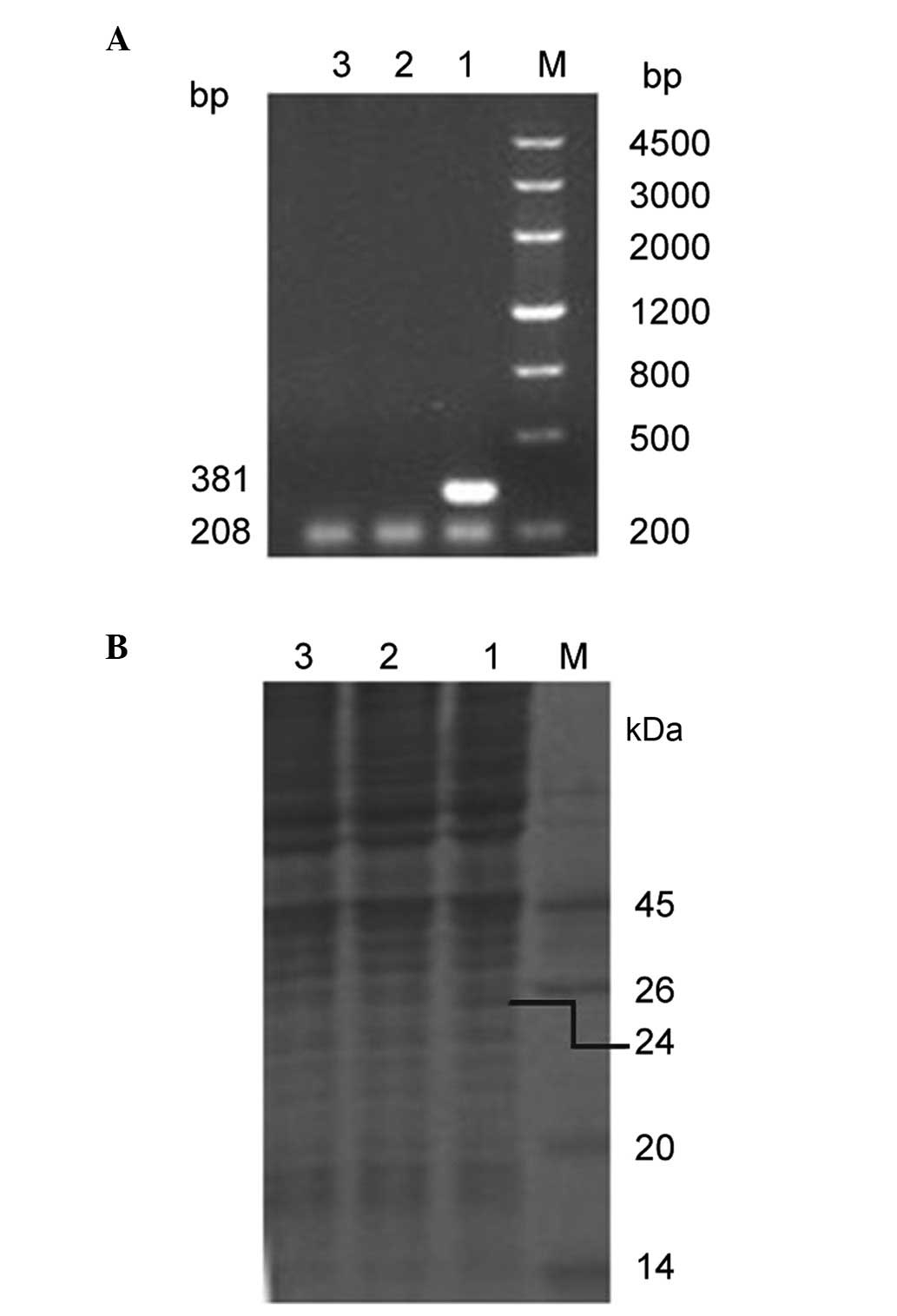
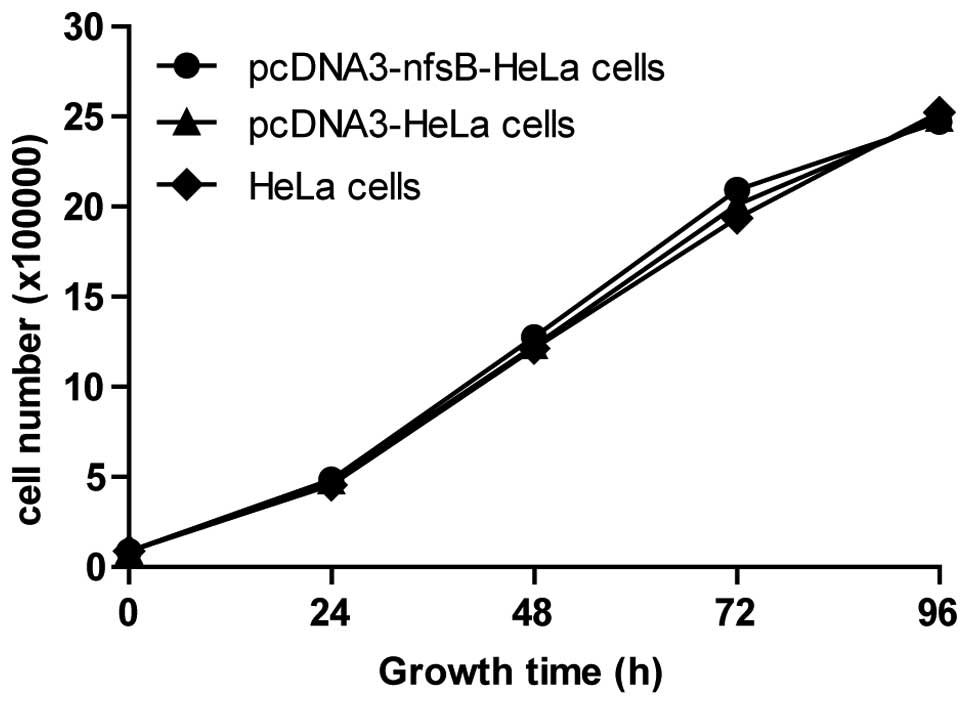
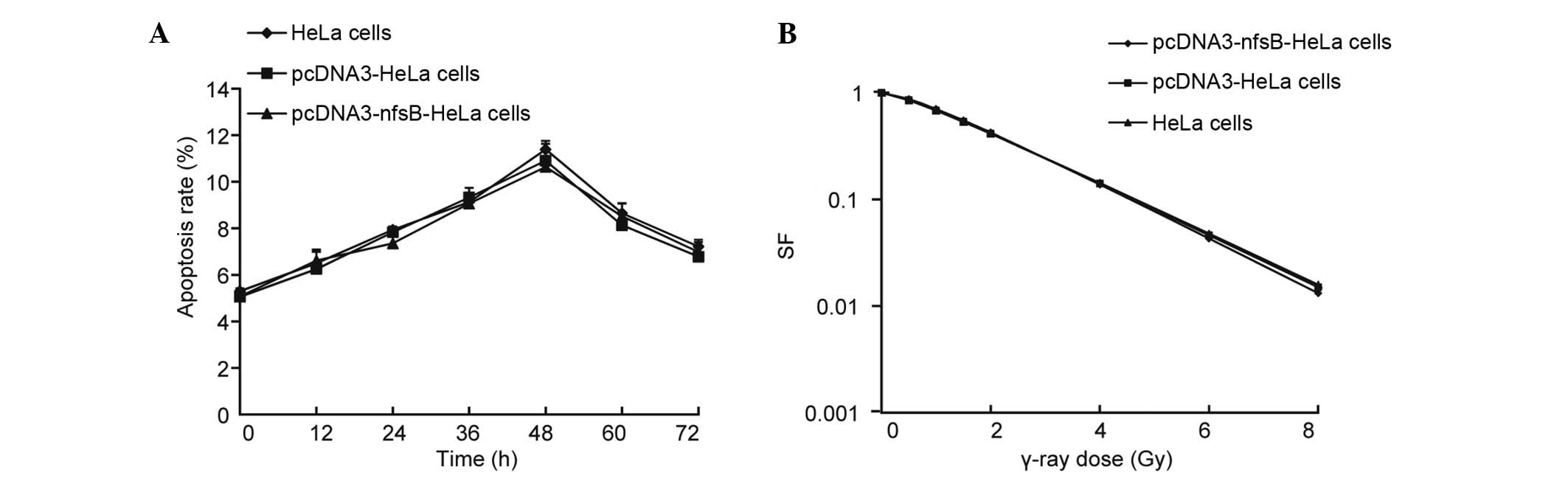
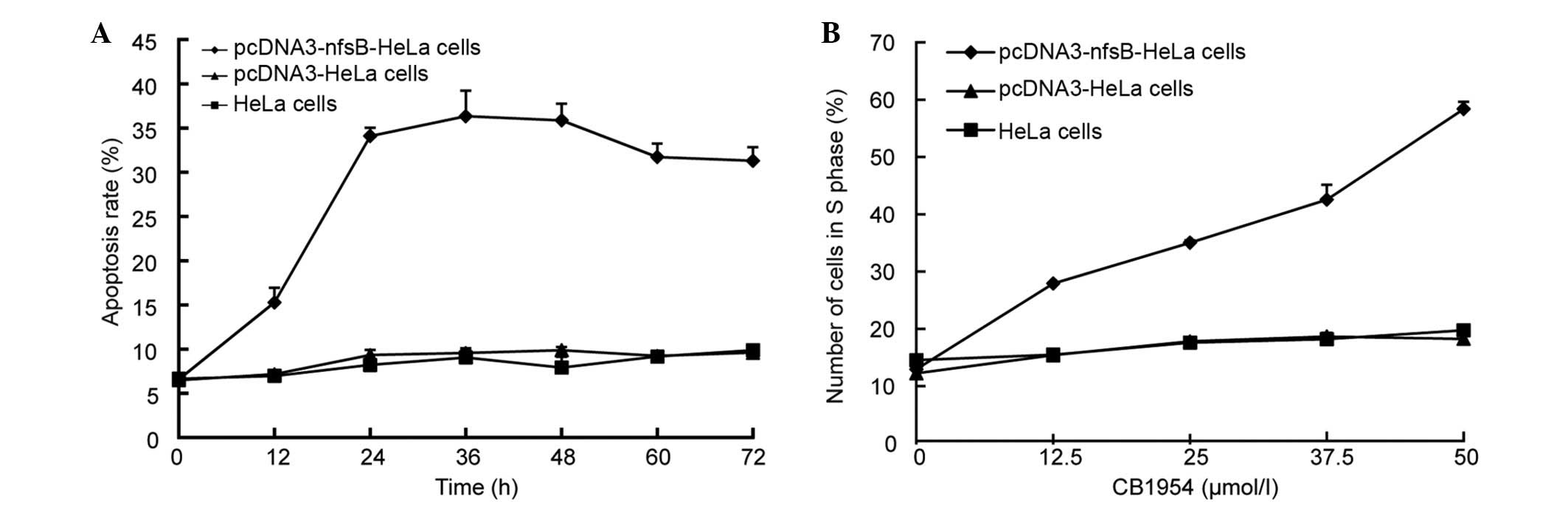
|
1
|
Carruthers KH, Metzger G, During MJ,
Muravlev A, Wang C and Kocak E: Gene-directed enzyme prodrug
therapy for localized chemotherapeutics in allograft and xenograft
tumor models. Cancer Gene Ther. 21:434–440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zawilska JB, Wojcieszak J and Olejniczak
AB: Prodrugs: A challenge for the drug development. Pharmacol Rep.
65:1–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Both GW: Gene-directed enzyme prodrug
therapy for cancer: A glimpse into the future? Discov Med.
8:97–103. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang Q, Liu XZ, Kang CS, Wang GX, Zhong Y
and Pu PY: The anti-glioma effect of suicide gene therapy using
BMSC expressing HSV/TK combined with overexpression of Cx43 in
glioma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:192–202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takahashi M, Valdes G, Hiraoka K, Inagaki
A, Kamijima S, Micewicz E, Gruber HE, Robbins JM, Jolly DJ, McBride
WH, et al: Radiosensitization of gliomas by intracellular
generation of 5-fluorouracil potentiates prodrug activator gene
therapy with a retroviral replicating vector. Cancer Gene Ther.
21:405–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wester HJ: Nuclear imaging probes: From
bench to bedside. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3470–3481. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patel P, Young JG, Mautner V, Ashdown D,
Bonney S, Pineda RG, Collins SI, Searle PF, Hull D, Peers E, et al:
A phase I/II clinical trial in localized prostate cancer of an
adenovirus expressing nitroreductase with CB1954 [correction of
CB1984]. Mol Ther. 17:1292–1299. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bhaumik S, Sekar TV, Depuy J, Klimash J
and Paulmurugan R: Noninvasive optical imaging of nitroreductase
gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy system in living animals. Gene
Ther. 19:295–302. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dachs GU, Hunt MA, Syddall S, Singleton DC
and Patterson AV: Bystander or no bystander for gene directed
enzyme prodrug therapy. Molecules. 14:4517–4545. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Palmer DH, Milner AE, Kerr DJ and Young
LS: Mechanism of cell death induced by the novel enzyme-prodrug
combination, nitroreductase/CB1954, and identification of synergism
with 5-fluorouracil. Br J Cancer. 89:944–950. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anlezark GM, Vaughan T, Fashola-Stone E,
Michael NP, Murdoch H, Sims MA, Stubbs S, Wigley S and Minton NP:
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens orthologue of Bacillus subtilis ywrO
encodes a nitroreductase enzyme which activates the prodrug CB
1954. Microbiology. 148:297–306. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qin C, Chen X, Bai Q, Davis MR and Fang Y:
Factors associated with radiosensitivity of cervical cancer.
Anticancer Res. 34:4649–4656. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harrington KJ and Nutting CM: Interactions
between ionizing radiation and drugs in head and neck cancer: How
can we maximize the therapeutic index? Curr Opin Investig Drugs.
3:807–811. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qu L, Wang Y, Gong L, Zhu J, Gong R and Si
J: Suicide gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
survivin promoter-driven expression of the herpes simplex virus
thymidine kinase gene. Oncol Rep. 29:1435–1440. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiong T, Li Y, Ni F and Zhang F:
Monitoring of bystander effect of herpes simplex virus thymidine
kinase/acyclovir system using fluorescence resonance energy
transfer technique. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 8:74–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alerie K, Brust D, Farnsworth J, Amir C,
Taher MM, Hershey C and Feden J: Improved radiosensitization of rat
glioma cells with adenovirus-expressed mutant herpes simplex
virus-thymidine kinase in combination with acyclovir. Cancer Gene
Ther. 7:879–884. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anello R, Cohen S, Atkinson G and Hall SJ:
Adenovirus mediated cytosine deaminase gene transduction and
5-fluorocytosine therapy sensitises mouse prostate cancer cells to
irradiation. J Urol. 164:2173–2177. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
White CL, Menghistu T, Twigger KR, Searle
PF, Bhide SA, Vile RG, Melcher AA, Pandha HS and Harrington KJ:
Escherichia coli nitroreductase plus CB1954 enhances the effect of
radiotherapy in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther. 15:424–433. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cobb LM, Connors TA, Elson LA, Khan AH,
Mitchley BC, Ross WC and Whisson ME:
2,4-Dinitro-5-ethyleneiminobenzamide (CB 1954): A potent and
selective inhibitor of growth of the Walker carcinoma 256. Biochem
Pharmacol. 18:1519–1527. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chung-Faye G, Palmer D, Anderson D, Clark
J, Downes M, Baddeley J, Hussain S, Murray PI, Searle P, Seymour L,
et al: Virus-directed, enzyme prodrug therapy with nitroimidazole
reductase: A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of its prodrug,
CB1954. Clin Cancer Res. 7:2662–2668. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sekar TV, Foygel K, Ilovich O and
Paulmurugan R: Noninvasive theranostic imaging of
HSV1-sr39TK-NTR/GCV-CB1954 dual-prodrug therapy in metastatic lung
lesions of MDA-MB-231 triple negative breast cancer in mice.
Theranostics. 4:460–474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|