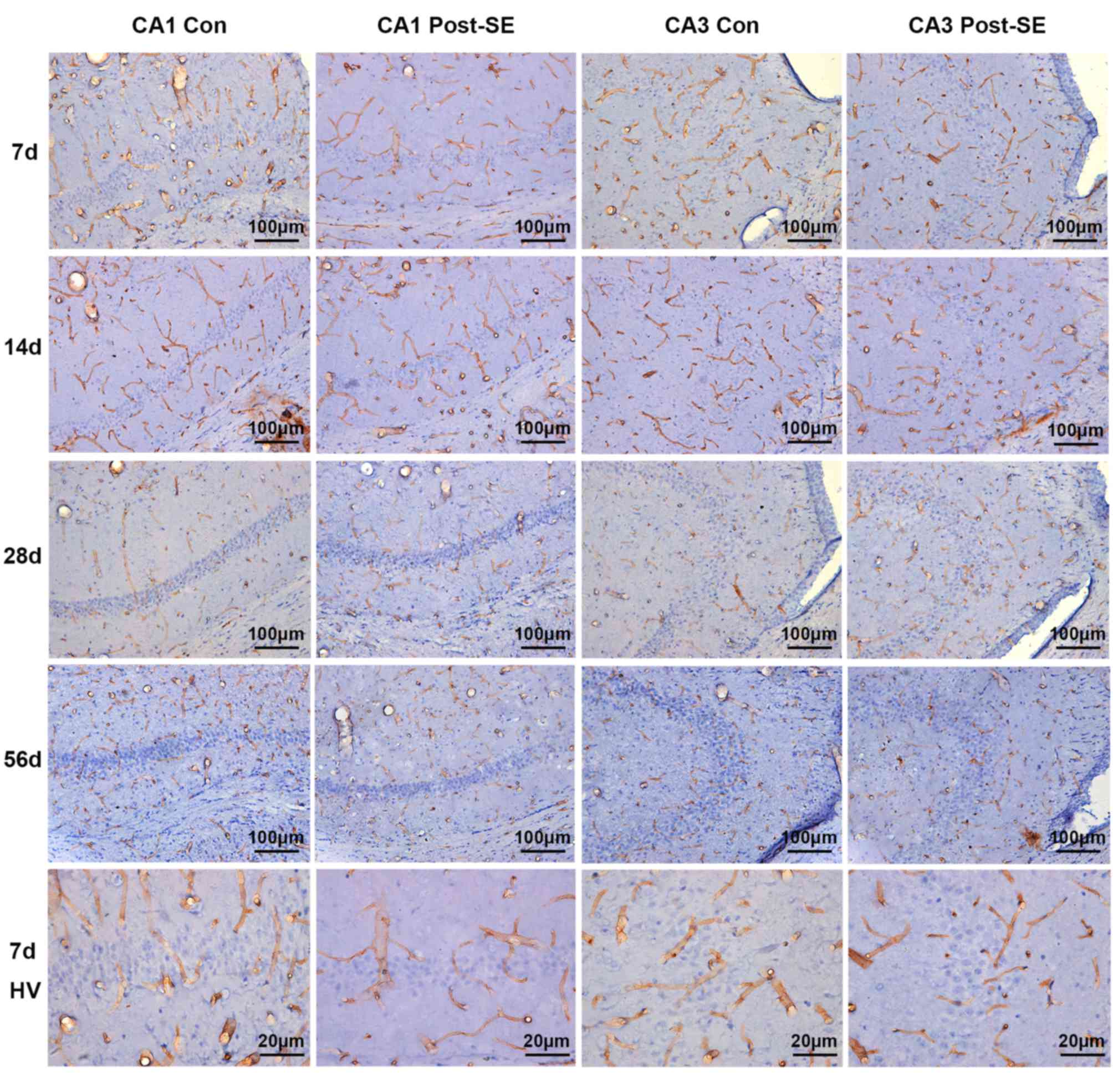
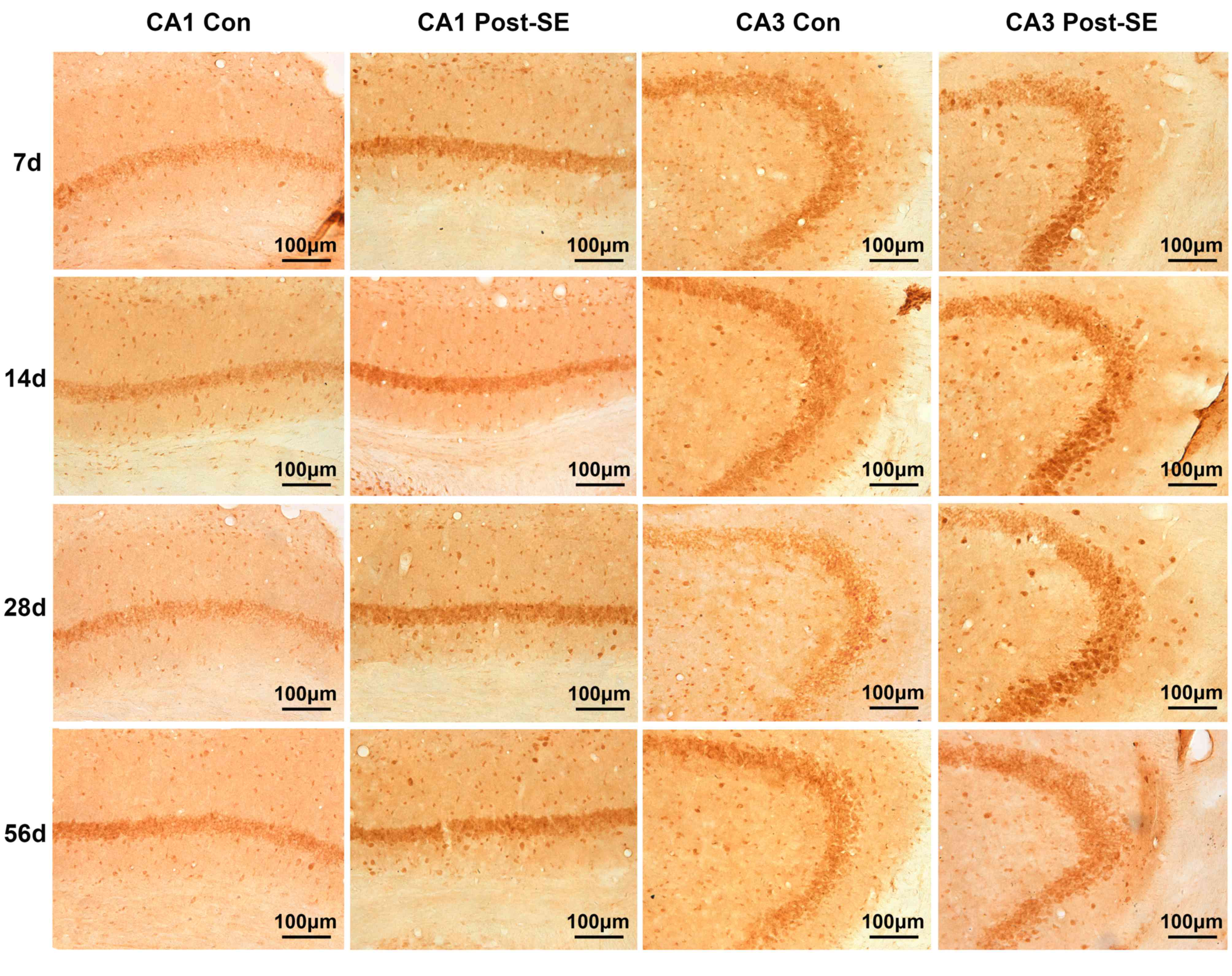
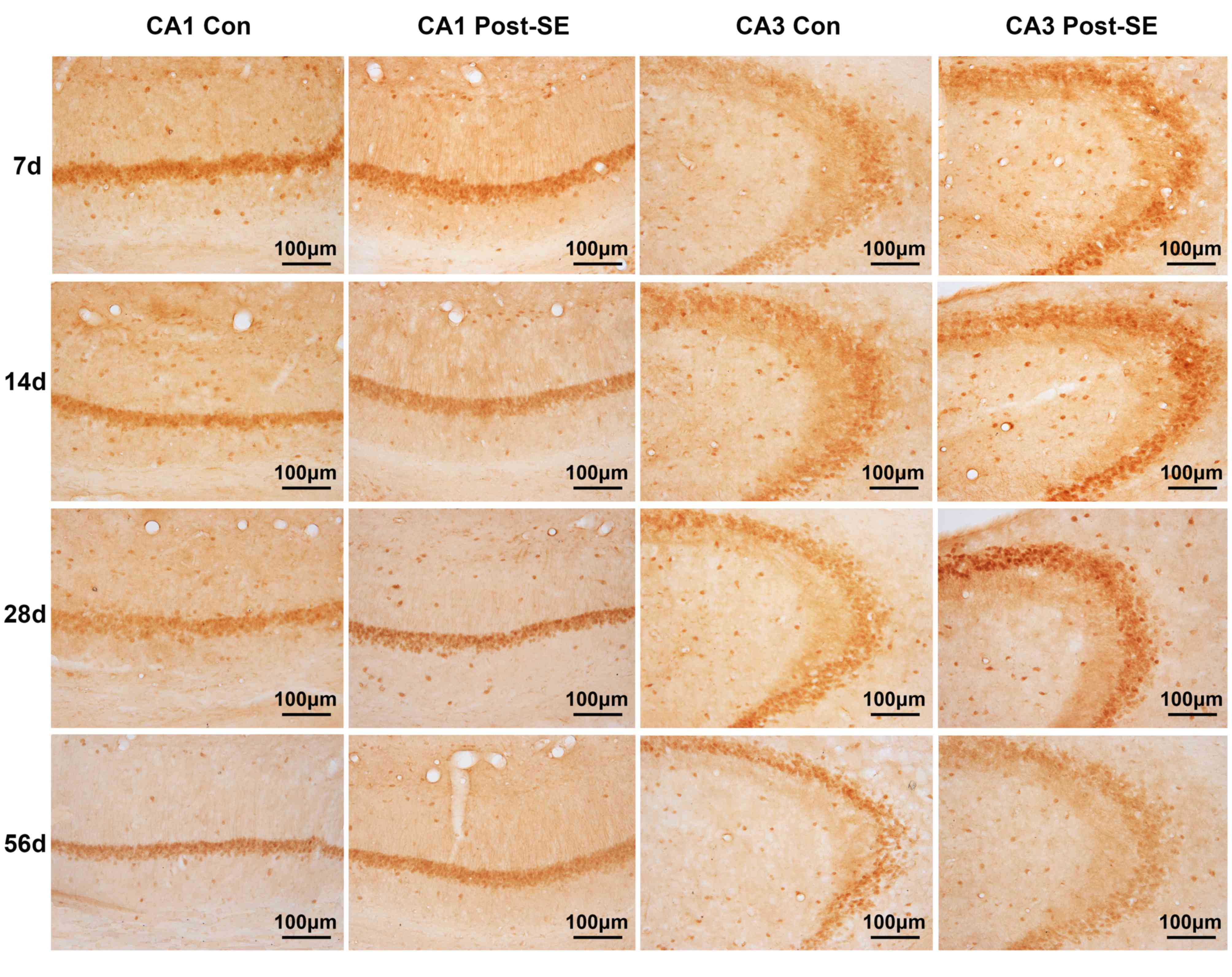
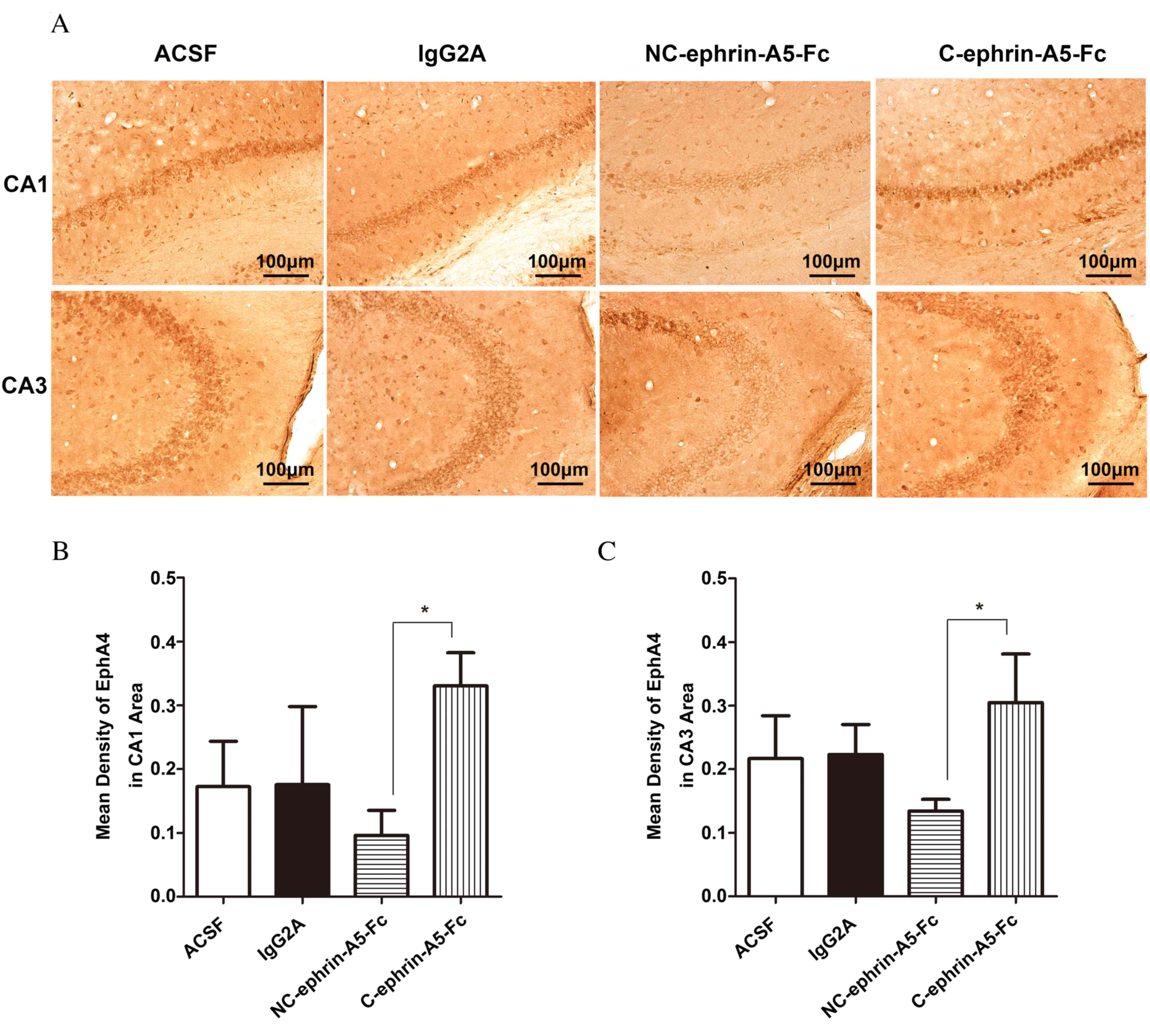
|
1
|
Perry MS and Duchowny M: Surgical versus
medical treatment for refractory epilepsy: Outcomes beyond seizure
control. Epilepsia. 54:2060–2070. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Turski WA, Cavalheiro EA, Schwarz M,
Czuczwar SJ, Kleinrok Z and Turski L: Limbic seizures produced by
pilocarpine in rats: Behavioural, electroencephalographic and
neuropathological study. Behav Brain Res. 9:315–335. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Curia G, Longo D, Biagini G, Jones RS and
Avoli M: The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J
Neurosci Methods. 172:143–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gröticke I, Hoffmann K and Löscher W:
Behavioral alterations in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe
epilepsy in mice. Exp Neurol. 207:329–349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu K, Li SY, Xiao B, Bi FF, Lu XQ and Wu
XM: Protective effects of quercetin against status epilepticus
induced hippocampal neuronal injury in rats: Involvement of
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Acta Neurol Belg.
111:205–212. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang L, Hernández VS, Estrada FS and
Luján R: Hippocampal CA field neurogenesis after pilocarpine
insult: The hippocampal fissure as a neurogenic niche. J Chem
Neuroanat. 56:45–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW
and Delgado-Escueta AV: Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies
(Internet). 4th. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology
Information (US); pp. 1–102. 2012
|
|
8
|
Zha XM, Dailey ME and Green SH: Role of
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in dendritic
spine remodeling during epileptiform activity in vitro. J Neurosci
Res. 87:1969–1979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang FR and Loke WK: Cyto-, axo- and
dendro-architectonic changes of neurons in the limbic system in the
mouse pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res.
89:43–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ndode-Ekane XE, Hayward N, Gröhn O and
Pitkänen A: Vascular changes in epilepsy: Functional consequences
and association with network plasticity in pilocarpine-induced
experimental epilepsy. Neuroscience. 166:312–332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mosch B, Reissenweber B, Neuber C and
Pietzsch J: Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: Important players in
angiogenesis and tumor angiogenesis. J Oncol.
2010:1352852010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Himanen JP, Rajashankar KR, Lackmann M,
Cowan CA, Henkemeyer M and Nikolov DB: Crystal structure of an Eph
receptor-ephrin complex. Nature. 414:933–938. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smith FM, Vearing C, Lackmann M, Treutlein
H, Himanen J, Chen K, Saul A, Nikolov D and Boyd AW: Dissecting the
EphA3/Ephrin-A5 interactions using a novel functional mutagenesis
screen. J Biol Chem. 279:9522–9531. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Greferath U, Canty AJ, Messenger J and
Murphy M: Developmental expression of EphA4-tyrosine kinase
receptor in the mouse brain and spinal cord. Mech Dev. 119:(Suppl
1). S231–S238. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jing X, Miwa H, Sawada T, Nakanishi I,
Kondo T, Miyajima M and Sakaguchi K: Ephrin-A1-mediated
dopaminergic neurogenesis and angiogenesis in a rat model of
Parkinson's disease. PLoS One. 7:e320192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Omoto S, Ueno M, Mochio S and Yamashita T:
Corticospinal tract fibers cross the ephrin-B3-negative part of the
midline of the spinal cord after brain injury. Neurosci Res.
69:187–195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Toyoda Y, Shinohara R, Thumkeo D, Kamijo
H, Nishimaru H, Hioki H, Kaneko T, Ishizaki T, Furuyashiki T and
Narumiya S: EphA4-dependent axon retraction and midline
localization of Ephrin-B3 are disrupted in the spinal cord of mice
lacking mDia1 and mDia3 in combination. Genes Cells. 18:873–885.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khodosevich K, Watanabe Y and Monyer H:
EphA4 preserves postnatal and adult neural stem cells in an
undifferentiated state in vivo. J Cell Sci. 124:1268–1279. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hara Y, Nomura T, Yoshizaki K, Frisén J
and Osumi N: Impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and vascular
formation in ephrin-A5-deficient mice. Stem Cells. 28:974–983.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ogita H, Kunimoto S, Kamioka Y, Sawa H,
Masuda M and Mochizuki N: EphA4-mediated Rho activation via
Vsm-RhoGEF expressed specifically in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Circ Res. 93:23–31. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shu Y, Xiao B, Wu Q, Liu T, Du Y, Tang H,
Chen S, Feng L, Long L and Li Y: The Ephrin-A5/EphA4 interaction
modulates neurogenesis and angiogenesis by the p-Akt and p-ERK
pathways in a mouse model of TLE. Mol Neurobiol. 53:561–576. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gerlai R and McNamara A: Anesthesia
induced retrograde amnesia is ameliorated by ephrinA5-IgG in mice:
EphA receptor tyrosine kinases are involved in mammalian memory.
Behav Brain Res. 108:133–143. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goldshmit Y, Spanevello MD, Tajouri S, Li
L, Rogers F, Pearse M, Galea M, Bartlett PF, Boyd AW and Turnley
AM: EphA4 blockers promote axonal regeneration and functional
recovery following spinal cord injury in mice. PLoS One.
6:e246362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Overman JJ, Clarkson AN, Wanner IB,
Overman WT, Eckstein I, Maguire JL, Dinov ID, Toga AW and
Carmichael ST: A role for ephrin-A5 in axonal sprouting, recovery,
and activity-dependent plasticity after stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 109:E2230–E2239. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ting MJ, Day BW, Spanevello MD and Boyd
AW: Activation of ephrin A proteins influences hematopoietic stem
cell adhesion and trafficking patterns. Exp Hematol. 38:1087–1098.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Peng Z, Xiao B and Houser CR:
Activation of ERK by spontaneous seizures in neural progenitors of
the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of epilepsy. Exp Neurol.
224:133–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Goldshmit Y and Bourne J: Upregulation of
EphA4 on astrocytes potentially mediates astrocytic gliosis after
cortical lesion in the marmoset monkey. J Neurotrauma.
27:1321–1332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Liu N, Wang Y, Wang R, Guo D and
Zhang C: Inhibition of EphA4 signaling after ischemia-reperfusion
reduces apoptosis of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neurosci Lett.
518:92–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Murai KK, Nguyen LN, Irie F, Yamaguchi Y
and Pasquale EB: Control of hippocampal dendritic spine morphology
through ephrin-A3/EphA4 signaling. Nat Neurosci. 6:153–160. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dudanova I, Kao TJ, Herrmann JE, Zheng B,
Kania A and Klein R: Genetic evidence for a contribution of
EphA:EphrinA reverse signaling to motor axon guidance. J Neurosci.
32:5209–5215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tremblay ME, Riad M, Bouvier D, Murai KK,
Pasquale EB, Descarries L and Doucet G: Localization of EphA4 in
axon terminals and dendritic spines of adult rat hippocampus. J
Comp Neurol. 501:691–702. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Filosa A, Paixão S, Honsek SD, Carmona MA,
Becker L, Feddersen B, Gaitanos L, Rudhard Y, Schoepfer R,
Klopstock T, et al: Neuron-glia communication via EphA4/ephrin-A3
modulates LTP through glial glutamate transport. Nat Neurosci.
12:1285–1292. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morin-Brureau M, Rigau V and Lerner-Natoli
M: Why and how to target angiogenesis in focal epilepsies.
Epilepsia. 53:(Suppl 6). 64–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Romariz SA, Kde O Garcia, Dde S Paiva,
Bittencourt S, Covolan L, Mello LE and Longo BM: Participation of
bone marrow-derived cells in hippocampal vascularization after
status epilepticus. Seizure. 23:386–389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rigau V, Morin M, Rousset MC, de Bock F,
Lebrun A, Coubes P, Picot MC, Baldy-Moulinier M, Bockaert J,
Crespel A and Lerner-Natoli M: Angiogenesis is associated with
blood-brain barrier permeability in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain.
130:1942–1956. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kaminski RM, Rogawski MA and Klitgaard H:
The potential of antiseizure drugs and agents that act on novel
molecular targets as antiepileptogenic treatments.
Neurotherapeutics. 11:385–400. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kastanauskaite A, Alonso-Nanclares L,
Blazquez-Llorca L, Pastor J, Sola RG and DeFelipe J: Alterations of
the microvascular network in sclerotic hippocampi from patients
with epilepsy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 68:939–950. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Alonso-Nanclares L and Defelipe J:
Alterations of the microvascular network in the sclerotic
hippocampus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy
Behav. 38:48–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|