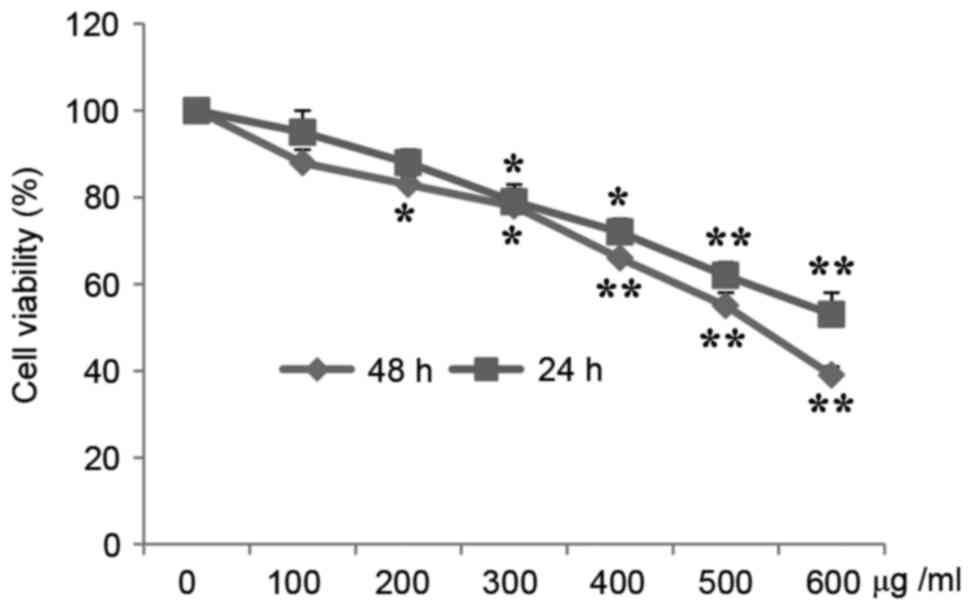
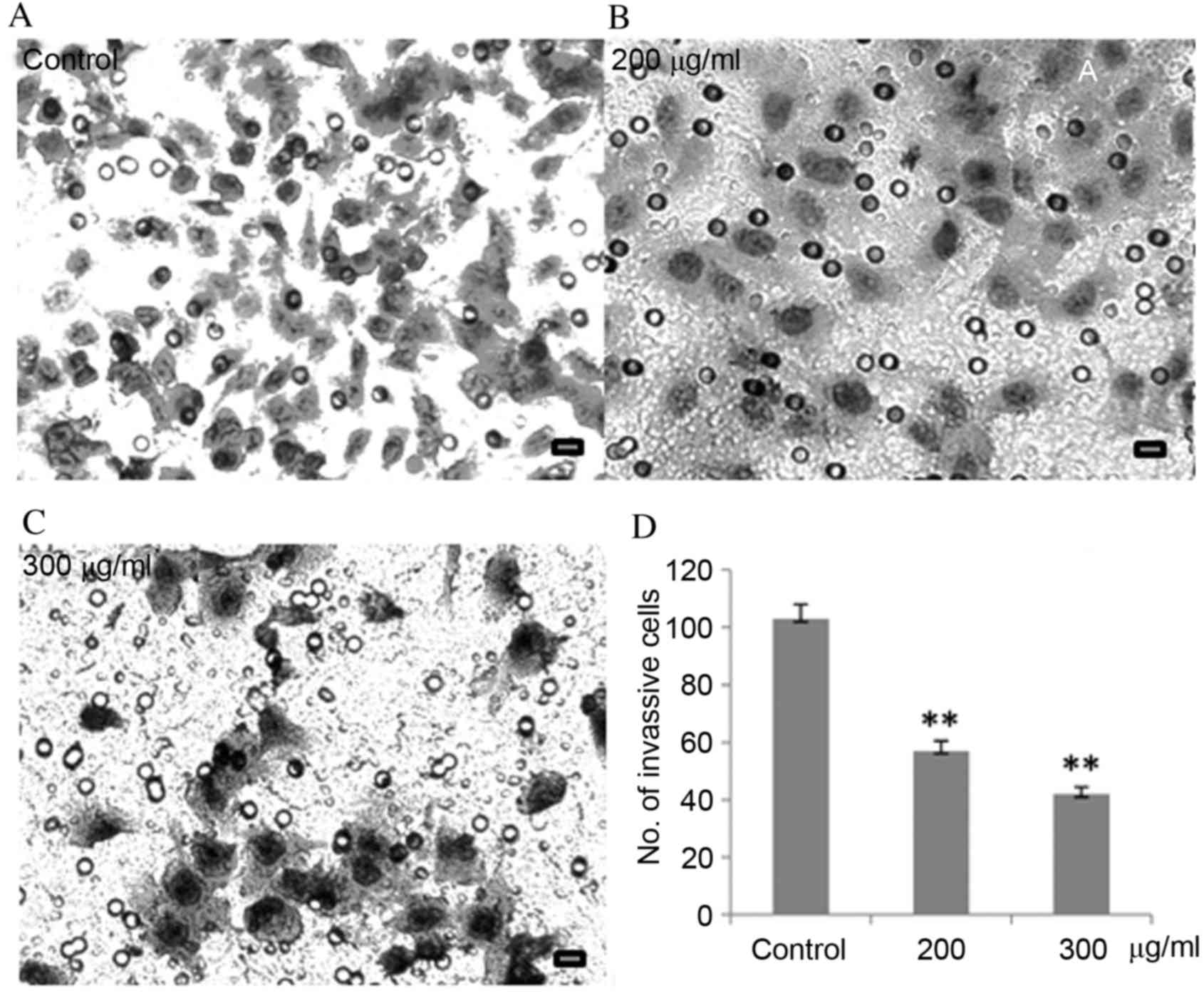
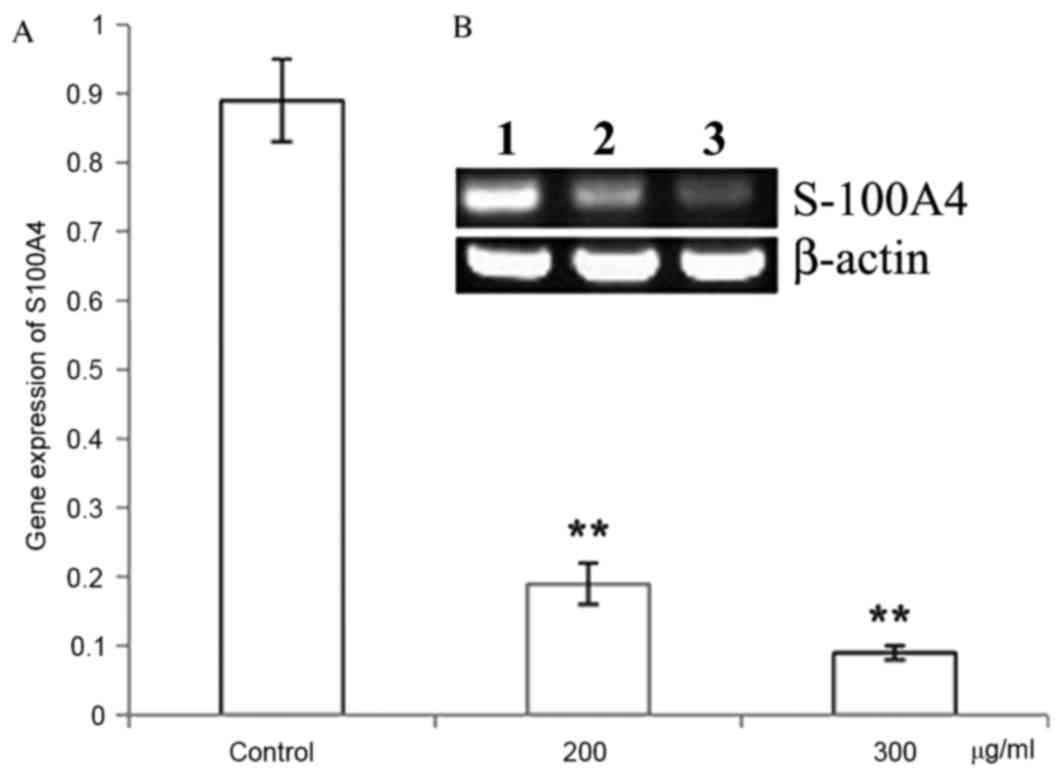
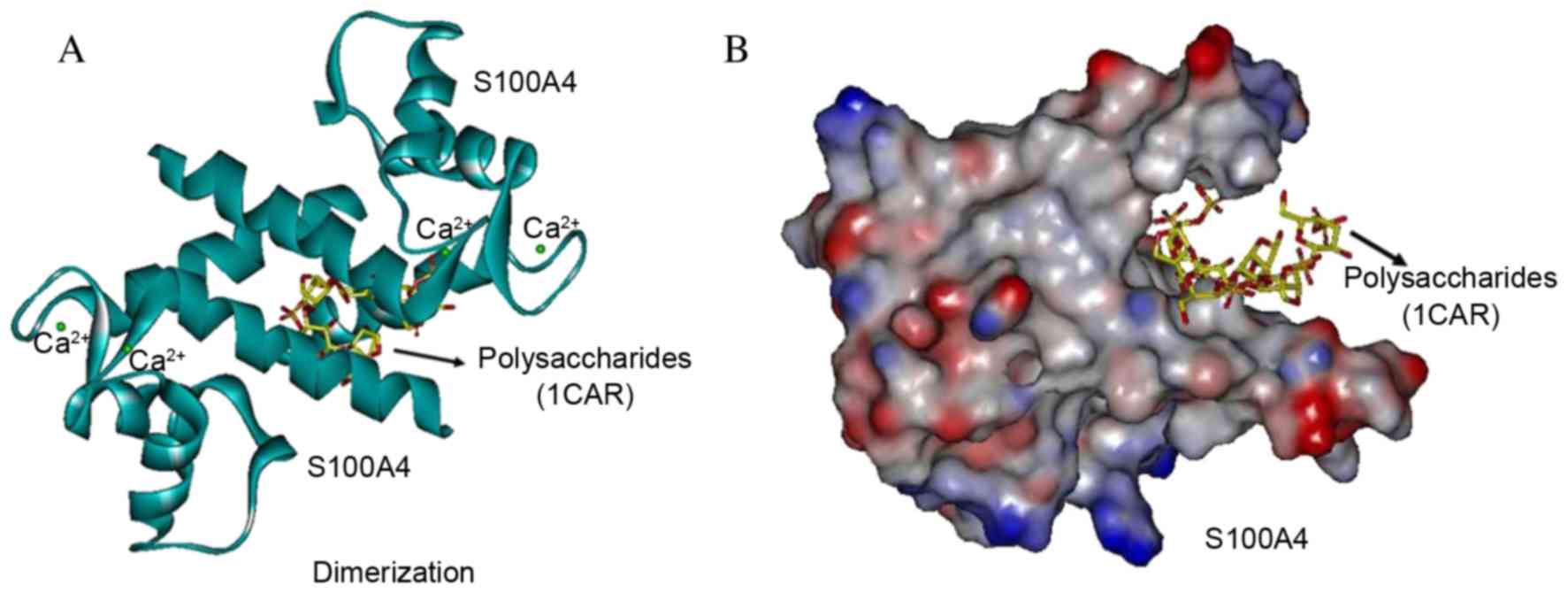
|
1
|
Maletzki C, Bodammer P, BreitrÜck A and
Kerkhoff C: S100 prteins as diagnostic and prognostic markers in
colorectal and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon.
12:e72402012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schäfer BW, Wicki R, Engelkamp D, Mattei
MG and Heizann CW: Isolation of a YAC clone covering a cluster of
nine S100 genes on human chromosome 1q21: Rationale for a new
nomenclature of the S100 calcium-binding protein family. Genomics.
25:638–643. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamamura T, Hitomi J, Nagasaki K, Suzuki
M, Takahashi E, Saito S, Tsukada T and Yamagchi K: Human CAAF1
gene-molecular cloning, gene structure, and chromosome mapping.
Bichem Biophys Res Commun. 221:356–360. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Roth J, Vogl T, Sorg C and Sunderkötter C:
Phagocyte-specific S100 proteins: A novel group of proinflammatory
molecules. Trends Immunol. 24:155–158. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guignard F, Mauel J and Markert M:
Identification and characterization of a novel human
neutrophilprotein related to the S100 family. Biochem. 309:395–401.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Marti T, Erttmann KD and Gallin MY:
Host-parasite interaction in human onchocerciasis: Identification
and sequence analysis of a novel human calgranulin. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 221:454–458. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ryckman C, Robichaud GA, Roy J, Cantin R,
Tremblay MJ and Tessier PA: HIV-1 transcription and virus
production are both accentuated by the proinflammatory
myeloid-related proteins in human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol.
169:3307–3313. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Donato R: S100: A multigenic family of
calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular
and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
33:637–668. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Donato R, Cannon BR, Sorci G, Riuzzi F,
Hsu K, Weber DJ and Geczy CL: Functions of S100 proteins. Curr Mol
Med. 13:24–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marenholz I, Heizmann CW and Fritz G: S100
proteins in mouse and man: From evolution to function and pathology
(including an update of the nomenclature). Biochem Biophys Res
Comun. 322:1111–1122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Orre LM, Panizza E, Kaminskyy VO, Vernet
E, Gräslund T, Zhivotovsky B and Lehtiö J: S100A4 interacts with
p53 in the nucleus and promotes p53 degradation. Oncogene.
32:5531–5540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ilg EC, Troxler H, Burgisser DM, Kuster T,
Markert M, Guignard F, Hunziker P, Birchler N and Heizmann CW:
Amino acid sequence determination of human S100A12 (P6, calgranulin
C, CGRP, CAAF1) by tandem mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 225:146–150. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cole AM, Kim YH, Tahk S, Hong T, Weis P,
Waring AJ and Ganz T: Calcitermin, a novel antimicrobial peptide
isolated from human airway secretions. FEBS Lett. 504:5–10. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Filipek A, Jastrzebska B, Nowotny M and
Kuznicki J: CacyBP/SIP, a calcyclin and Siah-1-interacting protein,
binds EF-hand proteins of the S100 family. J Biol Chem.
277:28848–28852. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schäfer BW and Heizmann CW: The S100
family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: Functions and
pathology. Trends Biochem Sci. 21:134–140. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sherbet GV and Lakshmi MS: S100A4 (MTS1)
calcium binding protein in cancer growth, invasion and metastasis.
Anticancer Res. 18:2415–2421. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mazzuccheli L: Protein S100A4: Too long
overlooked by pathologists? Am J Pathol. 160:7–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gribenko AV, Hopper JE and Makhatadze GI:
Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of a novel
member of the S100 family of EF-hand proteins. Biochemistry.
40:15538–15548. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taylor S, Herrington S, Prime W, Rudland
PS and Barraclough R: S100A4 (p9Ka) protein in colon carcinoma and
liver metastasis: Sssociation with carcinoma cell and
T-lymphocytes. Br J Cancer. 86:409–416. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boye K and Maelandsmo GM: S100A4 and
metastasis: A small actor playing many roles. Am J Pathol.
176:528–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cerezo LA, Kuncová K, Mann H, Tomcík M,
Zámecník J, Lukanidin E, Neidhart M, Gay S, Grigorian M, Vencovsky
J and Senolt L: The metastasis promoting protein S100A4 is
increased in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 50:1766–1772. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klingelhöfer J, Møller HD, Sumer EU, Berg
CH, Poulsen M, Kiryushko D, Soroka V, Ambartsumian N, Grigorian M
and Lukanidin EM: Epidermal growth factor receptor ligands as new
extracellular targets for the metastasis-promotingS100A4 protein.
FEBS J. 276:5936–5948. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pathuri P, Vogeley L and Luecke H: Crystal
structure of metastasis-associated protein S100A4 in the active
calcium-bound form. J Mol Biol. 383:62–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kiss B, Duelli A, Radnai L, Kékesi KA,
Katona G and Nyitray L: Crystal structure of the S100A4-nonmuscle
myosin IIA tail fragment complex reveals an asymmetric target
binding mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:6048–6053. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li ZH and Bresnick AR: The S100A4
metastasis factor regulates cellular motility via a direct
interaction with myosin-IIA. Cancer Res. 66:5173–5180. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tarabykina S, Scott DJ, Herzyk P, Hill TJ,
Tame JR, Kriajevska M, Lafitte D, Derrick PJ, Dodson GG, Maitland
NJ, et al: The dimerization interface of the metastasis-associated
protein S100A4 (Mts1): In vivo and in vitro studies. J Biol Chem.
276:24212–24222. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abdali S, Laere BD, Poulsen M, Grigorian
M, Lukanidin E and Klingelhöfer J: Toward methodology for detection
of cancer-promoting S100A4 protein conformations in subnanomolar
concentrations using Raman and SERS. J Phys Chem. 114:7274–7279.
2010.
|
|
28
|
Fang Z, Forslund N, Takenaga K, Lukanidin
E and Kozlova EN: Sensory neurite outgrowth on white matter
astrocytes is influenced by intracellular and extracellular S100A4
protein. J Neurosci Res. 83:619–626. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bettum IJ, Vasiliauskaite K, Nygaard V,
Clancy T, Pettersen SJ, Tenstad E, Maelandsmo GM and Prasmickaite
L: Metastasis-associated protein S100A4 induces a network of
inflammatory cytokines that activate stromal cells to acquire
pro-tumorigenic properties. Cancer Lett. 344:28–39. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luo C, Urgard E, Vooder T and Metspalu A:
The role of COX-2 and Nrf2/ARE in anti-inflammation and
antioxidative stress: Aging and anti-aging. Med Hypotheses.
77:174–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takahashi M, Konno C and Hikino H:
Isolation and hypoglycemic of coixan A, B and C, glycans of Coix
lachrymal-jobi var. Ma-yuen. seeds. Planta med. 64–65.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hsia SM, Chiang W, Ku YH and Wang PS:
Downregulation of progesterone biosynthesis in rat granulosa cells
by adlay(Coix lachrymal-jobi L. var. Ma-yuen Stapf.) bran extracts.
Int J Impot Res. 18:264–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baas P: Inductive and adjuvant treatment
strategies for localized nonsmall cell lung cancer in operable and
inoperable patients. Curr Opin Oncol. 14:180–184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yarrow JC, Perlman ZE, Westwood NJ and
Mitchison TJ: A high-throughput cell migration assay using scratch
wound healing, a comparison of image-based readout methods. BMC
Biotechnol. 4:212014.
|
|
35
|
Yao R, Davidson DD, Lopez-Beltran A,
MacLennan GT, Montironi R and Cheng L: The S100 proteins for
screening and prognostic grading of bladder cancer. Histol
Histopathol. 22:1025–1032. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu X, Liu W, Wu J, Li M, Wang J, Wu J and
Luo C: A polysaccharide fraction of adlay seed (Coix lachryma-jobi
L.) induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer A549
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:846–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arnott S, Scott WE, Rees DA and McNab CG:
Iota-carrageenan: Molecular structure and packing of polysaccharide
double helices in oriented fibres of divalent cation salts. J Mol
Biol. 90:253–267. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pathuri P, Vogeley L and Luecke H: Crystal
structure of metastasis-associated protein S100A4 in the active
calcium-bound form. J Mol Biol. 383:62–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Van Deursen JM: The role of senescent
cells in ageing. Nature. 509:439–446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim YJ, Kim MA, Im SA, Kim TM, Kim DW,
Yang HK, Heo DS, Lee KU, Choe KJ, Kim NK, et al:
Metastasis-associated protein S100A4 and p53 predict relapse in
curatively resected stage III and IV (M0) gastric cancer. Cancer
Invest. 26:152–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Garrett SC, Varney KM, Weber DJ and
Bresnick AR: S100A4, a mediator of metastasis. J Biol Chem.
281:677–680. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang L, Gao S, Jiang W, Luo C, Xu M,
Bohlin L, Rosendahl M and Huang W: Antioxidative dietary compounds
modulate gene expression associated with apoptosis, DNA repair,
inhibition of cell proliferation and migration. Int J Mol Sci.
15:16226–16245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Michel G, Helbert W, Kahn R, Dideberg O
and Kloareg B: The structural bases of the processive degradation
of iota-carrageenan, a main cell wall polysaccharide of red algae.
J Mol Biol. 334:421–433. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Abrantes VE, da Rocha BA Matias, da
Nóbrega Batista R, Silva-Filho JC, Teixeira CS, Cavada BS, Gadelha
CA, Ferreira SH, Figueiredo JG, Santi-Gadelha T and Delatorre P:
Molecular modeling of lectin-like protein from Acacia farnesiana
reveals a possible anti-inflammatory mechanism in
carrageenan-induced inflammation. Biomed Res Int.
2013:2534832013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bowers RR, Manevich Y, Townsend DM and Tew
KD: Sulfiredoxin redox-sensitive interaction with S100A4 and
non-muscle myosin IIA regulates cancer cell motility. Biochemistry.
51:7740–7754. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Elliott PR, Irvine AF, Jung HS, Tozawa K,
Pastok MW, Picone R, Badyal SK, Basran J, Rudland PS, Barraclough
R, et al: Asymmetric mode of Ca2+-S100A4 interaction
with nonmuscle myosin IIA generates nanomolar affinity required for
filament remodeling. Structure. 20:654–666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|