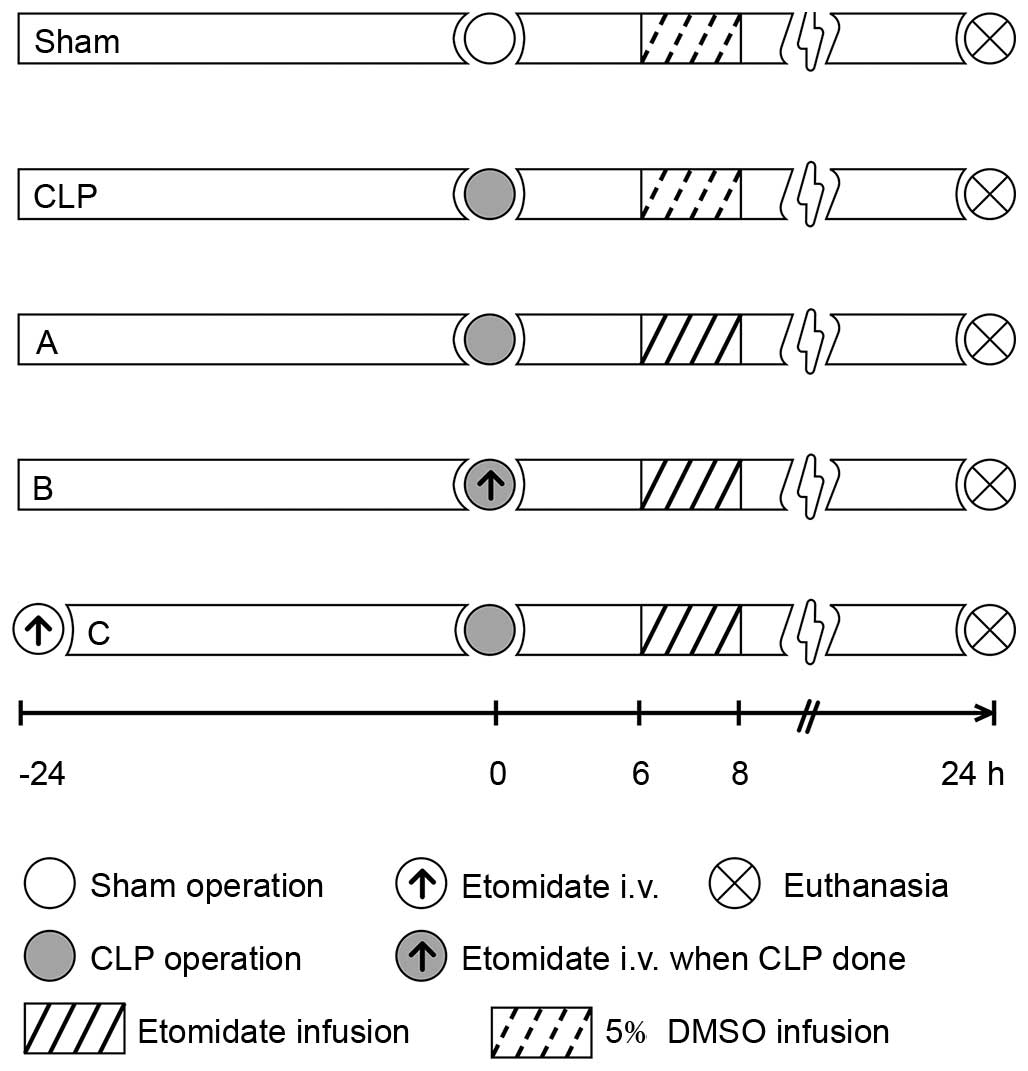
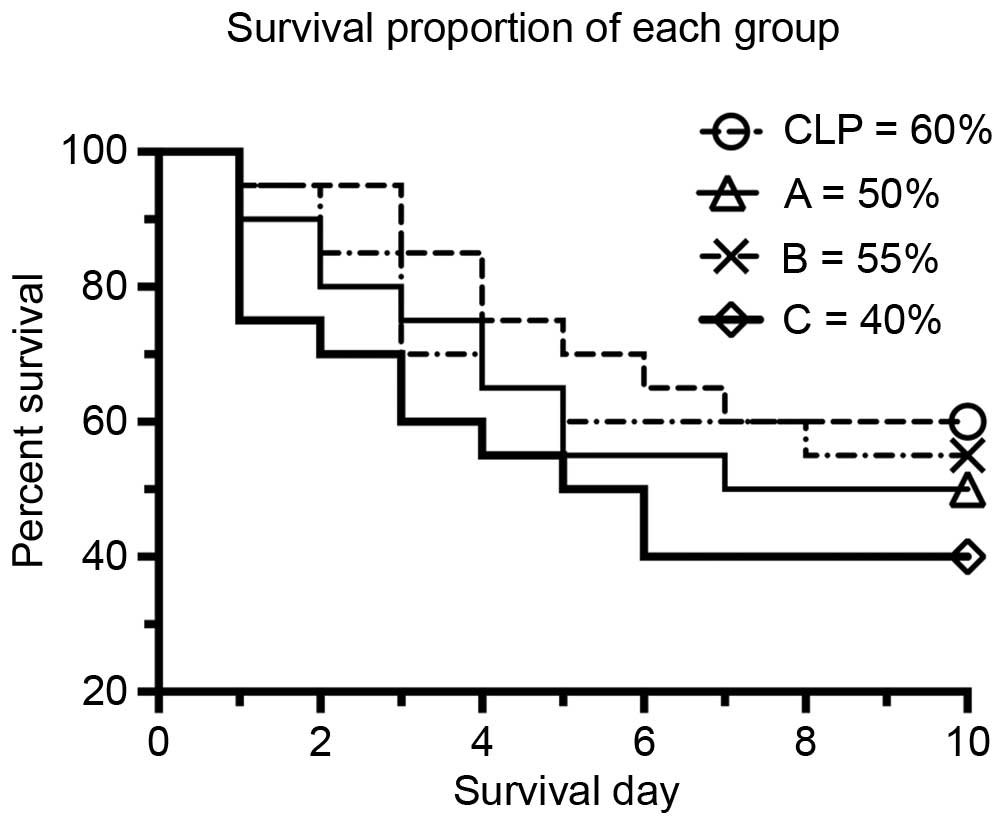
|
1
|
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D,
Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke
R, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for
management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med.
41:580–637. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forman SA: Clinical and molecular
pharmacology of etomidate. Anesthesiology. 114:695–707. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heinrich S, Schmidt J, Ackermann A, Moritz
A, Harig F and Castellanos I: Comparison of clinical outcome
variables in patients with and without etomidate-facilitated
anesthesia induction ahead of major cardiac surgery: A
retrospective analysis. Crit Care. 18:R1502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sunshine J, Deem S, Weiss N, Yanez ND,
Daniel S, Keech K, Brown M and Treggiari MM: Etomidate, adrenal
function, and mortality in critically ill patients. Respir Care.
58:639–646. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan CM, Mitchell AL and Shorr AF:
Etomidate is associated with mortality and adrenal insufficiency in
sepsis: A meta-analysis*. Crit Care Med. 40:2945–2953. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Li R, Zhu J, Wang Z, Lv S and
Xiong JY: Etomidate increases mortality in septic rats through
inhibition of nuclear factor kappa-B rather than by causing adrenal
insufficiency. J Surg Res. 193:399–406. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hughey CC, Hittel DS, Johnsen VL and
Shearer J: Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp in the conscious rat.
J Vis Exp. 24322011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
De Maio A, Torres MB and Reeves RH:
Genetic determinants influencing the response to injury,
inflammation, and sepsis. Shock. 23:11–17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dejager L, Pinheiro I, Dejonckheere E and
Libert C: Cecal ligation and puncture: The gold standard model for
polymicrobial sepsis? Trends Microbiol. 19:198–208. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng M, Ye JS, Wang Y-L, Chen C and Wang
CY: Posttreatment with propofol attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced up-regulation of inflammatory molecules
in primary microglia. Inflamm Res. 63:411–418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu Y, Liu Y, Huang H, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Lu F
and Zhou C, Huang L, Li X and Zhou C: Dexmedetomidine inhibits
inflammatory reaction in lung tissues of septic rats by suppressing
TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:5621542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim SN, Son SC, Lee SM, Kim CS, Yoo DG,
Lee SK, Hur GM, Park JB and Jeon BH: Midazolam inhibits
proinflammatory mediators in the lipopolysaccharide-activated
macrophage. Anesthesiology. 105:105–110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marketon JI and Sternberg EM: The
glucocorticoid receptor: A revisited target for toxins. Toxins
(Basel). 2:1357–1380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kulstad EB, Kalimullah EA, Tekwani KL and
Courtney DM: Etomidate as an induction agent in septic patients:
red flags or false alarms? West J Emerg Med. 11:161–172.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fragen RJ, Shanks CA, Molteni A and Avram
MJ: Effects of etomidate on hormonal responses to surgical stress.
Anesthesiology. 61:652–656. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wanscher M, Tønnesen E, Hüttel M and
Larsen K: Etomidate infusion and adrenocortical function. A study
in elective surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 29:483–485. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ayroldi E, Cannarile L, Migliorati G,
Nocentini G, Delfino DV and Riccardi C: Mechanisms of the
anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids: Genomic and
nongenomic interference with MAPK signaling pathways. FASEB J.
26:4805–4820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vandevyver S, Dejager L and Libert C: On
the trail of the glucocorticoid receptor: Into the nucleus and
back. Traffic. 13:364–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ayroldi E, Macchiarulo A and Riccardi C:
Targeting glucocorticoid side effects: Selective glucocorticoid
receptor modulator or glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper? A
perspective. FASEB J. 28:5055–5070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ling J and Kumar R: Crosstalk between NFkB
and glucocorticoid signaling: A potential target of breast cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 322:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg
A and Karin M: Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: Inhibition of
NF-kappaB activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis.
Science. 270:286–290. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abraham E, Laterre PF, Garbino J,
Pingleton S, Butler T, Dugernier T, Margolis B, Kudsk K, Zimmerli
W, Anderson P, et al: Lenercept (p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor
fusion protein) in severe sepsis and early septic shock: A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter phase III
trial with 1,342 patients. Crit Care Med. 29:503–510. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weber SU, Schewe JC, Lehmann LE, Müller S,
Book M, Klaschik S, Hoeft A and Stüber F: Induction of Bim and Bid
gene expression during accelerated apoptosis in severe sepsis. Crit
Care. 12:R1282008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Muenzer JT, Davis CG, Chang K, Schmidt RE,
Dunne WM, Coopersmith CM and Hotchkiss RS: Characterization and
modulation of the immunosuppressive phase of sepsis. Infect Immun.
78:1582–1592. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Payen JF, Dupuis C, Trouve-Buisson T,
Vinclair M, Broux C, Bouzat P, Genty C, Monneret D, Faure P, Chabre
O and Bosson JL: Corticosteroid after etomidate in critically ill
patients: A randomized controlled trial. Crit Care Med. 40:29–35.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanczkowski W, Alexaki VI, Tran N,
Großklaus S, Zacharowski K, Martinez A, Popovics P, Block NL,
Chavakis T, Schally AV and Bornstein SR: Hypothalamo-pituitary and
immune-dependent adrenal regulation during systemic inflammation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:14801–14806. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sanders RD, Godlee A, Fujimori T, Goulding
J, Xin G, Salek-Ardakani S, Snelgrove RJ, Ma D, Maze M and Hussell
T: Benzodiazepine augmented γ-amino-butyric acid signaling
increases mortality from pneumonia in mice. Crit Care Med.
41:1627–1636. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|