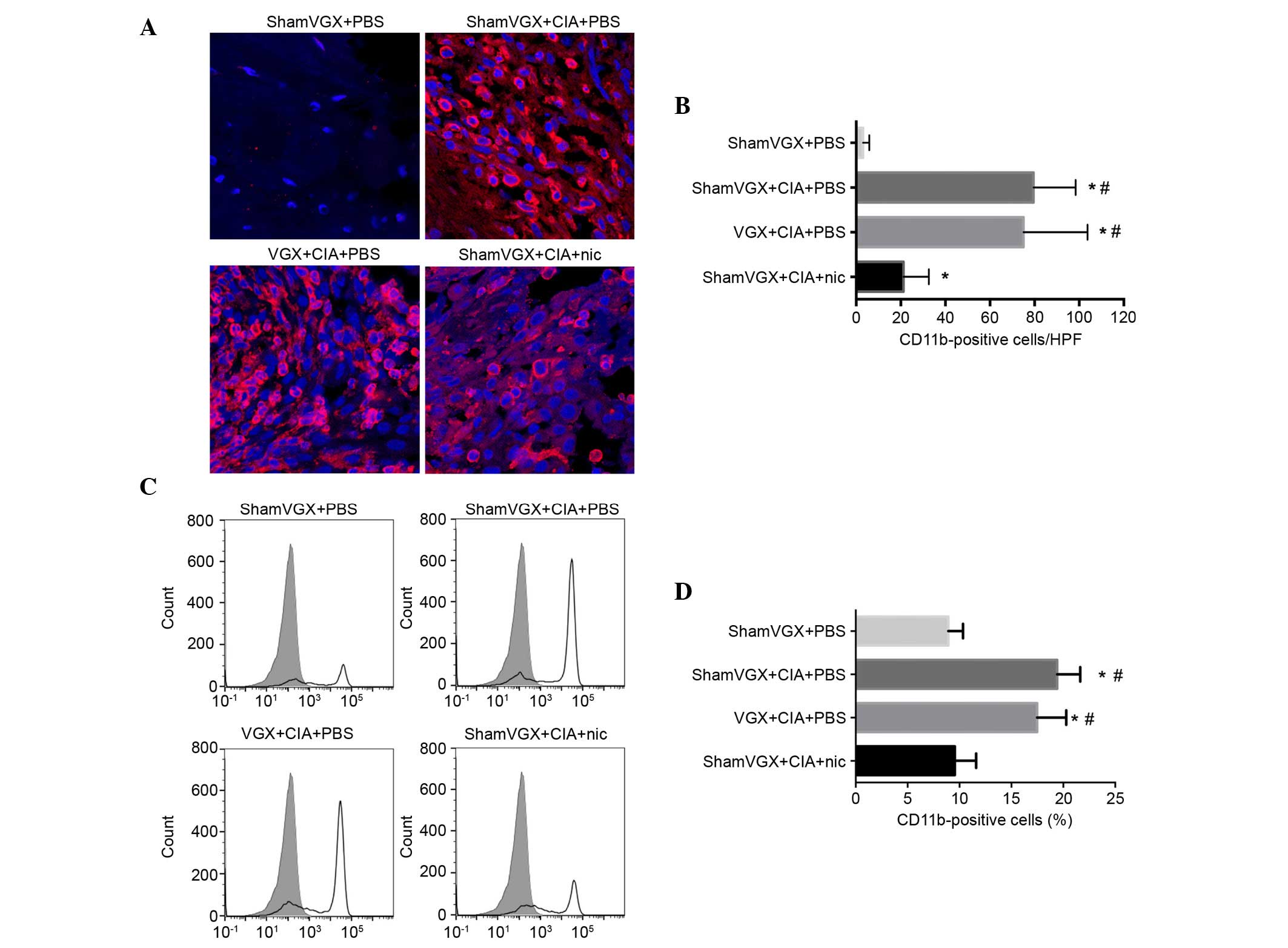
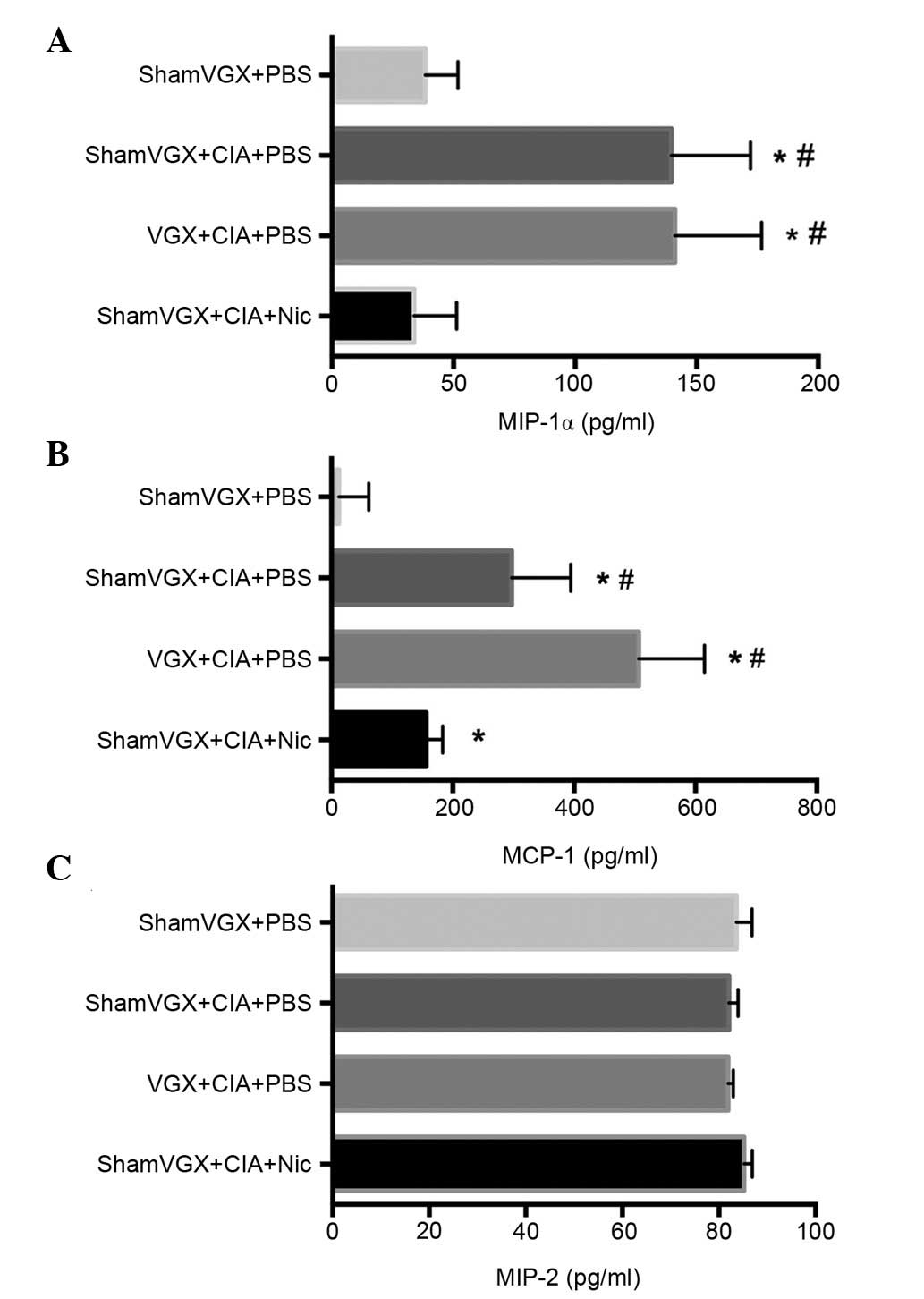
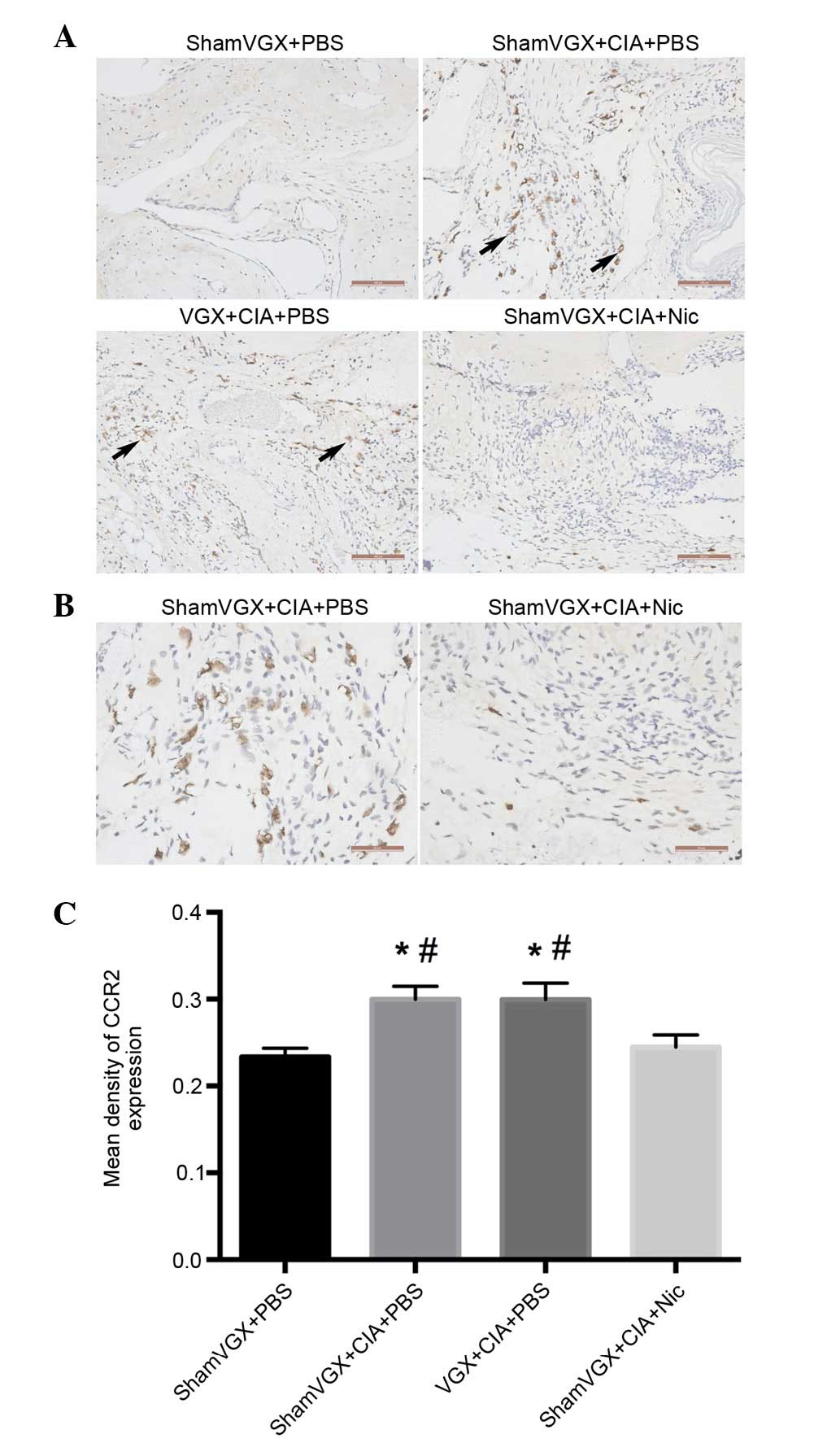
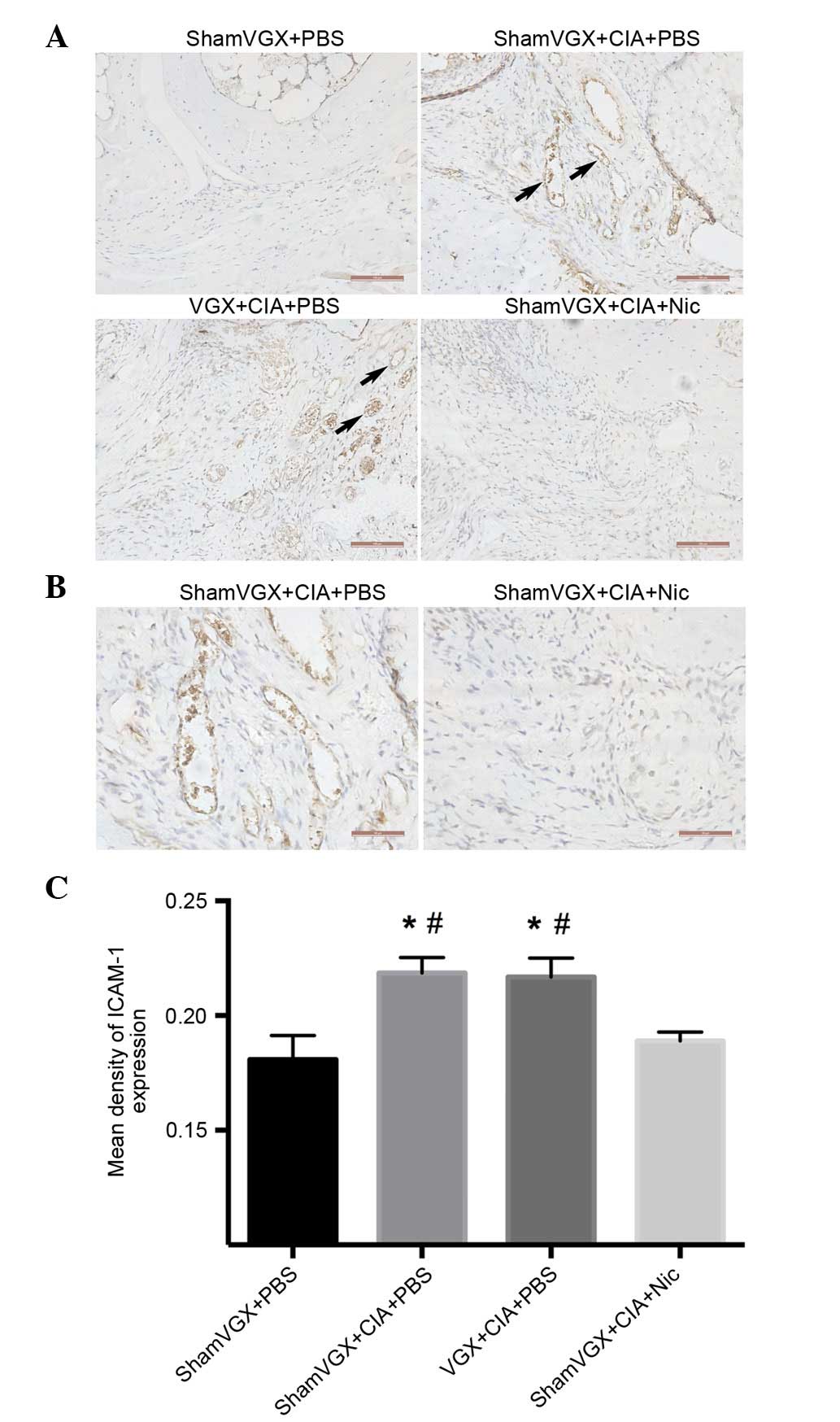
|
1
|
Davignon JL, Hayder M, Baron M, Boyer JF,
Constantin A, Apparailly F, Poupot R and Cantagrel A: Targeting
monocytes/macrophages in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 52:590–598. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kinne RW, Stuhlmüller B and Burmester GR:
Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages.
Arthritis Res Ther. 9:2242007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mulherin D, Fitzgerald O and Bresnihan B:
Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 39:115–124. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tak PP and Bresnihan B: The pathogenesis
and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: Advances
from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum.
43:2619–2633. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Richards PJ, Williams AS, Goodfellow RM
and Williams BD: Liposomal clodronate eliminates synovial
macrophages, reduces inflammation and ameliorates joint destruction
in antigen-induced arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 38:818–825.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Haringman JJ, Smeets TJ, Reinders-Blankert
P and Tak PP: Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in paired
peripheral blood mononuclear cells and synovial tissue of patients
with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and reactive arthritis.
Ann Rheum Dis. 65:294–300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hayashida K, Nanki T, Girschick H, Yavuz
S, Ochi T and Lipsky PE: Synovial stromal cells from rheumatoid
arthritis patients attract monocytes by producing MCP-1 and IL-8.
Arthritis Res. 3:118–126. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brühl H, Cihak J, Plachý J, Kunz-Schughart
L, Niedermeier M, Denzel A, Gomez M Rodriguez, Talke Y, Luckow B,
Stangassinger M and Mack M: Targeting of Gr-1+,
CCR2+ monocytes in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis
Rheum. 56:2975–2985. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H,
Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW and Tracey
KJ: Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory
response to endotoxin. Nature. 405:458–462. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boland C, Collet V, Laterre E, Lecuivre C,
Wittebole X and Laterre PF: Electrical vagus nerve stimulation and
nicotine effects in peritonitis-induced acute lung injury in rats.
Inflammation. 34:29–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao M, He X, Bi XY, Yu XJ, Gil Wier W and
Zang WJ: Vagal stimulation triggers peripheral vascular protection
through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in a rat model of
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol. 108:3452013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wilund KR, Rosenblat M, Chung HR, Volkova
N, Kaplan M, Woods JA and Aviram M: Macrophages from alpha 7
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice demonstrate
increased cholesterol accumulation and decreased cellular
paraoxonase expression: A possible link between the nervous system
and atherosclerosis development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
390:148–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosas-Ballina M, Goldstein RS,
Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Yang L, Valdés-Ferrer SI, Patel NB, Chavan S,
Al-Abed Y, Yang H and Tracey KJ: The selective alpha7 agonist
GTS-21 attenuates cytokine production in human whole blood and
human monocytes activated by ligands for TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR9,
and RAGE. Mol Med. 15:195–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li T, Zuo X, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Zhuang H,
Zhang L, Zhang H and Xiao X: The vagus nerve and nicotinic
receptors involve inhibition of HMGB1 release and early
pro-inflammatory cytokines function in collagen-induced arthritis.
J Clin Immunol. 30:213–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu S, Luo H, Xiao X, Zhang H, Li T and Zuo
X: Attenuation of collagen induced arthritis via suppression on
Th17 response by activating cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
with nicotine. Eur J Pharmacol. 735:97–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van Maanen MA, Lebre MC, van der Poll T,
LaRosa GJ, Elbaum D, Vervoordeldonk MJ and Tak PP: Stimulation of
nicotinic acetylcholine receptors attenuates collagen-induced
arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 60:114–122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE and Tak PP: Chemokine
and chemokine receptor blockade in arthritis, a prototype of
immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Neth J Med. 69:356–366.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Katschke KJ Jr, Rottman JB, Ruth JH, Qin
S, Wu L, LaRosa G, Ponath P, Park CC, Pope RM and Koch AE:
Differential expression of chemokine receptors on peripheral blood,
synovial fluid, and synovial tissue monocytes/macrophages in
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 44:1022–1032. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tracey KJ: The inflammatory reflex.
Nature. 420:853–859. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van Maanen MA, Stoof SP, Larosa GJ,
Vervoordeldonk MJ and Tak PP: Role of the cholinergic nervous
system in rheumatoid arthritis: Aggravation of arthritis in
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit gene knockout mice. Ann
Rheum Dis. 69:1717–1723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu S, Zhao H, Luo H, Xiao X, Zhang H, Li T
and Zuo X: GTS-21, an α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist,
modulates Th1 differentiation in CD4+T cells from
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Ther Med. 8:557–562.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haringman JJ, Gerlag DM, Zwinderman AH,
Smeets TJ, Kraan MC, Baeten D, McInnes IB, Bresnihan B and Tak PP:
Synovial tissue macrophages: A sensitive biomarker for response to
treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
64:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abeles AM and Pillinger MH: The role of
the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis: Cartilage
destruction and the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Bull
NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 64:20–24. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kennedy A, Fearon U, Veale DJ and Godson
C: Macrophages in synovial inflammation. Front Immunol. 2:522011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koch AE, Kunkel SL, Harlow LA, Mazarakis
DD, Haines GK, Burdick MD, Pope RM and Strieter RM: Macrophage
inflammatory protein-1 alpha. A novel chemotactic cytokine for
macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 93:921–928.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luther SA and Cyster JG: Chemokines as
regulators of T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2:102–107. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shahrara S, Proudfoot AE, Park CC, Volin
MV, Haines GK, Woods JM, Aikens CH, Handel TM and Pope RM:
Inhibition of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 ameliorates rat
adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 180:3447–3456. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haringman JJ, Ludikhuize J and Tak PP:
Chemokines in joint disease: The key to inflammation? Ann Rheum
Dis. 63:1186–1194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geissmann F, Jung S and Littman DR: Blood
monocytes consist of two principal subsets with distinct migratory
properties. Immunity. 19:71–82. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiménez-Sainz MC, Fast B, Mayor F Jr and
Aragay AM: Signaling pathways for monocyte chemoattractant protein
1-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Mol
Pharmacol. 64:773–782. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brühl H, Cihak J, Schneider MA, Plachý J,
Rupp T, Wenzel I, Shakarami M, Milz S, Ellwart JW, Stangassinger M,
et al: Dual role of CCR2 during initiation and progression of
collagen-induced arthritis: Evidence for regulatory activity of
CCR2+ T cells. J Immunol. 172:890–898. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Haringman JJ, Kraan MC, Smeets TJ,
Zwinderman KH and Tak PP: Chemokine blockade and chronic
inflammatory disease: Proof of concept in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 62:715–721. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amat M, Benjamim CF, Williams LM, Prats N,
Terricabras E, Beleta J, Kunkel SL and Godessart N: Pharmacological
blockade of CCR1 ameliorates murine arthritis and alters cytokine
networks in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 149:666–675. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takahashi HK, Iwagaki H, Hamano R, Yoshino
T, Tanaka N and Nishibori M: Effect of nicotine on IL-18-initiated
immune response in human monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 80:1388–1394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cirillo P, Pacileo M, De Rosa S, Calabrò
P, Gargiulo A, Angri V, Prevete N, Fiorentino I, Ucci G, Sasso L,
et al: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors reduce nicotine-induced
expression of cellular adhesion molecules in cultured human
coronary endothelial cells. J Vasc Res. 44:460–470. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Breen LT, McHugh PE and Murphy BP: HUVEC
ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 synthesis in response to potentially athero-prone
and athero-protective mechanical and nicotine chemical stimuli. Ann
Biomed Eng. 38:1880–1892. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|