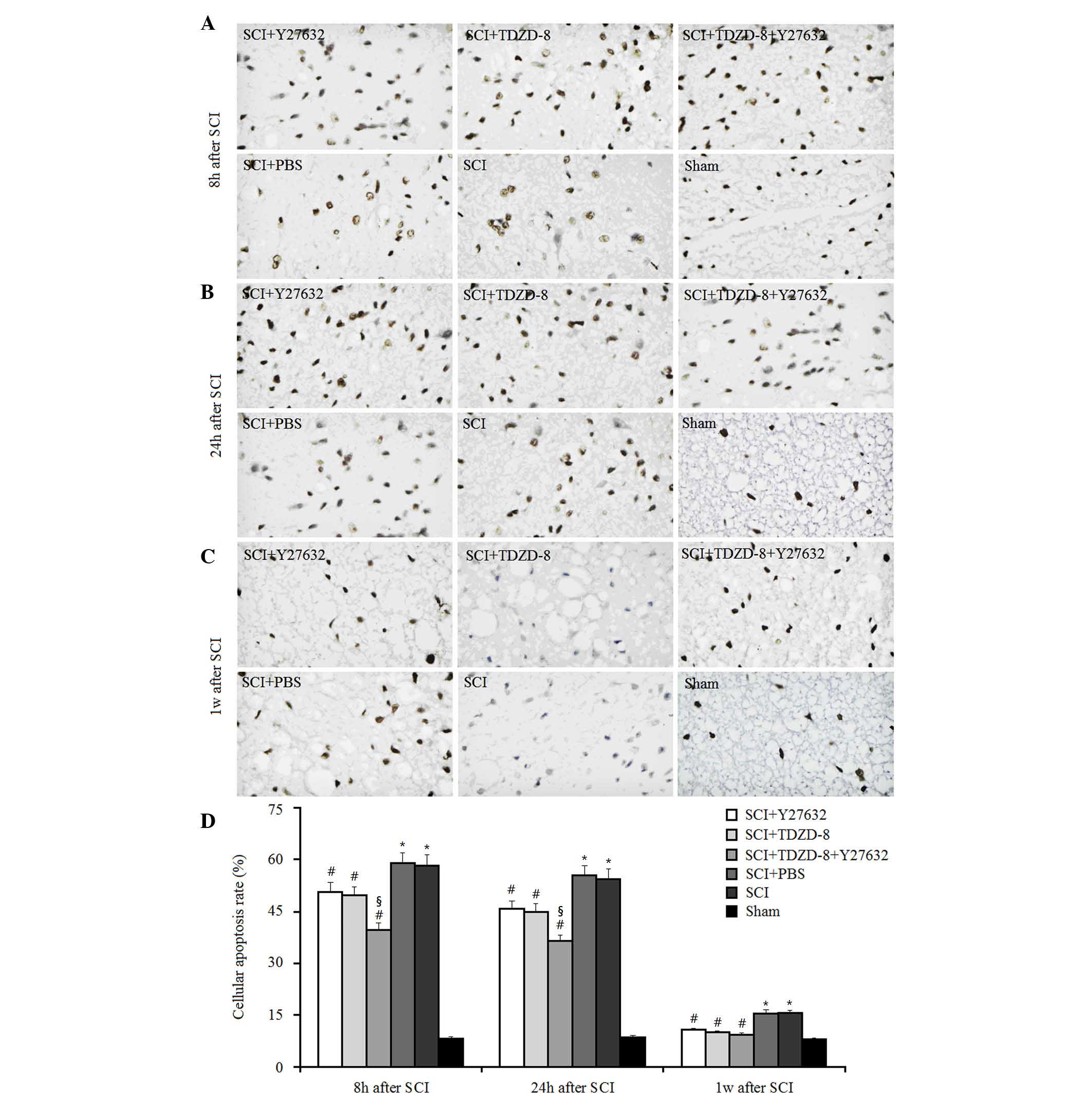
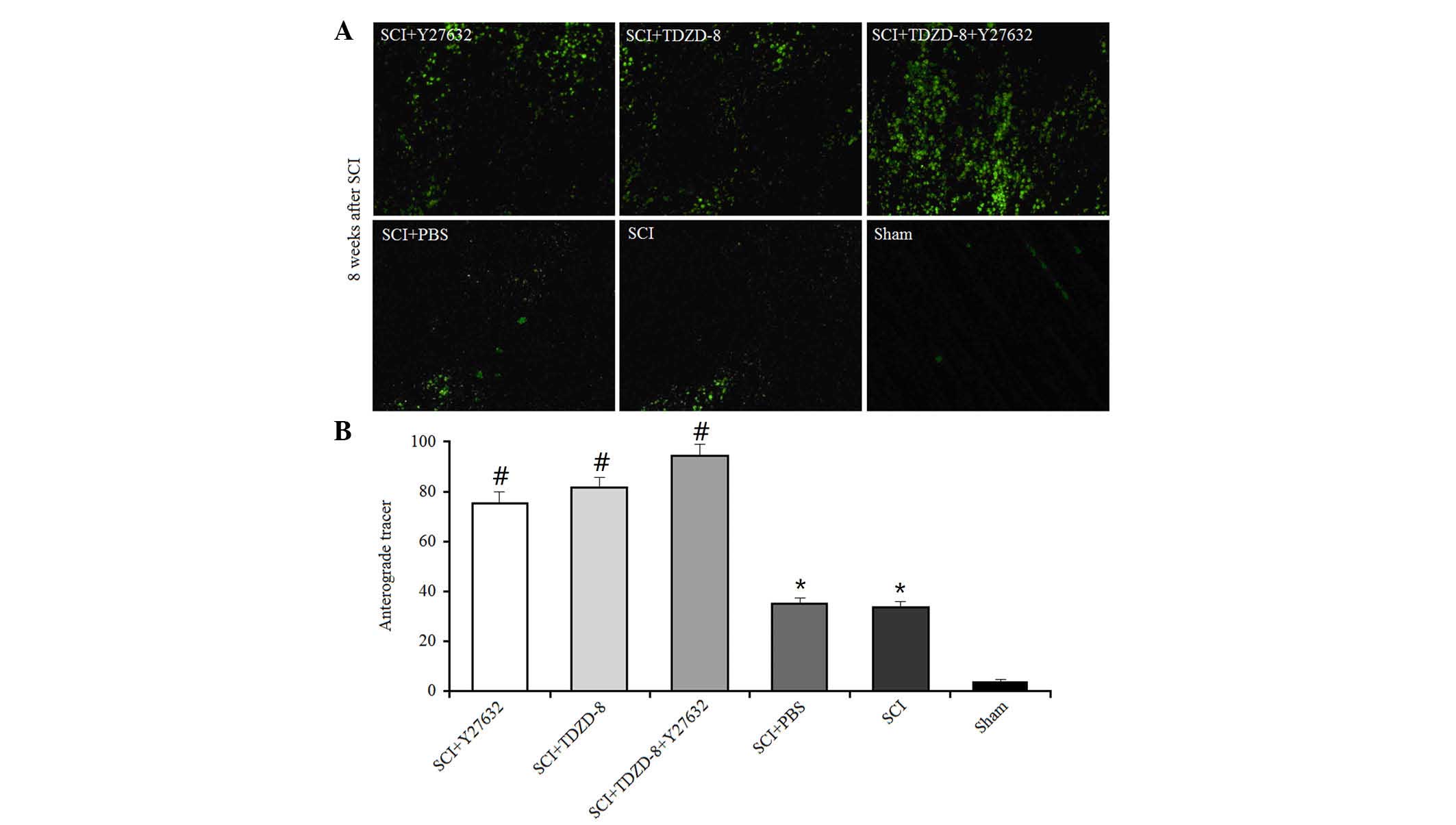
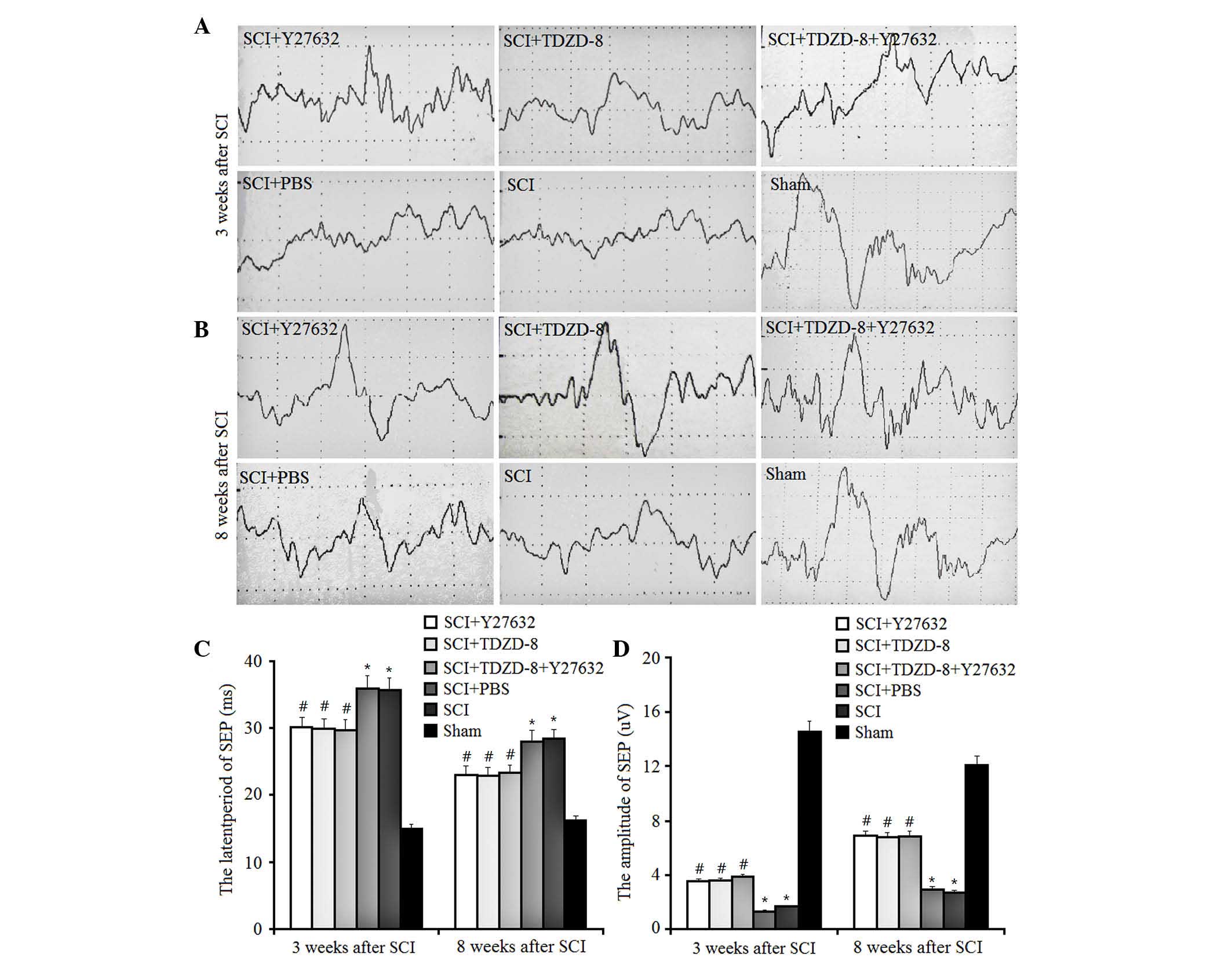
|
1
|
Horner PJ and Gage FH: Regenerating the
damaged central nervous system. Nature. 407:963–970. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen MS, Huber AB, van der Haar ME, Frank
M, Schnell L, Spillmann AA, Christ F and Schwab ME: Nogo-A is a
myelin-associated neurite outgrowth inhibitor and an antigen for
monoclonal antibody IN-1. Nature. 403:434–439. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Domeniconi M, Cao Z, Spencer T,
Sivasankaran R, Wang K, Nikulina E, Kimura N, Cai H, Deng K, Gao Y,
et al: Myelin-associated glycoprotein interacts with the Nogo66
receptor to inhibit neurite outgrowth. Neuron. 35:283–290. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang KC, Koprivica V, Kim JA, Sivasankaran
R, Guo Y, Neve RL and He Z: Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is
a nogo receptor ligand that inhibits neurite outgrowth. Nature.
417:941–944. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Madura T, Yamashita T, Kubo T, Fujitani M,
Hosokawa K and Tohyama M: Activation of Rho in the injured axons
following spinal cord injury. EMBO Rep. 5:412–417. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alabed YZ, Pool M, Ong Tone S, Sutherland
C and Fournier AE: GSK3 beta regulates myelin-dependent axon
outgrowth inhibition through CRMP4. J Neurosci. 30:5635–5643. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmandke A and Strittmatter SM and
Strittmatter SM: ROCK and Rho: Biochemistry and neuronal functions
of Rho-associated protein kinases. Neuroscientist. 13:454–469.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fournier AE, Takizawa BT and Strittmatter
SM: Rho kinase inhibition enhances axonal regeneration in the
injured CNS. J Neurosci. 23:1416–1423. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shao Z, Browning JL, Lee X, Scott ML,
Shulga-Morskaya S, Allaire N, Thill G, Levesque M, Sah D, McCoy JM,
et al: TAJ/TROY, an orphan TNF receptor family member, binds
Nogo-66 receptor 1 and regulates axonal regeneration. Neuron.
45:353–359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arimura N, Inagaki N, Chihara K, Ménager
C, Nakamura N, Amano M, Iwamatsu A, Goshima Y and Kaibuchi K:
Phosphorylation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 by
Rho-kinase. evidence for two separate signaling pathways for growth
cone collapse. J Biol Chem. 275:23973–23980. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoshimura T, Kawano Y, Arimura N, Kawabata
S, Kikuchi A and Kaibuchi K: GSK-3beta regulates phosphorylation of
CRMP-2 and neuronal polarity. Cell. 120:137–149. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou FQ and Snider WD: Cell biology.
GSK-3beta and microtubule assembly in axons. Science. 308:211–214.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mueller BK, Mack H and Teusch N: Rho
kinase, a promising drug target for neurological disorders. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 4:387–398. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim WY, Zhou FQ, Zhou J, Yokota Y, Wang
YM, Yoshimura T, Kaibuchi K, Woodgett JR, Anton ES and Snider WD:
Essential roles for GSK-3s and GSK-3-primed substrates in
neurotrophin-induced and hippocampal axon growth. Neuron.
52:981–996. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lingor P, Teusch N, Schwarz K, Mueller R,
Mack H, Bähr M and Mueller BK: Inhibition of Rho kinase (ROCK)
increases neurite outgrowth on chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan in
vitro and axonal regeneration in the adult optic nerve in vivo. J
Neurochem. 103:181–189. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chan CC, Khodarahmi K, Liu J, Sutherland
D, Oschipok LW, Steeves JD and Tetzlaff W: Dose-dependent
beneficial and detrimental effects of ROCK inhibitor Y27632 on
axonal sprouting and functional recovery after rat spinal cord
injury. Exp Neurol. 196:352–364. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cuzzocrea S, Genovese T, Mazzon E,
Crisafulli C, Di Paola R, Muià C, Collin M, Esposito E, Bramanti P
and Thiemermann C: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibition
reduces secondary damage in experimental spinal cord trauma. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 318:79–89. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kawasaki T, Nishio T, Kawaguchi S and
Kurosawa H: Spatiotemporal distribution of GAP-43 in the developing
rat spinal cord: A histological and quantitative immunofluorescence
study. Neurosci Res. 39:347–358. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park DY, Mayle RE, Smith RL,
Corcoran-Schwartz I, Kharazi AI and Cheng I: Combined
transplantation of human neuronal and mesenchymal stem cells
following spinal cord injury. Global Spine J. 3:1–6. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field
testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Caizhong X, Chunlei S, Beibei L, Zhiqing
D, Qinneng D and Tong W: The application of somatosensory evoked
potentials in spinal cord injury rehabilitation.
NeuroRehabilitation. 35:835–840. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim DH and Jahng TA: Continuous
brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) infusion after
methylprednisolone treatment in severe spinal cord injury. J Korean
Med Sci. 19:113–122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kubo T, Hata K, Yamaguchi A and Yamashita
T: Rho-ROCK inhibitors as emerging strategies to promote nerve
regeneration. Curr Pharm Des. 13:2493–2499. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jeon BT, Jeong EA, Park SY, Son H, Shin
HJ, Lee DH, Kim HJ, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Choi WS and Roh GS: The
Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y-27632 protects against
excitotoxicity-induced neuronal death in vivo and in vitro.
Neurotox Res. 23:238–248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fournier AE and Strittmatter SM: Repulsive
factors and axon regeneration in the CNS. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
11:89–94. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu BP, Fournier A, GrandPre T and
Strittmatter SM: Myelin-associated glycoprotein as a functional
ligand for the Nogo-66 receptor. Science. 297:1190–1193. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Buchsbaum RJ: Rho activation at a glance.
J Cell Sci. 120:1149–1152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Joshi AR, Bobylev I, Zhang G, Sheikh KA
and Lehmann HC: Inhibition of Rho-kinase differentially affects
axon regeneration of peripheral motor and sensory nerves. Exp
Neurol. 263:28–38. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dill J, Wang H, Zhou F and Li S:
Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 promotes axonal growth
and recovery in the CNS. J Neurosci. 28:8914–8928. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gopalakrishnan SM, Teusch N, Imhof C,
Bakker MH, Schurdak M, Burns DJ and Warrior U: Role of Rho kinase
pathway in chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan-mediated inhibition of
neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res. 86:2214–2226.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dubreuil CI, Winton MJ and McKerracher L:
Rho activation patterns after spinal cord injury and the role of
activated Rho in apoptosis in the central nervous system. J Cell
Biol. 162:233–243. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Collino M, Thiemermann C, Mastrocola R,
Gallicchio M, Benetti E, Miglio G, Castiglia S, Danni O, Murch O,
et al: Treatment with the glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibitor,
TDZD-8, affects transient cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in
the rat hippocampus. Shock. 30:299–307. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|